Abstract
Introduction: Ineffective communication is a main factor in engender of unwanted hospital errors and impede suitable patient care. SBAR technique (Situation-Background- Assessment- Recommendation) is a standard tool for building communication among healthcare professionals. While educating the SBAR technique requires appropriate educational methods, but this issue has been less investigated. So, the aim of present study was to compare the effect of educating the SBAR technique with role play and lecturing on communication skills of nurses in transferring patients to next shift. Methods: This quasi-experimental study conducted by participating 78 nurses who assigned to role play and lecturing groups randomly. SBAR technique was educated to each group separately. At the end of the learning session in each group, the skills of the participants in performing SBAR technique were investigated by the standard SBAR scale. Data analysis was performed by using SPSS statistical software version 11.5. Results: Comparison the total score of performing SBAR technique using independent samples t-test showed statistical differences between mean score of role play and lecturing groups. Similarly, comparison the scores of skill in performing each four parts of SBAR technique showed statistical differences between two groups. Conclusion: Role play is an effective educational method in teaching SBAR technique for nurses and it can be used as a tool for build effective communication between healthcare professionals.
Keywords: Communication, Nurses, Teaching
Introduction
Providing safe patient care is a challenge in today’s health care settings. Nowadays, despite advances in medical technology, effective interpersonal communication remains one of the basic principles in the delivery of health care. Consequently, interpersonal communication is a key to promote effective patient care. 1
Today, even patients who receive care from health care specialists still face many medical errors.2 In fact, over 60% of fatal hospital incidents occurred due to poor communication between healthcare providers.3 Ineffective communication between health care personnel is a major factor in the creation of the unwanted hospital incidents including: medication errors, delay in treatment process, mortality, injury, and error in surgical site.1 Painfully, many of these errors that jeopardize the patient safety resulted from improper communication and ineffective communication system, not for staff errors.3
Today, nurses are less using standard communication methods that can help them during shift change.3Ineffective commun- ication during shift change and transfer of patients increase the rate of medical errors and may result in loss of vital medical information.1 Therefore, using a standard tool for communication, especially at the time of shift change, is an opportunity for the creation of proper and effective communication between healthcare professionals.3
SBAR technique (Situation–Background–Assessment–Recommendation) is a tool that allows the medical team to communicate with each other in a standard way.4,5,6 SBAR is an easy and objective way to remember and building any communication, especially in critical situations.6 By using this method, correct transfer of medical information during shift change is achievable for nurses and identification of any error in information transfer process can be possible easily.3 In fact, SBAR is a structured method for transfer of vital information of patients that needs immediate attention and action. This technique enhances the communication between health professionals and increase patient safety. SBAR technique have four elements including: present situation of patient, previous background of patient, assessment of patient problems, and recommendations for solving the problems.5,6
However, using SBAR technique requires that nurses and other health professionals were adequately educated about it. Consequently, appropriate educational methods should be used for teaching this method. Role play is an appropriate educational method in this regard.7 Role play is a simulation technique that helps participants to experience decision-making process in an environment that is free from any concerns about the impact of these decisions on their real relationship.7,8 This method has been proposed for teaching in a controlled enviro- nment and aim is to improve the skills in performing a specific duty.8
In some Iranian studies the effects of teaching with role play were investigated on some learning outcomes of health care students. For example, Erfanian et al., investigated the effects of teaching using role play on students’ counseling and screening skills in encounter with patients who candidate for inserting intrauterine device (IUD).8 As another example, Rafiee et al., (2007) compare the caring behavior of nursing students after educating with role play and traditional method.7 These two studies showed that role play is an effective educational method for teaching students. Moreover, in another study Kesten used role play to teach SBAR technique for nursing students. The results of this study showed that nursing students who educated with role play showed more communication skills and less violence in communication comparing with students who were educated with traditional method.2
Role play as a teaching method has many benefits. In teaching by role play participants are able to experience different and problematic situations and perform different decisions and actions without stress. Therefore, this method is an excellent educational method when the aim of teaching is to increase interpersonal communication skills of partcipants.7,9 On the other hand, SBAR technique is designed for increase the communication skills of healthcare professionals. It should be noted that in extensive review of relevant literature there is few research evidence about the effects of teaching of SBAR technique by using role play on communication skill of health care providers. So, the aim of present study was to compare the effect of educating the SBAR technique with role play and lecturing on communication skills of nurses in transferring patients to next shift.
