Abstract
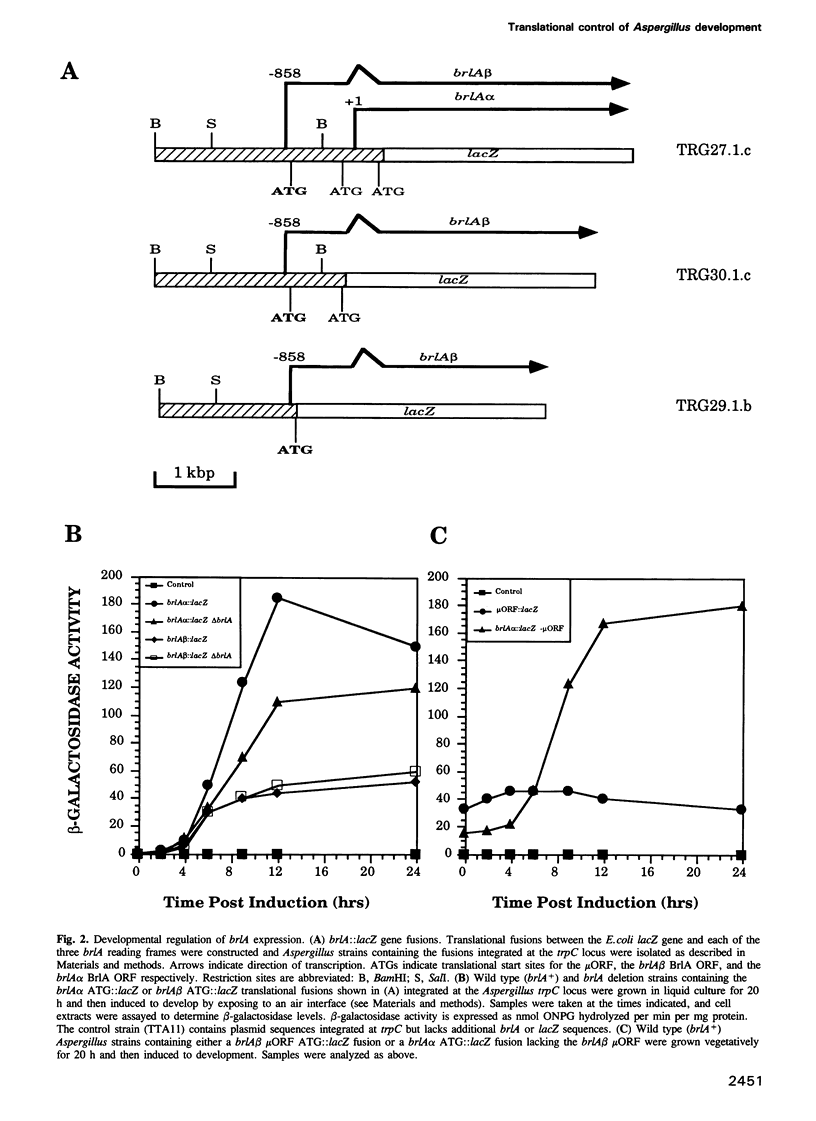
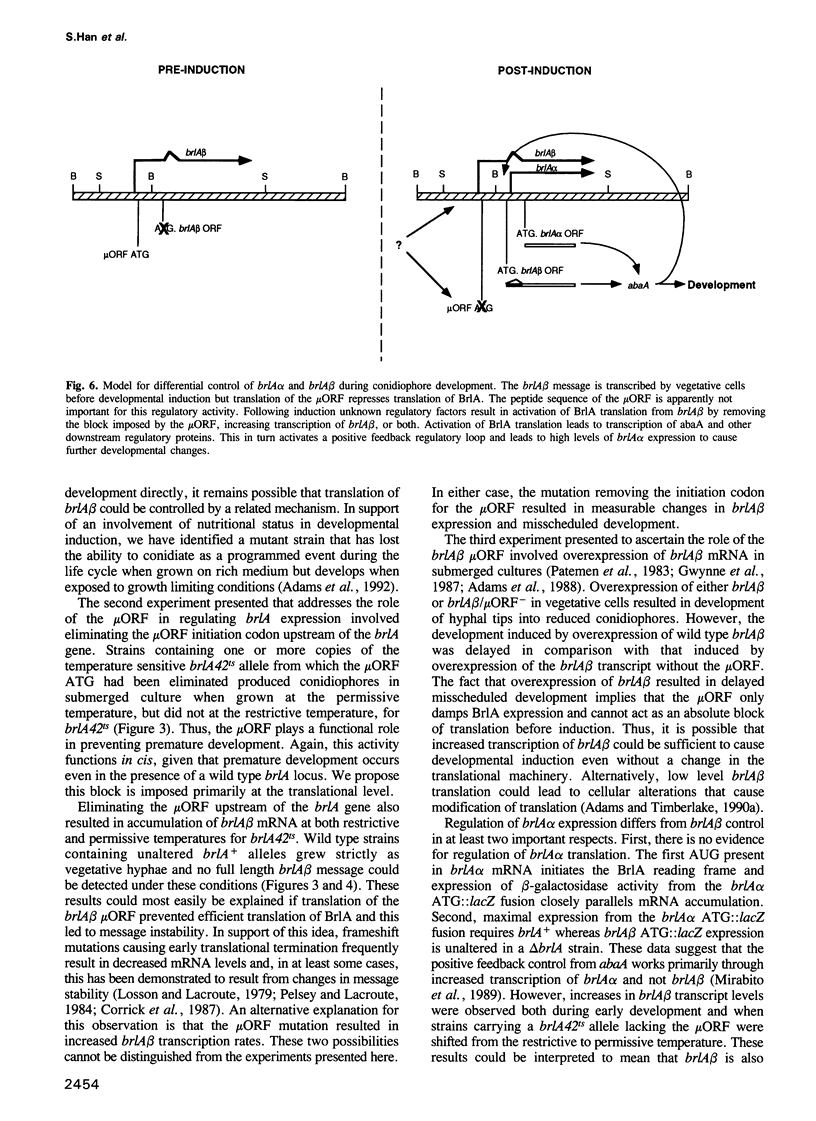
The Aspergillus nidulans brlA developmental regulatory locus consists of two overlapping transcription units, brlA alpha and brlA beta, which encode functionally related polypeptides. We used translational fusions between each of the predicted brlA reading frames and the Escherichia coli lacZ gene to test the hypothesis that developmental regulation of brlA alpha and brlA beta expression occurs through different mechanisms. brlA alpha is transcriptionally controlled and a large portion of brlA alpha-directed beta-galactosidase activity is regulated in a brlA-dependent manner. In contrast, brlA beta mRNA is constitutively transcribed but translation of the brlA polypeptide is prevented by the presence of a short open reading frame (microORF) present in the 5' end of brlA beta mRNA. Removing the microORF initiation codon leads to deregulated brlA expression, resulting in an inappropriate activation of development. We propose that one mechanism for developmental induction in A.nidulans involves translational control.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abastado J. P., Miller P. F., Jackson B. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Suppression of ribosomal reinitiation at upstream open reading frames in amino acid-starved cells forms the basis for GCN4 translational control. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):486–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Boylan M. T., Timberlake W. E. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Deising H., Timberlake W. E. brlA requires both zinc fingers to induce development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1815–1817. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Hide W. A., Yager L. N., Lee B. N. Isolation of a gene required for programmed initiation of development by Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3827–3833. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Developmental repression of growth and gene expression in Aspergillus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5405–5409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Upstream elements repress premature expression of an Aspergillus developmental regulatory gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4912–4919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. A large cluster of highly expressed genes is dispensable for growth and development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D. E., Gealt M., Pastushok M. Gene control of developmental competence in Aspergillus nidulans. Dev Biol. 1973 Sep;34(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D. E. Kinetics of differentiation of conidiophores and conidia by colonies of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):181–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M. T., Mirabito P. M., Willett C. E., Zimmerman C. R., Timberlake W. E. Isolation and physical characterization of three essential conidiation genes from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3113–3118. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck A. J. A mutational analysis of conidial development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1969 Oct;63(2):317–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrick C. M., Twomey A. P., Hynes M. J. The nucleotide sequence of the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and the molecular characterization of 5' mutations. Gene. 1987;53(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne D. I., Buxton F. P., Sibley S., Davies R. W., Lockington R. A., Scazzocchio C., Sealy-Lewis H. M. Comparison of the cis-acting control regions of two coordinately controlled genes involved in ethanol utilization in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer J. E., Timberlake W. E. Functional organization of the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2352–2359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence for translational regulation of the activator of general amino acid control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., Hughes S. G., Clutterbuck A. J. Cloning an Aspergillus nidulans developmental gene by transformation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1307–1311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käfer E. Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet. 1977;19:33–131. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. J., Timberlake W. E. Developmental regulation of laccase levels in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):509–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.509-517.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. A., Timberlake W. E. Aspergillus nidulans wetA activates spore-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli S. D., Clutterbuck A. J. A quantitative survey of conidiation mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. Y., Wu J., Miller B. L. StuA is required for cell pattern formation in Aspergillus. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1770–1782. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabito P. M., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Interactions of three sequentially expressed genes control temporal and spatial specificity in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTECORVO G., ROPER J. A., HEMMONS L. M., MACDONALD K. D., BUFTON A. W. J. The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv Genet. 1953;5:141–238. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pateman J. A., Doy C. H., Olsen J. E., Norris U., Creaser E. H., Hynes M. Regulation of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (AldDH) in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Feb 22;217(1208):243–264. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prade R. A., Timberlake W. E. The Aspergillus nidulans brlA regulatory locus consists of overlapping transcription units that are individually required for conidiophore development. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2439–2447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridmore R. D. New and versatile cloning vectors with kanamycin-resistance marker. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Dean R. A., Sewall T. C., Timberlake W. E. Rodletless, a new Aspergillus developmental mutant induced by directed gene inactivation. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1161–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Developmental gene regulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Molecular genetics of Aspergillus development. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:5–36. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Feller A., Messenguy F., Piérard A. The leader peptide of yeast gene CPA1 is essential for the translational repression of its expression. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton M. M., Timberlake W. E., Hondel C. A. A cosmid for selecting genes by complementation in Aspergillus nidulans: Selection of the developmentally regulated yA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):834–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]