Abstract
The synthesis of novel oxetanyl peptides, where the amide bond is replaced by a non-hydrolyzable oxetanylamine fragment, is reported. This new class of pseudo-dipeptides with the same H-bond donor/acceptor pattern found in proteins expands the repertoire of peptidomimetics.
With over 50 marketed drugs and an estimated $13 billion market in 2010, peptide drugs are important players in pharmaceuticals.1 This is however, a relatively small share of the total pharmaceuticals market given the broad range of biological activities displayed by this class of compounds. The discrepancy arises from some inherent limitations of peptides in the drug development process,1a,2 including short lifetimes in the stomach, intestine, and plasma, which often result in less than optimal pharmacokinetic profiles. However, the high specificity and potency as well as low toxicity of certain peptides along with advances in drug delivery have led to a renaissance.3
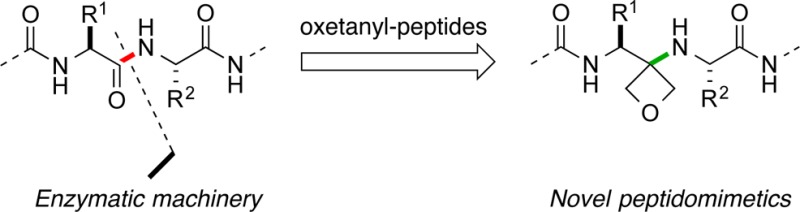
Thus, there are currently dozens of peptide drugs in clinical development in a broad range of therapeutic areas.4 As part of our ongoing interest in new building blocks for medicinal chemistry, we report herein a novel approach based upon the use of a 3-amino oxetane as a surrogate for a peptide bond (Figure 1a). The strategy aims at expanding the scope of peptidomimetics that display H-bond donor/acceptor patterns analogous to that of the parent amide bonds, without attendant susceptibility to enzymatic amide bond cleavage at the site of substitution (Figure 1b).
Figure 1.
Analysis and research plan.
Peptidomimicry has long sought to provide alternative structural building blocks for fragments or the whole of biologically relevant peptides in an effort to generate compounds with improved pharmacokinetic profiles. A number of creative approaches have been demonstrated including β-peptides and δ-peptide oligomers, peptoids, alkene isosteres, and oligo o-substituted aromatics,5 and expanding the portfolio of peptidomimetics is of continued interest in drug discovery.
In previous work we have suggested that 3,3-disubstituted oxetanes can be perceived as useful surrogates for carbonyl groups in small heterocycles, leading to analogs of lactams and ketones with improved physico-chemical properties.6 Because a primary pathway for degradation of peptides is amide bond hydrolysis, we reasoned that replacement of the amide carbonyl by an oxetane would result in a fragment with increased stability while at the same time give access to novel regions of chemical space. We aimed at developing a strategy for the use of oxetanyl peptides compatible with modern practices in peptide synthesis.7 Two strategies were considered for their preparation, which differ in the tactics employed to introduce the amino oxetane residues (Figure 1c).
The first approach (A) would utilize monomeric oxetanyl building blocks while the second (B) would rely on the use of prefabricated dipeptides with embedded oxetanes. Although the former parallels standard peptide synthesis methods, it would require optimization of the coupling conditions for each fragment. In approach B the coupling reactions leading to chain extension involve amide bond formation. In either case, the synthetic challenges include the identification of suitable reactions for the preparation of the building blocks and compatible coupling conditions for their incorporation into larger peptides without suffering unwanted side reactions.
In the initial design of the approach toward surrogate dipeptides (approach B in Figure 1c), we favored the 1,4-addition of amino acids to oxetanyl-substituted nitroolefins. Subsequent NO2-group reduction would lead to terminal primary amines. We first examined the synthesis of dimers (H2NAA1ox-AA2CO2H) incorporating the glycine surrogate in position AA1ox (Table 1). In practice, simple mixing of 1 and H-Ala-OnPr in DMSO at 23 °C resulted in clean 1,4-addition to afford 3 in 74% yield (entry 2). This reaction proved successful with other α amino esters, with products resulting from the addition of glycine, l-leucine, l-valine, l-proline, and l-phenylalanine formed in 52%–95% yield. The mild reaction conditions were compatible with many of the standard side-chain protecting groups used in modern solid-phase peptide syntheses. The reaction of tBu-protected l-tyrosine, l-serine, l-glutamic acid, and trityl protected l-asparagine with 1 afforded nitro alkanes 7, 8, 9, and 10 in 71%–87% yield. N-Trityl protected l-histidine and Boc-l-tryptophan furnished products 13 and 14 in 60% and 76% yield, respectively. N-Boc-protected l-lysine gave the nitroalkane 11 in 66% yield, and the l-methionine-containing nitro alkane 12 was formed in 98% yield.
