Abstract
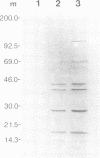
Theileria parva is an obligate, intracellular, parasitic protozoan that causes East Coast fever, an acute leukemia-like disease of cattle. T. parva and the related parasite, Theileria annulata, are unique among protozoa in that their intralymphocytic stages induce transformation of bovid lymphocytes. Comparison of in vitro protein kinase activities between uninfected IL-2-dependent T lymphoblasts and T. parva-infected lymphocytes revealed a 4.7- to 12-fold increase in total phosphorylation and the induction of a group of Theileria infection-specific phosphoproteins. The enzyme that phosphorylates these substrates is a serine/threonine kinase with substrate and effector specificities of casein kinase (CK) II. Northern blot analyses revealed a 3.9- to 6.0-fold increase in CKII alpha mRNA in the infected cells relative to the controls. Furthermore, a marked increase of CKII antigen was observed on Western blots of materials prepared from the infected cell lines. The antibovine CKII antibody used in these studies immunoprecipitated a protein kinase that phosphorylated casein in a reaction that was inhibited by low (nM) quantities of heparin. Our data show marked increases of bovine CKII at the transcriptional, translational and functional levels in T. parva-infected lymphocytes, relative to quiescent cells or IL-2-dependent parental lymphoblasts. Bovine CKII thus appears to be constitutively activated in these cells and we propose that this kinase may be an important element in the signal-transducing pathways activated by Theileria in bovid lymphocytes and perhaps in some leukemic cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Stimulation of casein kinase II by epidermal growth factor: relationship between the physiological activity of the kinase and the phosphorylation state of its beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):821–825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman P., Osheroff N. Regulation of casein kinase II activity by epidermal growth factor in human A-431 carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11958–11965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Black S. J., Brown W. C., Conrad P. A., Goddeeris B. M., Kinuthia S. W., Lalor P. A., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I., Morzaria S. P. Bovine T cells, B cells, and null cells are transformed by the protozoan parasite Theileria parva. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):462–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.462-467.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Edmonds C., Fisher C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Vousden K. H. The region of the HPV E7 oncoprotein homologous to adenovirus E1a and Sv40 large T antigen contains separate domains for Rb binding and casein kinase II phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaid A., Kaushal A., Baldwin C. L., Clevers H., Young J. R., Kemp S. J., MacHugh N. D., Toye P. G., Teale A. J. Identification of expressed bovine class I MHC genes at two loci and demonstration of physical linkage. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(4):247–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00230502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Grab D. J. Biological and biochemical characterization of bovine interleukin 2. Studies with cloned bovine T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3184–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Dang Q., Glover C. V., Gasser S. M. Casein kinase II phosphorylates the eukaryote-specific C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Marshak D. R. Serum-stimulated cell growth causes oscillations in casein kinase II activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7345–7348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Santoro N., Marshak D. R. Regulating cell growth: casein-kinase-II-dependent phosphorylation of nuclear oncoproteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):91–95. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Wu J. L., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the CKA1 gene encoding the alpha subunit of yeast casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4981–4990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Oligomeric structure and catalytic activity of G type casein kinase. Isolation of the two subunits and renaturation experiments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P. A., Iams K., Brown W. C., Sohanpal B., ole-MoiYoi O. K. DNA probes detect genomic diversity in Theileria parva stocks. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Oct;25(3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Dexter T. M. Growth factors in development, transformation, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90638-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus G. K., Glover C. V., Brutlag D. L., Dahmus M. E. Similarities in structure and function of calf thymus and Drosophila casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9001–9006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damuni Z., Reed L. J. Purification and properties of a protamine kinase and a type II casein kinase from bovine kidney mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 1;262(2):574–584. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBenedette M., Snow E. C. Induction and regulation of casein kinase II during B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2839–2845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelaere D. A., Coquerelle T. M., Roditi I. J., Eichhorn M., Williams R. O. Theileria parva infection induces autocrine growth of bovine lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4730–4734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelaere D. A., Spooner P. R., Barry W. C., Irvin A. D. Monoclonal antibody neutralizes the sporozoite stage of different Theileria parva stocks. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Jul;6(4):361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolska G., Meggio F., Szczegielniak J., Muszynska G., Pinna L. A. Purification and characterization of maize seedling casein kinase IIB, a monomeric enzyme immunologically related to the alpha subunit of animal casein kinase-2. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozier C., Denhez F., Coll J., Amouyel P., Quatannens B., Begue A., Stehelin D., Saule S. Induction of proliferation of neuroretina cells by long terminal repeat activation of the carboxy-terminal part of c-mil. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1995–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer M., Hall R., Shiels B., Tait A. Theileria annulata: alterations in phosphoprotein and protein kinase activity profiles of infected leukocytes of the bovine host, Bos taurus. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Mar;74(2):216–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90049-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Doxsey S., Stagg D. A., Young A. S. The entry of sporozoites of Theileria parva into bovine lymphocytes in vitro. Electron microscopic observations. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;27(1):10–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell A. H., Preston P. M., Ansell J. D. Establishment of Theileria-infected bovine cell lines in scid mice. Parasite Immunol. 1990 May;12(3):335–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filhol O., Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Cytoplasmic and nuclear distribution of casein kinase II: characterization of the enzyme uptake by bovine adrenocortical nuclear preparation. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9928–9936. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Harrison M. L. Induction of a substrate for casein kinase II during lymphocyte mitogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 19;804(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glineur C., Bailly M., Ghysdael J. The c-erbA alpha-encoded thyroid hormone receptor is phosphorylated in its amino terminal domain by casein kinase II. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1247–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Scheidtmann K. H., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A., Walter G. In vitro phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Kinetics of activation of casein kinase II by polyamines and reversal of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7011–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:308–317. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Signal transduction by the receptors for platelet-derived growth factor. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):193–196. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller-Harrison R. A., Czech M. P. Enhanced casein kinase II activity in COS-1 cells upon overexpression of either its catalytic or noncatalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14435–14439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller-Harrison R. A., Meisner H., Czech M. P. