Abstract
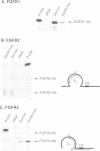
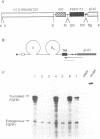
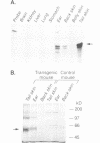
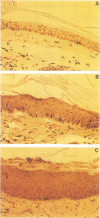
In this study we used a dominant-negative FGF receptor mutant to block FGF function in a specific tissue of transgenic mice. The mutant receptor, which is known to block signal transduction in cells when co-expressed with wild-type receptors, was targeted to suprabasal keratinocytes using a keratin 10 promoter. The transgene was expressed specifically in the skin and highest expression levels were found in the tail. Expression of the mutant receptor disrupted the organization of epidermal keratinocytes, induced epidermal hyperthickening and resulted in an aberrant expression of keratin 6. This suggests that FGF is essential for the morphogenesis of suprabasal keratinocytes and for the establishment of the normal program of keratinocyte differentiation. Our study demonstrates that dominant-negative growth factor receptors can be used to block selectively the action of a growth factor in specific tissues of transgenic mice.
Full text
PDF

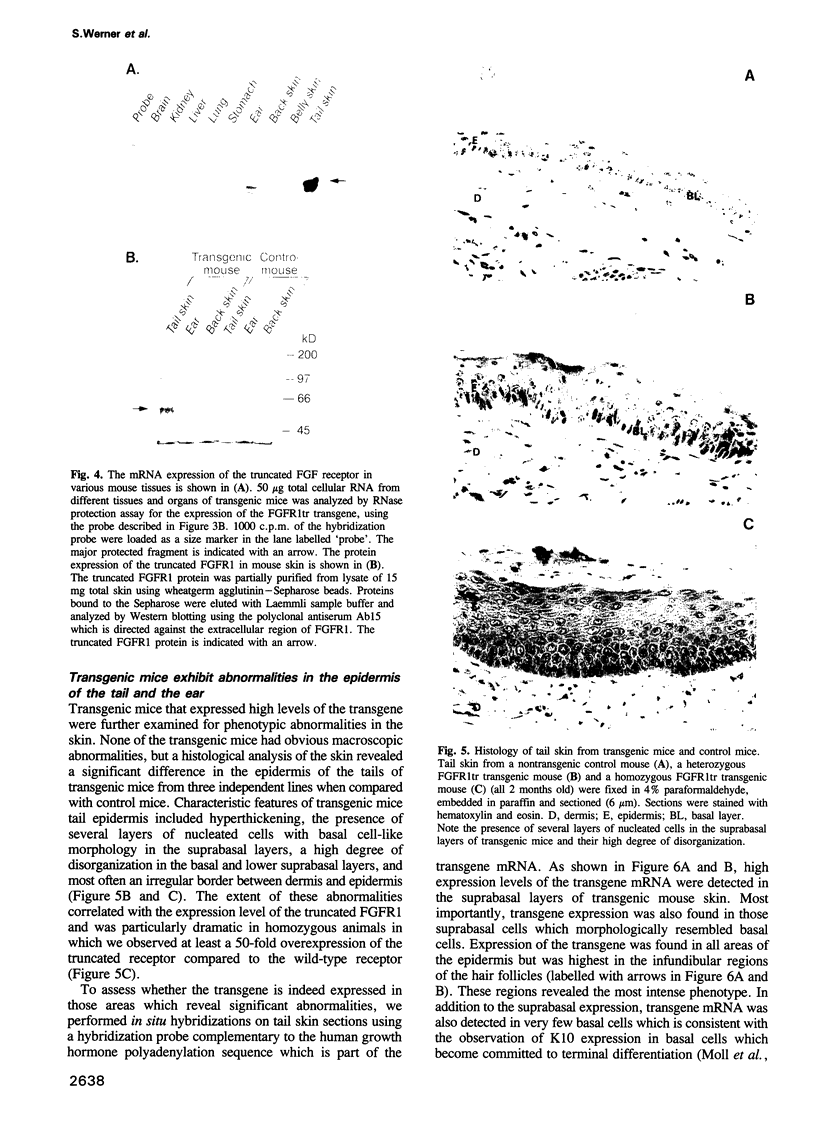
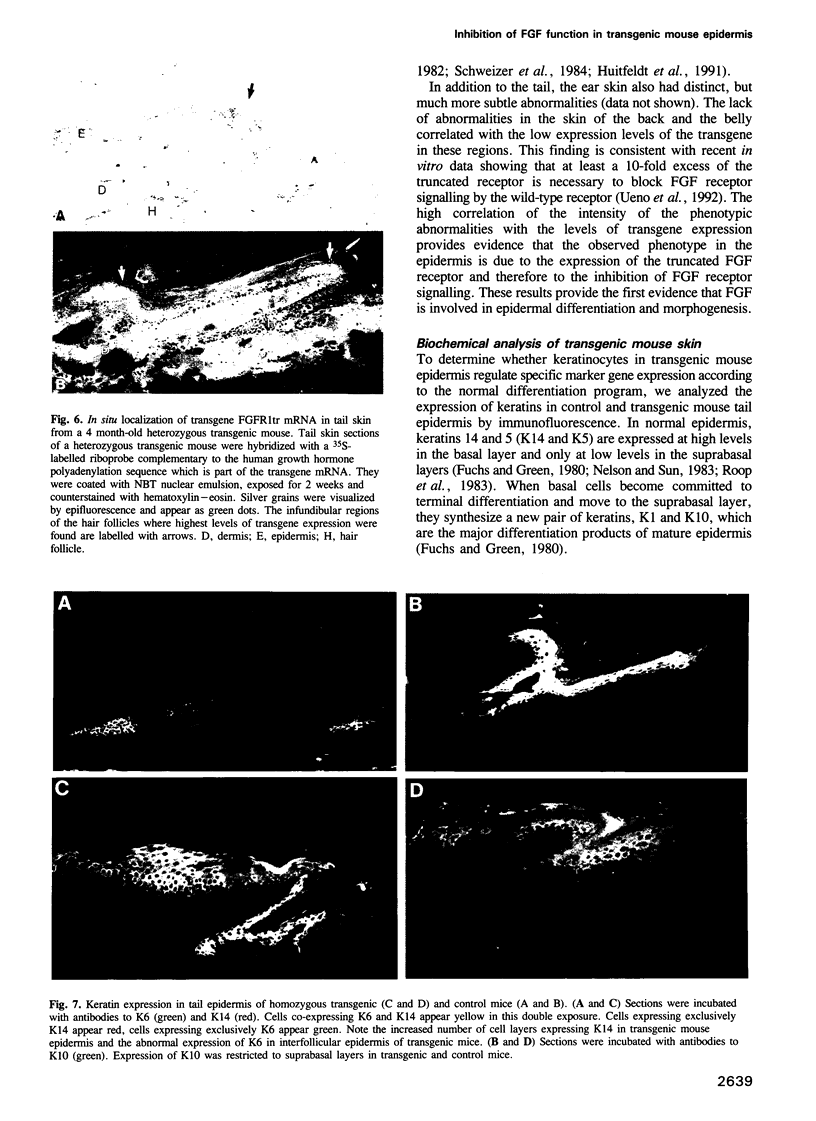




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailleul B., Surani M. A., White S., Barton S. C., Brown K., Blessing M., Jorcano J., Balmain A. Skin hyperkeratosis and papilloma formation in transgenic mice expressing a ras oncogene from a suprabasal keratin promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90115-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing M., Zentgraf H., Jorcano J. L. Differentially expressed bovine cytokeratin genes. Analysis of gene linkage and evolutionary conservation of 5'-upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):567–575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan D. S., Werner S., Williams L. T. A naturally occurring secreted form of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 binds basic FGF in preference over acidic FGF. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16076–16080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Esteves R. A., Coulombe P. A. Transgenic mice expressing a mutant keratin 10 gene reveal the likely genetic basis for epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh D. G., Sprugel K. H., Murray M. J., Ross R. PDGF and FGF stimulate wound healing in the genetically diabetic mouse. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1235–1246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebda P. A., Klingbeil C. K., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C. Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulation of epidermal wound healing in pigs. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6):626–631. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12513528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huitfeldt H. S., Heyden A., Clausen O. P., Thrane E. V., Roop D., Yuspa S. H. Altered regulation of growth and expression of differentiation-associated keratins in benign mouse skin tumors. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Nov;12(11):2063–2067. