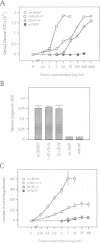
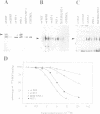
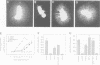
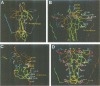
Abstract
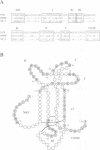
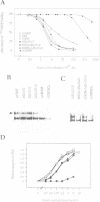
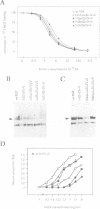
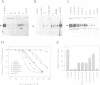
Neurotrophin-mediated cell survival and differentiation of vertebrate neurons is caused by ligand-specific binding to the Trk family of tyrosine kinase receptors. However, sites in the neurotrophins responsible for the binding to Trk receptors and the mechanisms whereby this interaction results in receptor activation and biological activity are unknown. Here we show that in nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), discontinuous stretches of amino acid residues group together on one side of the neurotrophin dimer forming a continuous surface responsible for binding to and activation of TrkA and TrkB receptors. Two symmetrical surfaces are formed along the two-fold axis of the neurotrophin dimer providing a model for ligand-mediated receptor dimerization. Mutated neurotrophins inducing similar levels of receptor phosphorylation showed different biological activities, suggesting that structural differences in a ligand may result in dissimilar responses in a given tyrosine kinase receptor. Our results allowed us to combine structural elements from NGF, BDNF and neurotrophin-3 to engineer a pan-neurotrophin that efficiently activates all Trk receptors and displays multiple neurotrophic specificities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Thoenen H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):549–553. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Hempstead B. L., Chao M. V. The low-affinity p75 nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor mediates NGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7106–7110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier L. R., Winslow J. W., Kaplan D. R., Nikolics K., Goeddel D. V., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Tapley P., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Lamballe F., Kovary K., Klein R., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. The trk tyrosine protein kinase mediates the mitogenic properties of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daopin S., Piez K. A., Ogawa Y., Davies D. R. Crystal structure of transforming growth factor-beta 2: an unusual fold for the superfamily. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):369–373. doi: 10.1126/science.1631557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Olson L., Persson H. Molecular cloning and neurotrophic activities of a protein with structural similarities to nerve growth factor: developmental and topographical expression in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Nye S. H., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Squinto S. P., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90629-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz R., Kolbeck R., Lottspeich F., Barde Y. A. Production and characterization of recombinant mouse neurotrophin-3. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 1;204(2):745–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallbök F., Ibáez C. F., Persson H. Evolutionary studies of the nerve growth factor family reveal a novel member abundantly expressed in Xenopus ovary. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):845–858. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Schleifer L. S., Chao M. V. Expression of functional nerve growth factor receptors after gene transfer. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):373–375. doi: 10.1126/science.2536190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer M., Pagliusi S. R., Hohn A., Leibrock J., Barde Y. A. Regional distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult mouse brain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2459–2464. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn A., Leibrock J., Bailey K., Barde Y. A. Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):339–341. doi: 10.1038/344339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M., Shooter E. M. Molecular characteristics of nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Persson H. Chimeric molecules with multiple neurotrophic activities reveal structural elements determining the specificities of NGF and BDNF. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2105–2110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Hallbök F., Ebendal T., Persson H. Structure-function studies of nerve growth factor: functional importance of highly conserved amino acid residues. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1477–1483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Hallbök F., Söderström S., Ebendal T., Persson H. Biological and immunological properties of recombinant human, rat, and chicken nerve growth factors: a comparative study. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Ibáez C. F., Nye S. H., McClain J., Jones P. F., Gies D. R., Belluscio L., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Squinto S. P. Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing S., Tapley P., Barbacid M. Nerve growth factor mediates signal transduction through trk homodimer receptors. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90066-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. Molecular cloning of a human gene that is a member of the nerve growth factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaisho Y., Yoshimura K., Nakahama K. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding a novel human neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81536-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Lamballe F., Bryant S., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for neurotrophin-4. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90209-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Nanduri V., Jing S. A., Lamballe F., Tapley P., Bryant S., Cordon-Cardo C., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90628-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., Hofer M., Hengerer B., Masiakowski P., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):149–152. doi: 10.1038/341149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Placode and neural crest-derived sensory neurons are responsive at early developmental stages to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald N. Q., Lapatto R., Murray-Rust J., Gunning J., Wlodawer A., Blundell T. L. New protein fold revealed by a 2.3-A resolution crystal structure of nerve growth factor. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):411–414. doi: 10.1038/354411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. Molecular investigations on the high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90130-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Dionne C. A., Li W., Li N., Spivak T., Honegger A. M., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Point mutation in FGF receptor eliminates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis without affecting mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):681–684. doi: 10.1038/358681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa S. H., Tager H. S. Role of the phenylalanine B25 side chain in directing insulin interaction with its receptor. Steric and conformational effects. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7332–7341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oefner C., D'Arcy A., Winkler F. K., Eggimann B., Hosang M. Crystal structure of human platelet-derived growth factor BB. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3921–3926. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. G., Marie J., Wilson E., Ives H. E., Escobedo J., Del Rosario M., Mirda D., Williams L. T. Point mutation of an FGF receptor abolishes phosphatidylinositol turnover and Ca2+ flux but not mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):678–681. doi: 10.1038/358678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Hsu C., Herzenberg L. A., Shooter E. M. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the rat nerve growth factor receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):593–597. doi: 10.1038/325593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziejewski C., Robinson R. C., DiStefano P. S., Taylor J. W. Dimeric structure and conformational stability of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Biochemistry. 1992 May 12;31(18):4431–4436. doi: 10.1021/bi00133a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Tébar A., Dechant G., Barde Y. A. Binding of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to the nerve growth factor receptor. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90107-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Tébar A., Dechant G., Götz R., Barde Y. A. Binding of neurotrophin-3 to its neuronal receptors and interactions with nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):917–922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Goeddel D. V., Nguyen T., Lewis M., Shih A., Laramee G. R., Nikolics K., Winslow J. W. Primary structure and biological activity of a novel human neurotrophic factor. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90203-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlunegger M. P., Grütter M. G. An unusual feature revealed by the crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of human transforming growth factor-beta 2. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):430–434. doi: 10.1038/358430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Hart C. E., Phillips P. E., Forstrom J. W., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8771–8778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter U., Angst C., Tien C. L., Drinkwater C. C., Lindsay R. M., Shooter E. M. NGF/BDNF chimeric proteins: analysis of neurotrophin specificity by homolog-scanning mutagenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Jan;12(1):306–318. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-01-00306.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Bandtlow C., Heumann R. The physiological function of nerve growth factor in the central nervous system: comparison with the periphery. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;109:145–178. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weskamp G., Reichardt L. F. Evidence that biological activity of NGF is mediated through a novel subclass of high affinity receptors. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90067-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore S. R., Friedman P. L., Larhammar D., Persson H., Gonzalez-Carvajal M., Holets V. R. Rat beta-nerve growth factor sequence and site of synthesis in the adult hippocampus. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Aug;20(4):403–410. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490200402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Schlessinger J., Chao M. V. Chimeric NGF-EGF receptors define domains responsible for neuronal differentiation. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1850551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]