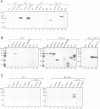
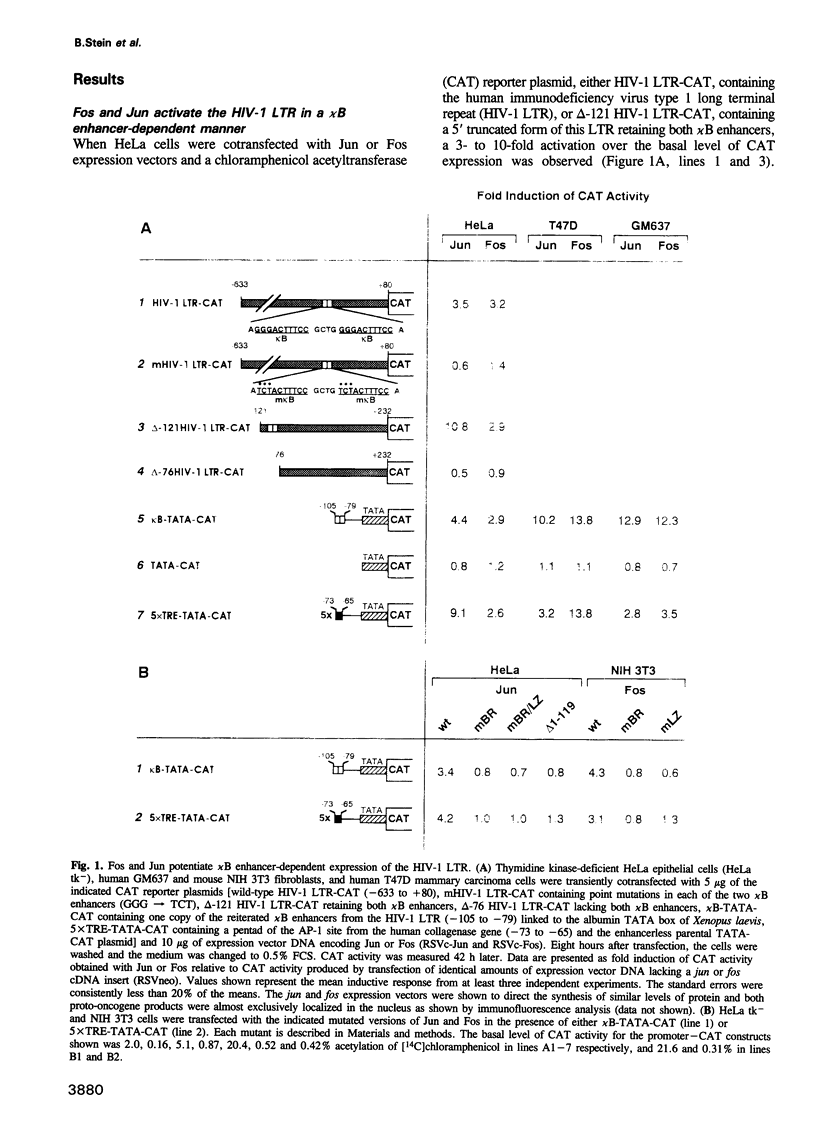
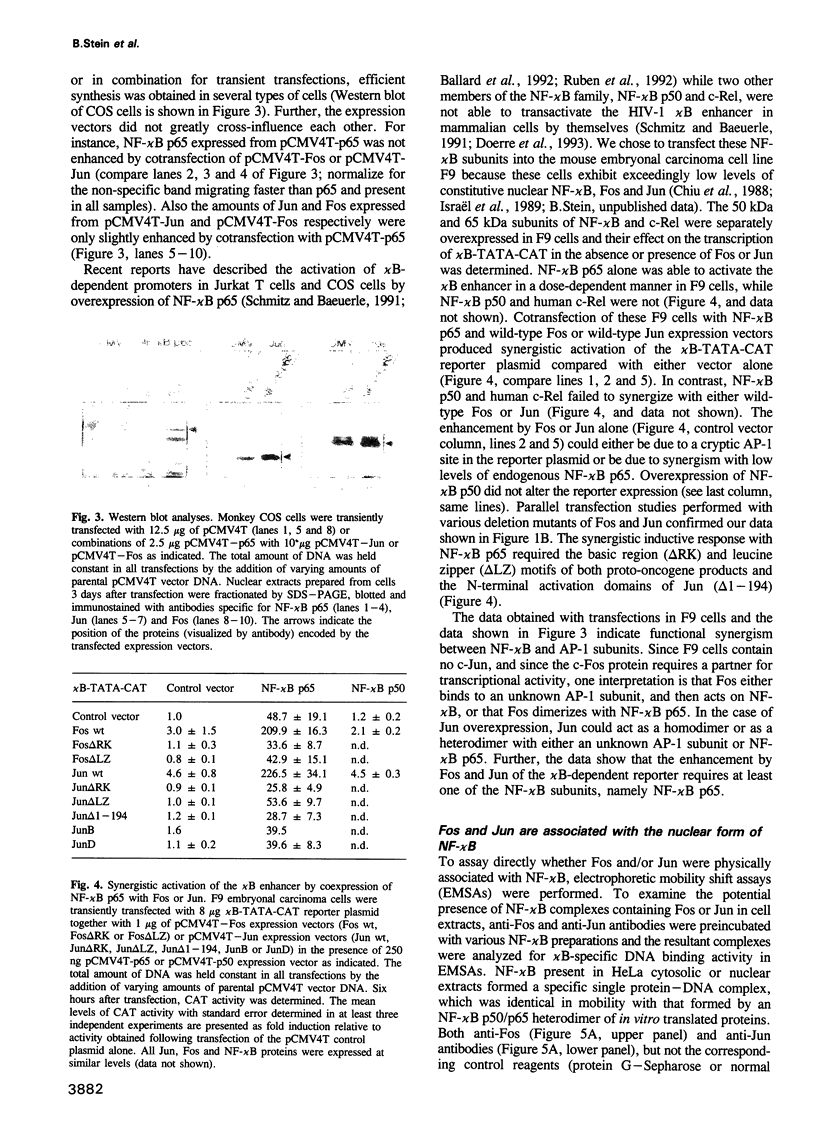
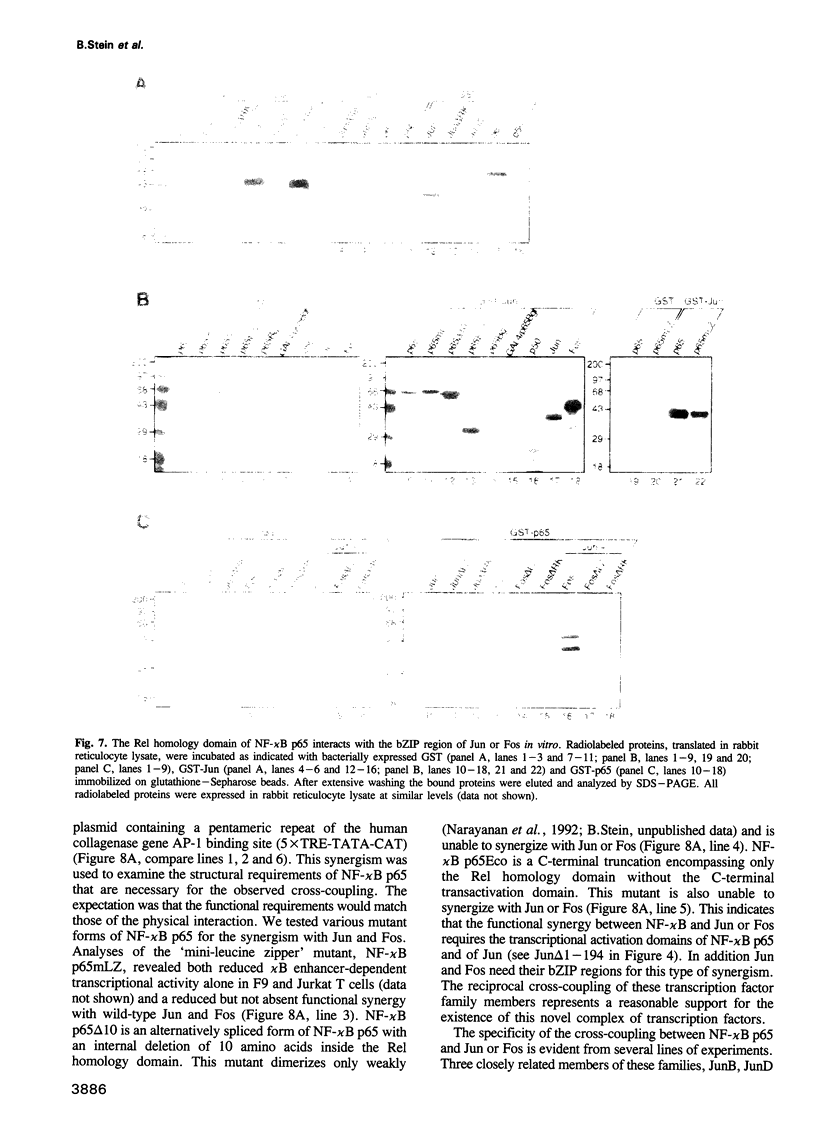
Abstract
NF-kappa B and AP-1 represent distinct mammalian transcription factors that target unique DNA enhancer elements. The heterodimeric NF-kappa B complex is typically composed of two DNA binding subunits, NF-kappa B p50 and NF-kappa B p65, which share structural homology with the c-rel proto-oncogene product. Similarly, the AP-1 transcription factor complex is comprised of dimers of the c-fos and c-jun proto-oncogene products or of closely related proteins. We now demonstrate that the bZIP regions of c-Fos and c-Jun are capable of physically interacting with NF-kappa B p65 through the Rel homology domain. This complex of NF-kappa B p65 and Jun or Fos exhibits enhanced DNA binding and biological function via both the kappa B and AP-1 response elements including synergistic activation of the 5' long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. These findings support a combinatorial mechanism of gene regulation involving the unexpected cross-coupling of two different classes of transcription factors to form novel protein complexes exhibiting potentiated biological activity.