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.11.2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lu J., Chen H., Werner S., Williams L. T. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;60:1–41. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. The fibroblast growth factor family: structural and biological properties. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):207–235. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Johnson D. E., Cousens L. S., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):57–60. doi: 10.1126/science.2544996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. The 50- and 58-kdalton keratin classes as molecular markers for stratified squamous epithelia: cell culture studies. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):244–251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Benoist C., Breathnach R. Transformation of mouse fibroblasts to methotrexate resistance by a recombinant plasmid expressing a prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1527–1531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Leder P. Ligand specificity and heparin dependence of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16305–16311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. G., Werner S., Chen G., Williams L. T. Two FGF receptor genes are differentially expressed in epithelial and mesenchymal tissues during limb formation and organogenesis in the mouse. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):233–243. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz V., Kelman Z., Avivi A., Neufeld G., Givol D., Yarden Y. PCR-based identification of new receptors: molecular cloning of a receptor for fibroblast growth factors. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger M., Jorcano J. L., Franke W. W. Complete sequence of a bovine type I cytokeratin gene: conserved and variable intron positions in genes of polypeptides of the same cytokeratin subfamily. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2261–2267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow H. J., Messmer T. O. Basic fibroblast growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I are strong mitogens for cultured mouse keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Nov;137(2):277–284. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Cheng C. K., Titterington L., Meyers C. A., Stanley J. R., Steinert P. M., Yuspa S. H. Synthetic peptides corresponding to keratin subunits elicit highly specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8037–8040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Cheng C. K., Toftgard R., Stanley J. R., Steinert P. M., Yuspa S. H. The use of cDNA clones and monospecific antibodies as probes to monitor keratin gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:426–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Cheng C. K., Yuspa S. H. Keratin gene expression in mouse epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Huitfeldt H., Kilkenny A., Yuspa S. H. Regulated expression of differentiation-associated keratins in cultured epidermal cells detected by monospecific antibodies to unique peptides of mouse epidermal keratins. Differentiation. 