Table 1. Synthesis of Dipeptides with Oxetanyl Glycine at AA1ox.
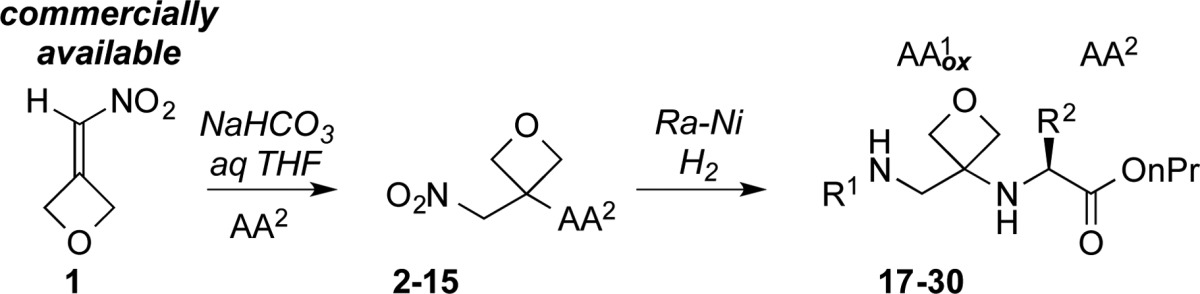
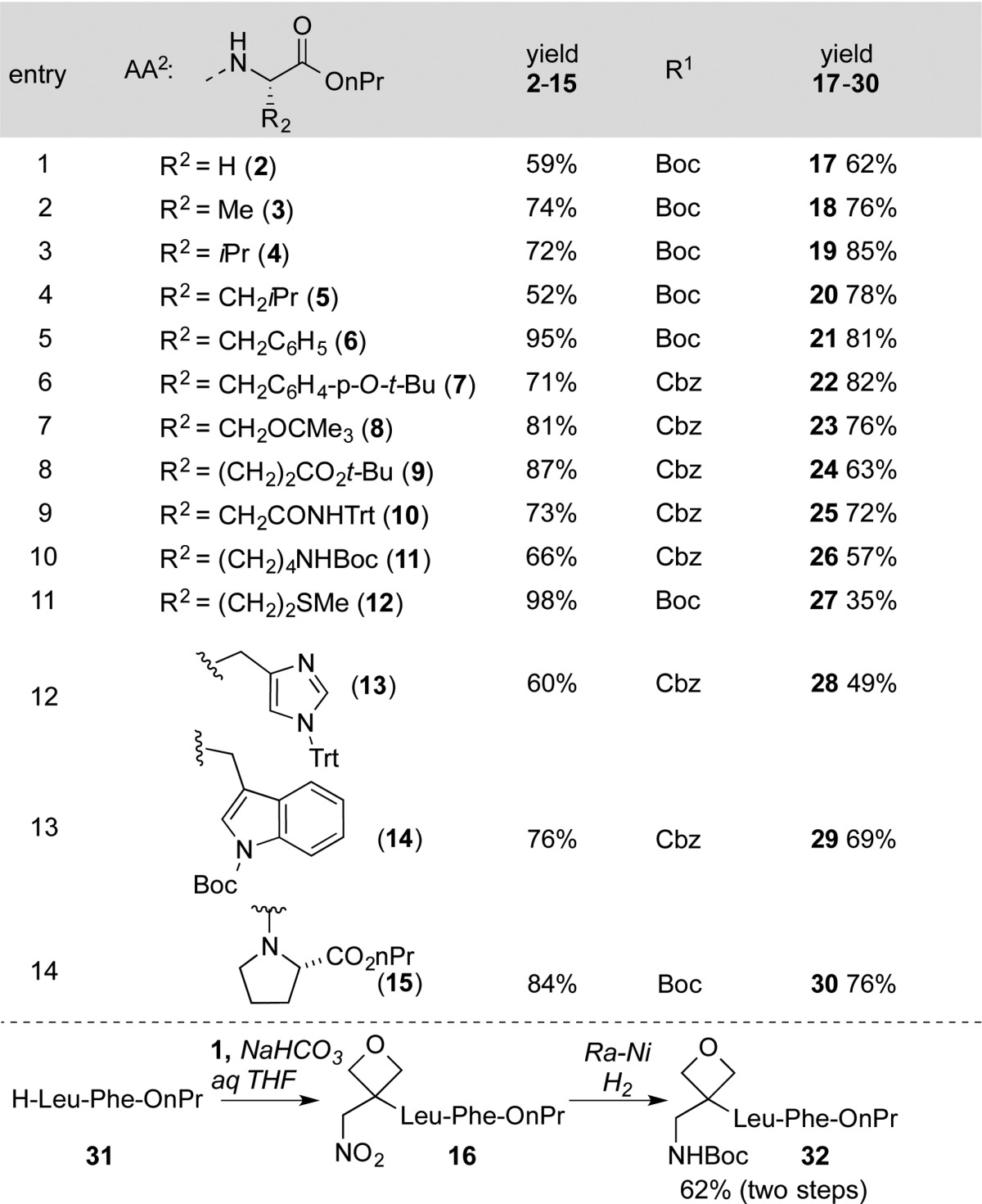
We next investigated NO2-group reduction and the protection of the resulting amine. Raney nickel proved to be the most practical reducing agent, leading to a procedure where reduction in the presence of either (Boc)2O or CbzOSu (aq NaHCO3 in 4:1 THF/H2O) using 1 atm of H2 consistently produced a protected amine in a single operation in good yield.8,9 This protocol has proven to be remarkably general and allows for the formation of enantiopure oxetanyl dipeptides using inexpensive amino esters from the chiral pool (Table 1). Simple alkyl-substituted Boc-protected dimers derived from glycine, l-alanine, l-leucine, l-valine, and l-phenylalanine are formed in high yield (Table 1, entries 1–5). Compounds bearing tBu ethers and esters (7–9), as well as trityl-protected amides 10 and Boc-protected amines 11, all generated products in 57%–82% yield (entries 6–9, 12). The derivatives of l-histidine and l-tryptophan