Materials and Methods
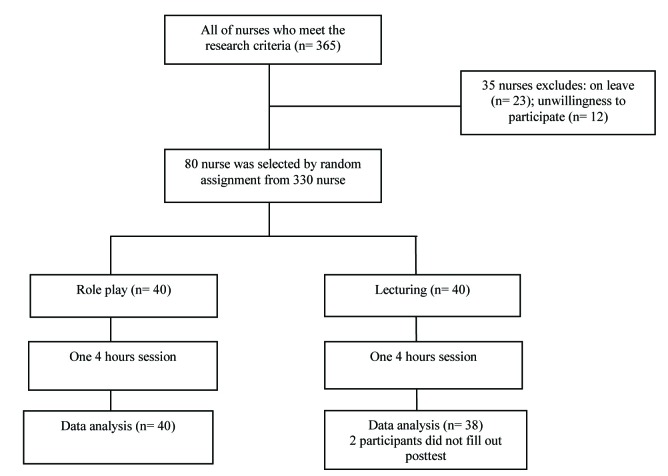
This quasi-experimental study used post-test only design with experimental and control groups to examine the effect of teaching the SBAR technique with two educational methods including role play and lecturing. The sample size was calculated based on previous Iranian studies.7,8 By considering test power= 0.8, α= 0.05, and Confidence Interval (CI)= 95% the optimal sample size for each group was determined as 35 nurses. Considering the probability of sample loss, the sample size for each group was estimated to be 40 nurses.
By the start of sampling, researchers obtained the list of all nurses working in Ayatollah Kashany teaching hospital form nursing services management office using census sampling method. Then, all of nurses invited to participate in the study through Health Information System (HIS). Then, of all nurses who were willing to participate in the study were asked to write down their user ID on prepared cards and send them to nursing office. After that, these cards were placed in basket and the clerk of nursing office removed cards from the basket randomly. Nurses with odd ID numbers were assigned to lecturing group and nurses with even numbers were assigned to role play group. This procedure was repeated until 40 nurses were included in each group.
Then, the SBAR technique was educated for lecturing group based of lecture, slideshow and citing examples. In role play group, a brief explanation of SBAR technique was presented. Then, the participants were divided into four groups. Hereinafter, all nurses engaged in hypothetical situations created by researcher and then discussed it in their groups. The researcher supervised the performance of groups in all phases and provided them with necessity feedbacks. The learning session for two groups was implemented in four hours session with one week apart. The education of SBAR technique with role play and lecturing was conducted by first author. This researcher designed hypothetical situations for each group in the end of sessions. Both groups of nurses were asked to put themselves in that situation and transfer their patient to next shift by SBAR technique. Then, the skills of each nurse in performing SBAR technique was assessed using standard SBAR scale.
This tool is a well-known and clear scale and its validity was approved by National Patient Safety Goals. This scale is applicable for different conditions and health care settings and its reliability was approved in previous studies.2 In present study the reliability of this scale was approved by using inter-rater reliability after assessment the performance of participants by two researchers (agreement percent = 98%). SBAR scale consists of four items. These items were including situation, background, assessment and recommendation. These items were not translated into Persian because they are very familiar and tangible words for Iranian nurses. This tool investigates the skill in transferring patients’ clinical information in four areas including: situation, background, assessment, and recommendation.6 For each part of SBAR technique, the score ranges from 0 to 1. Score 1 is for nurses who were doing any phases of the skill correctly. So, the final score for each nurse was ranged from 0 to 4 to for total SBAR technique.
It should be noted that all assessment of skills in doing SBAR technique in role play and lecturing groups was conducted by second researcher who was unaware of the arrangement of groups. The aim of the study was explained for all participants and they were assured that they could move from the study in any phases.
The normality of the distribution of research variables was examined using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Parametric tests were used for normally distributed variables and non-parametric test were used for non-normal ones. For analyzing nominal and ordinal variables chi-square, Mann-Whitney and Fisher exact tests were used bases on the type and normality of variables. For comparison the mean score of skill in performing communication technique between two groups independent t-test was used. Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistical software version 11.5 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
The study procedure is shown in figure 1.
Figure 1.
Clinical trial flowchart
Results
This research eventually included 40 nurses in role play group and 38 nurses in lecturing group. It should be noted that 2 nurses in lecturing group have not completed final assessment and excluded from the study. The data analysis showed that all research variables have normal distribution. Some demographic information of nurses is reported in table 1.
