Abstract
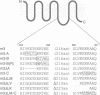
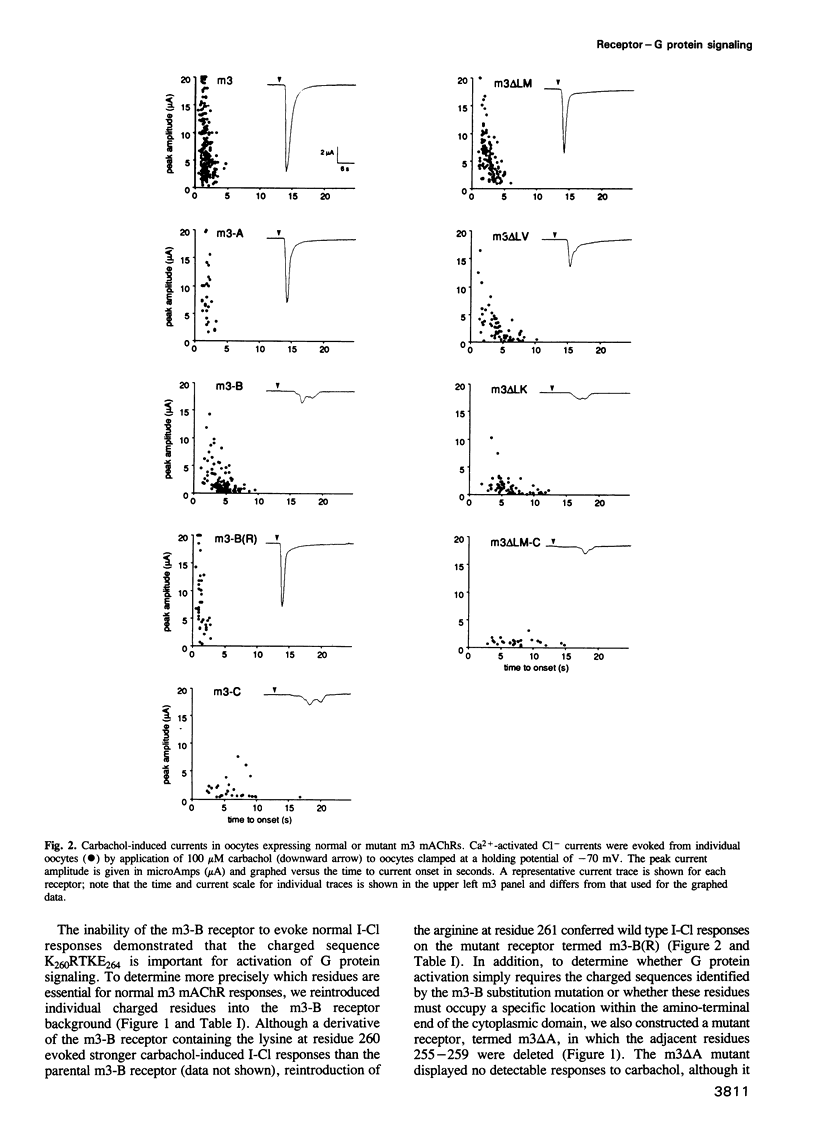
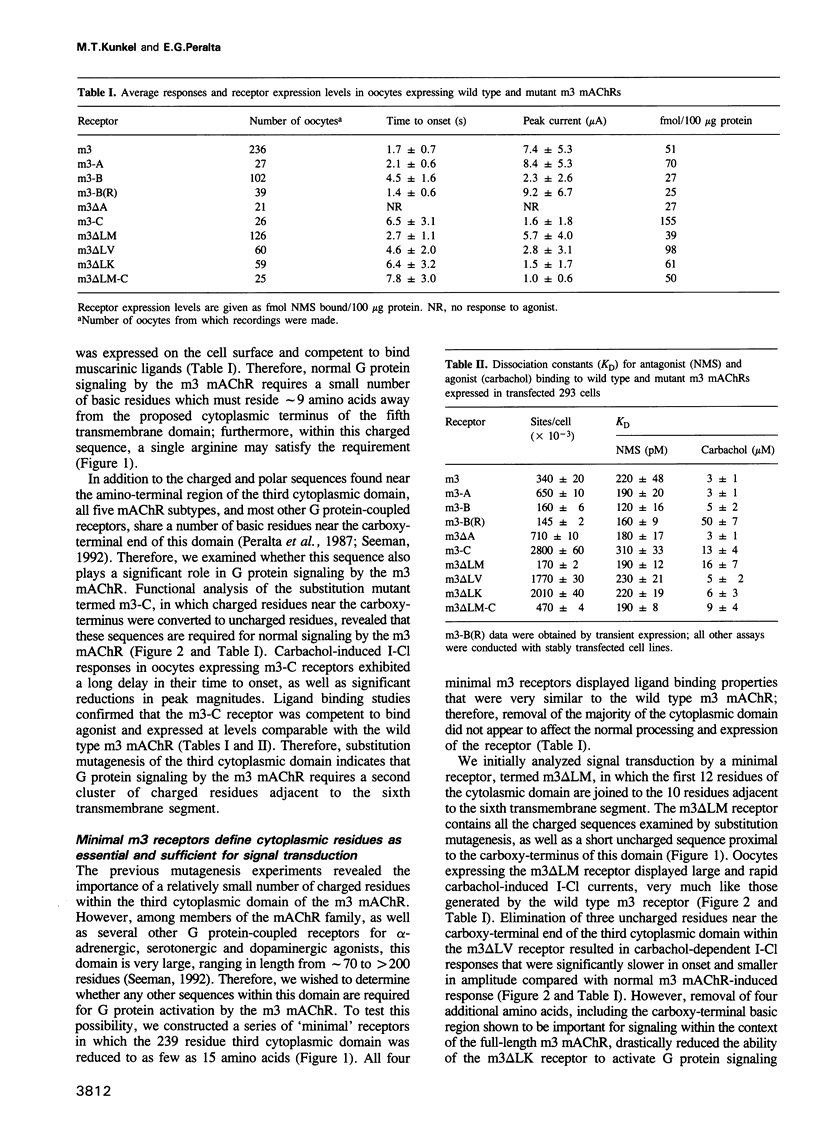
The five muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes, termed m1-m5, transduce agonist signals across the plasma membrane by activating guanine nucleotide binding (G) proteins. The large cytoplasmic domain joining the fifth and sixth transmembrane segments of mAChRs plays a critical role in controlling the specificity of G protein coupling. In this study, we determined which sequences within this domain are required for activation of signaling by the m3 mAChR. By measuring the ability of normal and mutant m3 mAChRs to couple to the G protein pathway leading to activation of phospholipase C and Ca(2+)-dependent chloride currents in RNA-injected Xenopus oocytes, we found that two clusters of charged residues near the fifth and sixth transmembrane segments were required for normal signaling; furthermore, the position of these sequences was critical for their function. Finally, analysis of deletion mutant m3 mAChRs confirmed the importance of these sequences; receptors containing as few as 22 out of 239 amino acids of the cytoplasmic domain were fully active in signaling if they included the critical charged residues. Sequence comparisons suggest that similar charged sequences may be required for signal transduction by many G protein-coupled receptors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Exum S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regions of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor involved in coupling to phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and enhanced sensitivity of biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2896–2900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman H. M., Neubig R. R. Two peptides from the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor alter receptor G protein coupling by distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11025–11029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell'Acqua M. L., Carroll R. C., Peralta E. G. Transfected m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors couple to G alpha i2 and G alpha i3 in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Activation and desensitization of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5676–5685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England B. P., Ackerman M. S., Barrett R. W. A chimeric D2 dopamine/m1 muscarinic receptor with D2 binding specificity mobilizes intracellular calcium in response to dopamine. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto I., Ikenaka K., Kondo T., Aimoto S., Kuno M., Mikoshiba K. Mast cell degranulating (MCD) peptide and its optical isomer activate GTP binding protein in rat mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80005-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S., Smrcka A., Nowak L., Wu D. G., Simon M., Sternweis P. C. Antibodies to the alpha q subfamily of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunits attenuate activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by hormones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20519–20524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Burnier J., Ross E. M. Regulation of Gi and Go by mastoparan, related amphiphilic peptides, and hydrophobic amines. Mechanism and structural determinants of activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14176–14186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Uzu S., Nakajima T., Ross E. M. Mastoparan, a peptide toxin from wasp venom, mimics receptors by activating GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins). J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6491–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Wakamatsu K., Takemitsu M., Fujino M., Nakajima T., Miyazawa T. Conformational change of mastoparan from wasp venom on binding with phospholipid membrane. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelsberg M. A., Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Constitutive activation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor by all amino acid substitutions at a single site. Evidence for a region which constrains receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1430–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Bujo H., Akiba I., Nakai J., Mishina M., Numa S. Location of a region of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor involved in selective effector coupling. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Girard S., Clapham D., Peralta E. Subcellular patterns of calcium release determined by G protein-specific residues of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):505–508. doi: 10.1038/350505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Hellmiss R., Duerson K., Ennulat D., David N., Clapham D., Peralta E. Distinct sequence elements control the specificity of G protein activation by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4381–4390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Nishimoto I. Detection of G protein-activator regions in M4 subtype muscarinic, cholinergic, and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors based upon characteristics in primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8342–8346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppi C., Wagner T., Crisari A., Camerini B., Tocchini Valentini G. P. Attenuation of GTPase activity of recombinant G(o) alpha by peptides representing sequence permutations of mastoparan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8268–8272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Differential regulation of PI hydrolysis and adenylyl cyclase by muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):434–437. doi: 10.1038/334434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Smith D. H., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Distinct primary structures, ligand-binding properties and tissue-specific expression of four human muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3923–3929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Wallner E., Czernilofsky A. P., Freissmuth M. Amphipathic alpha-helical structure does not predict the ability of receptor-derived synthetic peptides to interact with guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4637–4642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wess J., Brann M. R., Bonner T. I. Identification of a small intracellular region of the muscarinic m3 receptor as a determinant of selective coupling to PI turnover. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81633-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. K., Parker E. M., Ross E. M. Chimeric muscarinic cholinergic: beta-adrenergic receptors that activate Gs in response to muscarinic agonists. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6219–6224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]