furnished 28 and 29 in 49 and a 69% overall yield, respectively. To accommodate sulfur-bearing side chains, zinc/HCl was selected as a reducing agent (27). Dipeptides were also substrates for this process, with H-Leu-Phe-OnPr (31, Table 1) affording 32 in 62% yield (two steps).
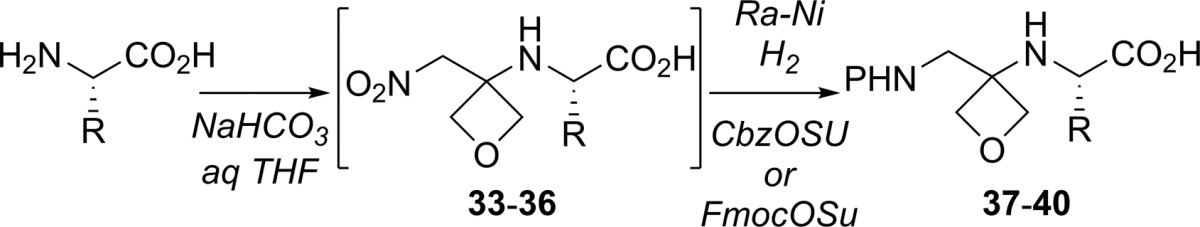
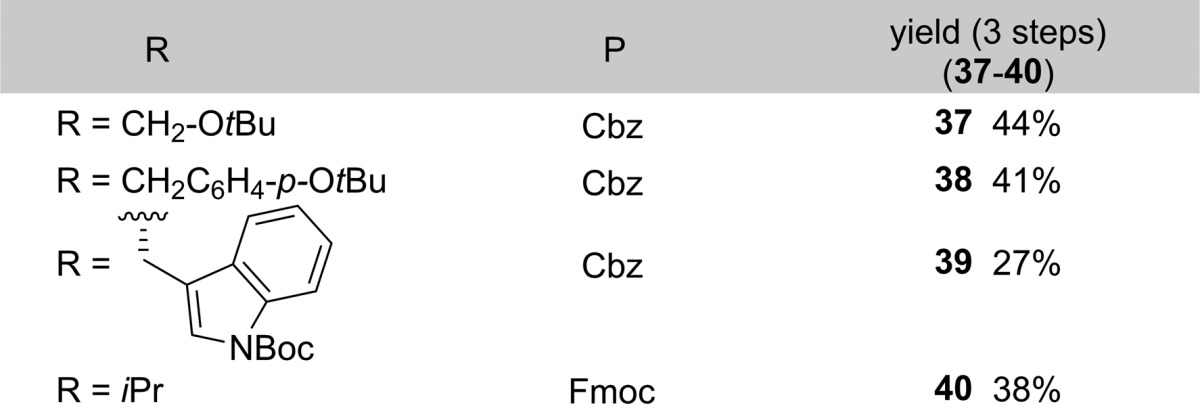
Preliminary results also showed that direct addition of unprotected amino acids to nitro-olefin 1 is possible (Table 2). Indeed, mixing a (orthogonally protected) free amino acid with 1 in THF/H2O in the presence of NaHCO3 afforded nitro-acid adducts 33–36. Crude mixtures were subjected to reduction of the nitro group with Raney Nickel and H2, followed by filtration and treatment with CbzCl or FmocOSu to afford N-protected amino acid dimers 37–40 in 27%–44% yield over three steps. This result constitutes, to the best of our knowledge, the first example of conjugate addition of unprotected amino acids to unsaturated nitro compounds, as well as a direct approach to dimers ready for further coupling.
