Abstract
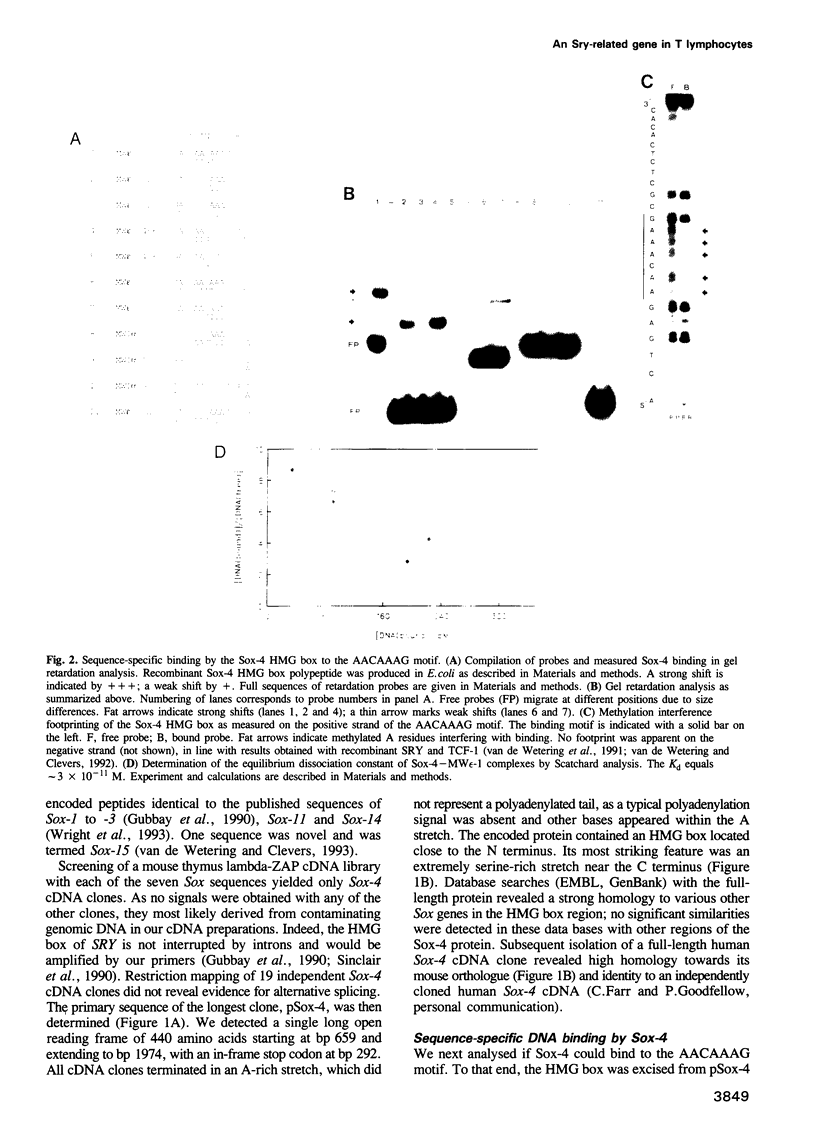
Previous studies in lymphocytes have described two DNA-binding HMG box proteins, TCF-1 and LEF-1, with affinity for the A/TA/TCAAAG motif found in several T cell-specific enhancers. Evaluation of cotransfection experiments in non-T cells and the observed inactivity of an AACAAAG concatamer in the TCF-1/LEF-1-expressing T cell line BW5147, led us to conclude that these two proteins did not mediate the observed enhancer effect. We therefore searched for additional HMG box proteins. By a PCR-aided strategy, we cloned Sox-4, a gene with homology to the HMG box region of the sex determining gene SRY. Sox-4 was expressed in T and pre-B lymphocyte lines and in the murine thymus. Significantly, BW5147 T cells did not express Sox-4. Recombinant Sox-4 bound with high affinity (Kd 3 x 10(-11) M) to the minor groove of the AACAAAG motif, most likely contacting all seven base pairs. In contrast with observations on TCF-1 and LEF-1, cotransfection with Sox-4 unveiled a transactivating capacity, which mapped to its serine-rich C terminus. This region remained functional upon grafting onto a GAL4 DNA-binding domain. Sox-4 is thus the first 'classical' transcription factor in the Sox gene family with separable DNA-binding and transactivation domains. Our observations indicate that a detailed understanding of T cell-specific gene control must integrate the concerted activity of at least three tissue-specific HMG box genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrop J., van Norren K., Clevers H. A gene family of HMG-box transcription factors with homology to TCF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):611–611. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Lonberg N., Dunlap S., Lacy E., Terhorst C. An enhancer located in a CpG-island 3' to the TCR/CD3-epsilon gene confers T lymphocyte-specificity to its promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Brand N., Dabhade N., Barton P., Ashworth A. A conserved family of genes related to the testis determining gene, SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2887–2887. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Connor F., Ashworth A. An SRY-related gene expressed during spermatogenesis in the mouse encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Harley V. R., Pontiggia A., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. SRY, like HMG1, recognizes sharp angles in DNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4497–4506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastrop J., Hoevenagel R., Young J. R., Clevers H. C. A common ancestor of the mammalian transcription factors TCF-1 and TCF-1 alpha/LEF-1 expressed in chicken T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Stehelin D., Clevers H. Ancestry and diversity of the HMG box superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2493–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasrin N., Buggs C., Kong X. F., Carnazza J., Goebl M., Alexander-Bridges M. DNA-binding properties of the product of the testis-determining gene and a related protein. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):317–320. doi: 10.1038/354317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M. A., van de Wetering M. L., Holstege F. C., Prosser H. M., Owen M. J., Clevers H. C. TCF-1, a T cell-specific transcription factor of the HMG box family, interacts with sequence motifs in the TCR beta and TCR delta enhancers. Int Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1189–1192. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.11.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M., van de Wetering M., Dooijes D., Klomp L., Winoto A., Georgopoulos K., Meijlink F., Clevers H. Cloning of murine TCF-1, a T cell-specific transcription factor interacting with functional motifs in the CD3-epsilon and T cell receptor alpha enhancers. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1133–1142. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M., van de Wetering M., Timmerman J., Kruisbeek A., Destree O., Meijlink F., Clevers H. Differential expression of the HMG box factors TCF-1 and LEF-1 during murine embryogenesis. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):439–448. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Littman D. R. Identification and characterization of a T-cell-specific enhancer adjacent to the murine CD4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5506–5515. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilham M. W., van Eijk M., van de Wetering M., Clevers H. C. The murine Sox-4 protein is encoded on a single exon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):2009–2009. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staben C., Yanofsky C. Neurospora crassa a mating-type region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Hawley D. K. TFIID binds in the minor groove of the TATA box. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90299-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto A., Iino Y., Maeda T., Watanabe Y., Yamamoto M. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ste11+ encodes a transcription factor with an HMG motif that is a critical regulator of sexual development. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1990–1999. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., van der Vliet P. C. The oct-1 homeo domain contacts only part of the octamer sequence and full oct-1 DNA-binding activity requires the POU-specific domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L., Huang J. K., Johnson B. H., Reeck G. R. A human placental cDNA clone that encodes nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1197–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Snopek B., Koopman P. Seven new members of the Sox gene family expressed during mouse development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):744–744. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sox 15, a novel member of the murine Sox family of HMG box transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1669–1669. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]