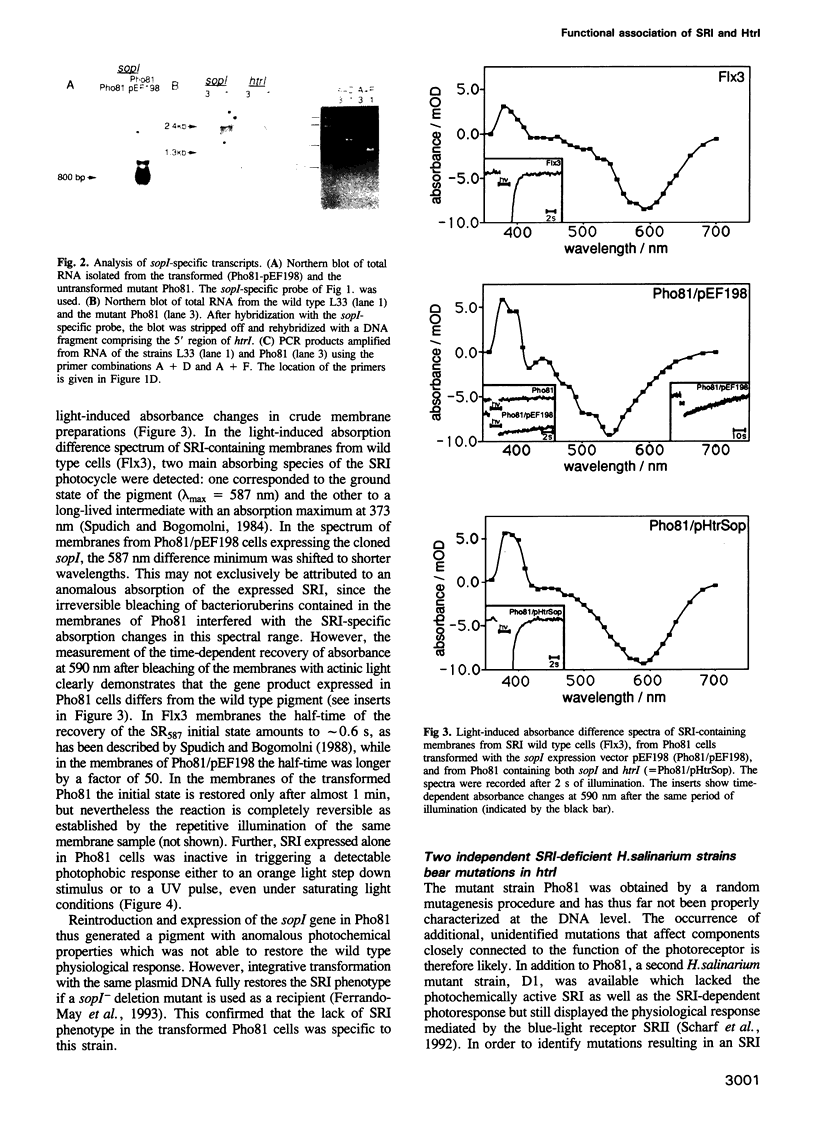
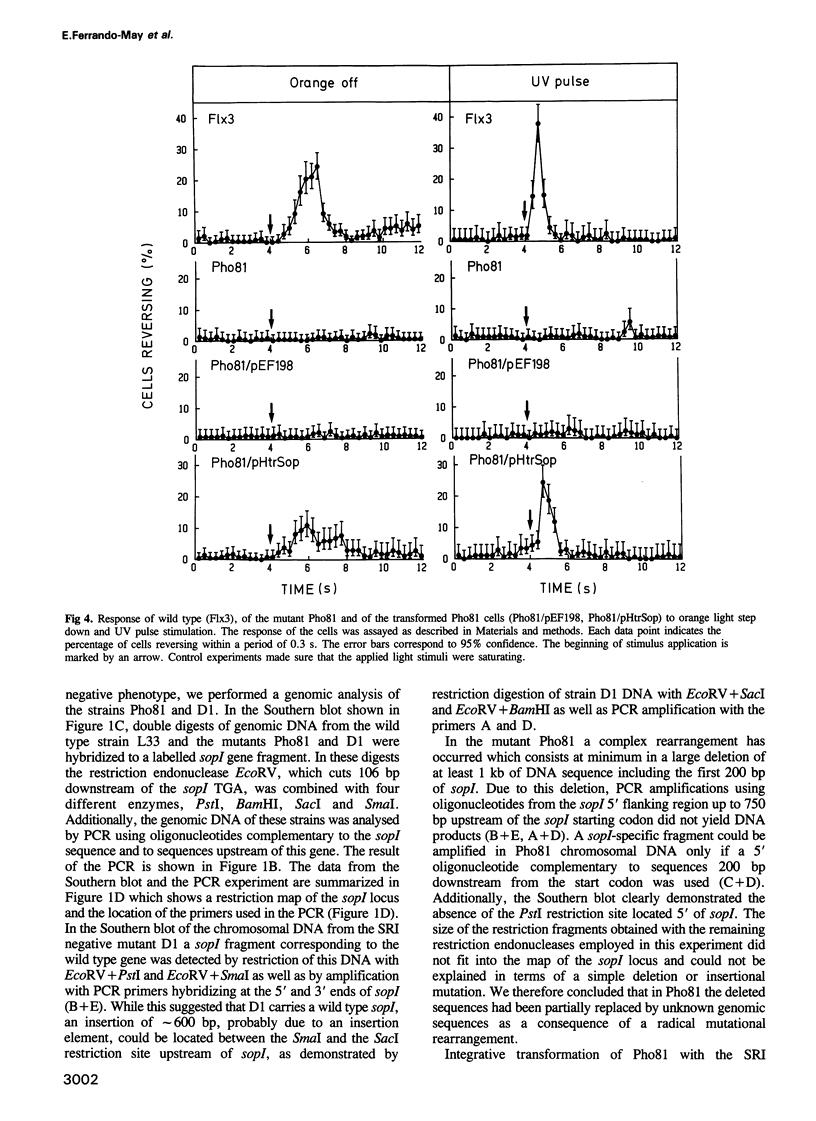
Abstract
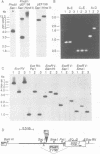
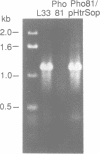
We have investigated the functional relationship between two proteins involved in the photosensory system of the archaeon Halobacterium salinarium: the photoreceptor sensory rhodopsin I (SRI) and the halobacterial transducer rhodopsin I (HtrI), which has been proposed to be the putative signal transducer of SRI, by genomic DNA analysis of two independent SRI negative mutants, Pho81 and D1. Southern and PCR analyses revealed that both strains bear alterations in the 5' flanking region of the gene encoding SRI, sopI. DNA sequence analysis confirmed the occurrence in this region of htrI, the gene encoding the putative transducer protein. PCR and Northern analyses have shown further that sopI and htrI are expressed as a single transcriptional unit, thus explaining the lack of SRI in mutants with a defective htrI. Expression of the cloned sopI under the control of a heterologous promoter did not restore the SRI-dependent photoresponse in the strain Pho81. Moreover, the photocycling rate of the expressed pigment was clearly lower than in wild type. HtrI is therefore essential for SRI function and most likely modulates the photochemical properties of the photoreceptor via direct physical interaction. Finally, reintroduction of both sopI and htrI into Pho81 and D1 restored the SRI photochemistry and its physiological function. Our results provide the first experimental evidence for the functional coupling between SRI and HtrI and corroborate the proposed model in which HtrI acts as the signal transducer of this archaeal seven-helix photoreceptor in a way analogous to the bacterial chemotaxis transducers.
Full text
PDF
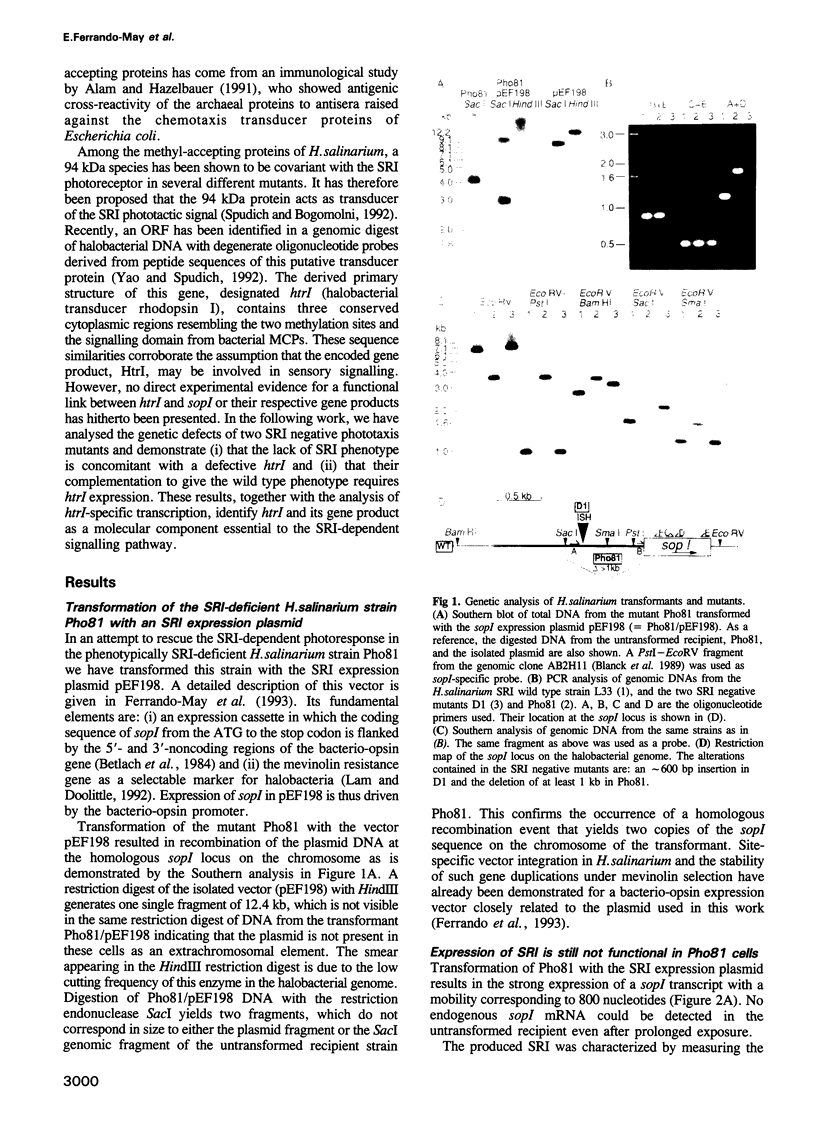



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Hazelbauer G. L. Structural features of methyl-accepting taxis proteins conserved between archaebacteria and eubacteria revealed by antigenic cross-reaction. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5837–5842. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5837-5842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Lebert M., Oesterhelt D., Hazelbauer G. L. Methyl-accepting taxis proteins in Halobacterium halobium. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):631–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Pfeifer F. Characterization of a halobacterial gene affecting bacterio-opsin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7949–7959. