Abstract
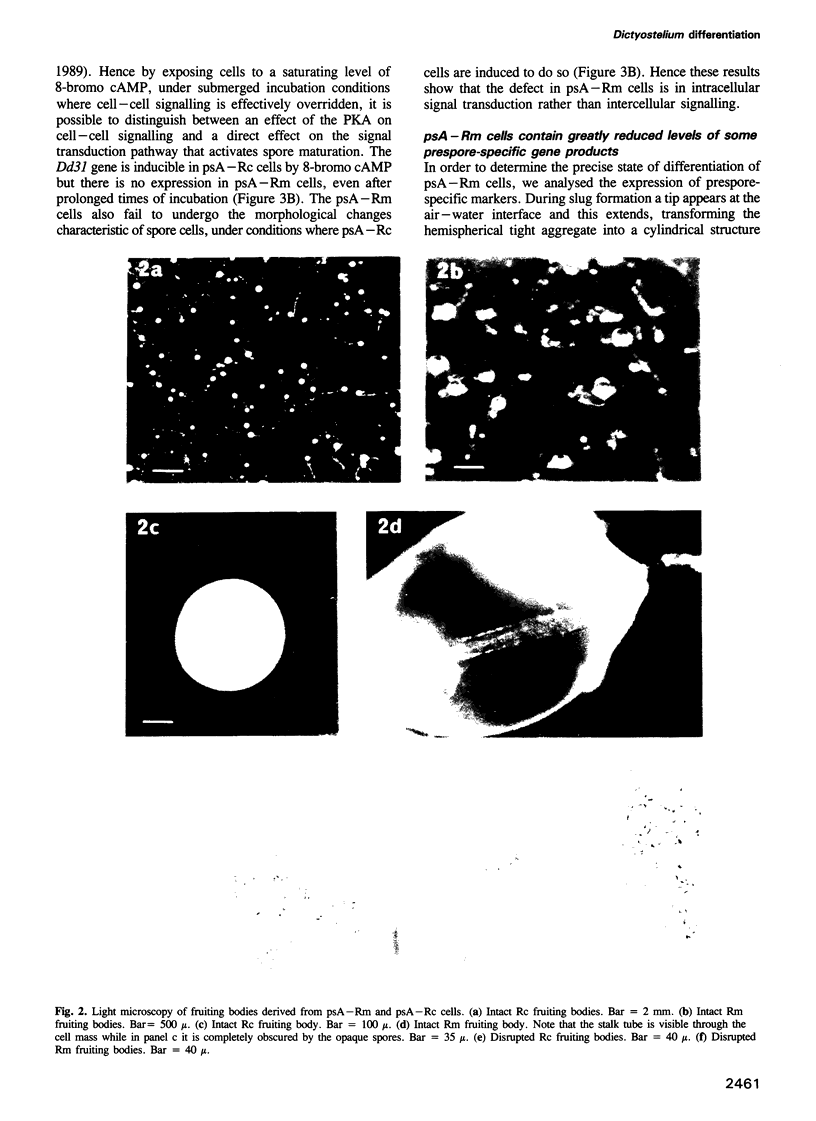
Expression of a dominant inhibitor of the Dictyostelium cAMP-dependent protein kinase in prespore cells blocks their differentiation into spore cells. The resultant structures comprise a normal stalk supporting a bolus of cells that fail to express a sporulation-specific gene and that show greatly reduced levels of expression of several prespore-specific genes. The latter result suggests that in addition to activating spore formation, the cAMP-dependent protein kinase may play a role in initial prespore cell differentiation. Development of the strain expressing the dominant inhibitor is hypersensitive to the inhibitory effects of ammonia, the molecule that is believed to repress entry into culmination during normal development. This result supports a model whereby a decrease in ambient ammonia concentration at culmination acts to elevate intracellular cAMP and hence induce terminal differentiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Yanagisawa K. A new class of rapidly developing mutants in Dictyostelium discoideum: implications for cyclic AMP metabolism and cell differentiation. Dev Biol. 1983 Jan;95(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anjard C., Pinaud S., Kay R. R., Reymond C. D. Overexpression of Dd PK2 protein kinase causes rapid development and affects the intracellular cAMP pathway of Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):785–790. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Lodish H. F. Regulation of dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs specific for prespore or prestalk cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. T., Har D., Suthers H. B. Ammonia and thermotaxis: Further evidence for a central role of ammonia in the directed cell mass movements of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2733–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSilver D. A., Benedict M. A., Ratner D. I. Effects of protein synthesis inhibition on the transcription and transcript stability of Dictyostelium prespore genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 23;1089(3):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90170-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine K. M., Bergmann J. E., Loomis W. F. Spore coat proteins of Dictyostelium discoideum are packaged in prespore vesicles. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Reindl N., Werner H., Hildebrandt M., Nellen W., Harwood A., Williams J., Nerke K. Optimization and in situ detection of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene. 1989 Dec 28;85(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Williams J. G. A Dictyostelium prespore-specific gene is transcriptionally repressed by DIF in vitro. Development. 1988 Jul;103(3):519–524. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.3.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Williams J. G., Meyer H. E., Por S. B., Smith E., Williams K. L., Gooley A. A. Structural characterization of Dictyostelium discoideum prespore-specific gene D19 and of its product, cell surface glycoprotein PsA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3458–3466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Williams J. G. Two vectors which facilitate gene manipulation and a simplified transformation procedure for Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene. 1987;59(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit I. N., Bonner J. T., Suthers H. B. Regulation of the anterior-like cell state by ammonia in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Genet. 1990;11(5-6):442–446. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020110519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Chapman A. L. A role for cAMP-dependent protein kinase A in early Dictyostelium development. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):18–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosnaugh K. L., Loomis W. F. Spore coat genes SP60 and SP70 of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5215–5218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomer R. H., Armstrong D., Leichtling B. H., Firtel R. A. cAMP induction of prespore and prestalk gene expression in Dictyostelium is mediated by the cell-surface cAMP receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8624–8628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. D., Bradbury J., Kay R. R., Peacey M. J. Intracellular pH and the control of cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):244–245. doi: 10.1038/303244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunzburg J., Veron M. A cAMP-dependent protein kinase is present in differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1063–1068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood A. J., Hopper N. A., Simon M. N., Bouzid S., Veron M., Williams J. G. Multiple roles for cAMP-dependent protein kinase during Dictyostelium development. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90266-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood A. J., Hopper N. A., Simon M. N., Driscoll D. M., Veron M., Williams J. G. Culmination in Dictyostelium is regulated by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohl H. R., Hamamoto S. T. Ultrastructure of spore differentiation in Dictyostelium: the prespore vacuole. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Mar;26(5):442–453. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Takeuchi I. Isolation and characterization of a prespore specific structure of the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Growth Differ. 1971 Dec;13(4):221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169x.1971.00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens P. M., Van Haastert P. J. Molecular basis of transmembrane signal transduction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):396–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.396-418.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn K. A., Berks M., Kay R. R., Williams J. G. Two distinct classes of prestalk-enriched mRNA sequences in Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1987 Aug;100(4):745–755. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. R., Garrod D., Tilly R. Requirement for cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):58–60. doi: 10.1038/271058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. R., Jermyn K. A. A possible morphogen controlling differentiation in Dictyostelium. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):242–244. doi: 10.1038/303242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. R. cAMP and spore differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3228–3231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R. Different molecular mechanisms for cAMP regulation of gene expression during Dictyostelium development. Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;122(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Cohen S. M., Loomis W. F., Lodish H. F. Developmental regulation of Dictyostelium discoideum actin gene fusions carried on low-copy and high-copy transformation vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3973–3983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopachik W. J., Dhokia B., Kay R. R. Selective induction of stalk-cell-specific proteins in Dictyostelium. Differentiation. 1985;28(3):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krefft M., Voet L., Gregg J. H., Mairhofer H., Williams K. L. Evidence that positional information is used to establish the prestalk-prespore pattern in Dictyostelium discoideum aggregates. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):201–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krefft M., Voet L., Mairhofer H., Williams K. L. Analysis of proportion regulation in slugs of Dictyostelium discoideum using a monoclonal antibody and a FACS-IV. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichtling B. H., Majerfeld I. H., Spitz E., Schaller K. L., Woffendin C., Kakinuma S., Rickenberg H. V. A cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Dictyostelium discoideum. II. Developmental regulation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):662–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Takeuchi I. Cell differentiation and fine structures in the development of the cellular slime molds. Dev Growth Differ. 1969 Dec;11(3):232–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169x.1969.00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Firtel R. A. A developmentally regulated, putative serine/threonine protein kinase is essential for development in Dictyostelium. Mech Dev. 1991 Sep;35(2):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90060-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Pinko C., Firtel R. A. cAMP regulation of early gene expression in signal transduction mutants of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Yonemoto W. M., Taylor S. S., Firtel R. A. DdPK3, which plays essential roles during Dictyostelium development, encodes the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10701–10705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Jermyn K. A., Duffy K., Blight K., Williams J. G. Two DIF-inducible, prestalk-specific mRNAs of Dictyostelium encode extracellular matrix proteins of the slug. Development. 1988 Oct;104(2):275–284. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Ratner D., Firtel R. A. Induction and modulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkle R. K., Cooper K. K., Rutherford C. L. Localization and levels of cyclic AMP during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1984 Oct;14(4):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Masento M. S., Jermyn K. A., Kay R. R. Chemical structure of the morphogen differentiation inducing factor from Dictyostelium discoideum. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):811–814. doi: 10.1038/328811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutzel R., Lacombe M. L., Simon M. N., de Gunzburg J., Veron M. Cloning and cDNA sequence of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Silan C., Firtel R. A. DNA-mediated transformation in Dictyostelium discoideum: regulated expression of an actin gene fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2890–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama M., Blumberg D. D. Interaction of cAMP with the cell-surface receptor induces cell-type-specific mRNA accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki T., Hasegawa M., Hamada Y., Tasaka M., Iwabuchi M., Takeuchi I. Molecular cloning of cell-type-specific cDNAs exhibiting new types of developmental regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1988 Mar;23(1-2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(88)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. L., Hong C. B., Loomis W. F. A prespore gene, Dd31, expressed during culmination of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1991 Apr;144(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. L., Loomis W. F. Disruption of the sporulation-specific gene spiA in Dictyostelium discoideum leads to spore instability. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1058–1070. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley B. B., Barclay S. L. Ammonia promotes accumulation of intracellular cAMP in differentiating amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1990 Jul;109(3):715–722. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.3.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., Van Lookeren Campagne M. M., Van Driel R., Spek W., Van Haastert P. J., Pinas J. Postaggregative differentiation induction by cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium: intracellular transduction pathway and requirement for additional stimuli. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):52–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., van Driel R. V. Induction of post-aggregative differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum by cAMP. Evidence of involvement of the cell surface cAMP receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):388–398. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Sussman M. Ammonia determines the choice of morphogenetic pathways in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. N., Driscoll D., Mutzel R., Part D., Williams J., Véron M. Overproduction of the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase blocks the differentiation of Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2039–2043. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. N., Pelegrini O., Veron M., Kay R. R. Mutation of protein kinase A causes heterochronic development of Dictyostelium. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):171–172. doi: 10.1038/356171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M., Schindler J., Kim H. "Sluggers", a new class of morphogenetic mutants of D. discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 1;116(1):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C. D., Gross J. D., Kay R. R. Cell differentiation without morphogenesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):717–719. doi: 10.1038/262717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duijn B., Inouye K. Regulation of movement speed by intracellular pH during Dictyostelium discoideum chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Ceccarelli A., McRobbie S., Mahbubani H., Kay R. R., Early A., Berks M., Jermyn K. A. Direct induction of Dictyostelium prestalk gene expression by DIF provides evidence that DIF is a morphogen. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90559-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Duffy K. T., Lane D. P., McRobbie S. J., Harwood A. J., Traynor D., Kay R. R., Jermyn K. A. Origins of the prestalk-prespore pattern in Dictyostelium development. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1157–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa K., Loomis W. F., Jr, Sussman M. Developmental regulation of the enzyme UDP-galactose polysaccharide transferase. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Franke J., Kessin R. H., Véron M. Detection and developmental regulation of the mRNA for the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of D. discoideum by cell-free translation. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):363–367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]