Table 1. Comparison some demographic characteristics of role play and lecturing groups.
| Variables |
Role play
N (%) |
Lecturing
N (%) |
Statistical indicators |
| Sex | X2=1.68; df=1; P=0.19 | ||
| Female | 38 (95) | 35 (92.2) | |
| Male | 2 (5) | 3 (7.8) | |
| Marital status | X2=0.83; df=1; P=0.61 | ||
| Single | 25 (62.5) | 22 (57.9) | |
| Married | 15 (37.5) | 16 (42.1) | |
| Age * | X2=1.82; df=2; P=0.73 | ||
| 25 - 35 | 19 (47.5) | 16 (42.1) | |
| 36-40 | 15 (37.5) | 12 (31.5) | |
| >40 | 2 (12.5) | 7 (18.4) | |
| Education | X2=1.87; df=1; P=0.63 | ||
| Bachelor | 39 (97.5) | 35 (92.2) | |
| Master of Sciences | 1 (2.5) | 3 (7.8) | |
| Employment status | X2=1.7; df=1; P=0.19 | ||
| Formal | 28 (70) | 27 (71.06) | |
| Informal | 12 (30) | 11 (28.94) | |
| Residence | X2=1.0; df=1; P=0.62 | ||
| Native | 35 (87.5) | 31 (81.6) | |
| Not native | 5 (12.5) | 7 (18.4) | |
| Position | X2=1.9; df=1; P=0.69 | ||
| Clinical nurse | 37 (92.5) | 36 (94.8) | |
| Head nurse | 3 (7.5) | 2 (5.2) |
*Some participants did not answer to this item
Comparison the total score of skill in performing SBAR technique by independent samples t-test showed that there was statistical difference between role play and lecturing groups (P= 0.001).
In other word, role play as an educational method has better effects on learning of SBAR communication technique. In addition, independent sample t-test was used for comparing the score of two groups in each four phases of SBAR technique separately. Comparison the mean score of role play group with lecturing group in situation part of SBAR technique showed meaningful statistical difference (P=0.001). Similarly, independent samples t-test showed statistical differences between mean scores of two groups in Background, Assessment and Recommendation parts of SBAR technique (P=0.001). Table 2 showed mean and standard deviation of scores of SBAR technique in two groups in four parts of technique.
Table 2. Mean and standard deviation of scores of role play and lecturing groups in performing SBAR technique.
| Variable |
Lecture group
(n= 38) Mean (SD) |
Role play
(n= 38) Mean (SD) |
95% CI * for difference | P- value ** |
| Situation | 0.421 (0.50) | 0.834 (0.37) | -0.57 , -0.18 | 0.001 |
| Background | 0.328 (0.46) | 0.725 (0.43) | -0.60 , -0.19 | 0.001 |
| Assessment | 0.302 (0.42) | 0.762 (0.39) | -0.64 , -0.27 | 0.001 |
| Recommendation | 0.144 (0.32) | 0.365 (0.49) | -0.68 , -0.32 | 0.001 |
| Total score | 1.193 (1.11) | 2.928 (1.20) | -2.28 , -1.19 | 0.001 |
*Confidence Interval, **P- value is for independent t-test
Discussion
Effective communication between health care professionals is inevitable and important factor in clinical decision making.10 The reason is that nurses, physicians and other healthcare professionals constantly face situations and conditions that needs properly and on time communication. Ineffective communication leads to unsatisfactory outcomes for patients.11 Firiesen et al., states that one of the five factors that inhibit effective communication between health care professionals is the multiple transfers of patients, together with the complexity of today’s health care system. These factors confuse the healthcare personnel.1 Unfortunately, these complexities exist in all healthcare settings and so several solutions are needed to overcome them. One of these solutions is identify and meet educational needs of healthcare personnel. These educations should be a way to build effective communication connections and lead to improvement in patient care.1
As the results of this study show, role play, compared to lecturing, significantly increase the communication skills of nurses in SBAR technique. It means that role play should be used in the teaching of communication skills for nurses or other health care professionals. In a similar study, Kesten used role play to improve communication skills in nursing students with SBAR technique. The results showed that students who educated by role play showed better performance effectiveness scores in comparison with students who were trained by theoretical training guidelines.2
Nurses are required to be trained about effective communication skills even when they graduated and began to independent clinical work. The importance of proper training of SBAR technique show that they have reduced unwanted hospital accidents and losing patients’ information by using this technique.5 Also, studies reported that proper use of communication methods decrease the errors in the site of surgery; improve the transfer process; and increase patient safety.5
In this study, comparison the four phase of SBAR technique, showed statistical differences between two groups. But, as evident in table 1, the lowest mean score obtained by two groups were in recommendation phase. This means that performance of nurses in this phase is weaker than other phases. For increase the quality of nursing care the nurses should be able to offer their comments and suggestions about patients’ problems. So, increase the ability of nurses in recommendation phase of SABR technique is necessary.
