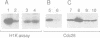Abstract
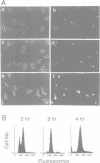
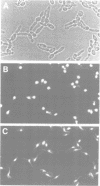
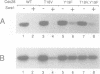
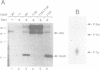
Wee1 is a protein kinase that negatively regulates p34cdc2 kinase activity. We have identified a Saccharomyces cerevisiae wee1 homolog encoded by the SWE1 gene. SWE1 overexpression arrests cells in G2 with short spindles whereas deletion of SWE1 did not alter the cell cycle but did eliminate the G2 delay observed in mih1- mutants. Swe1 immunoprecipitates were capable of tyrosine phosphorylating and inactivating p34CDC28 complexed with Clb2, a G2-type cyclin, but not p34CDC28 complexed with Cln2, a G1-type cyclin, consistent with the inability of Swe1 overexpression to inhibit the G1/S transition. These results suggest that specific cyclin subunits target p34CDC28 for distinct regulatory controls which may be important for ensuring proper p34CDC28 function during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of cdc13+ in mitotic control in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: possible interaction of the gene product with microtubules. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2321–2327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Behavior of spindles and spindle plaques in the cell cycle and conjugation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):511–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.511-523.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. Cell cycle arrest caused by CLN gene deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae resembles START-I arrest and is independent of the mating-pheromone signalling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6482–6490. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Newport J. W. Completion of DNA replication is monitored by a feedback system that controls the initiation of mitosis in vitro: studies in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90191-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Activation of human cyclin-dependent kinases in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):571–582. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Garrigues A. M., Labbé J. C., Lorca T., Picard A., Philippe M., Dorée M. Cyclin A potentiates maturation-promoting factor activation in the early Xenopus embryo via inhibition of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates cdc2. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1109–1120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Carr A. M., Nurse P. Fission yeast genes involved in coupling mitosis to completion of DNA replication. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2035–2046. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. B., Cross F. R. CLB5: a novel B cyclin from budding yeast with a role in S phase. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1695–1706. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. A. Isolation of cell size mutants of a fission yeast by a new selective method: characterization of mutants and implications for division control mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):746–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.746-754.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch I., Dahmann C., Surana U., Amon A., Nasmyth K., Goetsch L., Byers B., Futcher B. Characterization of four B-type cyclin genes of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):805–818. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Mendenhall M. D., Reed S. I. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae CKS1 gene, a homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe suc1+ gene, encodes a subunit of the Cdc28 protein kinase complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2034–2041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I., Hayles J., Nurse P. Cloning and sequencing of the cyclin-related cdc13+ gene and a cytological study of its role in fission yeast mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1988 Dec;91(Pt 4):587–595. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Culotti J., Pringle J. R., Reid B. J. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):46–51. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G. A. Sequence of the cell division gene CDC2 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; patterns of splicing and homology to protein kinases. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi M., Nagata A., Jinno S., Suto K., Okayama H. Wee1(+)-like gene in human cells. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):80–83. doi: 10.1038/353080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Adams A. E. Structural rearrangements of tubulin and actin during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):922–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Kraakman P., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The genes for yeast ribosomal proteins S24 and L46 are adjacent and divergently transcribed. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P. Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):75–85. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., McGowan C. H., Lenaers G., Jones R., Russell P. p80cdc25 mitotic inducer is the tyrosine phosphatase that activates p34cdc2 kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4301–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Klar A., Nurse P. Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:795–823. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):547–551. doi: 10.1038/256547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P. Regulatory genes controlling mitosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):627–637. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Lee M. S., Ogg S., Falk J. L., Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H. Cyclin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 in a wee1+ dependent manner. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1255–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Stotz A., Scherf C. DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:169–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reneke J. E., Blumer K. J., Courchesne W. E., Thorner J. The carboxy-terminal segment of the yeast alpha-factor receptor is a regulatory domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., Lew D. J., Henze M., Sugimoto K., Reed S. I. Cyclin-B homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function in S phase and in G2. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2021–2034. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley R., Hudson J., Young P. G. The wee1 protein kinase is required for radiation-induced mitotic delay. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):353–355. doi: 10.1038/356353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Moreno S., Reed S. I. Conservation of mitotic controls in fission and budding yeasts. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90967-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Hoyt M. A., Botstein D. Yeast mutants sensitive to antimicrotubule drugs define three genes that affect microtubule function. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):251–262. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Kahn R. A., Botstein D., Hoyt M. A. ADP ribosylation factor is an essential protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is encoded by two genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6690–6699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Kirschner M. W. Identification of cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation sites on nuclear lamin C. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90469-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]