Abstract
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) are two cytokines that are secreted by activated T cells and have similar effects on monocytes and B cells. We describe a mutant form of human interleukin-4 (hIL-4) that competitively antagonizes both hIL-4 and human interleukin-13 (hIL-13). The amino acid sequences of IL-4 and IL-13 are approximately 30% homologous and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy shows that both proteins have a highly alpha-helical structure. IL-13 competitively inhibited binding of hIL-4 to functional human IL-4 receptors (called hIL-4R) expressed on a cell line which responds to both hIL-4 and IL-13. Binding of hIL-4 to an hIL-4 responsive cell line that does not respond to IL-13, and binding of hIL-4 to cloned IL-4R ligand binding protein expressed on heterologous cells, were not inhibited by IL-13. hIL-4 bound with approximately 100-fold lower affinity to the IL-4R ligand binding protein than to functional IL-4R. The mutant hIL-4 antagonist protein bound to both IL-4R types with the lower affinity. The above results demonstrate that IL-4 and IL-13 share a receptor component that is important for signal transduction. In addition, our data establish that IL-4R is a complex of at least two components one of which is a novel affinity converting subunit that is critical for cellular signal transduction.
Full text
PDF

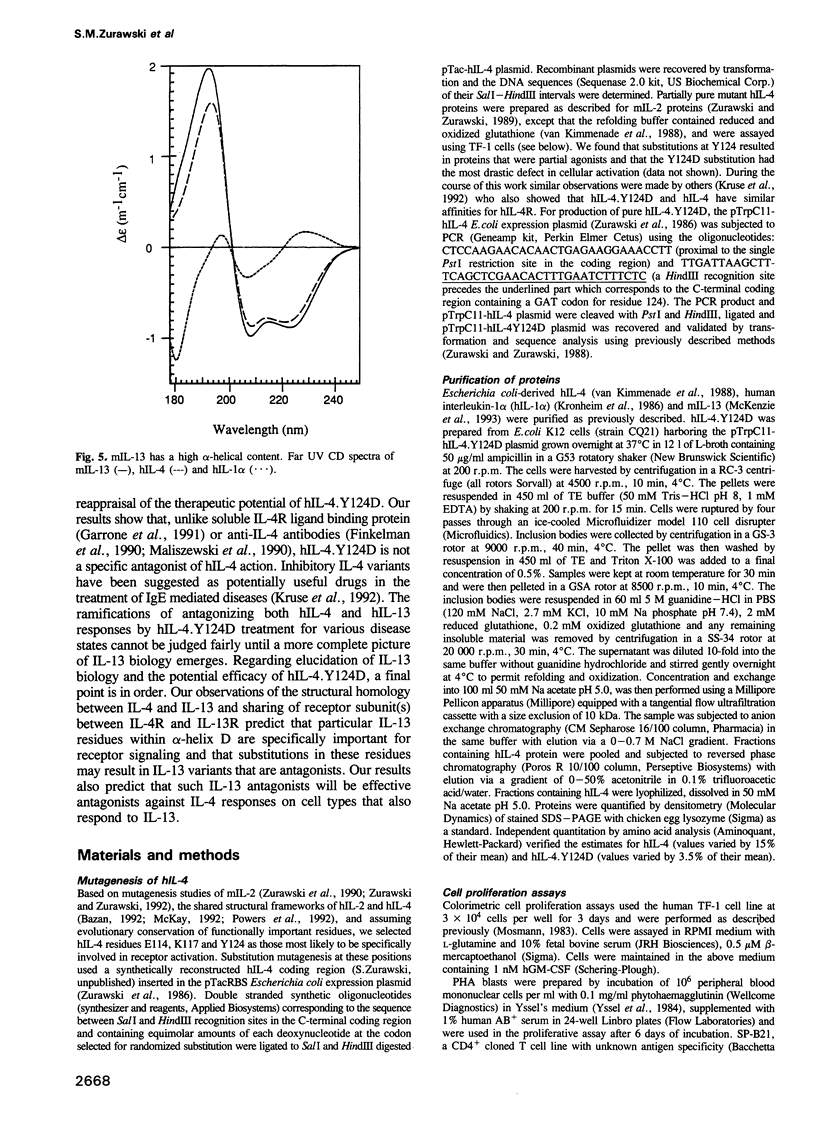


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai N., Nomura D., Villaret D., DeWaal Malefijt R., Seiki M., Yoshida M., Minoshima S., Fukuyama R., Maekawa M., Kudoh J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the chromosomal gene for human IL-4 and its expression. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):274–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetta R., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Abrams J., de Vries J. E., Spits H., Roncarolo M. G. Host-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones isolated from a human chimera produce IL-5, IL-2, IFN-gamma and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor but not IL-4. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):902–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., de Paoli P., Vallé A., Garcia E., Rousset F. Long-term human B cell lines dependent on interleukin-4 and antibody to CD40. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1702555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Haemopoietic receptors and helical cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Oct;11(10):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90139-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Unraveling the structure of IL-2. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):410–413. doi: 10.1126/science.1631562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Zurawski S. M., Mosmann T. R., Zurawski G. A family of small inducible proteins secreted by leukocytes are members of a new superfamily that includes leukocyte and fibroblast-derived inflammatory agents, growth factors, and indicators of various activation processes. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrillat H., Galizzi J. P., Djossou O., Arai N., Yokota T., Arai K., Banchereau J. High affinity binding of human interleukin 4 to cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):995–1001. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederichs K., Boone T., Karplus P. A. Novel fold and putative receptor binding site of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1779–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1837174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R., Vitetta E. S. Evidence that natural murine soluble interleukin 4 receptors may act as transport proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):673–681. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Holmes J., Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Schooley K. A., Coffman R. L., Mosmann T. R., Paul W. E. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Woerly G., Ryffel B. Identification of interleukin 4 receptor-associated proteins and expression of both high- and low-affinity binding on human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1637–1641. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Castle B., Djossou O., Harada N., Cabrillat H., Yahia S. A., Barrett R., Howard M., Banchereau J. Purification of a 130-kDa T cell glycoprotein that binds human interleukin 4 with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Zuber C. E., Harada N., Gorman D. M., Djossou O., Kastelein R., Banchereau J., Howard M., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding the human interleukin 4 receptor. Int Immunol. 