Abstract
Titin is a giant structural protein of striated muscle (M(r) approximately 3000 kDa) and single molecules span sarcomeres from the M- to Z-lines. We have cloned and sequenced the C-terminal region of the titin molecule, which is an integral part of M-lines and forms intimate contacts with the 165 and 190 kDa M-line proteins. In contrast to the regular motif patterns of the A-band portion of titin, the 5.7 kb of titin sequences from the M-line show a complex structure of immunoglobulin-C2 repeats, separated by unique interdomain insertion sequences. As a striking feature, one interdomain insertion comprises four KSP repeats analogous to the multi-phosphorylation repeats of neurofilament subunits H and M. In vitro phosphorylation assays with expressed titin KSP sequences detect high levels of titin KSP phosphorylating kinases in developing but not in differentiated muscle. Since this kinase activity can be depleted from myocyte extracts by antibodies against cdc2 kinase and p13suc1 beads, the titin KSP kinase is structurally related to cdc2 kinase. We suggest that titin C-terminal phosphorylation by SP-specific kinases is regulated during differentiation, and that this may control the assembly of M-line proteins into regular structures during myogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benian G. M., Kiff J. E., Neckelmann N., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):45–50. doi: 10.1038/342045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Nave R., Osborn M., Weber K. Repetitive titin epitopes with a 42 nm spacing coincide in relative position with known A band striations also identified by major myosin-associated proteins. An immunoelectron-microscopical study on myofibrils. J Cell Sci. 1989 Sep;94(Pt 1):119–125. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Weber K. Myogenesis in the mouse embryo: differential onset of expression of myogenic proteins and the involvement of titin in myofibril assembly. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel S. E., Greaser M. L., Schultz E., Wang S. M., Bulinski J. C., Lin J. J., Lessard J. L. Chicken cardiac myofibrillogenesis studied with antibodies specific for titin and the muscle and nonmuscle isoforms of actin and tropomyosin. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Mar;263(3):419–430. doi: 10.1007/BF00327276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel S. E., Wang S. M., Greaser M. L., Schultz E., Bulinski J. C., Lessard J. L. Skeletal muscle myofibrillogenesis as revealed with a monoclonal antibody to titin in combination with detection of the alpha- and gamma-isoforms of actin. Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;132(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Kusubata M., Okumura E., Kishimoto T. Phosphorylation of neurofilament H subunit at the tail domain by CDC2 kinase dissociates the association to microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21798–21803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Ito M., Hartshorne D. J., Rayment I. X-ray structure determination of telokin, the C-terminal domain of myosin light chain kinase, at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):840–851. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90226-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson L., Frey T., Zeeberg B., Dalldorf F., Caplow M. Inhibition of microtubule assembly by phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2472–2479. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Noble M. D., Ataliotis P., Tanaka Y., Yannoutsos N., Larsen L., Kioussis D. Direct derivation of conditionally immortal cell lines from an H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Wang K. Giant polypeptides of skeletal muscle titin: sedimentation equilibrium in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90750-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Barlow D. P., Gautel M., Gibson T., Holt J., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Leonard K., Wardale J., Whiting A. A regular pattern of two types of 100-residue motif in the sequence of titin. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):273–276. doi: 10.1038/345273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Gautel M., Lakey A., Trinick J. Towards a molecular understanding of titin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1711–1716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
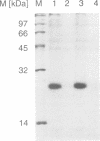
- Le Grice S. F., Grüninger-Leitch F. Rapid purification of homodimer and heterodimer HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by metal chelate affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
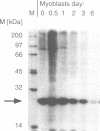
- Lees J. F., Shneidman P. S., Skuntz S. F., Carden M. J., Lazzarini R. A. The structure and organization of the human heavy neurofilament subunit (NF-H) and the gene encoding it. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1947–1955. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu P. W., Soong C. J., Tao M. Phosphorylation of ankyrin decreases its affinity for spectrin tetramer. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14958–14964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroto M., Vinós J., Marco R., Cervera M. Autophosphorylating protein kinase activity in titin-like arthropod projectin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90994-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Kimura S., Ohashi K., Kuwano Y. Connectin, an elastic protein of muscle. Identification of "titin" with connectin. J Biochem. 1981 Mar;89(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. W., Lazzarini R. A., Lee V. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Nelson D. L. The human mid-size neurofilament subunit: a repeated protein sequence and the relationship of its gene to the intermediate filament gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1617–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave R., Fürst D. O., Weber K. Visualization of the polarity of isolated titin molecules: a single globular head on a long thin rod as the M band anchoring domain? J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2177–2187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Kuwaki T., Sakai H. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) and pH of the medium control interaction between MAPs and actin filaments. J Biochem. 1981 Aug;90(2):575–578. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Lewis S. E. Differential turnover of phosphate groups on neurofilament subunits in mammalian neurons in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16298–16301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Sihag R. K. Neurofilament phosphorylation: a new look at regulation and function. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Nov;14(11):501–506. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90062-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi J., Yanagisawa M., Imamura M., Kasuya Y., Sakurai T., Tanaka T., Masaki T. Complete primary structure and tissue expression of chicken pectoralis M-protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20302–20310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Heitlinger E., Häner M., Aebi U., Nigg E. A. Disassembly of in vitro formed lamin head-to-tail polymers by CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1535–1544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U. B., Basset P., Daniel J. Y. Direct amplification of cDNA inserts from lambda libraries using the cloning-adapter as primer for PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3308–3308. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Izumo S. Mechanical stretch rapidly activates multiple signal transduction pathways in cardiac myocytes: potential involvement of an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1681–1692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden S. C., Pollard T. D. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins regulates their interaction with actin filaments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7064–7071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea T. B., Sihag R. K., Nixon R. A. Dynamics of phosphorylation and assembly of the high molecular weight neurofilament subunit in NB2a/d1 neuroblastoma. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1784–1792. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville L. L., Wang K. In vivo phosphorylation of titin and nebulin in frog skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):986–992. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soteriou A., Gamage M., Trinick J. A survey of interactions made by the giant protein titin. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jan;104(Pt 1):119–123. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano-Ohmuro H., Nakauchi Y., Kimura S., Maruyama K. Autophosphorylation of beta-connectin (titin 2) in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91604-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Maher P. A. Immunocytochemical studies of cardiac myofibrillogenesis in early chick embryos. I. Presence of immunofluorescent titin spots in premyofibril stages. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2781–2793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J. Elastic filaments and giant proteins in muscle. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90173-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. M., Greaser M. L., Schultz E., Bulinski J. C., Lin J. J., Lessard J. L. Studies on cardiac myofibrillogenesis with antibodies to titin, actin, tropomyosin, and myosin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1075–1083. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]