Abstract
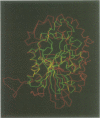
The crystal structure of recombinant rat prostatic acid phosphatase was determined to 3 A resolution with protein crystallographic methods. The enzyme subunit is built up of two domains, an alpha/beta domain consisting of a seven-stranded mixed beta-sheet with helices on both sides of the sheet and a smaller alpha domain. Two disulfide bridges between residues 129-340 and 315-319 were found. Electron density at two of the glycosylation sites for parts of the carbohydrate moieties was observed. The dimer of acid phosphatase is formed through two-fold interactions of edge strand 3 from one subunit with strand 3 from the second subunit, thus extending the beta-sheet from seven to 14 strands. Other subunit-subunit interactions involve conserved residues from loops between helices and beta-strands. The fold of the alpha/beta domain is similar to the fold observed in phosphoglycerate mutase. The active site is at the carboxy end of the parallel strands of the alpha/beta domain. There is a strong residual electron density at the phosphate binding site which probably represents a bound chloride ion. Biochemical properties and results from site-directed mutagenesis experiments of acid phosphatase are correlated to the three-dimensional structure.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Pilkis S. J. Evolution of a bifunctional enzyme: 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9642–9646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky O. Acid phosphatase. Adv Clin Chem. 1972;15:43–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. W., Watson H. C., Hodgson G. I. Structure of yeast phosphoglycerate mutase. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):301–303. doi: 10.1038/250301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. F., Clinton G. M. Human prostatic acid phosphatase has phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase activity. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):351–357. doi: 10.1042/bj2350351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. F., Waheed A., Risley J. M., Van Etten R. L. Carbohydrate removal fails to eliminate the heterogeneity of human prostatic acid phosphatase. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Jun 15;182(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostanin K., Harms E. H., Stevis P. E., Kuciel R., Zhou M. M., Van Etten R. L. Overexpression, site-directed mutagenesis, and mechanism of Escherichia coli acid phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22830–22836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley J. M., Van Etten R. L. Structures of the carbohydrate moieties of human prostatic acid phosphatase elucidated by H1 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 1;258(2):404–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiko K., Jänne O. A., Vihko P. Primary structure of rat secretory acid phosphatase and comparison to other acid phosphatases. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90009-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg L., Vihko P., Sajanti E., Vihko R. Clomiphene citrate administration to normogonadotropic subfertile men: blood hormone changes and activation of acid phosphatase in seminal fluid. Int J Androl. 1981 Jun;4(3):372–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1981.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J. M., Handschumacher M. D., Murthy H. M., Foster B. A., Wyckoff H. W. Refined structure of alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):417–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. L., Davidson R., Stevis P. E., MacArthur H., Moore D. L. Covalent structure, disulfide bonding, and identification of reactive surface and active site residues of human prostatic acid phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2313–2319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. L. Human prostatic acid phosphatase: a histidine phosphatase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;390:27–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb40302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihko P., Kurkela R., Porvari K., Herrala A., Lindfors A., Lindqvist Y., Schneider G. Rat acid phosphatase: overexpression of active, secreted enzyme by recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells, molecular properties, and crystallization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):799–803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihko P., Lukkarinen O., Kontturi M., Vihko R. Effectiveness of radioimmunoassay of human prostate-specific acid phosphatase in the diagnosis and follow-up of therapy in prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1981 Mar;41(3):1180–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihko P., Virkkunen P., Henttu P., Roiko K., Solin T., Huhtala M. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human prostatic acid phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. B., Crowder M. W., Averill B. A. Hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters: a biological problem with multiple chemical solutions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn S. I., Watson H. C., Harkins R. N., Fothergill L. A. Structure and activity of phosphoglycerate mutase. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):121–130. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T. Clinical significance of the human acid phosphatases: a review. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):604–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90630-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]