Abstract
Cytochrome b2, a protein of the yeast mitochondrial intermembrane space, is synthesized with an 80 residue bipartite presequence. The amino-terminal portion resembles a matrix-targeting signal. The carboxy-terminal portion acts as a 'sorting signal' for the intermembrane space and contains a hydrophobic stretch. In order to define this sorting signal, we fused the first 167 residues of the cytochrome b2 precursor to a passenger protein, expressed the fusion protein in yeast and selected for mutations that caused mislocalization of the passenger protein to the matrix. Most mutations mapped within the first 81 amino-terminal residues of the cytochrome b2 moiety. They were located in three regions, all downstream of the matrix-targeting domain: a cluster of three basic residues upstream of the hydrophobic stretch, the hydrophobic stretch itself and the first residue of mature cytochrome b2. The level of missorting caused by mutations within the hydrophobic stretch did not correlate with their effects on hydrophobicity, but appeared to be related to changes in the conformation of this stretch. We conclude that the intermembrane space sorting signal of cytochrome b2 is decoded by protein-protein interactions rather than by simple partitioning into a lipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF
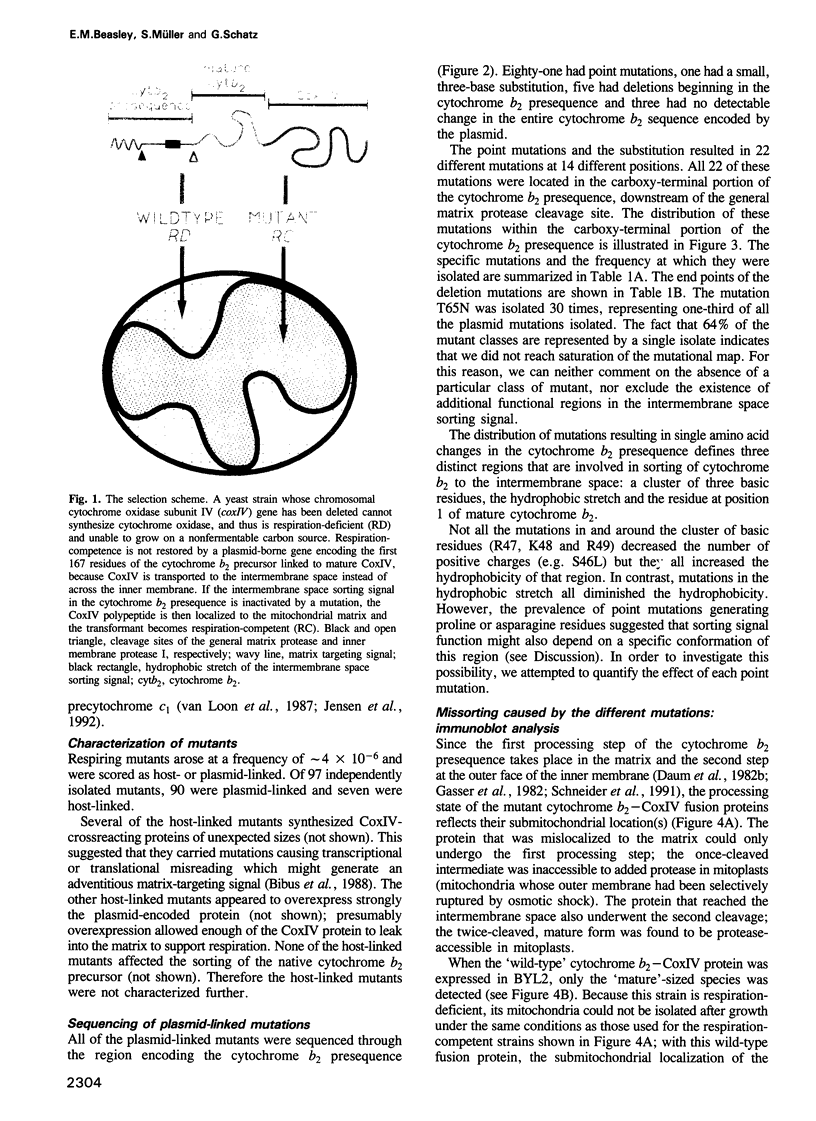







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audigier Y., Friedlander M., Blobel G. Multiple topogenic sequences in bovine opsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5783–5787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A., Schatz G. Sequences from a prokaryotic genome or the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene can restore the import of a truncated precursor protein into yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3117–3121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibus C. R., Lemire B. D., Suda K., Schatz G. Mutations restoring import of a yeast mitochondrial protein with a nonfunctional presequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13097–13102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inukai M., Inouye M. Dual functions of the signal peptide in protein transfer across the membrane. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Gasser S. M., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Energy-dependent, two-step processing of the intermembrane space enzyme cytochrome b2 by isolated yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13075–13080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowhan W., Bibus C. R., Schatz G. The cytoplasmically-made subunit IV is necessary for assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in yeast. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Ohashi A., Daum G., Böhni P. C., Gibson J., Reid G. A., Yonetani T., Schatz G. Imported mitochondrial proteins cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c1 are processed in two steps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):267–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. S., Beasley E. M., Schatz G. Protein sorting in mitochondria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Nov;17(11):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90487-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. S., Brandt A., Cunningham K., Müller S., Hallberg R. L., Schatz G. Cytochromes c1 and b2 are sorted to the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria by a stop-transfer mechanism. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):809–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90292-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. S. Protein import into isolated yeast mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;34:389–399. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61693-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiard B. Structure, expression and regulation of a nuclear gene encoding a mitochondrial protein: the yeast L(+)-lactate cytochrome c oxidoreductase (cytochrome b2). EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3265–3272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haid A., Suissa M. Immunochemical identification of membrane proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:192–205. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Protein sorting to mitochondria: evolutionary conservations of folding and assembly. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):930–938. doi: 10.1126/science.2406905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Ostermann J., Guiard B., Neupert W. Successive translocation into and out of the mitochondrial matrix: targeting of proteins to the intermembrane space by a bipartite signal peptide. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1027–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Müller U., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids of a yeast mitochondrial outer membrane protein can direct a nuclear-coded cytochrome oxidase subunit to the mitochondrial inner membrane. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3509–3518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Schatz G. The cleavable prepiece of an imported mitochondrial protein is sufficient to direct cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. FEBS Lett. 1984 Dec 10;178(2):306–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80622-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Suda K., Oppliger W., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids (less than half of the pre-sequence) of an imported mitochondrial protein can direct mouse cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the yeast mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2061–2068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. E., Schmidt S., Mark R. J. Mutations in a 19-amino-acid hydrophobic region of the yeast cytochrome c1 presequence prevent sorting to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4677–4686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koll H., Guiard B., Rassow J., Ostermann J., Horwich A. L., Neupert W., Hartl F. U. Antifolding activity of hsp60 couples protein import into the mitochondrial matrix with export to the intermembrane space. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1163–1175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90086-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa T., Sakaguchi M., Mihara K., Omura T. Structural requirements for interruption of protein translocation across rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biochem. 1990 Nov;108(5):829–834. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R. More than just a channel: provocative new features of protein traffic across the ER membrane. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Behrens M., Scherer P., Pratje E., Michaelis G., Schatz G. Inner membrane protease I, an enzyme mediating intramitochondrial protein sorting in yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):247–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Blobel G. A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Ibrahimi I., Cutler D., Dobberstein B., Bujard H. A novel in vitro transcription-translation system: accurate and efficient synthesis of single proteins from cloned DNA sequences. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3143–3148. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. Two nuclear mutations that block mitochondrial protein import in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost C. S., Lopez C. D., Prusiner S. B., Myers R. M., Lingappa V. R. Non-hydrophobic extracytoplasmic determinant of stop transfer in the prion protein. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):669–672. doi: 10.1038/343669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. P., Brändli A. W., Pesold-Hurt B., Blank D., Schatz G. Transport of proteins to the mitochondrial intermembrane space: the 'matrix-targeting' and the 'sorting' domains in the cytochrome c1 presequence. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2433–2439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. P., Schatz G. Transport of proteins to the mitochondrial intermembrane space: the 'sorting' domain of the cytochrome c1 presequence is a stop-transfer sequence specific for the mitochondrial inner membrane. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2441–2448. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







