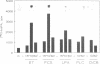
Abstract
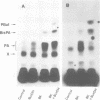
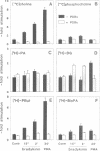
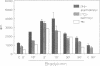
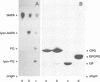
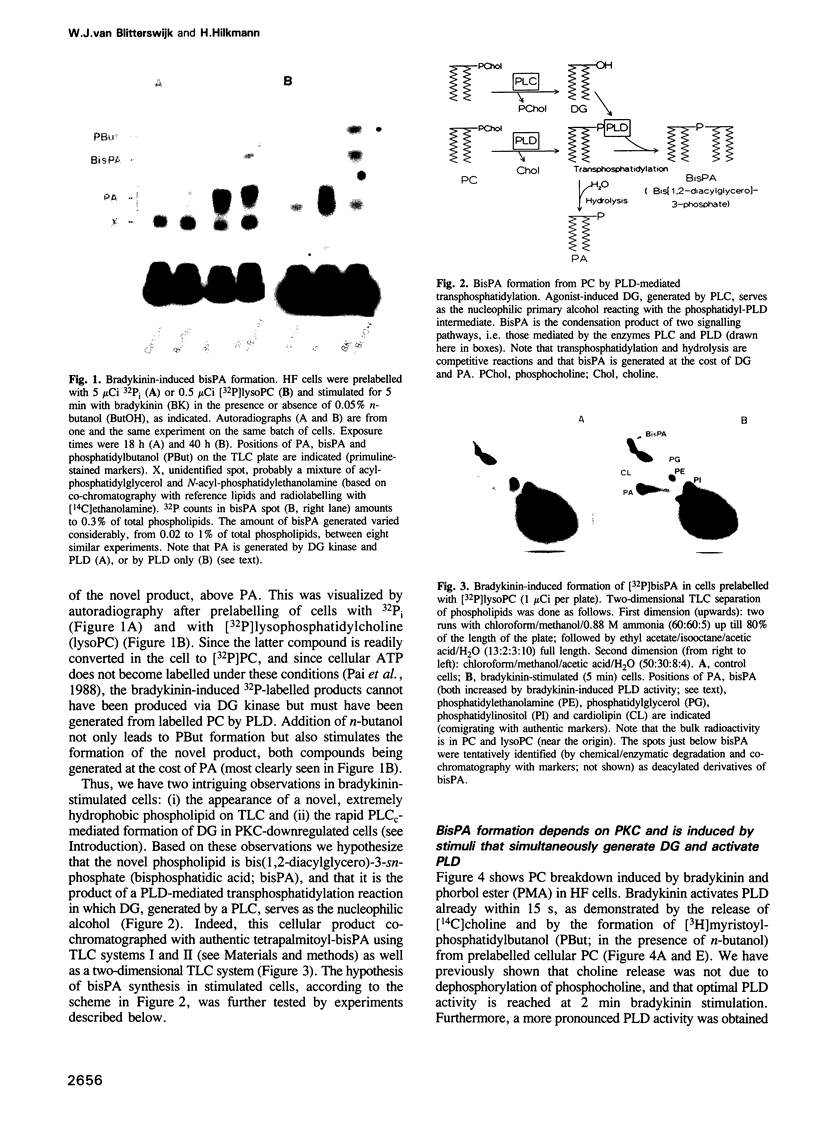
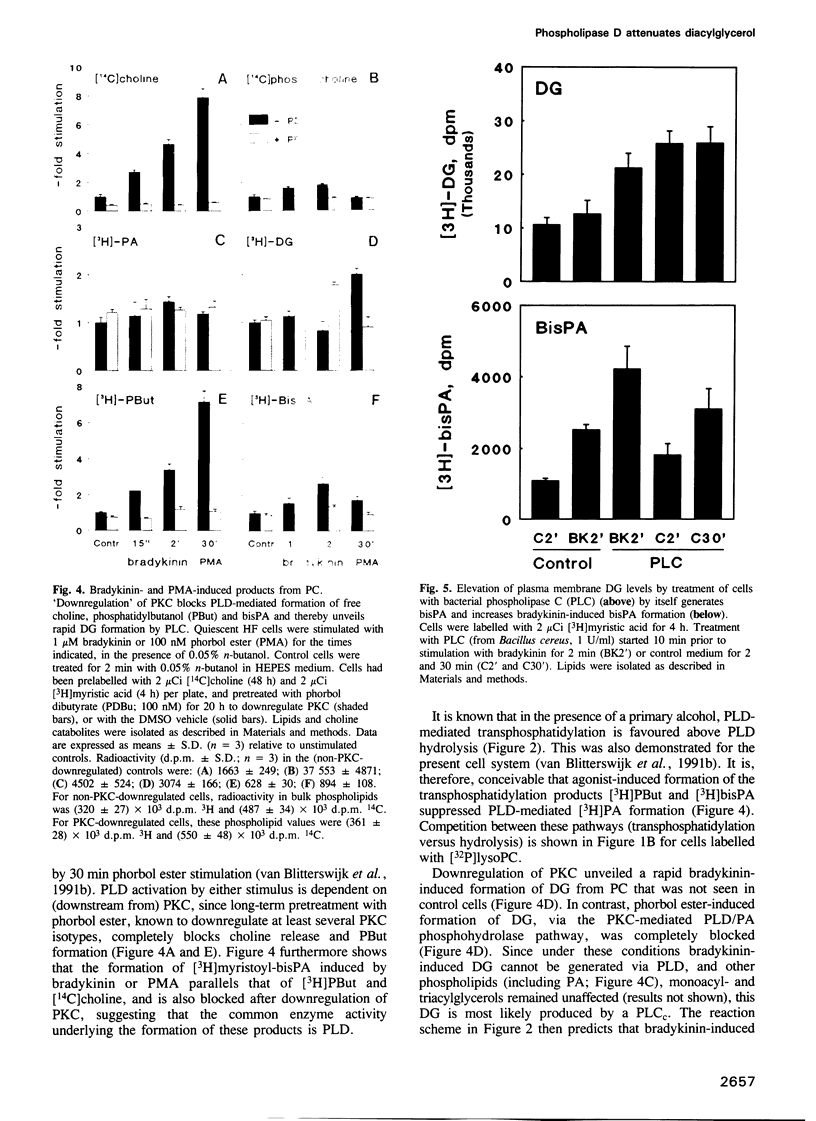
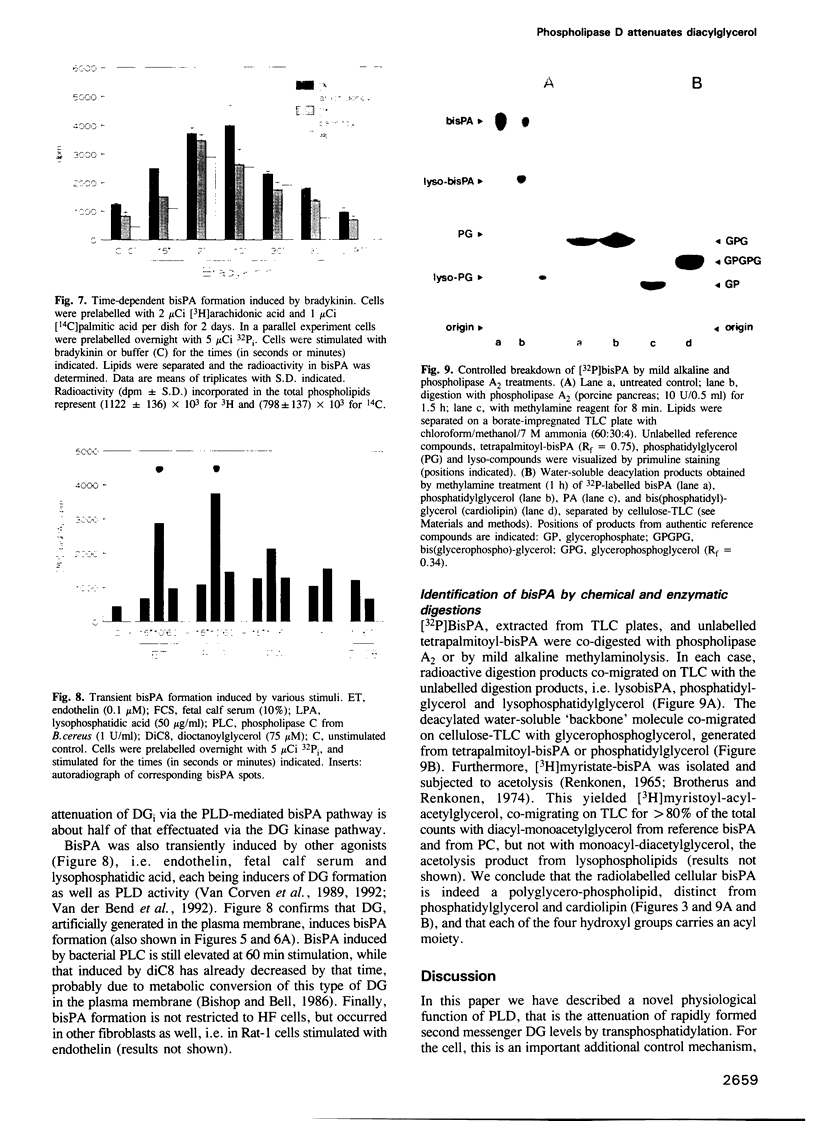
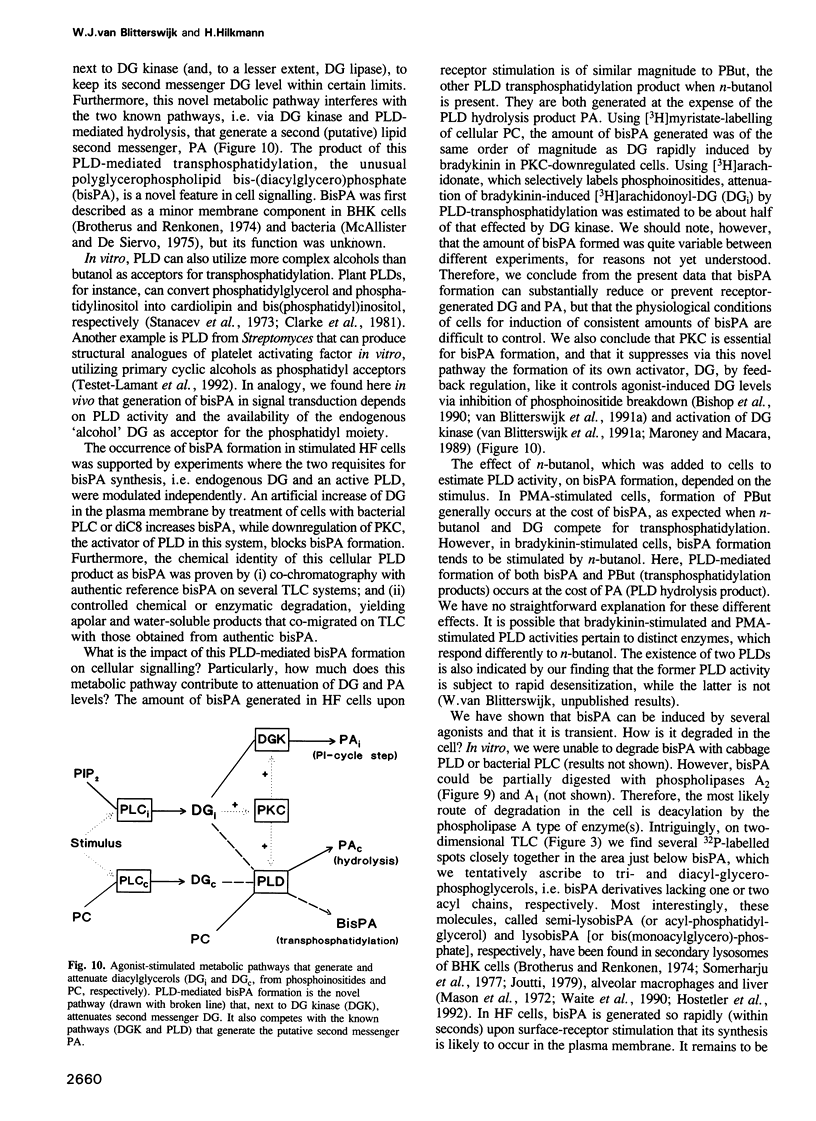
Generation and attenuation of lipid second messengers are key processes in cellular signalling. Receptor-mediated increase in 1,2-diacylglycerol (DG) levels is attenuated by DG kinase and DG lipase. We here report a novel mechanism of DG attenuation by phospholipase D (PLD), which also precludes the production of another (putative) second messenger, phosphatidic acid (PA). In the presence of an alcohol, PLD converts phosphatidylcholine (PC) into a phosphatidylalcohol (by transphosphatidylation) rather than into PA. We found in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts that PLD mediates transphosphatidylation from PC (donor) to the endogenous 'alcohol' DG (acceptor), yielding bis(1,2-diacylglycero)-3-sn-phosphate (bisphosphatidic acid; bisPA). This uncommon phospholipid is thus a condensation product of the phospholipase C (PLC) and PLD signalling pathways, where PLC produces DG and PLD couples this DG to a phosphatidyl moiety. Long-term phorbol ester treatment blocks bradykinin-induced activation of PLD and consequent bisPA formation, thereby unveiling rapid formation of DG. BisPA formation is rapid (15 s) and transient (peaks at 2-10 min) and is also induced by other stimuli capable of raising DG and activating PLD simultaneously, e.g. endothelin, lysophosphatidic acid, fetal calf serum, phorbol ester, dioctanoylglycerol or bacterial PLC. This novel metabolic route counteracts rapid accumulation of receptor-induced DG and PA, and assigns for the first time a physiological role to the transphosphatidylation activity of PLD, that is signal attenuation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., August J., Petrin J. M., Pai J. K. Regulation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second-messenger formation in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Potentiation by protein kinase C inhibitors. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):465–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2690465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., Bell R. M. Attenuation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second messengers. Metabolism of exogenous diacylglycerols by human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12513–12519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate-dependent protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6210–6213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherus J., Renkonen O. Isolation and characterisation of bis-phosphatidic acid and its partially deacylated derivatives from cultured BHK-cells. Chem Phys Lipids. 1974 Aug;13(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(74)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Dawson R. M. Alkaline O leads to N-transacylation. A new method for the quantitative deacylation of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1950301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. Formation of bis(phosphatidyl)inositol and phosphatidic acid by phospholipase D action on phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):521–523. doi: 10.1042/bj1950521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Wakelam M. J. Stimulated phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis as a signal transduction pathway in mitogenesis. Cell Signal. 1991;3(4):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90055-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. G., Comai K. Rapid separation of neutral lipids, free fatty acids and polar lipids using prepacked silica Sep-Pak columns. Lipids. 1988 Dec;23(12):1146–1149. doi: 10.1007/BF02535281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. Y., Huterer S. J., Wherrett J. R. Biosynthesis of bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate in liver and macrophage lysosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1992;209:104–110. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)09014-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joutti A. The stereoconfiguration of newly formed molecules of bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate in BHK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 26;575(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Amsterdam A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates phospholipase D in ovarian granulosa cells. Possible role in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11762–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M. Crosstalk among multiple signal-activated phospholipases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroney A. C., Macara I. G. Phorbol ester-induced translocation of diacylglycerol kinase from the cytosol to the membrane in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2537–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Stossel T. P., Vaughan M. Lipids of alveolar macrophages, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and their phagocytic vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2399–2407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister D. J., De Siervo A. J. Identification of bisphosphatidic acid and its plasmalogen analogues in the phospholipids of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):302–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.302-307.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorthuis BJHM, Hostetler K. Y. Biosynthesis of bis(monoacylglyceryl)phosphate and acylphosphatidylglycerol in rat liver mitochondrial. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3297–3302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKONEN O. INDIVIDUAL MOLECULAR SPECIES OF DIFFERENT PHOSPHOLIPID CLASSES. II. A METHOD OF ANALYSIS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Apr;42:298–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02540133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerharju P., Brotherus J., Kahma K., Renkonen O. Stereoconfiguration of bisphosphatidic and semilysobisphosphatidic acids from cultured hamster fibroblasts (BHK cells). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 26;487(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanacev N. Z., Stuhne-Sekalec L., Domazet Z. Enzymatic formation of cardiolipin from phosphatidylglycerol by the transphosphatidylation mechanism catalyzed by phospholipase D. Can J Biochem. 1973 Jun;51(6):747–753. doi: 10.1139/o73-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testet-Lamant V., Archaimbault B., Durand J., Rigaud M. Enzymatic synthesis of structural analogs of PAF-acether by phospholipase D-catalysed transphosphatidylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 12;1123(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90017-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Stacey D. W. A cytoplasmic protein inhibits the GTPase activity of H-Ras in a phospholipid-dependent manner. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.2237442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., King L., Thornburg T., Osthoff G., Thuren T. Y. Metabolism of phosphatidylglycerol and bis(monoacylglycero)-phosphate in macrophage subcellular fractions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21720–21726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. I. Biphasic formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine, controlled by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. II. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown by phospholipases C and D; involvement of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10344–10350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., van Rijswijk A., Jalink K., van der Bend R. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., Moolenaar W. H. Mitogenic action of lysophosphatidic acid and phosphatidic acid on fibroblasts. Dependence on acyl-chain length and inhibition by suramin. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2810163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bend R. L., de Widt J., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H., van Blitterswijk W. J. The biologically active phospholipid, lysophosphatidic acid, induces phosphatidylcholine breakdown in fibroblasts via activation of phospholipase D. Comparison with the response to endothelin. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):235–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2850235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]