Abstract
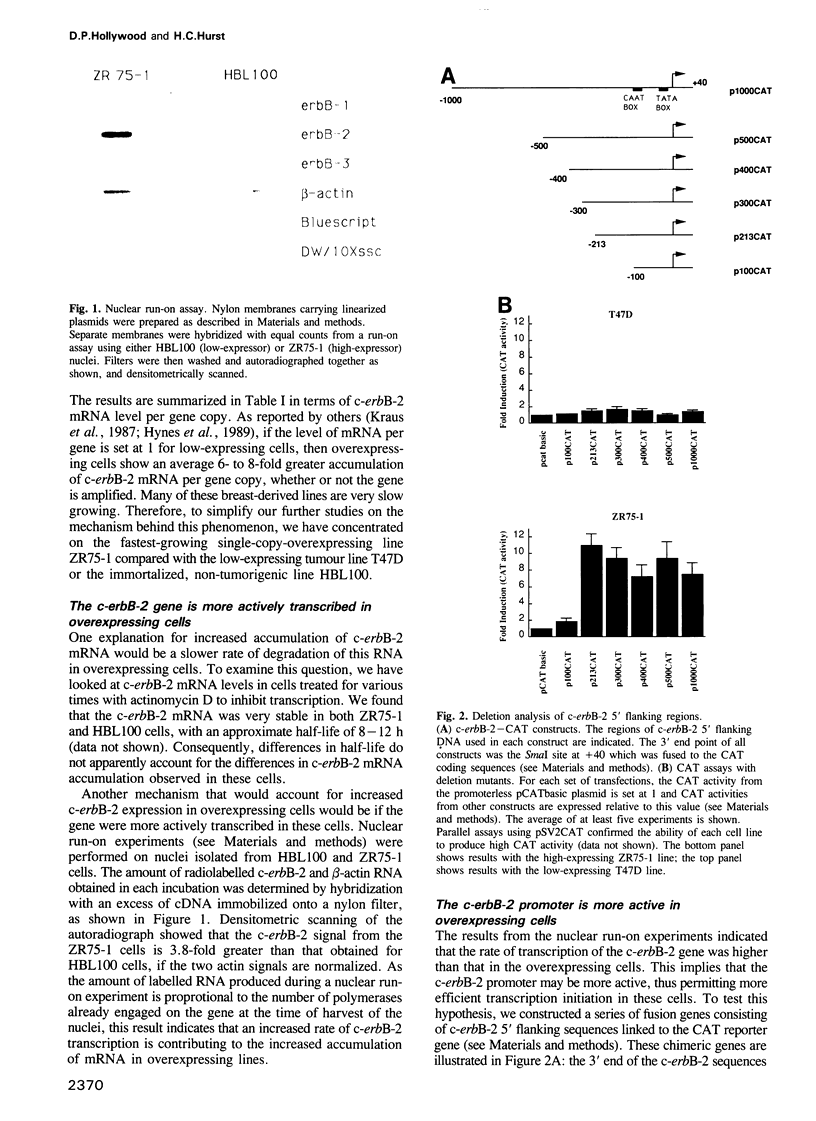
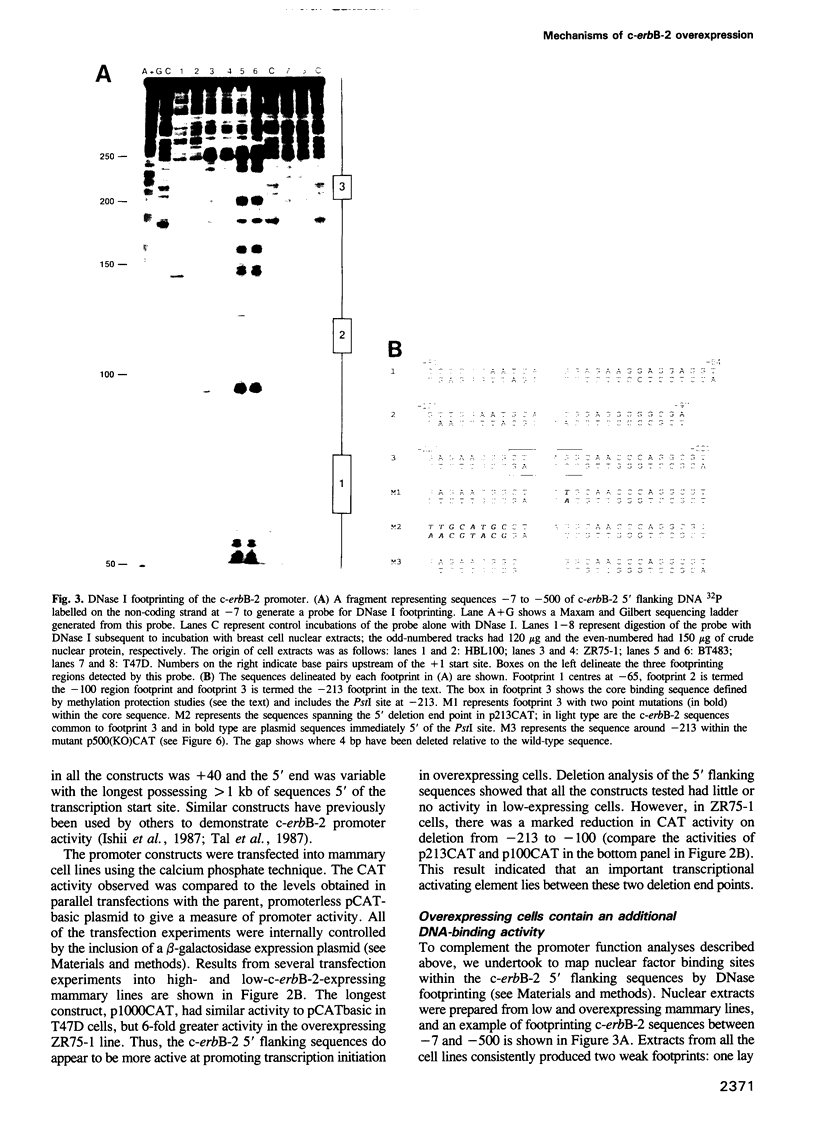
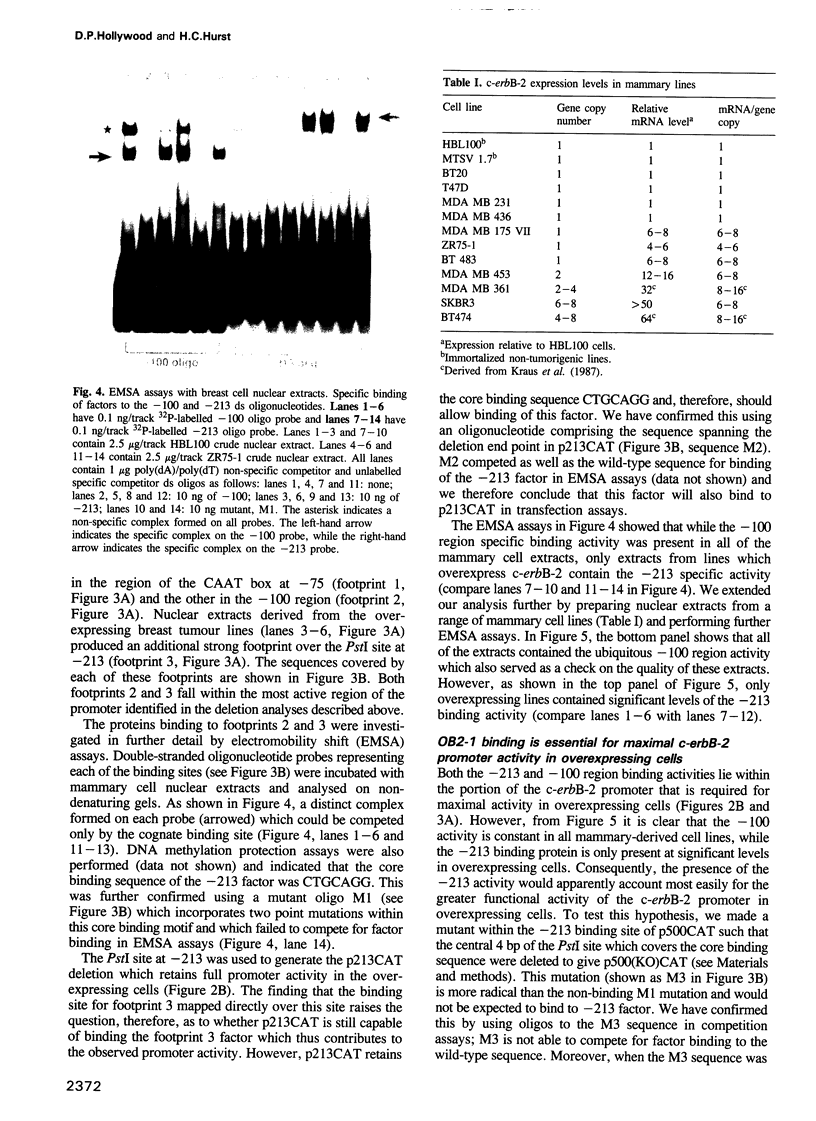
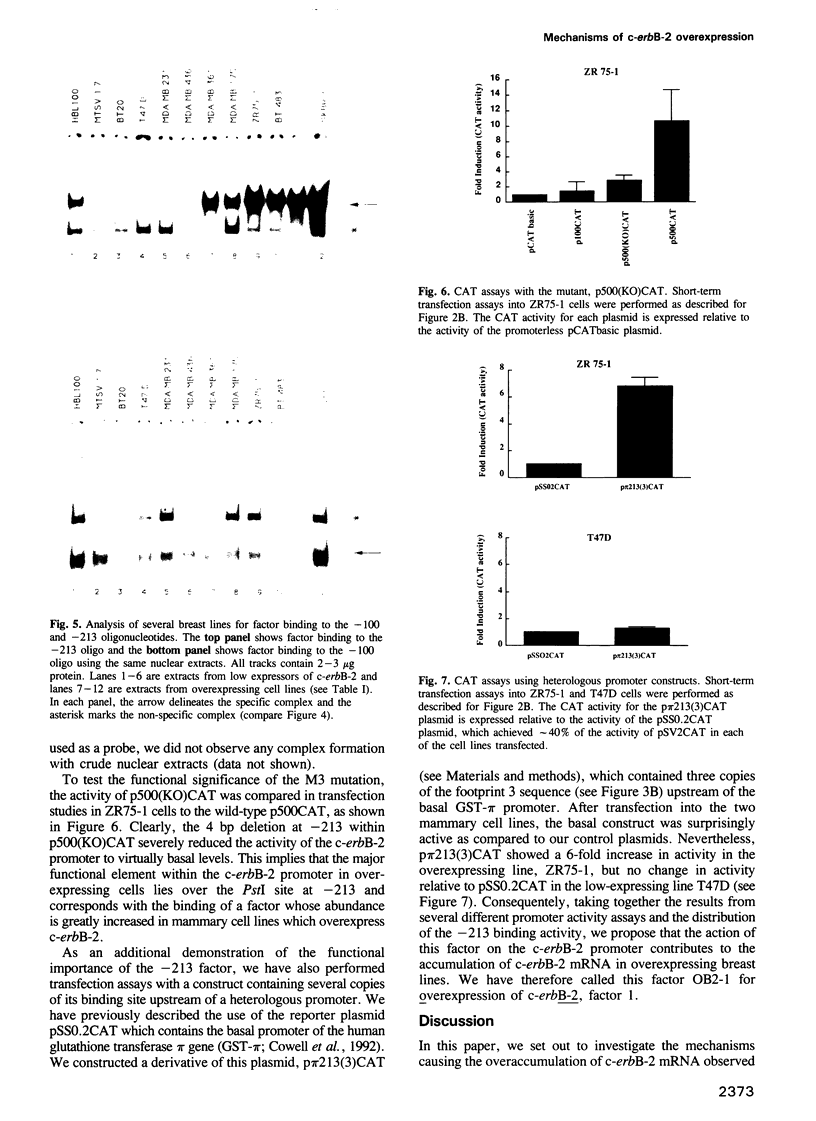
The c-erbB-2 receptor tyrosine kinase proto-oncogene product is overexpressed in 20-30% of breast carcinomas and this has been shown to correlate with poor prognosis. Previous analysis of tumour-derived lines has demonstrated that although the c-erbB-2 gene is often amplified, overexpression can occur from a single-copy gene. Moreover, whether or not the gene is amplified, overexpressing cells produce 6- to 8-fold more mRNA per gene copy than low-expressing cells. In this paper, we examine the possible mechanisms causing this deregulation of c-erbB-2 mRNA accumulation. Nuclear run-on studies indicated that the extra mRNA accumulation was due to increased transcription of the gene in overexpressing cells. Promoter analyses using c-erbB-2 5' flanking sequences linked to CAT showed that the promoter is more active in overexpressing cells. Coupling promoter deletion functional studies with footprinting experiments, using nuclear extracts derived from both low and overexpressing cells, allowed the identification of a DNA-binding protein, OB2-1, which is considerably more abundant in a range of overexpressing lines. We discuss the possible role of OB2-1 in c-erbB-2 overexpression in breast tumour lines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartek J., Bartkova J., Kyprianou N., Lalani E. N., Staskova Z., Shearer M., Chang S., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Efficient immortalization of luminal epithelial cells from human mammary gland by introduction of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen with a recombinant retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3520–3524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G., Skinner A., Hurst H. C. Transcriptional repression by a novel member of the bZIP family of transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3070–3077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. G., Ertl A. P., Gill G. N. Structure and inducible regulation of the human c-erb B2/neu promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4389–4393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Gerber H. A., Saurer S., Groner B. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 protein in human breast tumor cell lines. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):167–173. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglehart J. D., Kraus M. H., Langton B. C., Huper G., Kerns B. J., Marks J. R. Increased erbB-2 gene copies and expression in multiple stages of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6701–6707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Imamoto F., Yamanashi Y., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Characterization of the promoter region of the human c-erbB-2 protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4374–4378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda T., Yasui W., Yoshida K., Tsujino T., Nakayama H., Ito M., Ito H., Tahara E. Expression of ERBB2 in human gastric carcinomas: relationship between p185ERBB2 expression and the gene amplification. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):8002–8009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Swain S. M., Porter L., Steinberg S. M., Lippman M. E., Gelmann E. P. Heterogeneous expression of erbB-2 messenger RNA in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kury F. D., Schneeberger C., Sliutz G., Kubista E., Salzer H., Medl M., Leodolter S., Swoboda H., Zeillinger R., Spona J. Determination of HER-2/neu amplification and expression in tumor tissue and cultured cells using a simple, phenol free method for nucleic acid isolation. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1403–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leask A., Rosenberg M., Vassar R., Fuchs E. Regulation of a human epidermal keratin gene: sequences and nuclear factors involved in keratinocyte-specific transcription. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1985–1998. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine N. R., Barnes D. M., Hollywood D. P., Hughes C. M., Smith P., Dublin E., Prigent S. A., Gullick W. J., Hurst H. C. Expression of the ERBB3 gene product in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1992 Dec;66(6):1116–1121. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes H. C., Lillycrop K., Howell A., Craig R. K. C-erbB2 mRNA expression in human breast tumours: comparison with c-erbB2 DNA amplification and correlation with prognosis. Br J Cancer. 1990 Jan;61(1):39–45. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Cordon-Cardo C., Slamon D. J. Expression of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S., Bentley D. L. Distinct modes of transcription read through or terminate at the c-myc attenuator. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1085–1093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05147.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suen T. C., Hung M. C. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements involved in regulation of the neu gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6306–6315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., King C. R., Kraus M. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Human HER2 (neu) promoter: evidence for multiple mechanisms for transcriptional initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2597–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. R., Hung M. C. Cloning and characterization of the mouse neu promoter. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. M., Weiner D. B., Greene M. I., Maguire H. C., Jr Expression of c-erbB-2 in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Pathobiology. 1991;59(1):46–52. doi: 10.1159/000163614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C., Nicholson S., Angus B., Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J., Cairns J., Harris A. L., Horne C. H. Relationship between c-erbB-2 protein product expression and response to endocrine therapy in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1992 Jan;65(1):118–121. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Yoshimoto M., Murayama Y., Ebuchi M., Mori S., Yamamoto T., Sugano H., Toyoshima K. Association of elevated expression of the c-erbB-2 protein with spread of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Dec;80(12):1192–1198. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb01654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan D. H., Hung M. C. Identification and characterization of a novel enhancer for the rat neu promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1875–1882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D., Matin A., Hung M. C. The retinoblastoma gene product suppresses neu oncogene-induced transformation via transcriptional repression of neu. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10203–10206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]