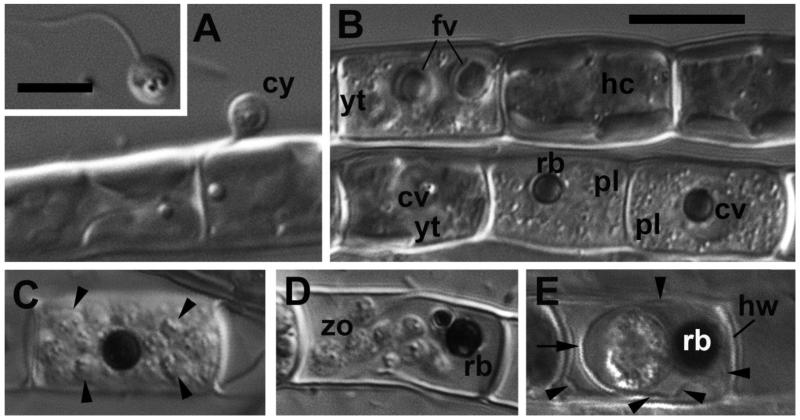
Figure 2. Main stages of the life cycle of Aphelidium aff. melosirae observed in living material by differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy.
A – cyst (cy) on the Tribonema filament. Insert – swimming zoospore. B – healthy cells of the host (hc), young trophont (yt) of parasitoid with food vacuoles (fv), a central vacuole (cv), and two plasmodia (pl) containing residual bodies (rb) in the central vacuole. C – mature sporangium with divided cells (arrowheads). D – mature zoospores (zo) and residual body (rb) inside the host cell wall. Note flexible ridges of the wall permitting the zoospores to come out. E – resting spore (sporocyst), surrounded by cyst wall (arrow) and spore wall (arrowheads) adpressed to the host cell wall (hw). The residual body lies in between of the cyst and spore walls.
Scale bars: insert in A – 5 μm, B – 10 μm for A-E.