Abstract
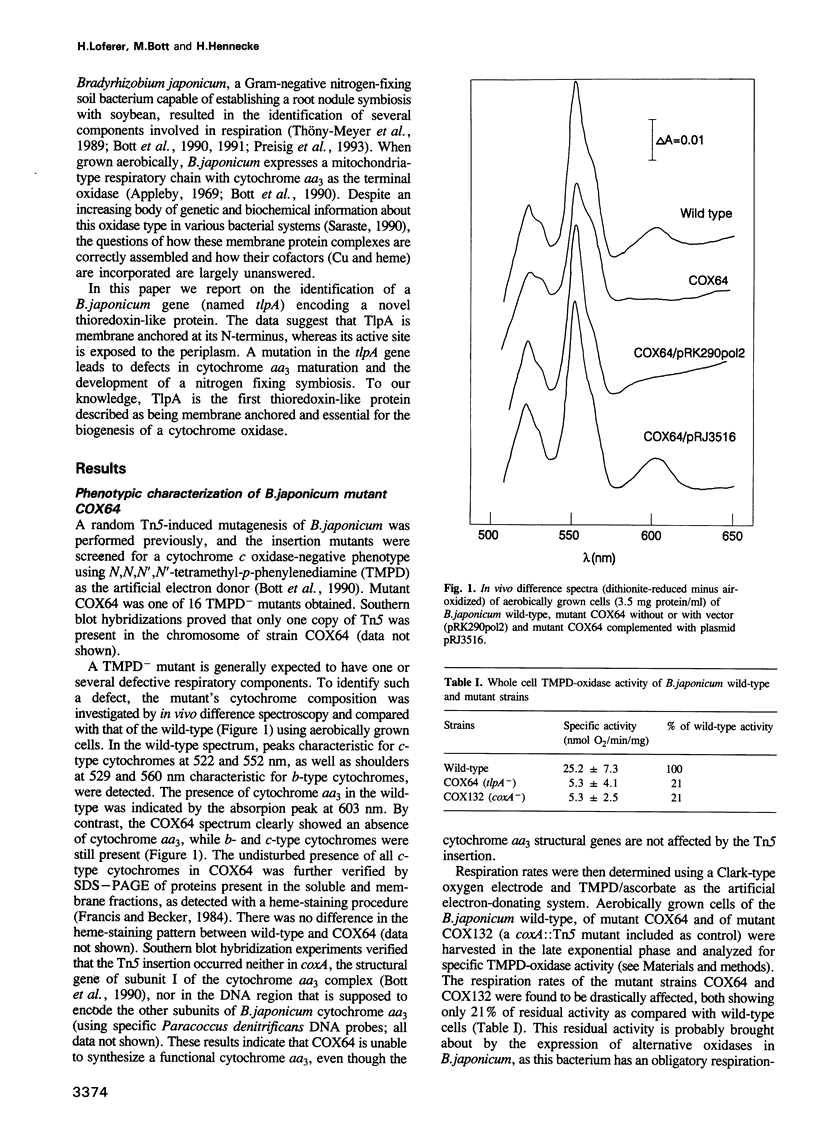
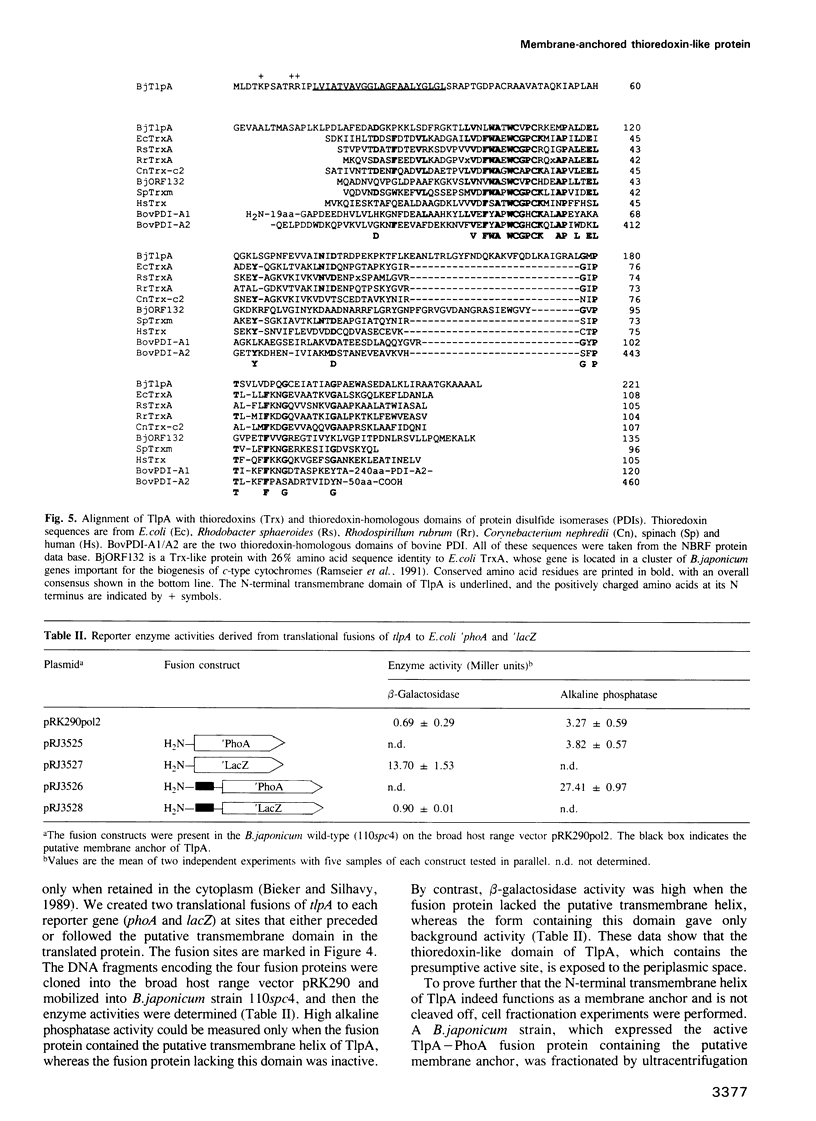
We report the discovery of a bacterial gene, tlpA, that codes for a hitherto unknown type of thioredoxin-like protein. The gene was found in the course of studying a Tn5 insertion mutant of the soybean root nodule symbiont Bradyrhizobium japonicum. The TlpA protein shared up to 31% amino acid sequence identity with various eukaryotic and prokaryotic thioredoxins and protein disulfide isomerases, and possessed a characteristic active-site sequence, Trp-Cys-Val-Pro-Cys. In contrast to all members of the thioredoxin family known to date, TlpA was shown to be anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane by means of an N-terminal transmembrane domain, while the active site-containing part of the protein faced the periplasm. The tlpA mutant had a pleiotropic phenotype in that it was defective in the development of a nitrogen fixing endosymbiosis and exhibited a strongly decreased oxidase activity, as compared with the wild-type. Holocytochrome aa3 was spectroscopically undetectable in the mutant, whereas the apoprotein of subunit one (CoxA) of this oxidase was still synthesized and incorporated into the cytoplasmic membrane. Since cytochrome aa3 is not a prerequisite for the development of symbiosis, the results suggest that TlpA is involved in at least two independent cellular processes, one of which is an essential periplasmic step in the maturation of cytochrome aa3.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Av-Gay Y., Schreiber R., Cohen G. Characterization of a broad-range disulfide reductase from Streptomyces clavuligerus and its possible role in beta-lactam antibiotic biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):623–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.623-629.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Kamitani S., Kusukawa N., Ito K. In vitro catalysis of oxidative folding of disulfide-bonded proteins by the Escherichia coli dsbA (ppfA) gene product. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22440–22445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby C. A. Electron transport systems of Rhizobium japonicum. II. Rhizobium haemoglobin, cytochromes and oxidases in free-living (cultured) cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 14;172(1):88–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA is important for the translocation of exported proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Bolliger M., Hennecke H. Genetic analysis of the cytochrome c-aa3 branch of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum respiratory chain. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2147–2157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Preisig O., Hennecke H. Genes for a second terminal oxidase in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1992;158(5):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00245362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Ritz D., Hennecke H. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum cycM gene encodes a membrane-anchored homolog of mitochondrial cytochrome c. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6766–6772. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6766-6772.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Determinants of membrane protein topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement-Metral J. D. Activation of ALA synthetase by reduced thioredoxin in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides Y. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):116–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Ellis L., Blacher R. W., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Sequence of protein disulphide isomerase and implications of its relationship to thioredoxin. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):267–270. doi: 10.1038/317267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Gleason F. K., Holmgren A. Structural and functional relations among thioredoxins of different species. Proteins. 1991;11(1):13–28. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L. B., Saurugger P., Woodward C. Identification of the three-dimensional thioredoxin motif: related structure in the ORF3 protein of the Staphylococcus aureus mer operon. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis R. T., Jr, Becker R. R. Specific indication of hemoproteins in polyacrylamide gels using a double-staining process. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan Z. R. Yeast thioredoxin genes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1692–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhus E., Steinrücke P., Ludwig B. Paracoccus denitrificans cytochrome c1 gene replacement mutants. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2392–2400. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2392-2400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason F. K., Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and related proteins in procaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;4(4):271–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi A., Cerchia L., De Rosa M., Rossi M., Bartolucci S. Isolation of a thermostable enzyme catalyzing disulfide bond formation from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 25;303(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia T., Finel M., Harms N., Nakari T., Raitio M., Wikström M., Saraste M. Deletion of the gene for subunit III leads to defective assembly of bacterial cytochrome oxidase. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3571–3579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Wright A. Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5107–5111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13963–13966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katti S. K., LeMaster D. M., Eklund H. Crystal structure of thioredoxin from Escherichia coli at 1.68 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):167–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90313-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. C., Padmanaban G. Role of heme in the synthesis of cytochrome c oxidase in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11130–11134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübben M., Kolmerer B., Saraste M. An archaebacterial terminal oxidase combines core structures of two mitochondrial respiratory complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):805–812. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin: a subunit of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):780–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern K., Ehrmann M., Beckwith J. Decoding signals for membrane protein assembly using alkaline phosphatase fusions. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2773–2782. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P. Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobrega M. P., Nobrega F. G., Tzagoloff A. COX10 codes for a protein homologous to the ORF1 product of Paracoccus denitrificans and is required for the synthesis of yeast cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14220–14226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noiva R., Lennarz W. J. Protein disulfide isomerase. A multifunctional protein resident in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3553–3556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peek J. A., Taylor R. K. Characterization of a periplasmic thiol:disulfide interchange protein required for the functional maturation of secreted virulence factors of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6210–6214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig O., Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. Genes for a microaerobically induced oxidase complex in Bradyrhizobium japonicum are essential for a nitrogen-fixing endosymbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitio M., Jalli T., Saraste M. Isolation and analysis of the genes for cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2825–2833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier T. M., Göttfert M. Codon usage and G + C content in Bradyrhizobium japonicum genes are not uniform. Arch Microbiol. 1991;156(4):270–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00262997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier T. M., Winteler H. V., Hennecke H. Discovery and sequence analysis of bacterial genes involved in the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7793–7803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Thioredoxin is required for filamentous phage assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):29–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzgaber-Müller J., Schatz G. Heme is necessary for the accumulation and assembly of cytochrome c oxidase subunits in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M. Structural features of cytochrome oxidase. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):331–366. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann P., Maeda K., Tsugita A. Isomers in thioredoxins of spinach chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücke P., Gerhus E., Ludwig B. Paracoccus denitrificans mutants deleted in the gene for subunit II of cytochrome c oxidase also lack subunit I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7676–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny-Meyer L., James P., Hennecke H. From one gene to two proteins: the biogenesis of cytochromes b and c1 in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5001–5005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny-Meyer L., Stax D., Hennecke H. An unusual gene cluster for the cytochrome bc1 complex in Bradyrhizobium japonicum and its requirement for effective root nodule symbiosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):683–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomb J. F. A periplasmic protein disulfide oxidoreductase is required for transformation of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10252–10256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang M. L., Schiff J. A. Sulfate-reducing pathway in Escherichia coli involving bound intermediates. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):923–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.923-933.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Capitanio N., Nobrega M. P., Gatti D. Cytochrome oxidase assembly in yeast requires the product of COX11, a homolog of the P. denitrificans protein encoded by ORF3. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2759–2764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Webb H., Hirst T. R. A homologue of the Escherichia coli DsbA protein involved in disulphide bond formation is required for enterotoxin biogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1949–1958. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]