Table 2. Synthesis of Dipeptides with Oxetanyl Glycine at AA1ox.
Through minor modifications of this protocol, other oxetanyl amino acid residues were incorporated at the AA1ox position. The synthesis of these compounds is exemplified in Table 3. The sequence begins with the Et3N-promoted addition of the nitro alkanes 41–45 to oxetan-3-one.10 After conversion of nitro alcohols obtained to the corresponding mesylates, in situ treatment with glycine propyl ester then afforded nitro alkanes 46–51, which were in turn transformed to oxetanyl dipeptides 52–57. The transient formation of tetrasubstituted nitro alkenes was advantageous because of their tendency otherwise to undergo cyclization to the corresponding isoxazole under basic conditions.11 The sequence proved to be high-yielding and efficient with a variety of substituted nitro alkanes featuring the side chains of leucine (41), O-tert-butyl tyrosine (42), glutamine tert-butyl ester (43), N-Boc lysine (44), and Ts-tryptophan (45). This process entails six synthetic transformations and is carried out with purification of only one intermediate.
Table 3. Synthesis of Oxetanyl Dipeptides with AA1 ≠ Gly.
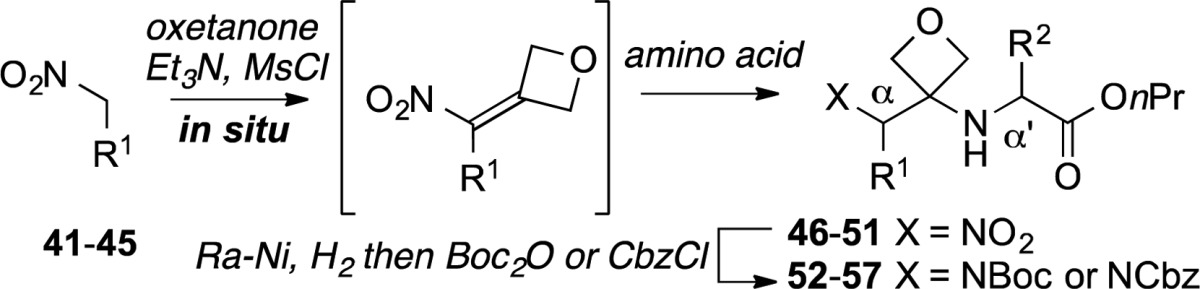
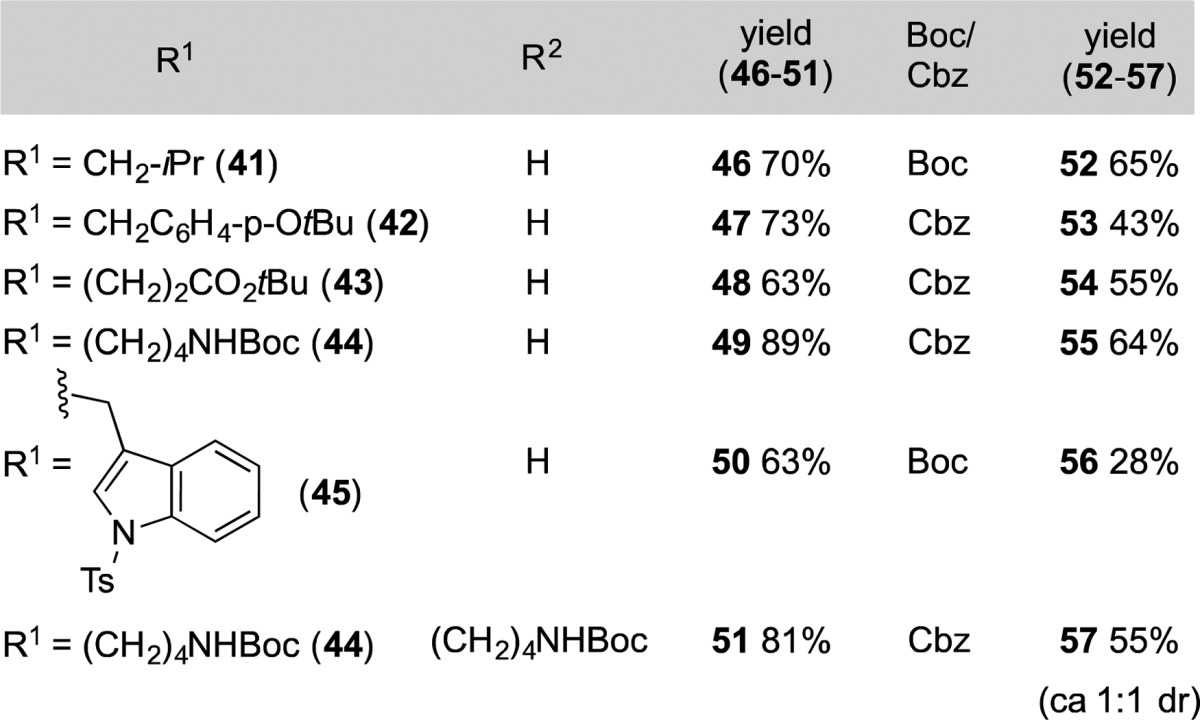