However, as emphasized by Firiesen et al., organizational support and commitment of mangers are two essential factors in successful usage of SABR technique. This support should contain providing learning opportunities, technical and official supports, supervision, and feedback.1 In other words, in today’s health care system organizations are required to create a culture and structure that facilitates appropriate and valid communication between health care staff. In this culture, the nurses should encourage to talk about the actual or potential problems they have in communication with themselves and with other healthcare staff. As we know, any problems in effective communication among health care professionals may create many problems and put patients at risk of harm. Therefore, this culture helps to protect patient safety and prevent unwanted hospital accidents.
The results of this study have some limitations. One limitation was a different work shift of nurses who participated in the study. This problem can affect the leaning outcomes of participants. Therefore, we recommended that similar studies should be conducted in samples of nurses with similar working shifts. These studies can lead to more valid results. In addition, because of familiarity with two role play and lecturing, the teaching for two groups was conducted by first researcher. This bias be able to affect the results of the study and should be considered as a limitation of the study.
Conclusion
Role play is an effective educational method in teaching SBAR technique for nurses and it can be used as a tool for build effective communication between healthcare professionals.
Acknowledgments
This research project was conducted by supports from Ayatollah Kashany teaching hospital affiliated to Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. Thanks for all of nurses who participated in this study and nursing services management office of Ayatollah Kashany teaching hospital that support the study.
Ethical issues
None to be declared.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
References
- 1.Firiesen MA, Hughes RG, Zorn M. Communication: patient safety and the nursing work environment. Nebr Nurse. 2007-2008;40(4):11–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kesten KS. Role-play using SBAR technique to improve observed communication skills in senior nursing students. J Nurs Educ. 2011;50(2):79–87. doi: 10.3928/01484834-20101230-02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chacko V, Varvarelis N, Kemp DG.e Hand-offs: an IBM lotus domino application for ensuring patient safety and enhancing resident supervision in hand-off communications. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2006; 874. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Velji K, Baker GR, Fancott C, Andreoli A, Boaro N, Tardif G, Aimone E, Sinclair L. Effectiveness of an adapted SBAR communication tool for a rehabilitation setting. Health C Q. 2008;11(3):72–9. doi: 10.12927/hcq.2008.19653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Haig KM, Sutton S, Whittington J. SBAR: a shared mental model for improving communication between clinicians. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2006;32(3):167–75. doi: 10.1016/s1553-7250(06)32022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Thomas CM, Bertram E, Johnson D. The SBAR communication technique: teaching nursing students professional communication skills. Nurse Educ. 2009;34(4):176–80. doi: 10.1097/NNE.0b013e3181aaba54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rafii F, Oskouie F, Mohammadi R, Yarandi A, F F, Peyrovi H, Haghani H. Caring behaviors of student nurses following clinical experience through role play and traditional method. Iran Journal of Nursing. 2007;20(50):7–19. (Persian) [Google Scholar]
- 8.Erfanian F, Khadivzadeh T, Khadem N, Khajedelooie M. The effect of teaching by role playing on students' counseling and screening skills toward IUD clients. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2009;8(2):275–83. (Persian) [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rafii F, Oskouie F, Peyrovi H, Haghani H. A comparative study of the effectiveness of the clinical practice of fundamental nursing through role-play versus traditional method on caring behaviors of sophomore-level nursing students. Iran Journal of Nursing . 2009; 22(60):42–52. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Renz SM, Boltz MP, Wagner LM, Capezuti EA, Lawrence TE. Examining the feasibility and utility of an SBAR protocol in long-term care. Geriatr Nurs. 2013;34(4):295–301. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2013.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Woodhall LJ, Vertacnik L, McLaughlin M. Implementation of the SBAR communication technique in a tertiary center. J Emerg Nurs. 2008;34(4):314–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jen.2007.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]