Abstract
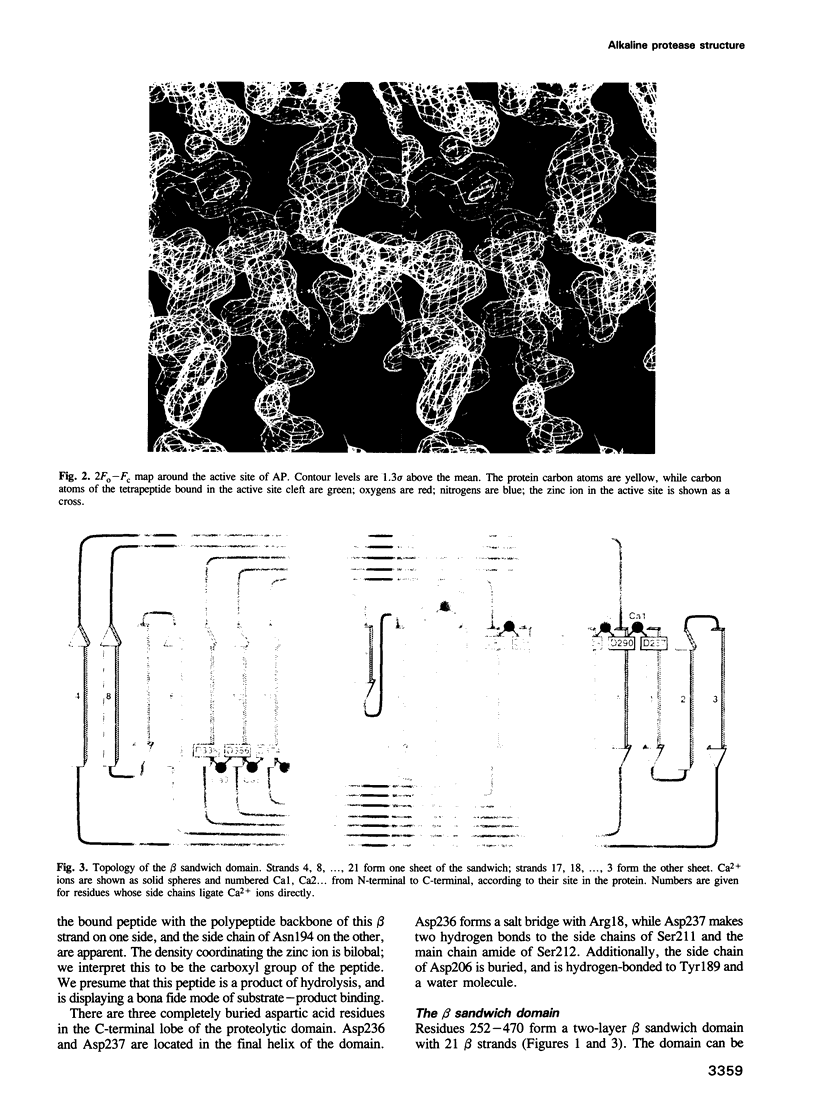
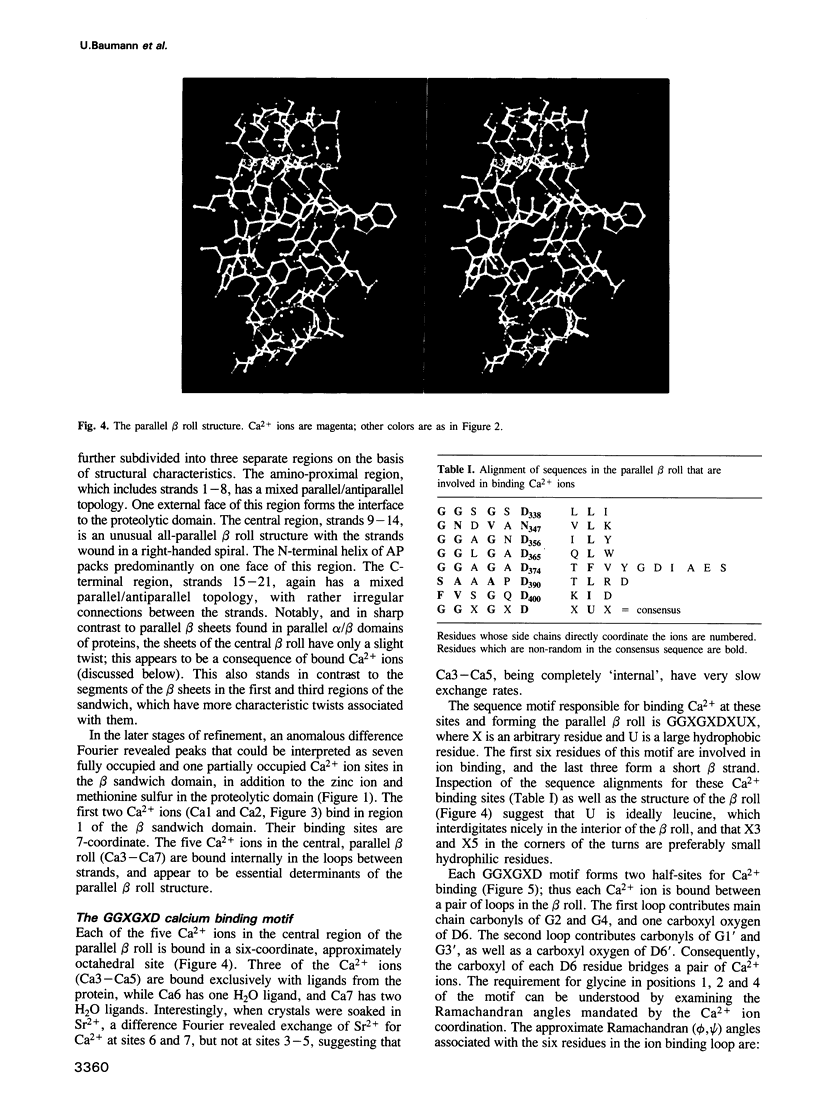
The three-dimensional structure of the alkaline protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a zinc metalloprotease, has been solved to a resolution of 1.64 A by multiple isomorphous replacement and non-crystallographic symmetry averaging between different crystal forms. The molecule is elongated with overall dimensions of 90 x 35 x 25 A; it has two distinct structural domains. The N-terminal domain is the proteolytic domain; it has an overall tertiary fold and active site zinc ligation similar to that of astacin, a metalloprotease isolated from a European freshwater crayfish. The C-terminal domain consists of a 21-strand beta sandwich. Within this domain is a novel 'parallel beta roll' structure in which successive beta strands are wound in a right-handed spiral, and in which Ca2+ ions are bound within the turns between strands by a repeated GGXGXD sequence motif, a motif that is found in a diverse group of proteins secreted by Gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode W., Gomis-Rüth F. X., Huber R., Zwilling R., Stöcker W. Structure of astacin and implications for activation of astacins and zinc-ligation of collagenases. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):164–167. doi: 10.1038/358164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahler G. S., Barras F., Keen N. T. Cloning of genes encoding extracellular metalloproteases from Erwinia chrysanthemi EC16. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5803–5815. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5803-5815.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proteases B and C are synthesized and secreted as zymogens without a signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9083–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong F., Lazdunski A., Cami B., Murgier M. Sequence of a cluster of genes controlling synthesis and secretion of alkaline protease in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: relationships to other secretory pathways. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90160-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou A., Hamilton W. D., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium nodulation gene nodO encodes a Ca2(+)-binding protein that is exported without N-terminal cleavage and is homologous to haemolysin and related proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):349–354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomis-Rüth F. X., Stöcker W., Huber R., Zwilling R., Bode W. Refined 1.8 A X-ray crystal structure of astacin, a zinc-endopeptidase from the crayfish Astacus astacus L. Structure determination, refinement, molecular structure and comparison with thermolysin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 20;229(4):945–968. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo J., Duong F., Wandersman C., Murgier M., Lazdunski A. The secretion genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease are functionally related to those of Erwinia chrysanthemi proteases and Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong Y. Q., Ghebrehiwet B. Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase and alkaline protease on serum complement and isolated components C1q and C3. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Feb;62(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90065-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat R. T., Parmely M. J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease degrades human gamma interferon and inhibits its bioactivity. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2925-2932.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Thirup S. Using known substructures in protein model building and crystallography. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):819–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Jarchau T., Benz R., Goebel W. The repeat domain of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is responsible for its Ca2+-dependent binding to erythrocytes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):553–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00330494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama K., Yoshimura K., Marumoto R., Kikuchi M., Lee I. S., Hase T., Matsubara H. Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5843–5855. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Morihara K., Atsumi Y., Takeuchi H., Kawamoto S., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Fukushima J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for alkaline proteinase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO 3455. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4083–4088. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4083-4088.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Mutational analysis supports a role for multiple structural features in the C-terminal secretion signal of Escherichia coli haemolysin. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2391–2403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Identification of two different hemolysin determinants in uropathogenic Proteus isolates. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2183–2190. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2183-2190.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]