Abstract
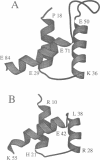
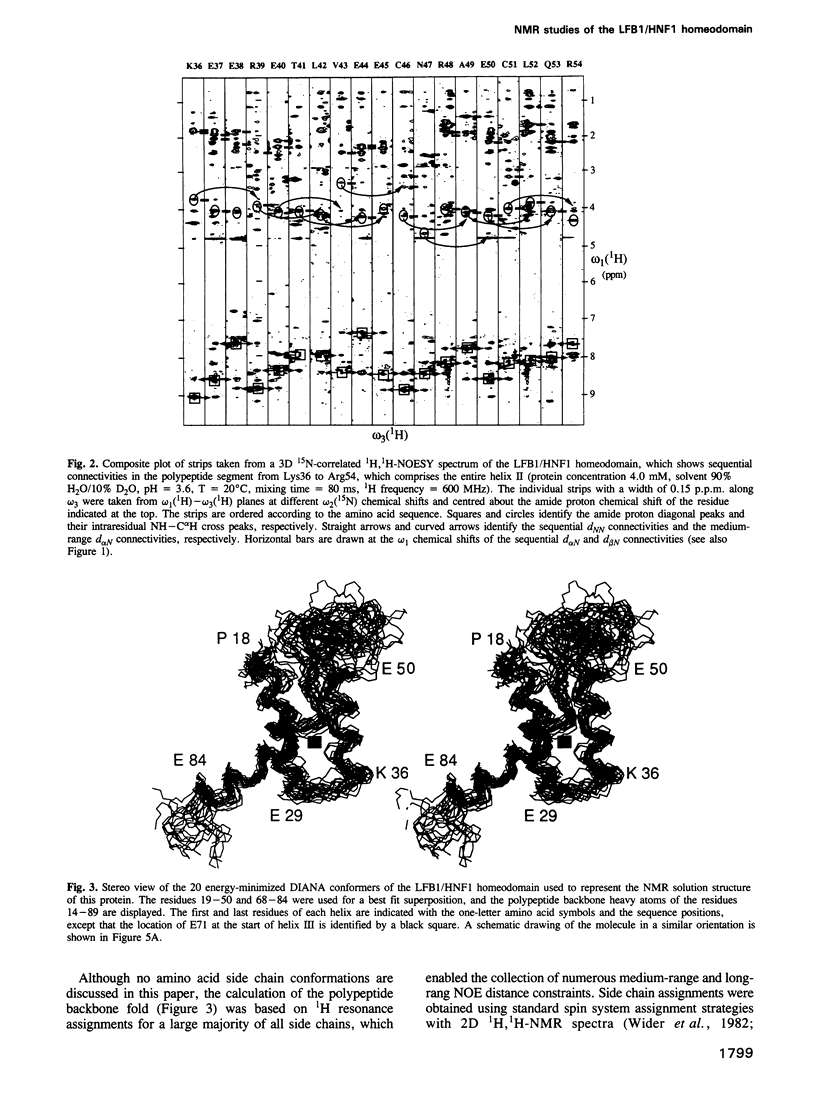
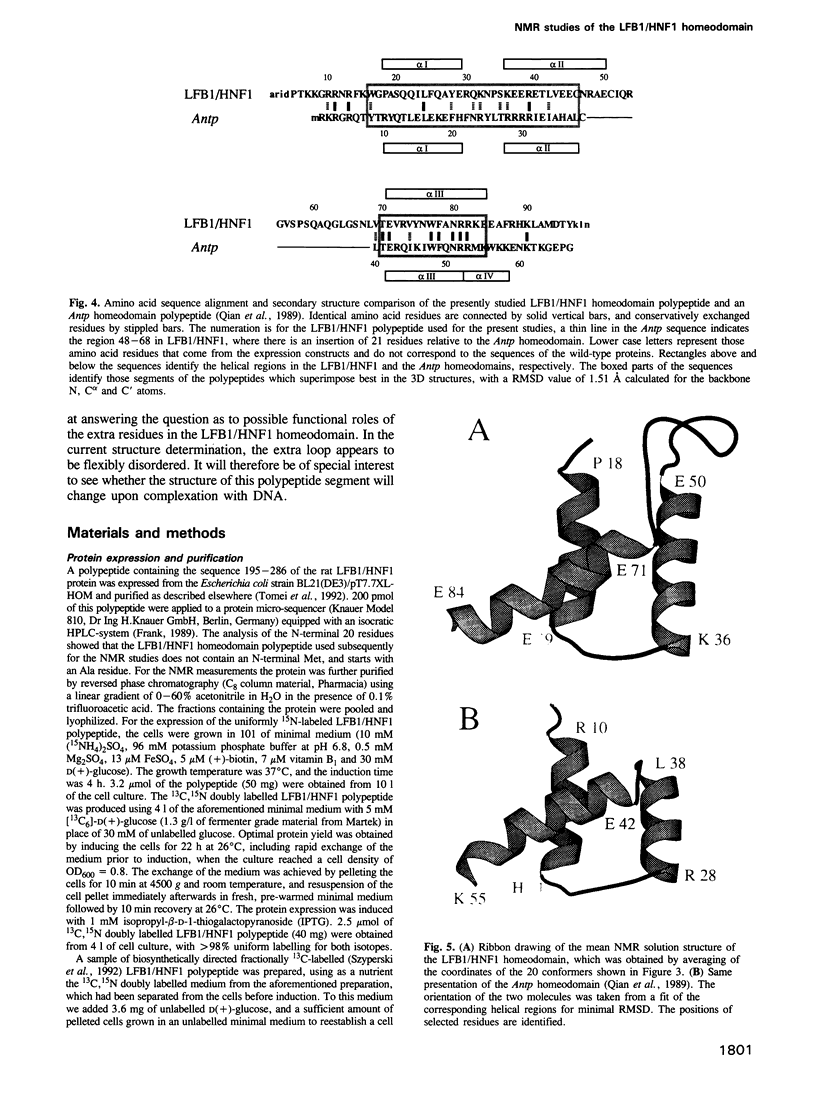
The three-dimensional backbone fold of a polypeptide fragment from the rat LFB1/HNF1 transcription factor was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in solution. This fragment contains an amino acid sequence that is approximately 22% homologous to the well known homeodomains, but which contains 81 amino acid residues as compared with 60 residues in 'typical' homeodomains. For the present studies we used a recombinant 99 amino acid polypeptide containing this sequence in positions 10-90, which was uniformly labelled with 15N and also doubly labelled with 15N and 13C. The NMR structure of this polypeptide contains three alpha-helices comprising the residues 18-29, 36-50 and 71-84, a loop formed by residues 30-35, and a long stretch of non-regular secondary structure linking the second and third helices. The relative location and orientation of the helices is very similar to that in the Antennapedia (Antp) homeodomain structure, despite the fact that helix II is elongated by about one turn. This confirms a recently advanced hypothesis based on sequence comparisons that this polypeptide segment of LFB1/HNF1 might represent a homeodomain-like structural element. The helix-turn-helix motif, which has been shown to comprise the DNA recognition helix in the Antp homeodomain, can readily be recognized in the LFB1/HNF1 homeodomain, in spite of an extensive modification of the primary structure. The two residues of the tight turn in the Antp homeodomain are replaced by a 23 residue linker region between the two helices in LFB1/HNF1, which bulges out from the rest of the molecule and thus enables the formation of a non-classical helix--turn--helix motif.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Computation of sterically allowed proton-proton distances and statistical analysis of proton-proton distances in single crystal protein conformations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):321–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Neri D., Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Wüthrich K. Precise vicinal coupling constants 3JHN alpha in proteins from nonlinear fits of J-modulated [15N,1H]-COSY experiments. J Biomol NMR. 1992 May;2(3):257–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01875320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Qian Y., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Determination of the three-dimensional structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain from Drosophila in solution by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90155-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Cortese R. Transcriptional regulation of liver-specific gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):960–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90114-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll P. C., Gronenborn A. M., Wingfield P. T., Clore G. M. Determination of the secondary structure and molecular topology of interleukin-1 beta by use of two- and three-dimensional heteronuclear 15N-1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4668–4682. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles C., Güntert P., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Efficient analysis of protein 2D NMR spectra using the software package EASY. J Biomol NMR. 1991 Jul;1(2):111–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01877224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M. The homeodomain of the transcription factor LF-B1 has a 21 amino acid loop between helix 2 and helix 3. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90708-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güntert P., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Efficient computation of three-dimensional protein structures in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data using the program DIANA and the supporting programs CALIBA, HABAS and GLOMSA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):517–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90754-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güntert P., Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Structure determination of the Antp (C39----S) homeodomain from nuclear magnetic resonance data in solution using a novel strategy for the structure calculation with the programs DIANA, CALIBA, HABAS and GLOMSA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90755-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güntert P., Wüthrich K. Improved efficiency of protein structure calculations from NMR data using the program DIANA with redundant dihedral angle constraints. J Biomol NMR. 1991 Nov;1(4):447–456. doi: 10.1007/BF02192866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Gene duplications in the structural evolution of chymotrypsin. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 15;128(1):49–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1, a member of a novel class of dimerizing homeodomain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri D., Wider G., Wüthrich K. Complete 15N and 1H NMR assignments for the amino-terminal domain of the phage 434 repressor in the urea-unfolded form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Monaci P., Tomei L., De Francesco R., Nuzzo M., Stunnenberg H., Cortese R. A myosin-like dimerization helix and an extra-large homeodomain are essential elements of the tripartite DNA binding structure of LFB1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1225–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90687-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure determination for the Antennapedia homeodomain by nuclear magnetic resonance and evidence for a helix-turn-helix motif. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4305–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Calibration of the angular dependence of the amide proton-C alpha proton coupling constants, 3JHN alpha, in a globular protein. Use of 3JHN alpha for identification of helical secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyperski T., Neri D., Leiting B., Otting G., Wüthrich K. Support of 1H NMR assignments in proteins by biosynthetically directed fractional 13C-labeling. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Jul;2(4):323–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01874811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomei L., Cortese R., De Francesco R. A POU-A related region dictates DNA binding specificity of LFB1/HNF1 by orienting the two XL-homeodomains in the dimer. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4119–4129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):347–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wider G., Lee K. H., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Glucagon bound to perdeuterated dodecylphosphocholine micelles. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):367–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Spitzfaden C., Memmert K., Widmer H., Wider G. Protein secondary structure determination by NMR. Application with recombinant human cyclophilin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80808-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]