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D., Ferrando E., Schegk E. S., Lottspeich F. Primary structure of sensory rhodopsin I, a prokaryotic photoreceptor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3963–3971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Daniels C. J., Reeve J. N. Gene structure, organization, and expression in archaebacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(4):287–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Lam W. L., Charlebois R. L., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation methods for halophilic archaebacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):148–152. doi: 10.1139/m89-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrando E., Schweiger U., Oesterhelt D. Homologous bacterio-opsin-encoding gene expression via site-specific vector integration. Gene. 1993 Mar 15;125(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90743-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. L., Nuttall S. D., Dyall-Smith M. L. Construction and use of halobacterial shuttle vectors and further studies on Haloferax DNA gyrase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3807–3813. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3807-3813.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Mevinolin-resistant mutations identify a promoter and the gene for a eukaryote-like 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in the archaebacterium Haloferax volcanii. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5829–5834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Pfeifer F., Boyer H., Betlach M. Characterization of a second gene involved in bacterio-opsin gene expression in a halophilic archaebacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4903–4909. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4903-4909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Quantitation of photochromism of sensory rhodopsin-I by computerized tracking of Halobacterium halobium cells. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Signal formation in the halobacterial photophobic response mediated by a fourth retinal protein (P480). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90654-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Schäfer W., Oesterhelt D. Signal transduction in Halobacterium depends on fumarate. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):355–362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Yanofsky C. Translational coupling during expression of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Hüdepohl U., Zillig W. Mutational analysis of an archaebacterial promoter: essential role of a TATA box for transcription efficiency and start-site selection in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9509–9513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf B., Pevec B., Hess B., Engelhard M. Biochemical and photochemical properties of the photophobic receptors from Halobacterium halobium and Natronobacterium pharaonis. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schegk E. S., Oesterhelt D. Isolation of a prokaryotic photoreceptor: sensory rhodopsin from halobacteria. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2925–2933. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimz A. Methylation of membrane proteins is involved in chemosensory and photosensory behavior of Halobacterium halobium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80719-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Nomura M. Mutational alterations of translational coupling in the L11 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3495–3507. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3495-3507.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiridonova V. A., Akhmanova A. S., Kagramanova V. K., Köpke A. K., Mankin A. S. Ribosomal protein gene cluster of Halobacterium halobium: nucleotide sequence of the genes coding for S3 and L29 equivalent ribosomal proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):153–159. doi: 10.1139/m89-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Takahashi T., Spudich J. L. Sensory rhodopsins I and II modulate a methylation/demethylation system in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7746–7750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Sensory rhodopsin I: receptor activation and signal relay. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00762677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Sensory rhodopsins of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:193–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Alam M., Lebert M., Spudich J. L., Oesterhelt D., Hazelbauer G. L. Characterization of Halobacterium halobium mutants defective in taxis. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2328–2335. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2328-2335.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Selection and properties of phototaxis-deficient mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl R., Meyer B., Desel H. A polychromatic flash photolysis apparatus (PFPA). J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Nov;10(1-2):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao V. J., Spudich J. L. Primary structure of an archaebacterial transducer, a methyl-accepting protein associated with sensory rhodopsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11915–11919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]