Using the strategy described above, the synthesis of complex oxetanyl peptide surrogates substituted at both Cα and Cα′ positions was possible in a sequence requiring minimal chromatographic purification (52–57, Table 3). However, the ease of separation of the diastereomeric oxetanyl dipeptides generated was substrate-dependent. This constitutes a current limitation, and efforts are ongoing to devise a workable approach to this problem.
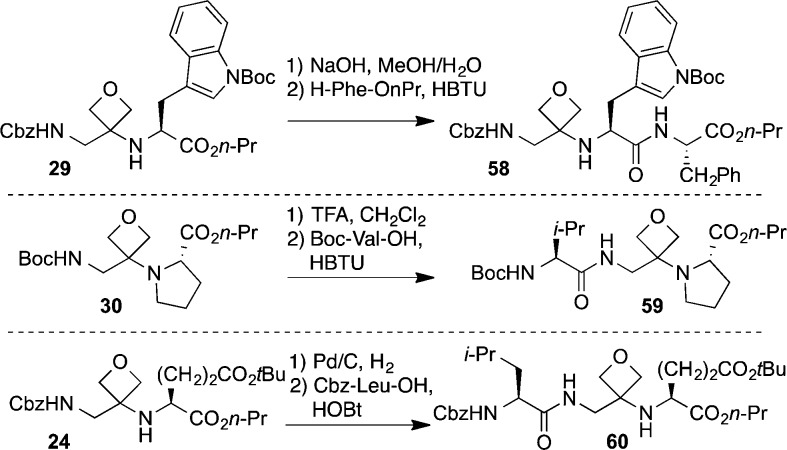
We next explored conditions for the incorporation of the oxetanyl dipeptide surrogates into a peptide chain (Figure 2). We were delighted to observe that oxetanyl dipeptides were compatible with standard peptide coupling approaches. Thus, basic hydrolysis of the ester in 29 followed by workup and exposure of the unpurified acid to HBTU-mediated peptide coupling with H-Phe-OnPr·HCl afforded protected tripeptide 58 in 76% yield over two steps. It is important to note that 58 was obtained as a single diastereoisomer, showing that no racemization of AA2 occurs during saponification. Chain elongation at the N-terminus of the oxetanyl dipeptide is also possible as shown in Figure 2 for 30 → 59 and 24 → 60.
Figure 2.
Reactions of oxetanyl dipeptides.