1987;35(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer J., Kinjo M., Fürstenberger G., Winter H. Sequential expression of mRNA-encoded keratin sets in neonatal mouse epidermis: basal cells with properties of terminally differentiating cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Keeble W. W., Hendrickson J. E., Coffey R. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R. Growth of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in serum-free medium is stimulated by acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Mar;138(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler A., Kopan R., Duvic M., Fuchs E. Use of monospecific antisera and cRNA probes to localize the major changes in keratin expression during normal and abnormal epidermal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):427–446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A. Fibroblast growth factors. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):434–440. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3315806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi R., Rifkin D. B. Recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates wound healing in healing-impaired db/db mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):245–251. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Colbert H., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Inhibition of PDGF beta receptor signal transduction by coexpression of a truncated receptor. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):844–848. doi: 10.1126/science.1851331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Gunn M., Dell K., Tseng A., Jr, Williams L. A truncated form of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibits signal transduction by multiple types of fibroblast growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Eichner R., Sun T. T. Monoclonal antibody analysis of keratin expression in epidermal diseases: a 48- and 56-kdalton keratin as molecular markers for hyperproliferative keratinocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1397–1406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Duan D. S., de Vries C., Peters K. G., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Differential splicing in the extracellular region of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 generates receptor variants with different ligand-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Peters K. G., Longaker M. T., Fuller-Pace F., Banda M. J., Williams L. T. Large induction of keratinocyte growth factor expression in the dermis during wound healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6896–6900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., Champion J. E., McMahon A. P. A molecular analysis of mouse development from 8 to 10 days post coitum detects changes only in embryonic globin expression. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):493–500. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]