Abstract
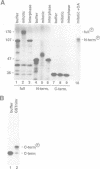
The Wee1 protein kinase negatively regulates the entry into mitosis by catalyzing the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of the Cdc2 protein. To examine the potential mechanisms for Wee1 regulation during the cell cycle, we have introduced a recombinant form of the fission yeast Wee1 protein kinase into Xenopus egg extracts. We find that the Wee1 protein undergoes dramatic changes in its phosphorylation state and kinase activity during the cell cycle. The Wee1 protein oscillates between an underphosphorylated 107 kDa form during interphase and a hyperphosphorylated 170 kDa version at mitosis. The mitosis-specific hyperphosphorylation of the Wee1 protein results in a substantial reduction in its activity as a Cdc2-specific tyrosine kinase. This phosphorylation occurs in the N-terminal region of the protein that lies outside the C-terminal catalytic domain, which was recently shown to be a substrate for the fission yeast Nim1 protein kinase. These experiments demonstrate the existence of a Wee1 regulatory system, consisting of both a Wee1-inhibitory kinase and a Wee1-stimulatory phosphatase, which controls the phosphorylation of the N-terminal region of the Wee1 protein. Moreover, these findings indicate that there are apparently two potential mechanisms for negative regulation of the Wee1 protein, one involving phosphorylation of its C-terminal domain by the Nim1 protein and the other involving phosphorylation of its N-terminal region by a different kinase.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. R., Tang Z., Dunphy W. G. Negative regulation of the wee1 protein kinase by direct action of the nim1/cdr1 mitotic inducer. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):919–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90580-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Activation of human cyclin-dependent kinases in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):571–582. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Garrigues A. M., Labbé J. C., Lorca T., Picard A., Philippe M., Dorée M. Cyclin A potentiates maturation-promoting factor activation in the early Xenopus embryo via inhibition of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates cdc2. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1109–1120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilotter H., Nurse P., Young P. G. Genetic and molecular analysis of cdr1/nim1 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics. 1991 Feb;127(2):309–318. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann I., Clarke P. R., Marcote M. J., Karsenti E., Draetta G. Phosphorylation and activation of human cdc25-C by cdc2--cyclin B and its involvement in the self-amplification of MPF at mitosis. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):53–63. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Walker D. H., Maller J. L. Periodic changes in phosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc25 phosphatase regulate its activity. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):927–939. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Ogg S., Xu M., Parker L. L., Donoghue D. J., Maller J. L., Piwnica-Worms H. cdc25+ encodes a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates p34cdc2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and proteolytic peptide mapping of proteins immobilized to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P. Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):75–85. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Dunphy W. G., Russell P., Gould S. J., Newport J. W. Cloning and characterization of Xenopus cdc2, a component of MPF. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:377–384. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., McGowan C. H., Lenaers G., Jones R., Russell P. p80cdc25 mitotic inducer is the tyrosine phosphatase that activates p34cdc2 kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4301–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):547–551. doi: 10.1038/256547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Lee M. S., Ogg S., Falk J. L., Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H. Cyclin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 in a wee1+ dependent manner. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1255–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Moreno S., Reed S. I. Conservation of mitotic controls in fission and budding yeasts. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90967-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]