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the beta subunit of human casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9053–9058. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu E., Rubin C. S. Casein kinase II from Caenorhabditis elegans. Properties and developmental regulation of the enzyme; cloning and sequence analyses of cDNA and the gene for the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5072–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iams K. P., Young J. R., Nene V., Desai J., Webster P., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Musoke A. J. Characterisation of the gene encoding a 104-kilodalton microneme-rhoptry protein of Theileria parva. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Feb;39(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin A. D., Brown C. G., Kanhai G. K., Stagg D. A. Comparative growth of bovine lymphosarcoma cells and lymphoid cells infected with Theileria parva in athymic (nude) mice. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):713–714. doi: 10.1038/255713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V., Stein B., Baumann I., Dobbelaere D. A., Herrlich P., Williams R. O. Infection with the intracellular protozoan parasite Theileria parva induces constitutively high levels of NF-kappa B in bovine T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4677–4686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K., Czech M. P. Insulin-like growth factor I and insulin rapidly increase casein kinase II activity in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15872–15875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N., Kuenzel E. A., Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Lüscher B., Sommercorn J. Casein kinase II as a potentially important enzyme concerned with signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Maridor G., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II is a predominantly nuclear enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):43–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. J., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Characterization of the catalytic subunit of casein kinase II expressed in Escherichia coli and regulation of activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5664–5669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Piening C., Sommercorn J., Takio K., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Subunit structure of casein kinase II from bovine testis. Demonstration that the alpha and alpha' subunits are distinct polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7638–7644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozeman F. J., Litchfield D. W., Piening C., Takio K., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding the alpha and the alpha' subunits of casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8436–8447. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Kuenzel E. A., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myc oncoproteins are phosphorylated by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1111–1119. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manai M., Cozzone A. J. Two-dimensional separation of phosphoamino acids from nucleoside monophosphates. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):12–18. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maridor G., Park W., Krek W., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II. cDNA sequences, developmental expression, and tissue distribution of mRNAs for alpha, alpha', and beta subunits of the chicken enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2362–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martensen T. M. Chemical properties, isolation, and analysis of O-phosphates in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:3–23. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Simon S., Kikkawa U., Eckhart W. The p53 tumour suppressor protein is phosphorylated at serine 389 by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3253–3260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Czech M. P. Phosphorylation of transcriptional factors and cell-cycle-dependent proteins by casein kinase II. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90076-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Heller-Harrison R., Buxton J., Czech M. P. Molecular cloning of the human casein kinase II alpha subunit. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):4072–4076. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Goddeeris B. M., Teale A. J. Bovine cytotoxic T cell clones which recognize lymphoblasts infected with two antigenically different stocks of the protozoan parasite Theileria parva. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1703–1709. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulner-Lorillon O., Cormier P., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Poulhe R., Osborne H., Bellé R. M-phase-specific cdc2 protein kinase phosphorylates the beta subunit of casein kinase II and increases casein kinase II activity. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulner-Lorillon O., Marot J., Cayla X., Pouhle R., Belle R. Purification and characterization of a casein-kinase-II-type enzyme from Xenopus laevis ovary. Biological effects on the meiotic cell division of full-grown oocyte. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):107–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münstermann U., Fritz G., Seitz G., Lu Y. P., Schneider H. R., Issinger O. G. Casein kinase II is elevated in solid human tumours and rapidly proliferating non-neoplastic tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Sikorski R., Reed S. I., Vogelstein B. Human p53 and CDC2Hs genes combine to inhibit the proliferation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1357–1365. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabha R., Chen-Wu J. L., Hanna D. E., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the yeast CKA2 gene: casein kinase II is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs H. P., Jans D. A., Fan H., Peters R. The rate of nuclear cytoplasmic protein transport is determined by the casein kinase II site flanking the nuclear localization sequence of the SV40 T-antigen. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):633–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Charlton L. A., Paddon H. B., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of echinoderm casein kinase II. Regulation by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):829–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2830829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding alpha and beta subunits of Drosophila melanogaster casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3409–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. N., Egerton M., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Multiple signal transduction pathways activated through the T cell receptor for antigen. Semin Immunol. 1991 Sep;3(5):325–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh T. J., Huang K. P. Glycogen synthase (casein) kinase-1: tissue distribution and subcellular localization. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. Induction of casein kinase II during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3839–3843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Mulligan J. A., Lozeman F. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of casein kinase II in response to insulin and to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Kuenzel E. A., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Amino acid sequence of the beta subunit of bovine lung casein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Allende C. C., Weinmann R., Allende J. E. The phosphorylation of nucleoplasmin by casein kinase-2 is resistant to heparin inhibition. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 21;226(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80561-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Zheng K., Kopatz I., Naiman T., Canaani D. Mapping of the human casein kinase II catalytic subunit genes: two loci carrying the homologous sequences for the alpha subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7125–7129. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu I. J., Spector D. L., Bae Y. S., Marshak D. R. Immunocytochemical localization of casein kinase II during interphase and mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1217–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ole-MoiYoi O. K., Sugimoto C., Conrad P. A., Macklin M. D. Cloning and characterization of the casein kinase II alpha subunit gene from the lymphocyte-transforming intracellular protozoan parasite Theileria parva. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 14;31(27):6193–6202. doi: 10.1021/bi00142a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]