1990;2(7):669–675. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.7.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrone P., Djossou O., Galizzi J. P., Banchereau J. A recombinant extracellular domain of the human interleukin 4 receptor inhibits the biological effects of interleukin 4 on T and B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1365–1369. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N., Castle B. E., Gorman D. M., Itoh N., Schreurs J., Barrett R. L., Howard M., Miyajima A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding the murine interleukin 4 receptor based on ligand binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N., Yang G., Miyajima A., Howard M. Identification of an essential region for growth signal transduction in the cytoplasmic domain of the human interleukin-4 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22752–22758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzerda R. L., March C. J., Mosley B., Lyman S. D., Vanden Bos T., Gimpel S. D., Din W. S., Grabstein K. H., Widmer M. B., Park L. S. Human interleukin 4 receptor confers biological responsiveness and defines a novel receptor superfamily. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):861–873. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Zurawski G. Receptor binding and internalization of mouse interleukin-2 derivatives that are partial agonists. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13185–13190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Tange T., Terasawa T., Chiba S., Kuwaki T., Miyagawa K., Piao Y. F., Miyazono K., Urabe A., Takaku F. Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):323–334. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse N., Tony H. P., Sebald W. Conversion of human interleukin-4 into a high affinity antagonist by a single amino acid replacement. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3237–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le H. V., Ramanathan L., Labdon J. E., Mays-Ichinco C. A., Syto R., Arai N., Hoy P., Takebe Y., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P. Isolation and characterization of multiple variants of recombinant human interleukin 4 expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10817–10823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yokota T., Otsuka T., Meyerson P., Villaret D., Coffman R., Mosmann T., Rennick D., Roehm N., Smith C. Isolation and characterization of a mouse interleukin cDNA clone that expresses B-cell stimulatory factor 1 activities and T-cell- and mast-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2061–2065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A., Woodcock J. M., Milton S. E., Lewis A., Elliott M. J., Gillis D., Ireland R., Olwell E., Park L. S. Interleukin-5, interleukin-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor cross-compete for binding to cell surface receptors on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24741–24747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Sato T. A., Vanden Bos T., Waugh S., Dower S. K., Slack J., Beckmann M. P., Grabstein K. H. Cytokine receptors and B cell functions. I. Recombinant soluble receptors specifically inhibit IL-1- and IL-4-induced B cell activities in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3028–3033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B. Response. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):412–413. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5068.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie A. N., Culpepper J. A., de Waal Malefyt R., Brière F., Punnonen J., Aversa G., Sato A., Dang W., Cocks B. G., Menon S. Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3735–3739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Chalon P., Derocq J. M., Dumont X., Guillemot J. C., Kaghad M., Labit C., Leplatois P., Liauzun P., Miloux B. Interleukin-13 is a new human lymphokine regulating inflammatory and immune responses. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):248–250. doi: 10.1038/362248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Hara T., Kitamura T. Common subunits of cytokine receptors and the functional redundancy of cytokines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. G., Dolganov G. M., Robbins S. E., Hinton L. M., Lovett M. The selective isolation of novel cDNAs encoded by the regions surrounding the human interleukin 4 and 5 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5173–5179. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Subunit promiscuity among hemopoietic growth factor receptors. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90564-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma Y., Sideras P., Naito T., Bergstedt-Lindquist S., Azuma C., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Kinashi T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y. Cloning of cDNA encoding the murine IgG1 induction factor by a novel strategy using SP6 promoter. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):640–646. doi: 10.1038/319640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka T., Villaret D., Yokota T., Takebe Y., Lee F., Arai N., Arai K. Structural analysis of the mouse chromosomal gene encoding interleukin 4 which expresses B cell, T cell and mast cell stimulating activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):333–344. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandit J., Bohm A., Jancarik J., Halenbeck R., Koths K., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of dimeric human recombinant macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1358–1362. doi: 10.1126/science.1455231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Friend D., Grabstein K., Urdal D. L. Characterization of the high-affinity cell-surface receptor for murine B-cell-stimulating factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Garrett D. S., March C. J., Frieden E. A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Three-dimensional solution structure of human interleukin-4 by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1673–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestle J. P., Schär H. P., Grütter M. G. Crystal structure of the cytokine interleukin-1 beta. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):339–343. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02818.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punnonen J., Aversa G., Cocks B. G., McKenzie A. N., Menon S., Zurawski G., de Waal Malefyt R., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3730–3734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Ijssel H., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. Establishment of human T lymphocyte clones highly cytotoxic for an EBV-transformed B cell line in serum-free medium: isolation of clones that differ in phenotype and specificity. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Takebe Y., Arai N., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Recombinant interleukin 4 promotes the growth of human T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1142–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Otsuka T., Mosmann T., Banchereau J., DeFrance T., Blanchard D., De Vries J. E., Lee F., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a human interleukin cDNA clone, homologous to mouse B-cell stimulatory factor 1, that expresses B-cell- and T-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., De Vries J. E., Koken M., Van Blitterswijk W., Spits H. Serum-free medium for generation and propagation of functional human cytotoxic and helper T cell clones. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Imler J. L., Zurawski G. Partial agonist/antagonist mouse interleukin-2 proteins indicate that a third component of the receptor complex functions in signal transduction. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3899–3905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Mosmann T. R., Benedik M., Zurawski G. Alterations in the amino-terminal third of mouse interleukin 2: effects on biological activity and immunoreactivity. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3354–3360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Identification of three critical regions within mouse interleukin 2 by fine structural deletion analysis. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1061–1069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Mouse interleukin-2 structure-function studies: substitutions in the first alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p70 receptor binding and mutations in the fifth alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p55 receptor binding. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2583–2590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Receptor antagonist and selective agonist derivatives of mouse interleukin-2. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kimmenade A., Bond M. W., Schumacher J. H., Laquoi C., Kastelein R. A. Expression, renaturation and purification of recombinant human interleukin 4 from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]