In conclusion, we have reported the design and synthesis of novel oxetanyl peptides, which expands the peptidomimetic structural space. We have developed a strategy for the incorporation of the oxetane fragment onto the peptide backbone that relies on standard peptide coupling techniques and that is amenable to the preparation of a range of amino acid dimer combinations. We have also shown that the embedded amino oxetanyl fragments are stable to a variety of acidic, basic, reductive, and oxidative reaction conditions. Further studies to establish the physicochemical and biological properties, as well as enzymatic stability, of these new building blocks are ongoing and will be reported in due course.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the NIH (USA) through a Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award to M.M. (GM090547), the Japan Society for Promotion of Science for a fellowship to R.Y., and ETH (TH 10-07-03) is acknowledged. SpiroChem AG is acknowledged for a generous gift of oxetan-3-one and nitromethyleneoxetane.
Supporting Information Available
Experimental procedures and full spectroscopic data for all new compounds. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Funding Statement
National Institutes of Health, United States
Supplementary Material
References
- a Vlieghe P.; Lisowski V.; Martinez J.; Khrestchatisky M. Drug Discovery Today 2010, 15, 40–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Thaler A. M. Chem. Eng. News 30 May 2011, 892213–20. [Google Scholar]
- a Shen W.-C. Drug Discovery Today 2003, 8, 607–608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Torchilin V.; Lukyanov A. N. Drug Discovery Today 2003, 8, 259–266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Pernot M.; Vanderesse R.; Frochot C.; Guillemin F.; Barberi-Heyob M. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 793–802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Vives E.; Brodin P.; Lebleu B. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16010–16017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; For reviews on cell-penetrating peptides, see:; b Brasseur R.; Divita G. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 2177–2181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Fonseca S. B.; Pereira M. P.; Kelley S. O. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2009, 61, 953–964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Search performed in March 2013: Thomson-Reuters Integrity.
- For selected reviews, see:; a Foldamers: Structure, Properties and Applications; Hecht S., Huc I., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2007. [Google Scholar]; b Peptidomimetics Protocols; Kazmierski W. M., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, 1999. [Google Scholar]; c Ko E.; Liu J.; Burgess K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4411–4421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Seebach D.; Gardiner J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1366–1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; e Smith A.; Charnley A.; Hirschmann R. Chem. Rev. 2011, 44, 180–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; f Cheng R.; Gellman S.; Degrado W. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3219–3232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Davis J.; Tsou L.; Hamilton A. D. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 326–334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; h Yin H.; Hamilton A. D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4130–4163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; i Weltler M.; Barron A. E. Biopolymers 2011, 96, 556–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; j Fowler S.; Blackwell H. E. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1508–1524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Bukhard J.; Tchitchanov B.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5379–5382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Researchers at Pfizer have carried out a comparative analysis of the metabolic stability of oxetanes versus other oxygen-containing rings; see: Stepan A. F. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7772–7783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Researchers at Merck have also reported the addition nucleophiles to oxetan-3-tert-butylsulfinimine to access oxetanyl amines without substituents on the amino group, see:; b Hamzik P. J.; Brubaker J. D. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1116–1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; See also:; c Wuitschik G.; Rogers-Evans M.; Müller K.; Fischer H.; Wagner B.; Schuler F.; Polonchuk L.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7736–7739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Wuitschik G.; Rogers-Evans M.; Buckl A.; Bernasconi M.; Marki M.; Godel T.; Fischer H.; Wagner B.; Parrilla I.; Schuler F.; Schneider J.; Alker A.; Schweizer W. B.; Müller K.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4512–4515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; e Wuitschik G.; Carreira E. M.; Wagner B.; Fischer H.; Parrilla I.; Schuler F.; Rogers-Evans M.; Müller K. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3227–3246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Azetidines:; f Burkhard J. A.; Wagner B.; Fischer H.; Schuler F.; Müller K.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3524–3527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Burkhard J. A.; Carreira E. M. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3525–3526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; h Burkhard J. A.; Guérot C.; Knust H.; Rogers-Evans M.; Carreira E. M. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1944–1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoiton N. L.Chemistry of Peptide Synthesis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura O.; Yanagimichi T.; Kobayashi T.; Ishibashi H. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interestingly the use of other esters (Me, Bn) proved inferior.
- Oxetan-3-one (CAS 6704-31-0) is commercially available on multikilogram scale from SpiroChem AG.
- Bukhard J. A.; Tchitchanov B.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5379–5382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.