Abstract
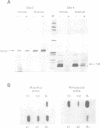
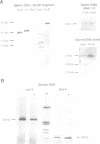
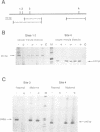
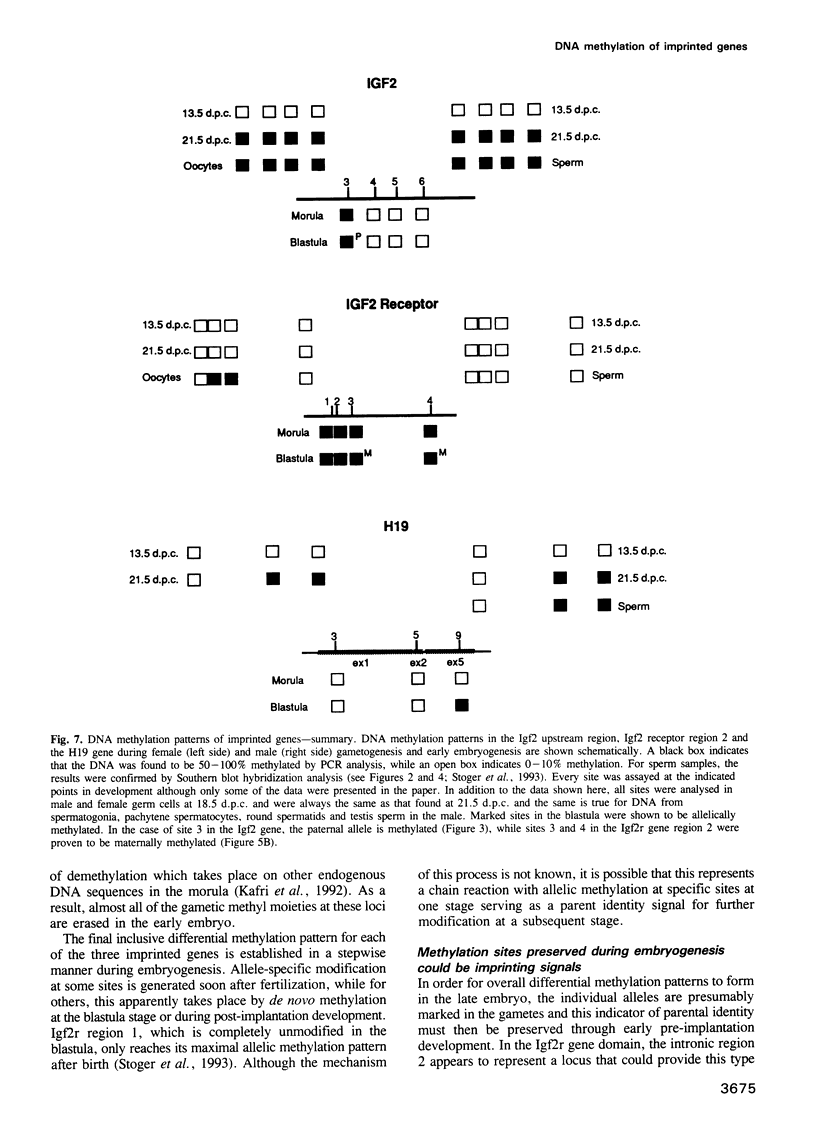
We have investigated the DNA methylation patterns in genomically imprinted genes of the mouse. Both Igf2 and H19 are associated with clear-cut regions of allele-specific paternal modification in late embryonic and adult tissues. By using a sensitive PCR assay, it was possible to follow the methylation state of individual HpaII sites in these genes through gametogenesis and embryogenesis. Most of these CpG moieties are not differentially modified in the mature gametes and also become totally demethylated in the early embryo in a manner similar to non-imprinted endogenous genes. Thus, the overall allele-specific methylation pattern at these sites must be established later during embryogenesis after the blastula stage. In contrast, sites in an Igf2r gene intron and one CpG residue in the Igf2 upstream region have allele-specific modification patterns which are established either in the gametes or shortly after fertilization and are preserved throughout pre-implantation embryogenesis. These studies suggest that only a few DNA modifications at selective positions in imprinted genes may be candidates for playing a role in the maintenance of parental identity during development.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariel M., McCarrey J., Cedar H. Methylation patterns of testis-specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2317–2321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Stöger R., Herrmann B. G., Saito K., Schweifer N. The mouse insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor is imprinted and closely linked to the Tme locus. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):84–87. doi: 10.1038/349084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Zemel S., Tilghman S. M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):153–155. doi: 10.1038/351153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Vogt T. F., Beier D. R., Leder P. Parental-specific methylation of an imprinted transgene is established during gametogenesis and progressively changes during embryogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90140-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich B., Robinson W. P., Knoblauch H., Buiting K., Schmidt K., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Horsthemke B. Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parent-of-origin specific DNA methylation in 15q11-13. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00220089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Migeon B. R. Sex difference in methylation of single-copy genes in human meiotic germ cells: implications for X chromosome inactivation, parental imprinting, and origin of CpG mutations. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 May;16(3):267–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01233363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Waters M. F., Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Glenn C. C., Avidano K. M., Nicholls R. D. A DNA methylation imprint, determined by the sex of the parent, distinguishes the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith A. C., Sasaki H., Cattanach B. M., Surani M. A. Parental-origin-specific epigenetic modification of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):751–755. doi: 10.1038/362751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D., Keshet I., Shani M., Levine A., Razin A., Cedar H. Demethylation of CpG islands in embryonic cells. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):239–241. doi: 10.1038/351239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M., Zuccotti M., Monk M. Methylation of CpG sites of two X-linked genes coincides with X-inactivation in the female mouse embryo but not in the germ line. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):161–166. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne C. M., McAleer M. A., Love J. M., Aitman T. J., Cornall R. J., Ghosh S., Knight A. M., Prins J. B., Todd J. A. Additional microsatellite markers for mouse genome mapping. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(4):273–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00352339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafri T., Ariel M., Brandeis M., Shemer R., Urven L., McCarrey J., Cedar H., Razin A. Developmental pattern of gene-specific DNA methylation in the mouse embryo and germ line. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):705–714. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Reed M. L., Ozçelik T., Francke U., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Maternal imprinting of the mouse Snrpn gene and conserved linkage homology with the human Prader-Willi syndrome region. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):259–264. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock L. F., Takagi N., Martin G. R. Methylation of the Hprt gene on the inactive X occurs after chromosome inactivation. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R., Hsu K. C., Eddy E. M., Klevecz R. R., Bolen J. L. Isolation of viable mouse primordial germ cells by antibody-directed flow sorting. J Exp Zool. 1987 Apr;242(1):107–111. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402420116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Boubelik M., Lehnert S. Temporal and regional changes in DNA methylation in the embryonic, extraembryonic and germ cell lineages during mouse embryo development. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):371–382. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajantila A., Budowle B., Ström M., Johnsson V., Lukka M., Peltonen L., Ehnholm C. PCR amplification of alleles at the DIS80 locus: comparison of a Finnish and a North American Caucasian population sample, and forensic casework evaluation. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):816–825. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Jones P. A., Chaillet J. R., Ferguson-Smith A. C., Barton S. C., Reik W., Surani M. A. Parental imprinting: potentially active chromatin of the repressed maternal allele of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II (Igf2) gene. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1843–1856. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer R., Kafri T., O'Connell A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L., Razin A. Methylation changes in the apolipoprotein AI gene during embryonic development of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11300–11304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöger R., Kubicka P., Liu C. G., Kafri T., Razin A., Cedar H., Barlow D. P. Maternal-specific methylation of the imprinted mouse Igf2r locus identifies the expressed locus as carrying the imprinting signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90160-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surani M. A., Reik W., Allen N. D. Transgenes as molecular probes for genomic imprinting. Trends Genet. 1988 Mar;4(3):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Yamazaki K., Suzuki R., Fujimoto H., Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Higashinakagawa T. Parental methylation patterns of a transgenic locus in adult somatic tissues are imprinted during gametogenesis. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):831–839. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel S., Bartolomei M. S., Tilghman S. M. Physical linkage of two mammalian imprinted genes, H19 and insulin-like growth factor 2. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):61–65. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]