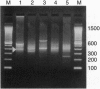
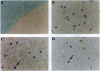
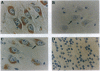
Abstract
Representational difference analysis was used to search for pathogens in multiple sclerosis brains. We detected a 341-nucleotide fragment that was 99.4% identical to the major DNA binding protein gene of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6). Examination of 86 brain specimens by PCR demonstrated that HHV-6 was present in > 70% of MS cases and controls and is thus a commensal virus of the human brain. By DNA sequencing, 36/37 viruses from MS cases and controls were typed as HHV-6 variant B group 2. Other herpesviruses, retroviruses, and measles virus were detected infrequently or not at all. HHV-6 expression was examined by immunocytochemistry with monoclonal antibodies against HHV-6 virion protein 101K and DNA binding protein p41. Nuclear staining of oligodendrocytes was observed in MS cases but not in controls, and in MS cases it was observed around plaques more frequently than in uninvolved white matter. MS cases showed prominent cytoplasmic staining of neurons in gray matter adjacent to plaques, although neurons expressing HHV-6 were also found in certain controls. Since destruction of oligodendrocytes is a hallmark of MS, these studies suggest an association of HHV-6 with the etiology or pathogenesis of MS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agulnick A. D., Thompson J. R., Iyengar S., Pearson G., Ablashi D., Ricciardi R. P. Identification of a DNA-binding protein of human herpesvirus 6, a putative DNA polymerase stimulatory factor. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):1003–1009. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen I., Brankin B. Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis--the immune diathesis and the role of viruses. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Mar;52(2):95–105. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caserta M. T., Hall C. B., Schnabel K., McIntyre K., Long C., Costanzo M., Dewhurst S., Insel R., Epstein L. G. Neuroinvasion and persistence of human herpesvirus 6 in children. J Infect Dis. 1994 Dec;170(6):1586–1589. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.6.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S., Marousek G. I. Analysis of interstrain variation in a putative immediate-early region of human herpesvirus 6 DNA and definition of variant-specific sequences. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):370–376. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. W., Huang M. L., Ashley R., Corey L. Human herpesvirus 6 DNA in peripheral blood cells and saliva from immunocompetent individuals. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1262–1267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1262-1267.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Multiple sclerosis and viruses: an overview. Neurology. 1980 Jul;30(7 Pt 2):80–91. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.7_part_2.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobyski W. R., Knox K. K., Majewski D., Carrigan D. R. Brief report: fatal encephalitis due to variant B human herpesvirus-6 infection in a bone marrow-transplant recipient. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1356–1360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Pathak S., Scallan M., Amor S., Dyson H. Replication of the A7(74) strain of Semliki Forest virus is restricted in neurons. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):627–637. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Webb H. E. Semliki Forest virus-induced, immune-mediated demyelination: adoptive transfer studies and viral persistence in nude mice. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):377–385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U. A., Carrigan D. R., Carss A. L., Arno J. Two groups of human herpesvirus 6 identified by sequence analyses of laboratory strains and variants from Hodgkin's lymphoma and bone marrow transplant patients. J Gen Virol. 1993 Apr;74(Pt 4):613–622. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-4-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Long C. E., Schnabel K. C., Caserta M. T., McIntyre K. M., Costanzo M. A., Knott A., Dewhurst S., Insel R. A., Epstein L. G. Human herpesvirus-6 infection in children. A prospective study of complications and reactivation. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 18;331(7):432–438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408183310703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. M., Lee C. Y., Lee P. I., Chen J. M., Wang P. J. Meningitis caused by human herpesvirus-6. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Dec;66(12):1443–1444. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.12.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human herpesvirus-6 strain groups: a nomenclature. Arch Virol. 1993;129(1-4):363–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01316913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Yamada S., Takahashi T., Takahashi Y., Togashi T., Okuno T., Yamanishi K. Meningo-encephalitis associated with HHV-6 related exanthem subitum. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1990 Oct;79(10):987–989. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1990.tb11369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T. The virology of demyelinating diseases. Ann Neurol. 1994;36 (Suppl):S54–S60. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs S. F., Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Schachter F., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Genomic analysis of the human B-lymphotropic virus (HBLV). Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):601–603. doi: 10.1126/science.3020691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. K., Carrigan D. R. Active human herpesvirus (HHV-6) infection of the central nervous system in patients with AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 May 1;9(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. K., Carrigan D. R. Disseminated active HHV-6 infections in patients with AIDS. Lancet. 1994 Mar 5;343(8897):577–578. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91524-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Epidemiologic evidence for multiple sclerosis as an infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Oct;6(4):382–427. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.4.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisitsyn N., Lisitsyn N., Wigler M. Cloning the differences between two complex genomes. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):946–951. doi: 10.1126/science.8438152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luppi M., Barozzi P., Maiorana A., Marasca R., Torelli G. Human herpesvirus 6 infection in normal human brain tissue. J Infect Dis. 1994 Apr;169(4):943–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.4.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Sánchez-Martínez D., Dominguez G., Black J. B., Anton E., Greenamoyer C., Dambaugh T. R. A strongly immunoreactive virion protein of human herpesvirus 6 variant B strain Z29: identification and characterization of the gene and mapping of a variant-specific monoclonal antibody reactive epitope. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):521–531. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. P. Virus-induced demyelination in man: models for multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg. 1992 Apr;5(2):188–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Leibowitz J. L., Powell H. C., Lampert P. W. Neonatal infection with the Daniels strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. Lab Invest. 1983 Dec;49(6):672–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M. Multiple sclerosis: basic concepts and hypothesis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 May;64(5):570–576. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(12)65563-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Markham P. D., Josephs S. F., Sturzenegger S., Kaplan M., Halligan G., Biberfeld P., Wong-Staal F., Kramarsky B. Isolation of a new virus, HBLV, in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):596–601. doi: 10.1126/science.2876520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi S. R., Key M. E., Kalra K. L. Antigen retrieval in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: an enhancement method for immunohistochemical staining based on microwave oven heating of tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Jun;39(6):741–748. doi: 10.1177/39.6.1709656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola P., Merelli E., Marasca R., Poggi M., Luppi M., Montorsi M., Torelli G. Human herpesvirus 6 and multiple sclerosis: survey of anti-HHV-6 antibodies by immunofluorescence analysis and of viral sequences by polymerase chain reaction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 Aug;56(8):917–919. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.8.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeper T. A., Horwitz C. A., Ablashi D. V., Salahuddin S. Z., Saxinger C., Saltzman R., Schwartz B. The spectrum of clinical and laboratory findings resulting from human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) in patients with mononucleosis-like illnesses not resulting from Epstein-Barr virus or cytomegalovirus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jun;93(6):776–783. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.6.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling A. J., Pathak S., Jagelman S., Webb H. E. Virus-associated demyelination. A model using avirulent Semliki Forest virus infection of mice. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga S., Yoshikawa T., Asano Y., Kozawa T., Nakashima T., Kobayashi I., Yazaki T., Yamamoto H., Kajita Y., Ozaki T. Clinical and virological analyses of 21 infants with exanthem subitum (roseola infantum) and central nervous system complications. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jun;33(6):597–603. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W., Rosario I. P., Conrad A., Syndulko K. Human neuro-specimen banking 1961-1992. The National Neurological Research Specimen Bank (a donor program of pre- and post-mortem tissues and cerebrospinal fluid/blood; and a collection of cryopreserved human neurological specimens for neuroscientists). J Neural Transm Suppl. 1993;39:5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilborn F., Schmidt C. A., Brinkmann V., Jendroska K., Oettle H., Siegert W. A potential role for human herpesvirus type 6 in nervous system disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jan;49(1-2):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Kondo K., Mukai T., Kondo T., Nagafuji H., Kato T., Okuno T., Kurata T. Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) infection in the central nervous system. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1992 Jun;34(3):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1992.tb00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Okuno T., Shiraki K., Takahashi M., Kondo T., Asano Y., Kurata T. Identification of human herpesvirus-6 as a causal agent for exanthem subitum. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Yamawaki M., Vandevelde M. Restricted canine distemper virus infection of oligodendrocytes. Lab Invest. 1993 Mar;68(3):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]