Abstract
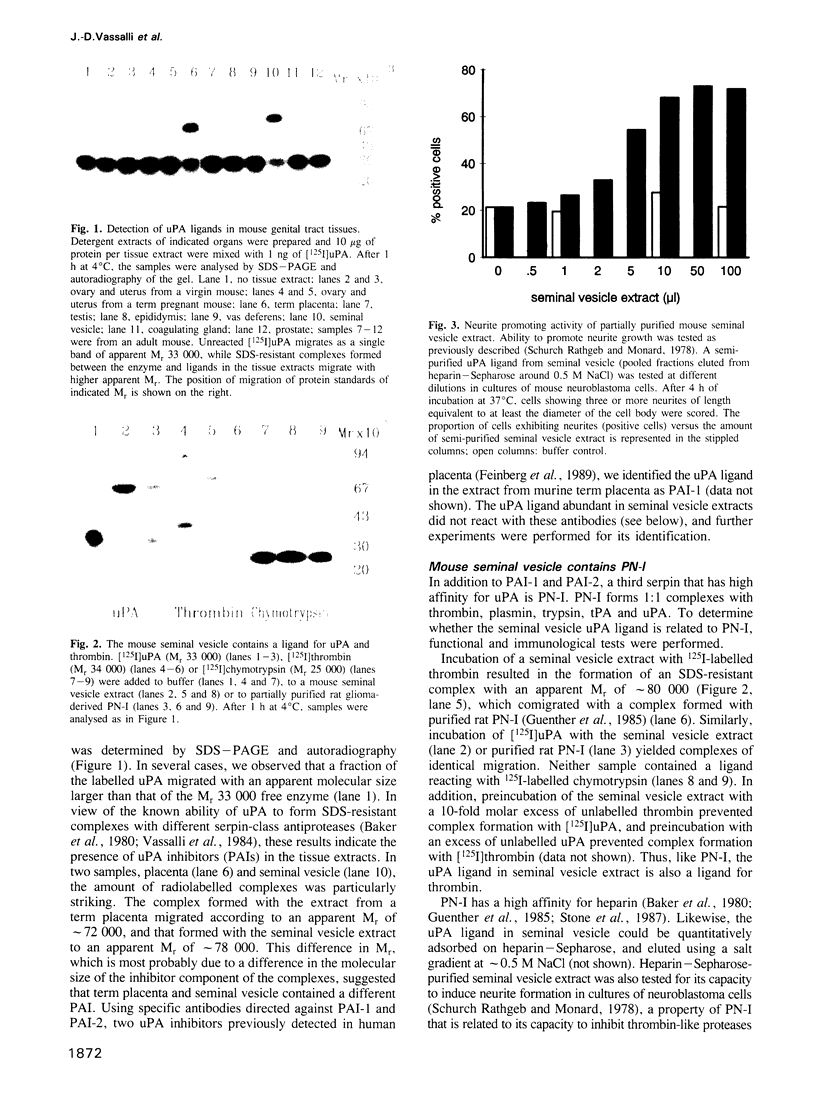
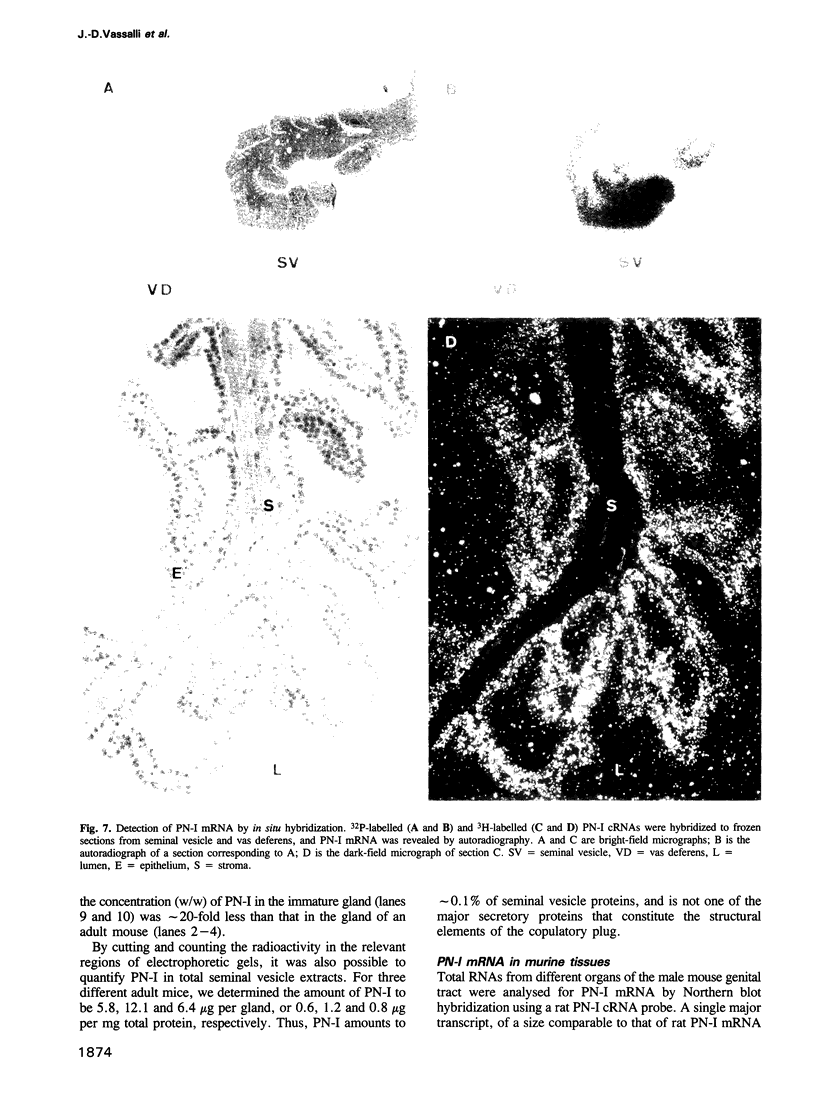
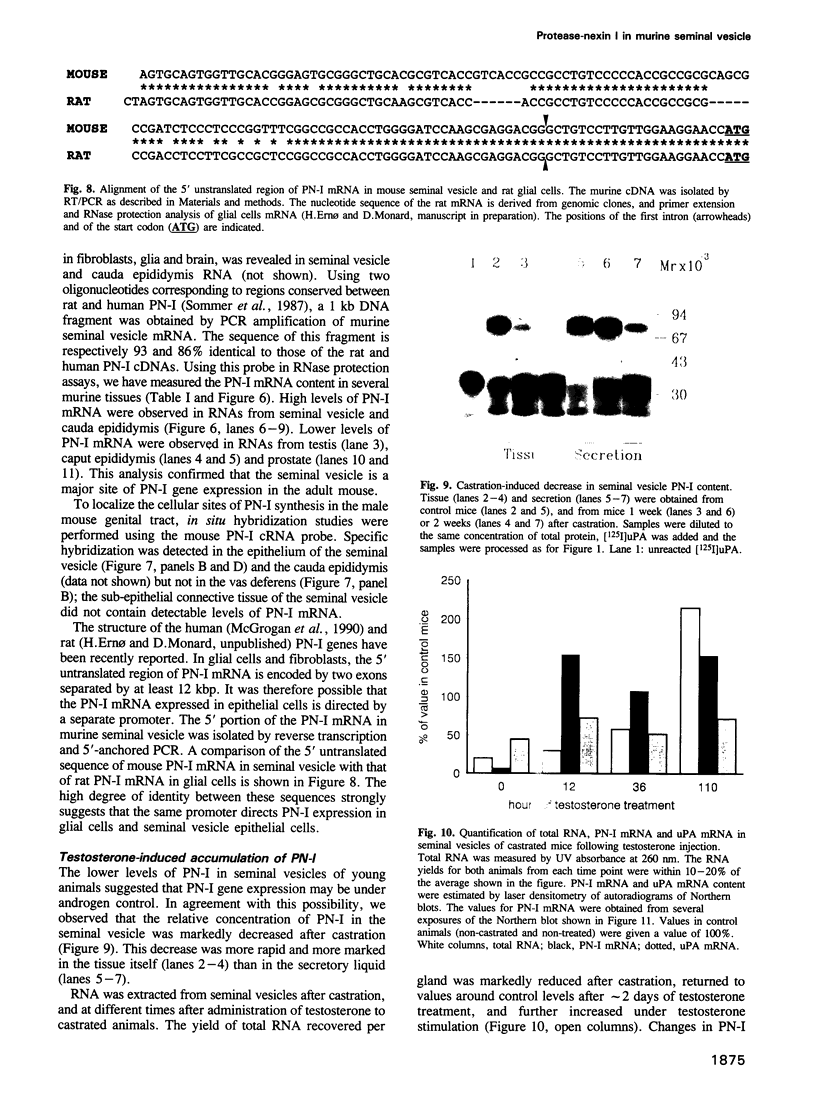
A search for inhibitors of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) in the male and female murine genital tracts revealed high levels of a uPA ligand in the seminal vesicle. This ligand is functionally, biochemically and immunologically indistinguishable from protease-nexin I (PN-I), a serpin ligand of thrombin and uPA previously detected only in mesenchymal cells and astrocytes. A survey of murine tissues indicates that PN-I mRNA is most abundant in seminal vesicles, where it represents 0.2-0.4% of the mRNAs. PN-I is synthesized in the epithelium of the seminal vesicle, as determined by in situ hybridization, and is secreted in the lumen of the gland. PN-I levels are much lower in immature animals, and strongly decreased upon castration. Testosterone treatment of castrated males rapidly restores PN-I mRNA levels, indicating that PN-I gene expression is under androgen control.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Means A. R., Wright E. J., Singh S. P., Tiver K. K. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for two major androgen-dependent secretory proteins of 18.5 kilodaltons synthesized by the rat epididymis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4956–4961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Belin D., Failly-Crépin C., Vassalli J. D. Glucocorticoid modulation of plasminogen activators and of one of their inhibitors in the human mammary carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 15;47(2):364–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Belin D., Failly-Crépin C., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in a human mammary cell line (HBL-100). Modulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9309–9315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Pentecost B. T., McLachlan J. A., Teng C. T. The androgen-dependent mouse seminal vesicle secretory protein IV: characterization and complementary deoxyribonucleic acid cloning. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):707–716. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A., Matheson B. A., Wines D. R., Brady J. M., MacDonald R. J., Funder J. W. Androgen dependence of specific kallikrein gene family members expressed in rat prostate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16132–16137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Baker J. B. Phorbol ester and mitogens stimulate human fibroblast secretions of plasmin-activatable plasminogen activator and protease nexin, an