Full text
PDF




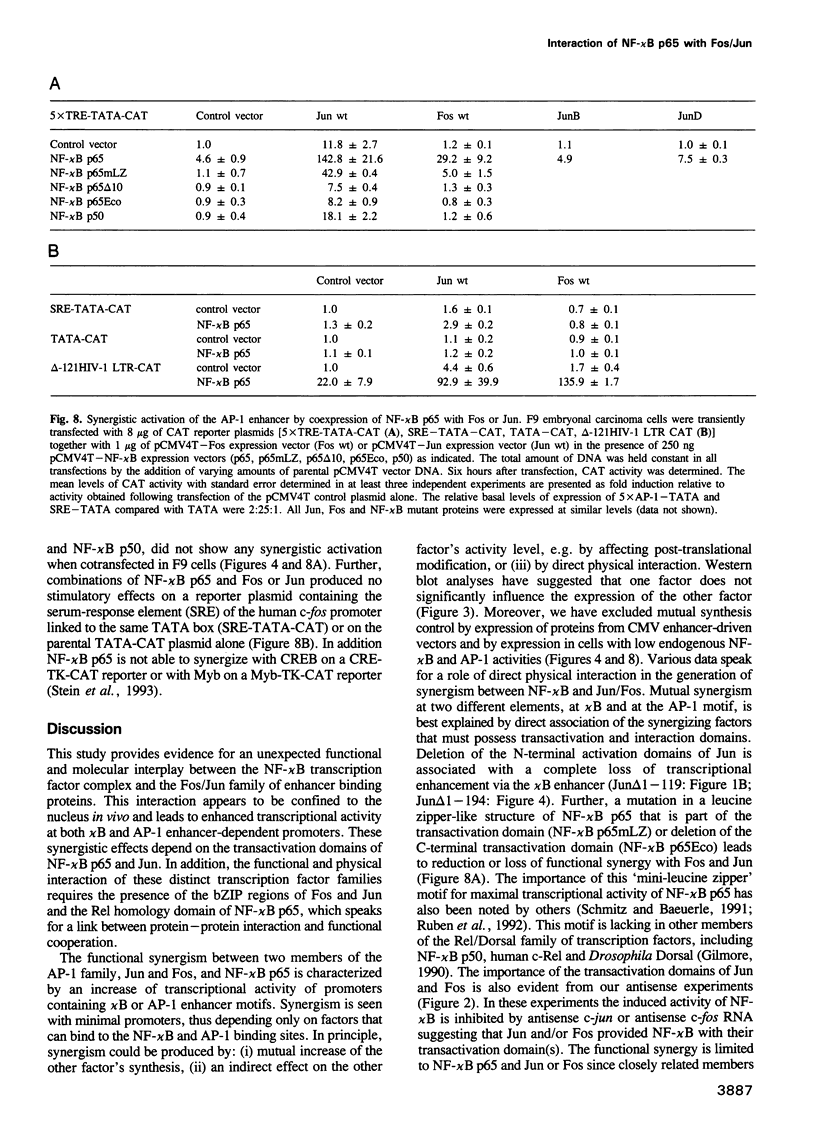




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Smeal T., Meek J., Karin M. Jun and v-jun contain multiple regions that participate in transcriptional activation in an interdependent manner. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Vandenberg M. T., Marshak D. R., Curran T., Abate C. Jun is phosphorylated by several protein kinases at the same sites that are modified in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4694–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Azizkhan J. C., Jensen D. E., Beg A. A., Coodly L. R. Induction of NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4943–4951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister A. J., Kouzarides T. Basic peptides enhance protein/DNA interaction in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3523–3523. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow P. P., Horgan J. G., Taylor K. J. Neonatal periventricular leukomalacia: real-time sonographic diagnosis with CT correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Jul;145(1):155–160. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Ferreira P. C., Gentz R., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. The product of a fos-related gene, fra-1, binds cooperatively to the AP-1 site with Jun: transcription factor AP-1 is comprised of multiple protein complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):173–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Protooncogene c-fos as a transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:37–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzanski P., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. Both N- and C-terminal domains of RelB are required for full transactivation: role of the N-terminal leucine zipper-like motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1572–1582. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerre S., Sista P., Sun S. C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. The c-rel protooncogene product represses NF-kappa B p65-mediated transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Josephs S. F., Curran T. The Fos complex and Fos-related antigens recognize sequence elements that contain AP-1 binding sites. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1150–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.2964084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganchi P. A., Sun S. C., Greene W. C., Ballard D. W. I kappa B/MAD-3 masks the nuclear localization signal of NF-kappa B p65 and requires the transactivation domain to inhibit NF-kappa B p65 DNA binding. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1339–1352. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W. HIV-1, HTLV-1 and normal T-cell growth: transcriptional strategies and surprises. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliday E. M., Ramesha C. S., Ringold G. TNF induces c-fos via a novel pathway requiring conversion of arachidonic acid to a lipoxygenase metabolite. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):109–115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T. H., Lamph W. W., Prywes R. Mapping of epidermal growth factor-, serum-, and phorbol ester-responsive sequence elements in the c-jun promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4472–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Yano O., Logeat F., Kieran M., Kourilsky P. Two purified factors bind to the same sequence in the enhancer of mouse MHC class I genes: one of them is a positive regulator induced upon differentiation of teratocarcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5245–5257. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Müller R. Structure-function analysis of fos protein: a single amino acid change activates the immortalizing potential of v-fos. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. Interference between pathway-specific transcription factors: glucocorticoids antagonize phorbol ester-induced AP-1 activity without altering AP-1 site occupation in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Kim S. J., Angel P., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Karin M., Wilder R. L. Interleukin-1 stimulates and all-trans-retinoic acid inhibits collagenase gene expression through its 5' activator protein-1-binding site. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;4(7):973–980. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Slater E. P., Jooss K. U., Beato M., Müller R. Mutual transrepression of Fos and the glucocorticoid receptor: involvement of a functional domain in Fos which is absent in FosB. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2827–2834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lücke-Huhle C., Mai S., Herrlich P. UV-induced early-domain binding factor as the limiting component of simian virus 40 DNA amplification in rodent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4812–4818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muegge K., Williams T. M., Kant J., Karin M., Chiu R., Schmidt A., Siebenlist U., Young H. A., Durum S. K. Interleukin-1 costimulatory activity on the interleukin-2 promoter via AP-1. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.2799385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Ruben S. M., Higgins K. A., Rosen C. A. Identification of a naturally occurring transforming variant of the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):367–370. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Cato A. C., Herrlich P. Interference of pathway specific transcription factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 11;1129(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90501-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radler-Pohl A., Sachsenmaier C., Gebel S., Auer H. P., Bruder J. T., Rapp U., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced activation of AP-1 involves obligatory extranuclear steps including Raf-1 kinase. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Nuclear proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:539–557. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Visvader J., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Fos-Jun interaction: mutational analysis of the leucine zipper domain of both proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):770–781. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Visvader J., Wamsley P., Verma I. M. Trans-dominant negative mutants of Fos and Jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Verrier B., Müller R. Products of the fos and jun proto-oncogenes bind cooperatively to the AP1 DNA recognition sequence. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Aug;88:133–139. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9088133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Zorbas H., Winnacker E. L., Baeuerle P. A. The NF-kappa B transcription factor induces DNA bending which is modulated by its 65-kD subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6497–6502. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Gebel S., Stein B., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. Nuclear oncoproteins determine the genetic program in response to external stimuli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):779–787. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Chedid M., Suttles J., Pollok B. A., Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and cyclic AMP induce kappa immunoglobulin light-chain expression via activation of an NF-kappa B-like DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Angel P., Meek J., Karin M. Different requirements for formation of Jun: Jun and Jun: Fos complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2091–2100. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Angel P., van Dam H., Ponta H., Herrlich P., van der Eb A., Rahmsdorf H. J. Ultraviolet-radiation induced c-jun gene transcription: two AP-1 like binding sites mediate the response. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Mar;55(3):409–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Krämer M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H., Herrlich P. UV-induced transcription from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat and UV-induced secretion of an extracellular factor that induces HIV-1 transcription in nonirradiated cells. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4540–4544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4540-4544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. jun: oncogene and transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]