Abstract
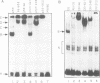
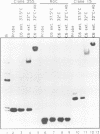
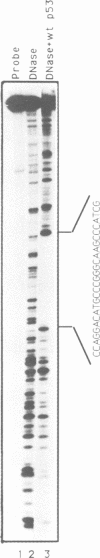
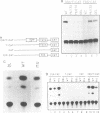
An immune selection procedure was employed in order to isolate p53 binding sites from mouse genomic DNA. Two DNA clones capable of tight specific interaction with wild type p53 were subjected to further characterization. In both cases, the p53 binding regions displayed a high degree of sequence homology with the consensus binding site defined for human genomic DNA. One of the clones was found to be derived from the LTR of a retrovirus-like element (a member of the GLN family). The region encompassing the GLN LTR p53 binding site could confer p53 responsiveness upon a heterologous promoter. Furthermore, the expression of the endogenous, chromosomally integrated GLN elements was significantly induced upon activation of wild type p53 in cells harboring a temperature sensitive p53 mutant. Finally, it was demonstrated that p53 - MDM2 complexes fail to bind tightly to such a p53 binding site. This may contribute to the inhibition by MDM2 of p53-mediated transcriptional activation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Juven T., Haffner R., Oren M. mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):461–468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Oren M. Enhanced binding of a 95 kDa protein to p53 in cells undergoing p53-mediated growth arrest. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh S. S., Trusko S. P., George D. L. Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.2218501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Rodel J., Peled A., Oren M. Frequent p53 mutations in chemically induced murine fibrosarcoma. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1593–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itin A., Keshet E. A novel retroviruslike family in mouse DNA. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):301–307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.301-307.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Schiff R., Itin A. Mouse retrotransposons: a cellular reservoir of long terminal repeat (LTR) elements with diverse transcriptional specificities. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:215–251. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner M. S., Mack D. H., Finicle A. B., Crook T., Vousden K. H., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus E6 proteins bind p53 in vivo and abrogate p53-mediated repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone L. R., White A., Sprouse J., Livanos E., Jacks T., Tlsty T. D. Altered cell cycle arrest and gene amplification potential accompany loss of wild-type p53. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):923–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Czyzyk L. UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Oren M., Levine A. J. The structural relationships between 54,000-molecular-weight cellular tumor antigens detected in viral- and nonviral-transformed cells. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90620-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenarh M. Biochemical, immunological, and functional aspects of the growth-suppressor/oncoprotein p53. Crit Rev Oncog. 1992;3(3):233–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke R. W., Miller C. W., Kato G. J., Simon K. J., Chen D. L., Dang C. V., Koeffler H. P. A potential transcriptional activation element in the p53 protein. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1829–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. p53: the ultimate tumor suppressor gene? FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3169–3176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragimov N., Krauskopf A., Navot N., Rotter V., Oren M., Aloni Y. Wild-type but not mutant p53 can repress transcription initiation in vitro by interfering with the binding of basal transcription factors to the TATA motif. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1183–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad A., Carroll R. B. The tumor suppressor p53 is bound to RNA by a stable covalent linkage. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1598–1606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schärer E., Iggo R. Mammalian p53 can function as a transcription factor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Ginsberg D., Oren M. Identification of a minimal transforming domain of p53: negative dominance through abrogation of sequence-specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5581–5592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Deppert W. DNA binding properties of murine p53. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y., Tainsky M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Strong L. C., Wahl G. M. Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Grunwald D., Wilder S., Kimchi A., May E., Lawrence J. J., May P., Oren M. p53-mediated cell death: relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]