Abstract
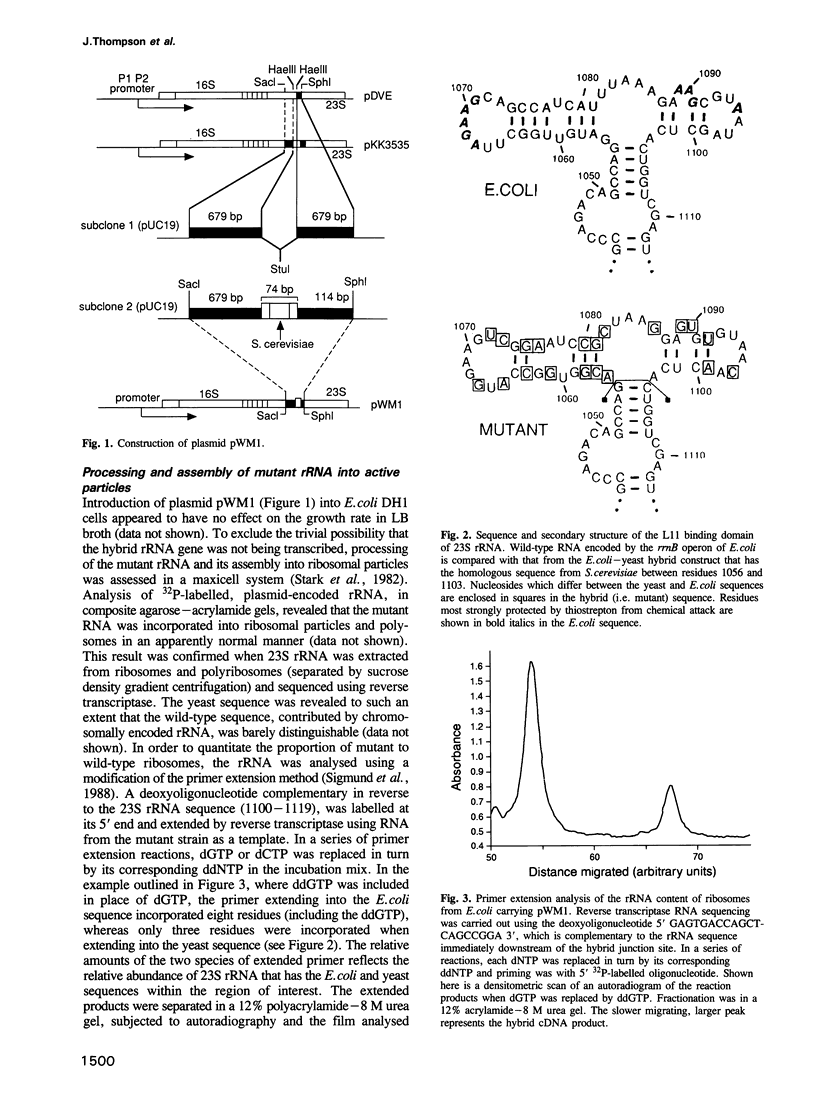
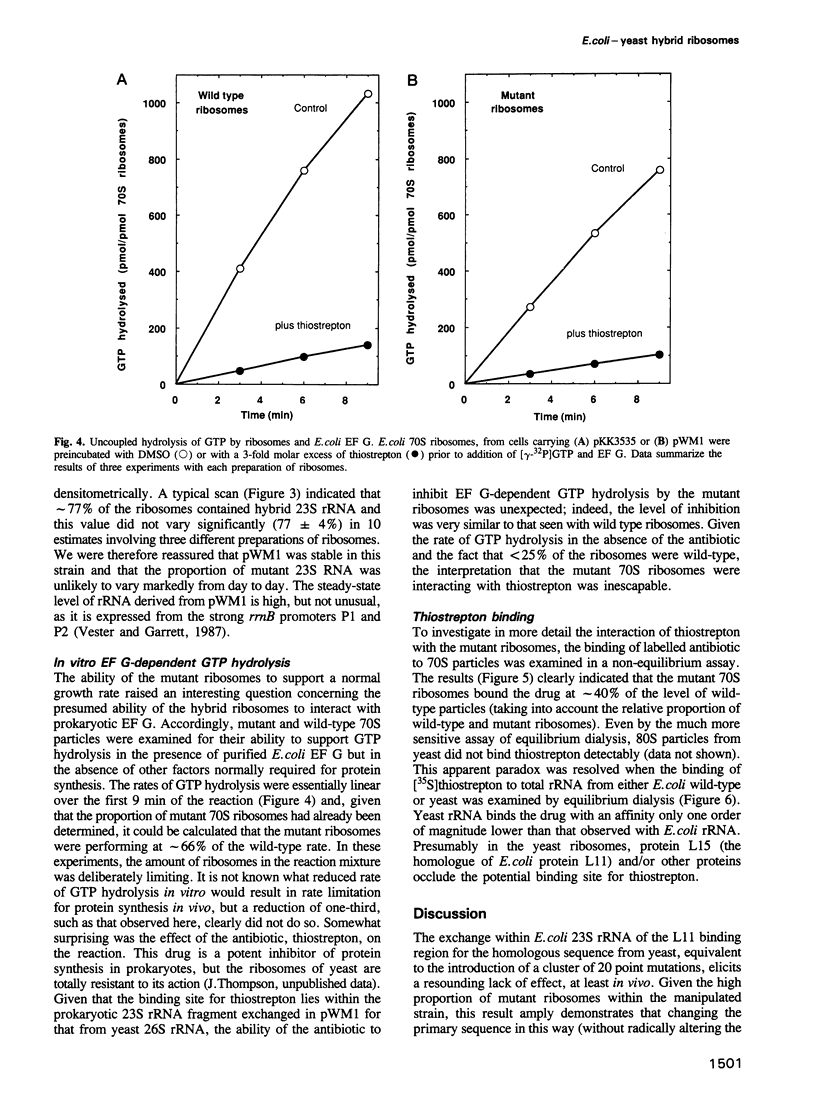
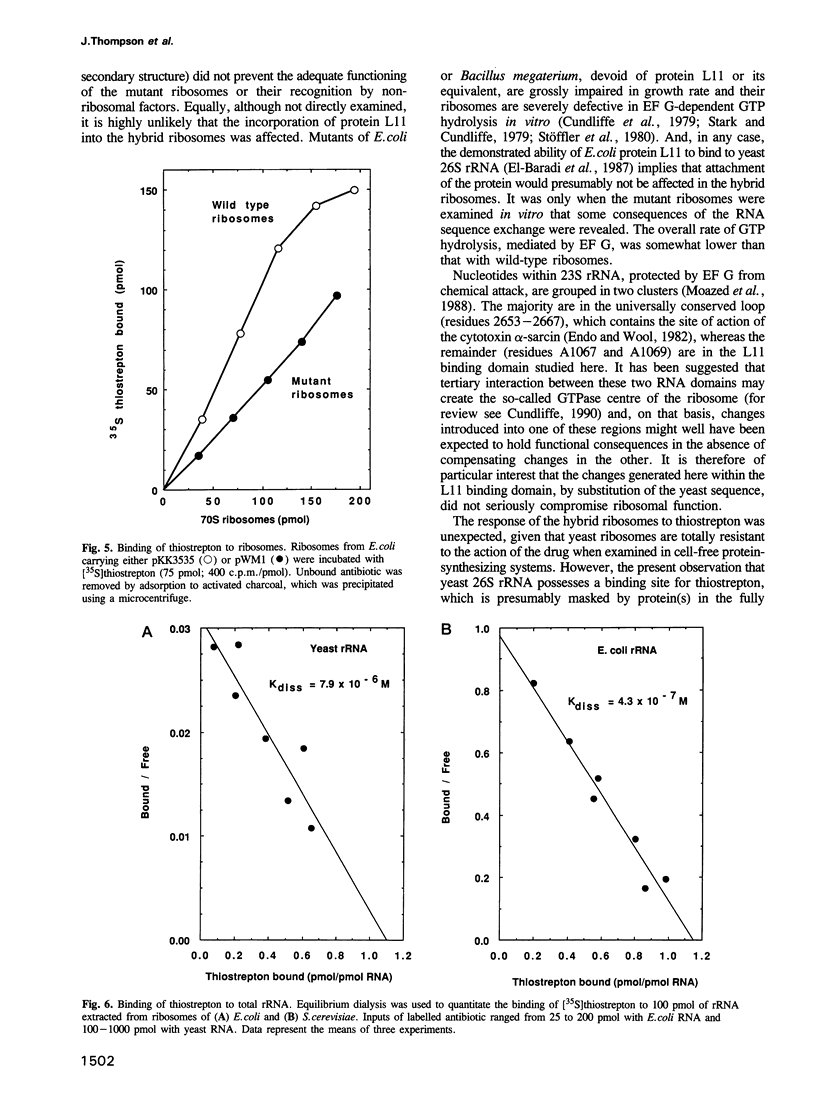
Replacement of the protein L11 binding domain within Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) by the equivalent region from yeast 26S rRNA appeared to have no effect on the growth rate of E.coli cells harbouring a plasmid carrying the mutated rrnB operon. The hybrid rRNA was correctly processed and assembled into ribosomes, which accumulated normally in polyribosomes. Of the total ribosomal population, < 25% contained wild-type, chromosomally encoded rRNA; the remainder were mutant. The hybrid ribosomes supported GTP hydrolysis dependent upon E.coli elongation factor G, although at a somewhat reduced rate compared with wild-type particles, and were sensitive to the antibiotic, thiostrepton, a potent inhibitor of ribosomal GTPase activity that binds to 23S rRNA within the L11 binding domain. That thiostrepton could indeed bind to the mutant ribosomes, although at a reduced level relative to that seen with wild-type ribosomes, was confirmed in a non-equilibrium assay. The rationale for the ability of the hybrid ribosomes to bind the antibiotic, given that yeast ribosomes do not, was provided when yeast rRNA was shown by equilibrium dialysis to bind thiostrepton only 10-fold less tightly than did E.coli rRNA. The extreme conservation of secondary, but not primary, structure in this region between E.coli and yeast rRNAs allows the hybrid ribosomes to function competently in protein synthesis and also preserves the interaction with thiostrepton.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauclerk A. A., Hummel H., Holmes D. J., Böck A., Cundliffe E. Studies of the GTPase domain of archaebacterial ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):245–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Atmadja J., Stiege W., Schüler D. A detailed model of the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in situ in the 30 S subunit. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., Dixon P., Stark M., Stöffler G., Ehrlich R., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Cannon M. Ribosomes in thiostrepton-resistant mutants of Bacillus megaterium lacking a single 50 S subunit protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 5;132(2):235–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon P. G., Beven J. E., Cundliffe E. Properties of the ribosomes of antibiotic producers: effects thiostrepton and micrococcin on the organisms which produce them. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):850–855. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A. Antibiotic interactions at the GTPase-associated centre within Escherichia coli 23S rRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):607–611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):142–148. doi: 10.1038/342142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Conçalves P. M., Boon K., Raué H. A., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. The conserved GTPase center and variable region V9 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae 26S rRNA can be replaced by their equivalents from other prokaryotes or eukaryotes without detectable loss of ribosomal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1469–1473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P. C., Lu M., Draper D. E. Recognition of the highly conserved GTPase center of 23 S ribosomal RNA by ribosomal protein L11 and the antibiotic thiostrepton. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1257–1268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90932-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt F. J., Thompson J., Lee K., Dijk J., Cundliffe E. The binding site for ribosomal protein L11 within 23 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12301–12305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Borden A., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:673–690. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköld S. E. Chemical crosslinking of elongation factor G to the 23S RNA in 70S ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4923–4932. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Gourse R. L., Jemiolo D. K., Dahlberg A. E. A mutation in an Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA operon that blocks the production of precursor 23 S ribosomal RNA by RNase III in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90339-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M., Cundliffe E. On the biological role of ribosomal protein BM-L11 of Bacillus megaterium, homologous with Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L11. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):767–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Cundliffe E., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Dabbs E. R. Mutants of Escherichia coli lacking ribosomal protein L11. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10517–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Cundliffe E., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of Escherichia coli 23 S ribosomal RNA at position 1067 within the GTP hydrolysis centre. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Cundliffe E., Stark M. Binding of thiostrepton to a complex of 23-S rRNA with ribosomal protein L11. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Cundliffe E. The binding of thiostrepton to 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90156-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Schmidt F., Cundliffe E. Site of action of a ribosomal RNA methylase conferring resistance to thiostrepton. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7915–7917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vester B., Garrett R. A. A plasmid-coded and site-directed mutation in Escherichia coli 23S RNA that confers resistance to erythromycin: implications for the mechanism of action of erythromycin. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T. T., de Regt V. C., Einerhand S. W., Teixido J., Planta R. J., Ballesta J. P., Raué H. A. Ribosomal proteins EL11 from Escherichia coli and L15 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae bind to the same site in both yeast 26 S and mouse 28 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



