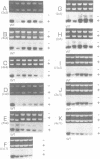
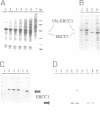
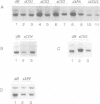
Abstract
Nucleotide excision repair (NER), one of the major cellular DNA repair systems, removes a wide range of lesions in a multi-enzyme reaction. In man, a NER defect due to a mutation in one of at least 11 distinct genes, can give rise to the inherited repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum (XP), Cockayne's syndrome or PIBIDS, a photosensitive form of the brittle hair disease trichothiodystrophy. Laboratory-induced NER-deficient mutants of cultured rodent cells have been classified into 11 complementation groups (CGs). Some of these have been shown to correspond with human disorders. In cell-free extracts prepared from rodent CGs 1-5 and 11, but not in a mutant from CG6, we find an impaired repair of damage induced in plasmids by UV light and N-acetoxy-acetylaminofluorene. Complementation analysis in vitro of rodent CGs is accomplished by pairwise mixing of mutant extracts. The results show that mutants from groups 2, 3, 5 and XP-A can complement all other CGs tested. However, selective non-complementation in vitro was observed in mutual mixtures of groups 1, 4, 11 and XP-F, suggesting that the complementing activities involved somehow affect each other. Depletion of wild-type human extracts from ERCC1 protein using specific anti-ERCC1 antibodies concomitantly removed the correcting activities for groups 4, 11 and XP-F, but not those for the other CGs. Furthermore, we find that 33 kDa ERCC1 protein sediments as a high mol. wt species of approximately 120 kDa in a native glycerol gradient.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

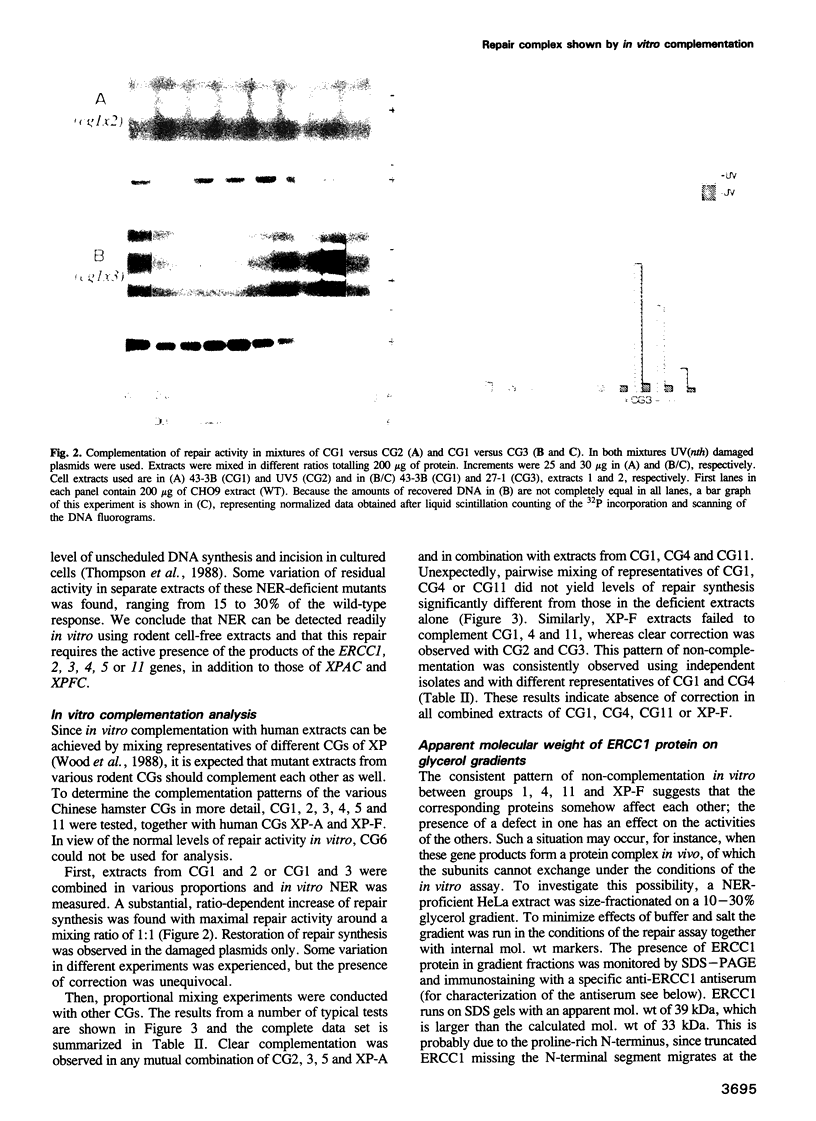





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly V., Sommers C. H., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Specific complex formation between proteins encoded by the yeast DNA repair and recombination genes RAD1 and RAD10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8273–8277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell L., Cooper A. J., Friedberg E. C. Stable and specific association between the yeast recombination and DNA repair proteins RAD1 and RAD10 in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3041–3049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggerstaff M., Robins P., Coverley D., Wood R. D. Effect of exogenous DNA fragments on human cell extract-mediated DNA repair synthesis. Mutat Res. 1991 May;254(3):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggerstaff M., Wood R. D. Requirement for ERCC-1 and ERCC-3 gene products in DNA excision repair in vitro. Complementation using rodent and human cell extracts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6879–6885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Hanawalt P. C. Enhanced repair of pyrimidine dimers in coding and non-coding genomic sequences in CHO cells expressing a prokaryotic DNA repair gene. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Sep;8(9):1333–1336. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.9.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D. B., Cleaver J. E., Glaser D. A. Large-scale isolation of UV-sensitive clones of CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 May;6(3):407–418. doi: 10.1007/BF01542792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D., Greiner C., Lewis K., Ford R., Adair G., Thompson L. Summary of complementation groups of UV-sensitive CHO cell mutants isolated by large-scale screening. Mutagenesis. 1989 Sep;4(5):349–354. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.5.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R. Mutant rodent cell lines sensitive to ultraviolet light, ionizing radiation and cross-linking agents: a comprehensive survey of genetic and biochemical characteristics. Mutat Res. 1993 Jan;293(2):99–118. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(93)90062-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. A role for the human single-stranded DNA binding protein HSSB/RPA in an early stage of nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3873–3880. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. Requirement for the replication protein SSB in human DNA excision repair. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):538–541. doi: 10.1038/349538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejter W. L., McDaniel L. D., Johns D., Friedberg E. C., Schultz R. A. Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and gene transfer: involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne's syndrome, helicases, and DNA repair: what's the relationship? Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):887–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90384-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Yeung A. T. The UvrABC endonuclease of Escherichia coli. Photochem Photobiol. 1990 Jun;51(6):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F. SSL2, a suppressor of a stem-loop mutation in the HIS4 leader encodes the yeast homolog of human ERCC-3. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90621-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J., Keyse S. M., Lindahl T., Wood R. D. DNA excision repair in cell extracts from human cell lines exhibiting hypersensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 1;51(13):3384–3390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Kahn R., Wood R. D. Localization of DNA repair synthesis by human cell extracts to a short region at the site of a lesion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21788–21792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata H., Numata M., Tohda H., Yasui A., Oikawa A. Isolation of two chloroethylnitrosourea-sensitive Chinese hamster cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular genetics of eukaryotic DNA excision repair. Cancer Cells. 1990 Oct;2(10):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. How relevant is the Escherichia coli UvrABC model for excision repair in eukaryotes? J Cell Sci. 1991 Dec;100(Pt 4):687–691. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.4.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. Nucleotide excision repair. II: From yeast to mammals. Trends Genet. 1993 Jun;9(6):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90121-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegent J. E., Jasen in de Wal N., Baan R. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Van der Ploeg M. 2-Acetylaminofluorene-modified probes for the indirect hybridocytochemical detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Zeeland A. A., Backendorf C. M., Bridges B. A., Collins A., Fuchs R. P., Margison G. P., Montesano R., Moustacchi E. Workshop on DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;273(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R. Three complementation groups in Cockayne syndrome. Mutat Res. 1982 Dec;106(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lommel L., Hanawalt P. C. The genetic defect in the Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant UV61 permits moderate selective repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in an expressed gene. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep;255(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90052-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance M. A., Berry S. A. Cockayne syndrome: review of 140 cases. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jan 1;42(1):68–84. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. F., Schmidt W. J., Chaney S. G., Sancar A. Limitations of the in vitro repair synthesis assay for probing the role of DNA repair in platinum resistance. Chem Biol Interact. 1992 Feb;81(3):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(92)90079-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numata M., Hata H., Shiomi T., Matsunaga T., Mori T., Nikaido O., Yasui A., Oikawa A. Identification of cellular defect in UVS1, a UV-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary mutant cell line. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):495–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan A., Wood R. D. Identical defects in DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group G and rodent ERCC group 5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):185–188. doi: 10.1038/363185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Guzder S. N., Koken M. H., Jaspers-Dekker I., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. RAD25 (SSL2), the yeast homolog of the human xeroderma pigmentosum group B DNA repair gene, is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11416–11420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riboni R., Botta E., Stefanini M., Numata M., Yasui A. Identification of the eleventh complementation group of UV-sensitive excision repair-defective rodent mutants. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 1;52(23):6690–6691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins P., Jones C. J., Biggerstaff M., Lindahl T., Wood R. D. Complementation of DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group A cell extracts by a protein with affinity for damaged DNA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3913–3921. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Nouspikel T., Corlet J., Ucla C., Bairoch A., Clarkson S. G. Complementation of the DNA repair defect in xeroderma pigmentosum group G cells by a human cDNA related to yeast RAD2. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):182–185. doi: 10.1038/363182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Prakash S. RAD1, an excision repair gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is also involved in recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3619–3626. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Prakash S. RAD10, an excision repair gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is involved in the RAD1 pathway of mitotic recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2485–2491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Structure and function of the (A)BC excinuclease of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90005-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji K. K., Kenny M. K., Wood R. D. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for DNA excision repair. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90416-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghat-Ullah, Sancar A. Substrate overlap and functional competition between human nucleotide excision repair and Escherichia coli photolyase and (a)BC excision nuclease. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5711–5718. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghatullah, Husain I., Carlton W., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision repair in vitro: repair of pyrimidine dimers, psoralen and cisplatin adducts by HeLa cell-free extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4471–4484. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Collins A. R., Riboni R., Klaude M., Botta E., Mitchell D. L., Nuzzo F. Novel Chinese hamster ultraviolet-sensitive mutants for excision repair form complementation groups 9 and 10. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):3965–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Giliani S., Nardo T., Marinoni S., Nazzaro V., Rizzo R., Trevisan G. DNA repair investigations in nine Italian patients affected by trichothiodystrophy. Mutat Res. 1992 Mar;273(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90073-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Miura N., Satokata I., Miyamoto I., Yoshida M. C., Satoh Y., Kondo S., Yasui A., Okayama H., Okada Y. Analysis of a human DNA excision repair gene involved in group A xeroderma pigmentosum and containing a zinc-finger domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):73–76. doi: 10.1038/348073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Satokata I., Ogita Z., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a mouse DNA repair gene that complements the defect of group-A xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mitchell D. L., Regan J. D., Bouffler S. D., Stewart S. A., Carrier W. L., Nairn R. S., Johnson R. T. CHO mutant UV61 removes (6-4) photoproducts but not cyclobutane dimers. Mutagenesis. 1989 Mar;4(2):140–146. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Shiomi T., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A. An eighth complementation group of rodent cells hypersensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):605–612. doi: 10.1007/BF01535314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Varshavsky A. Cloning and functional analysis of the ubiquitin-specific protease gene UBP1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12021–12028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., Mullenders L. H., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mayne L. V. The genetic defect in Cockayne syndrome is associated with a defect in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in transcriptionally active DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4707–4711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Stefanini M., Giliani S., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group H falls into complementation group D. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep;255(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. ERCC2: cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a human nucleotide excision repair gene with high homology to yeast RAD3. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1437–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Burki H. J. Repair capability and the cellular age response for killing and mutation induction after UV. Mutat Res. 1982 Aug;95(2-3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Robins P., Lindahl T. Complementation of the xeroderma pigmentosum DNA repair defect in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Mitchell D. L., Venema J., van Hoffen A., van Zeeland A. A., Mullenders L. H., de Wit J., Simons J. W. DNA repair characteristics and mutability of the UV-sensitive V79 Chinese hamster cell mutant V-B11 (complementation group 7). Mutagenesis. 1991 May;6(3):179–183. doi: 10.1093/mutage/6.3.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Janssen J. H., de Wit J., Hoeijmakers J. H., Thompson L. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. Transfection of the cloned human excision repair gene ERCC-1 to UV-sensitive CHO mutants only corrects the repair defect in complementation group-2 mutants. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Vredeveldt G., Mayne L. V., Odijk H., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. The cloned human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-1 fails to correct xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups A through I. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;217(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]