antiactivator/antiplasmin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):323–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- España F., Gilabert J., Estellés A., Romeu A., Aznar J., Cabo A. Functionally active protein C inhibitor/plasminogen activator inhibitor-3 (PCI/PAI-3) is secreted in seminal vesicles, occurs at high concentrations in human seminal plasma and complexes with prostate-specific antigen. Thromb Res. 1991 Nov 1;64(3):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90002-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. F., Kao L. C., Haimowitz J. E., Queenan J. T., Jr, Wun T. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 in human trophoblasts. PAI-1 is an immunocytochemical marker of invading trophoblasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festoff B. W., Rao J. S., Rayford A., Hantaï D. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in the neuromuscular system: II. Serpins and serpin: protease complex receptors increase during in vitro myogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Aug;144(2):272–279. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H. Human mucus proteinase inhibitor (human MPI). Human seminal inhibitor I (HUSI-I), antileukoprotease (ALP), secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369 (Suppl):79–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor S., Odink K., Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity belongs to the protease nexins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):687–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90511-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronke R. S., Knauer D. J., Veeraraghavan S., Baker J. B. A form of protease nexin I is expressed on the platelet surface during platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):472–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite-promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D. Thrombin modulates and reverses neuroblastoma neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. E., Harris M. A., Johnson C. M., Bean M. F., Dodd J. G., Matusik R. J., Carr S. A., Crabb J. W. Structural characterization of the rat seminal vesicle secretion II protein and gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9896–9903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Hemingway A. L. Effects of androgens on the transcription of secretory protein genes in rat seminal vesicle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;76(1-3):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90259-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Bosco D., Sappino A. P., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator and mouse spermatozoa: urokinase synthesis in the male genital tract and binding of the enzyme to the sperm cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1281–1289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Carrell R. W. Implications of the three-dimensional structure of alpha 1-antitrypsin for structure and function of serpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):8951–8966. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. L., Chen S. W., Chen Y. H. Purification and characterization of a trypsin inhibitor from mouse seminal vesicle secretion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90540-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Skriver L., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Danø K. Distribution of urokinase-type plasminogen activator immunoreactivity in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):894–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell M., Christensson A., Abrahamsson P. A., Stenflo J., Lilja H. Protein C inhibitor in human body fluids. Seminal plasma is rich in inhibitor antigen deriving from cells throughout the male reproductive system. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1094–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI115689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low D. A., Baker J. B., Koonce W. C., Cunningham D. D. Released protease-nexin regulates cellular binding, internalization, and degradation of serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier R., Spreyer P., Ortmann R., Harel A., Monard D. Induction of glia-derived nexin after lesion of a peripheral nerve. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):548–550. doi: 10.1038/342548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. S., Needham M., Parker M. G. A secretory protease inhibitor requires androgens for its expression in male sex accessory tissues but is expressed constitutively in pancreas. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3711–3717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02705.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Niday E., Limat A., Solomon F. Inhibition of protease activity can lead to neurite extension in neuroblastoma cells. Prog Brain Res. 1983;58:359–364. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möritz A., Lilja H., Fink E. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA encoding the human acrosin-trypsin inhibitor (HUSI-II). FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80099-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Kistler M. K., Kistler W. S. Effect of castration on the synthesis of seminal vesicle secretory protein IV in the rat. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3525–3529. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard E., Meier R., Halfter W., Rovelli G., Monard D. Detection of glia-derived nexin in the olfactory system of the rat. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt D. E., Cotman C. W., Nieto-Sampedro M., Rowe J. W., Knauer D. J. Identification of a protease inhibitor produced by astrocytes that is structurally and functionally homologous to human protease nexin-I. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 7;415(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Vihko K. K. Local synthesis of plasminogen by the seminiferous tubules of the testis. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80810-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifman A. L., Mansson P. E., Carter D. B., Yamada K., Harris M. M., Harris S. E. Structure of the androgen dependent SVS VI protein as derived from cDNA. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Sep;59(1-2):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurch-Rathgeb Y., Mongard D. Brain development influences the appearance of glial factor-like activity in rat brain primary cultures. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):308–309. doi: 10.1038/273308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J., Gloor S. M., Rovelli G. F., Hofsteenge J., Nick H., Meier R., Monard D. cDNA sequence coding for a rat glia-derived nexin and its homology to members of the serpin superfamily. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6407–6410. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Nick H., Hofsteenge J., Monard D. Glial-derived neurite-promoting factor is a slow-binding inhibitor of trypsin, thrombin, and urokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jan;252(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Dayer J. M., Wohlwend A., Belin D. Concomitant secretion of prourokinase and of a plasminogen activator-specific inhibitor by cultured human monocytes-macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1653–1668. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Lee P. J., M'Timkulu T., Chan W. P., Loor R. Human prostate-specific antigen: structural and functional similarity with serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3166–3170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlwend A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator-specific inhibitors in mouse macrophages: in vivo and in vitro modulation of their synthesis and secretion. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1278–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]












