Abstract
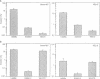
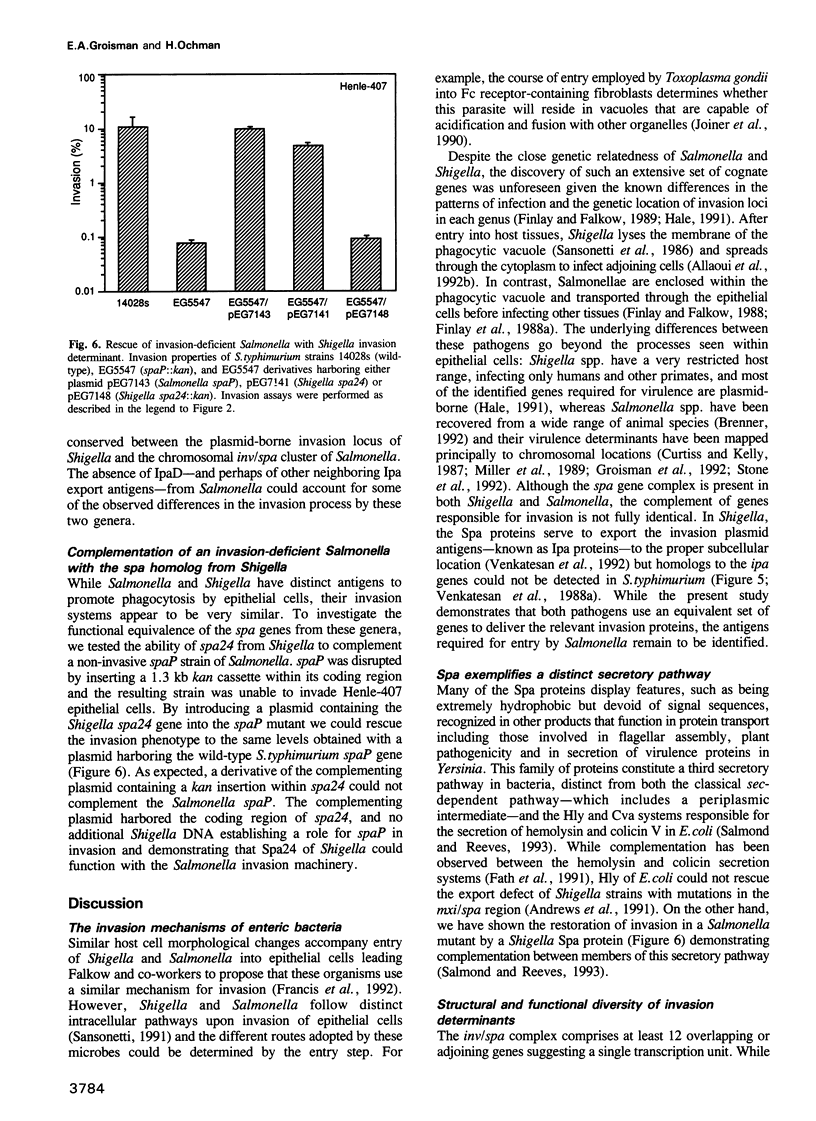
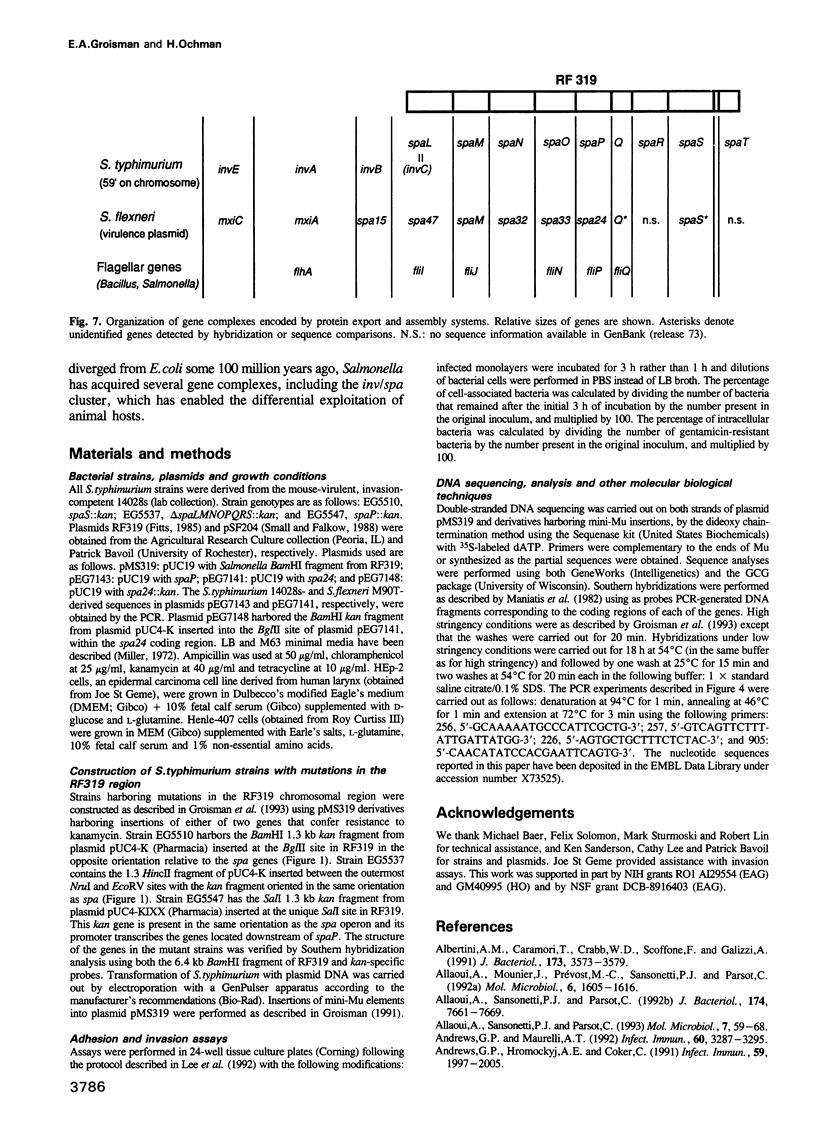
The enteric pathogens Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri differ in most virulence attributes including infectivity, pathology and host range. We have identified a new assemblage of genes responsible for invasion properties of Salmonella which is remarkably similar in order, arrangement and sequence to the gene cluster controlling the presentation of surface antigens (spa) on the virulence plasmid of Shigella. In Salmonella, this chromosomally encoded complex consists of over 12 genes, mutations in which abolish bacterial entry into epithelial cells. Although these genera use distinct invasion antigens, a non-invasive spa mutant of Salmonella could be rescued by the corresponding Shigella homolog. While spa promotes equivalent functions in Shigella and Salmonella, this constellation of genes has been acquired independently by each genus and displays motifs used by diverse antigen export systems including those required for flagellar assembly and protein secretion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Caramori T., Crabb W. D., Scoffone F., Galizzi A. The flaA locus of Bacillus subtilis is part of a large operon coding for flagellar structures, motility functions, and an ATPase-like polypeptide. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3573–3579. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3573-3579.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaoui A., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. icsB: a Shigella flexneri virulence gene necessary for the lysis of protrusions during intercellular spread. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1605–1616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiJ, a lipoprotein involved in secretion of Shigella Ipa invasins, is homologous to YscJ, a secretion factor of the Yersinia Yop proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7661–7669. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7661-7669.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Hromockyj A. E., Coker C., Maurelli A. T. Two novel virulence loci, mxiA and mxiB, in Shigella flexneri 2a facilitate excretion of invasion plasmid antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1997–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1997-2005.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Maurelli A. T. mxiA of Shigella flexneri 2a, which facilitates export of invasion plasmid antigens, encodes a homolog of the low-calcium-response protein, LcrD, of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3287–3295. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3287-3295.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts J., Finlay B. B. Identification of Salmonella typhimurium invasiveness loci. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Aug;38(8):852–857. doi: 10.1139/m92-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff D. S., Ordal G. W. Identification and characterization of FliY, a novel component of the Bacillus subtilis flagellar switch complex. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2715–2723. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff D. S., Weinreich M. D., Ordal G. W. Nucleotide sequences of Bacillus subtilis flagellar biosynthetic genes fliP and fliQ and identification of a novel flagellar gene, fliZ. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4017–4025. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4017-4025.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst R. K., Dombroski D. M., Merrick J. M. Anaerobiosis, type 1 fimbriae, and growth phase are factors that affect invasion of HEp-2 cells by Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2014–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2014-2016.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90003-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath M. J., Skvirsky R. C., Kolter R. Functional complementation between bacterial MDR-like export systems: colicin V, alpha-hemolysin, and Erwinia protease. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7549–7556. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7549-7556.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella as an intracellular parasite. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1833–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Starnbach M. N., Falkow S. Morphological and cytoskeletal changes in epithelial cells occur immediately upon interaction with Salmonella typhimurium grown under low-oxygen conditions. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3077–3087. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Distribution of the invA, -B, -C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurium among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2901-2908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Ginocchio C., Costeas P. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella invasion gene invA: homology of InvA to members of a new protein family. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4338–4349. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4338-4349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginocchio C., Pace J., Galán J. E. Identification and molecular characterization of a Salmonella typhimurium gene involved in triggering the internalization of salmonellae into cultured epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. S., Fitch W. M. Evolution of antibiotic resistance genes: the DNA sequence of a kanamycin resistance gene from Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):57–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A. In vivo genetic engineering with bacteriophage Mu. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:180–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04010-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Parra-Lopez C., Salcedo M., Lipps C. J., Heffron F. Resistance to host antimicrobial peptides is necessary for Salmonella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11939–11943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Sturmoski M. A., Solomon F. R., Lin R., Ochman H. Molecular, functional, and evolutionary analysis of sequences specific to Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):167–170. doi: 10.1038/335167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang I., Lim S. M., Shaw P. D. Cloning and characterization of pathogenicity genes from Xanthomonas campestris pv. glycines. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1923–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1923-1931.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson S., Bergman T., Vanooteghem J. C., Cornelis G., Wolf-Watz H. YopB and YopD constitute a novel class of Yersinia Yop proteins. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.71-80.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irikura V. M., Kihara M., Yamaguchi S., Sockett H., Macnab R. M. Salmonella typhimurium fliG and fliN mutations causing defects in assembly, rotation, and switching of the flagellar motor. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):802–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.802-810.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Determinants for thermoinducible cell binding and plasmid-encoded cellular penetration detected in the absence of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1998–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1998-2005.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Fuhrman S. A., Miettinen H. M., Kasper L. H., Mellman I. Toxoplasma gondii: fusion competence of parasitophorous vacuoles in Fc receptor-transfected fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Lee C. A., Falkow S. Invasion by Salmonella typhimurium is affected by the direction of flagellar rotation. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2475-2480.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoramian-Falsafi T., Harayama S., Kutsukake K., Pechère J. C. Effect of motility and chemotaxis on the invasion of Salmonella typhimurium into HeLa cells. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jul;9(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90039-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibak H., Taiz L., Starke T., Bernasconi P., Gogarten J. P. Evolution of structure and function of V-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Aug;24(4):415–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00762534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M. Mechanism and evolution of the uncoupling protein of brown adipose tissue. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90194-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Falkow S. The ability of Salmonella to enter mammalian cells is affected by bacterial growth state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jones B. D., Falkow S. Identification of a Salmonella typhimurium invasion locus by selection for hyperinvasive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Ezaki T., Miura H., Matsui K., Yabuuchi E. Intact motility as a Salmonella typhi invasion-related factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1967–1973. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1967-1973.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Parkinson J. S. Genetic analysis of the bacterial flagellum. Trends Genet. 1991 Jun;7(6):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90436-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick B. A., Stocker B. A., Laux D. C., Cohen P. S. Roles of motility, chemotaxis, and penetration through and growth in intestinal mucus in the ability of an avirulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium to colonize the large intestine of streptomycin-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2209–2217. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2209-2217.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves P. Evolution of Salmonella O antigen variation by interspecific gene transfer on a large scale. Trends Genet. 1993 Jan;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90067-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond G. P., Reeves P. J. Membrane traffic wardens and protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J. Genetic and molecular basis of epithelial cell invasion by Shigella species. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S285–S292. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Shope S. R. Anaerobic growth of Salmonella typhimurium results in increased uptake by Henle 407 epithelial and mouse peritoneal cells in vitro and repression of a major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):437–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.437-440.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. L., Falkow S. Identification of regions on a 230-kilobase plasmid from enteroinvasive Escherichia coli that are required for entry into HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):225–229. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.225-229.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. L., Isberg R. R., Falkow S. Comparison of the ability of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter and replicate within HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1674–1679. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1674-1679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. H., Selander R. K. Molecular genetic basis for complex flagellar antigen expression in a triphasic serovar of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):956–960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone B. J., Garcia C. M., Badger J. L., Hassett T., Smith R. I., Miller V. L. Identification of novel loci affecting entry of Salmonella enteritidis into eukaryotic cells. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3945–3952. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3945-3952.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Kopecko D. J. Characterization of invasion plasmid antigen genes (ipaBCD) from Shigella flexneri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9317–9321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Surface presentation of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens requires the products of the spa locus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1990–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1990-2001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Buysse J. M., Vandendries E., Kopecko D. J. Development and testing of invasion-associated DNA probes for detection of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.261-266.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler A. P., Homma M., Irikura V. M., Macnab R. M. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in flagellar filament regrowth and sequence similarity of FliI to F0F1, vacuolar, and archaebacterial ATPase subunits. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3564-3572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]