Abstract
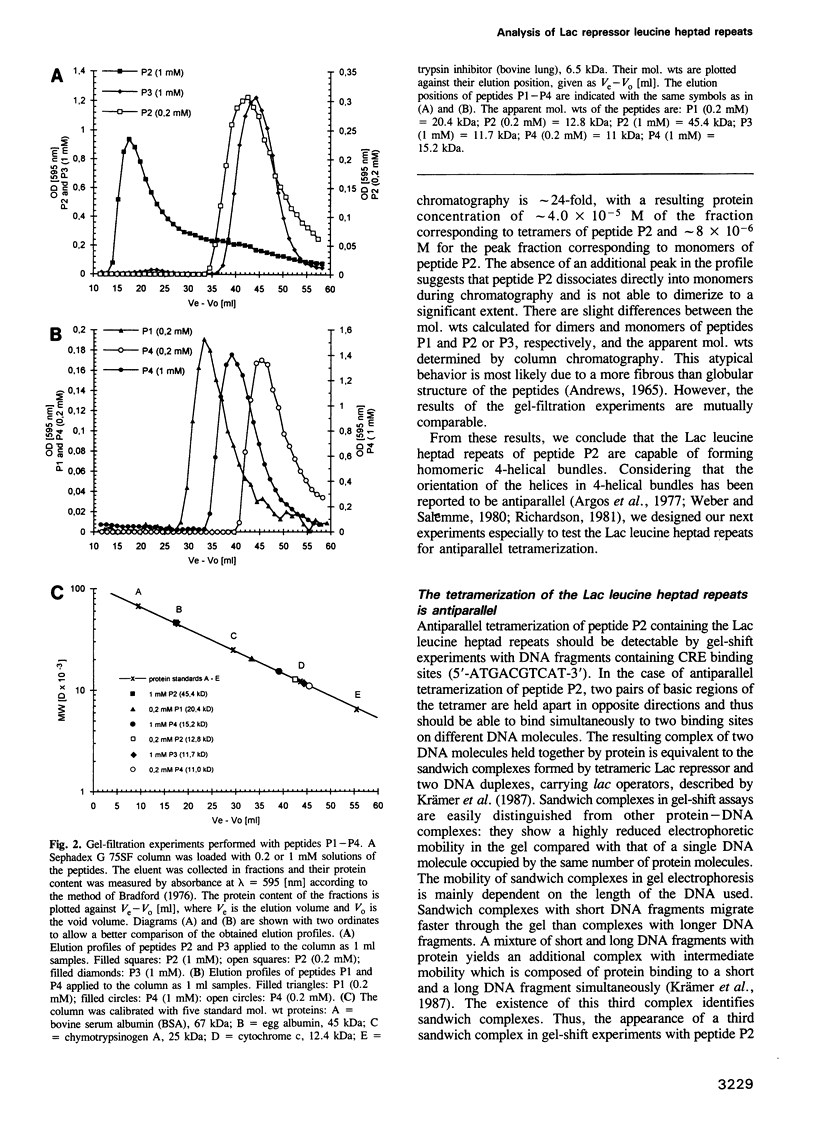
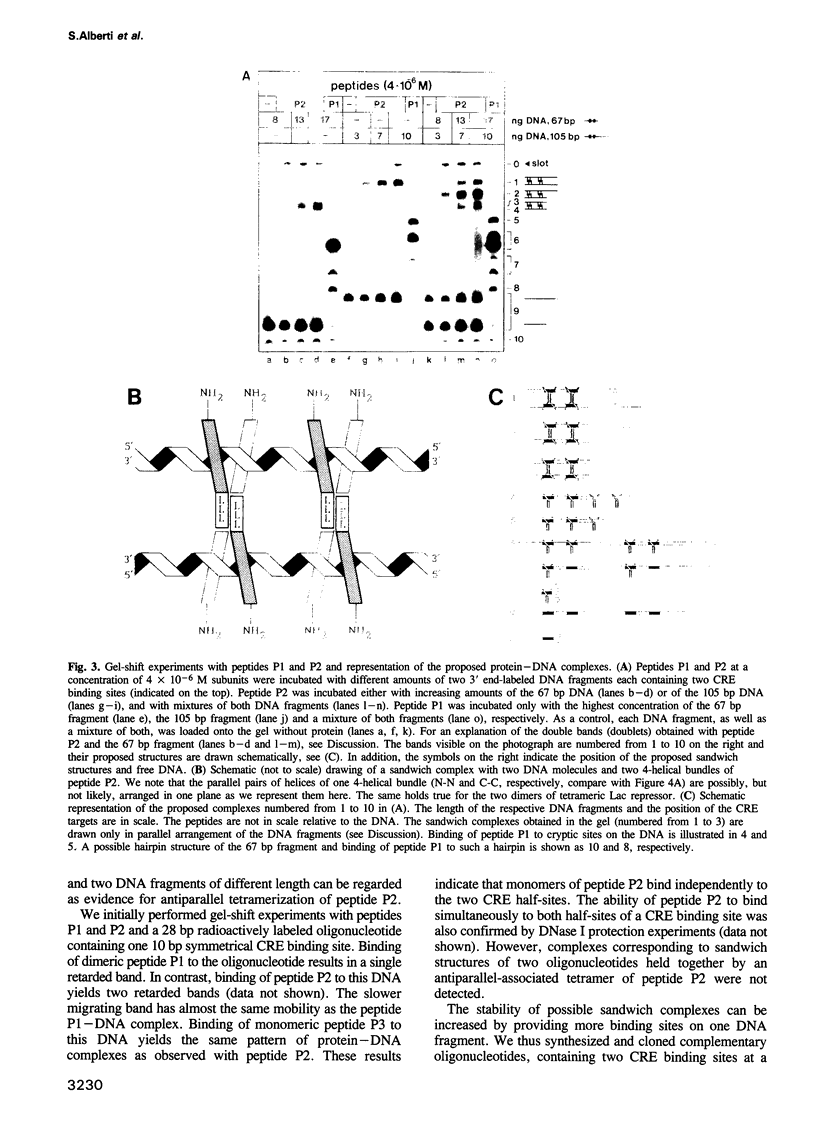
Gel-filtration experiments indicate that a peptide (P2) composed of the basic region of GCN4 fused to the leucine heptad repeats of Lac repressor forms tetrameric aggregates. Gel-shift experiments were performed to determine the orientation of the helices in the tetrameric P2 aggregate. Sandwich-complex formation of peptide P2 with two DNA fragments containing two symmetrical CRE binding sites (5'-ATGACGTCAT-3') at a distance of 21 bp suggests antiparallel aggregation of the Lac leucine heptad repeats. Thus, we conclude that the leucine heptad repeats of Lac repressor have the ability to form homomeric 4-helical bundles with an antiparallel arrangement of the helices. This topology enables the two DNA fragments in the sandwich complexes to be held together by two tetramers of peptide P2. Replacement of the uncharged amino acids of the helical g and e positions of peptide P2 by the corresponding charged residues of GCN4 (peptide P4) results in a dimeric and parallel aggregation of the leucine heptad repeats, and consequently abolishes the potential to form sandwich structures. Similarly, a hybrid Lac repressor in which the GCN4 leucine zipper replaces the natural Lac leucine heptad repeats forms dimers only. It regains the ability to form tetramers when the charged amino acids in helical positions g and e are replaced by uncharged alanines.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Cognate DNA binding specificity retained after leucine zipper exchange between GCN4 and C/EBP. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):922–926. doi: 10.1126/science.2530632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alber T. Structure of the leucine zipper. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti S., Oehler S., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. Dimer-to-tetramer assembly of Lac repressor involves a leucine heptad repeat. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. A four-helical super-secondary structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besse M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Synthetic lac operator mediates repression through lac repressor when introduced upstream and downstream from lac promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1377–1381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakerian A. E., Tesmer V. M., Manly S. P., Brackett J. K., Lynch M. J., Hoh J. T., Matthews K. S. Evidence for leucine zipper motif in lactose repressor protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou K. C., Maggiora G. M., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Energetics of the structure of the four-alpha-helix bundle in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4295–4299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hol W. G., Halie L. M., Sander C. Dipoles of the alpha-helix and beta-sheet: their role in protein folding. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):532–536. doi: 10.1038/294532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki H., Kadowaki T., Wondisford F. E., Taylor S. I. Use of polymerase chain reaction catalyzed by Taq DNA polymerase for site-specific mutagenesis. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Sartorius J., Oehler S., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Recognition helices of lac and lambda repressor are oriented in opposite directions and recognize similar DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7947–7951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. Tropomyosin coiled-coil interactions: evidence for an unstaggered structure. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Mechanism of specificity in the Fos-Jun oncoprotein heterodimer. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):699–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler S., Eismann E. R., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. The three operators of the lac operon cooperate in repression. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):973–979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace H. C., Lu P., Lewis M. lac repressor: crystallization of intact tetramer and its complexes with inducer and operator DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1870–1873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Sasmor H., Betz J. L. A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Schmeissner U., Miller J. H. Mutations affecting the quaternary structure of the lac repressor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3359–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Vincent A. C., Struhl K. Mutations that define the optimal half-site for binding yeast GCN4 activator protein and identify an ATF/CREB-like repressor that recognizes similar DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5077–5086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons A., Tils D., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Possible ideal lac operator: Escherichia coli lac operator-like sequences from eukaryotic genomes lack the central G X C pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Identification of three residues in the basic regions of the bZIP proteins GCN4, C/EBP and TAF-1 that are involved in specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Salemme F. R. Structural and functional diversity in 4-alpha-helical proteins. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):82–84. doi: 10.1038/287082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]