Abstract
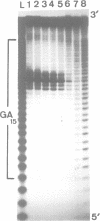
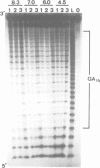
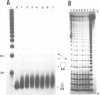
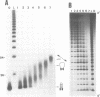
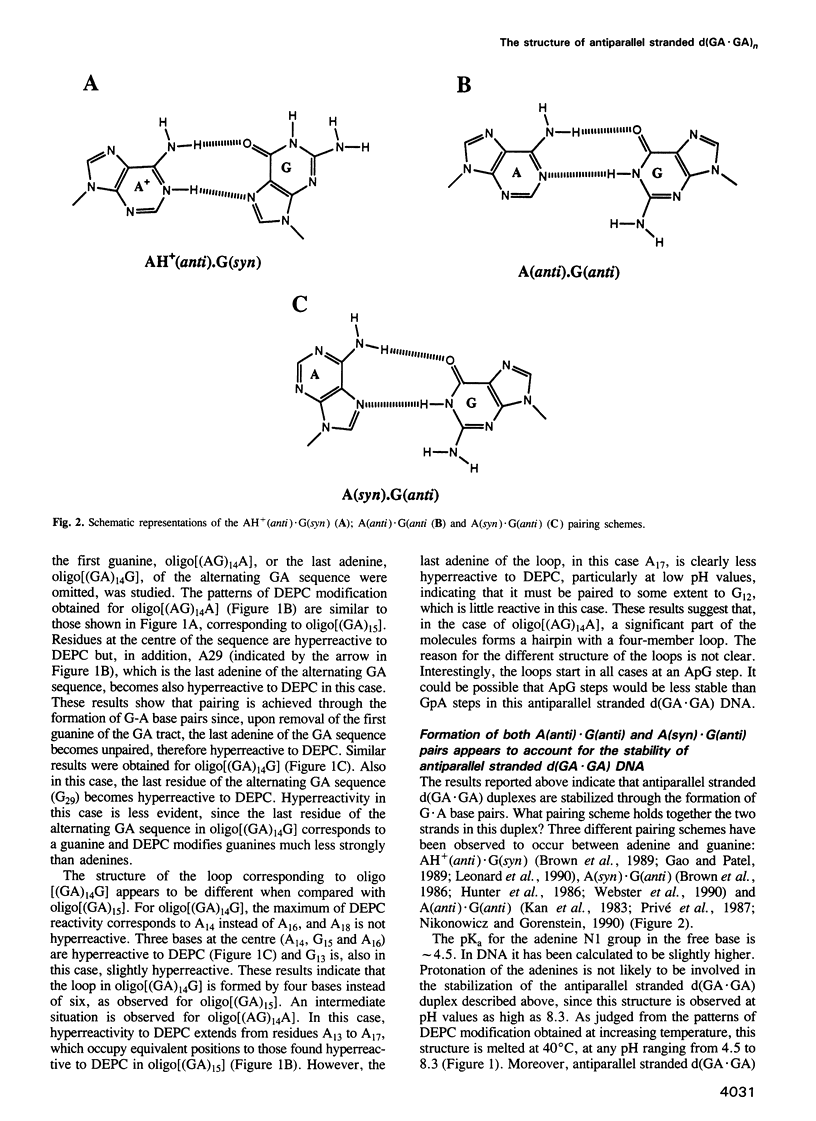
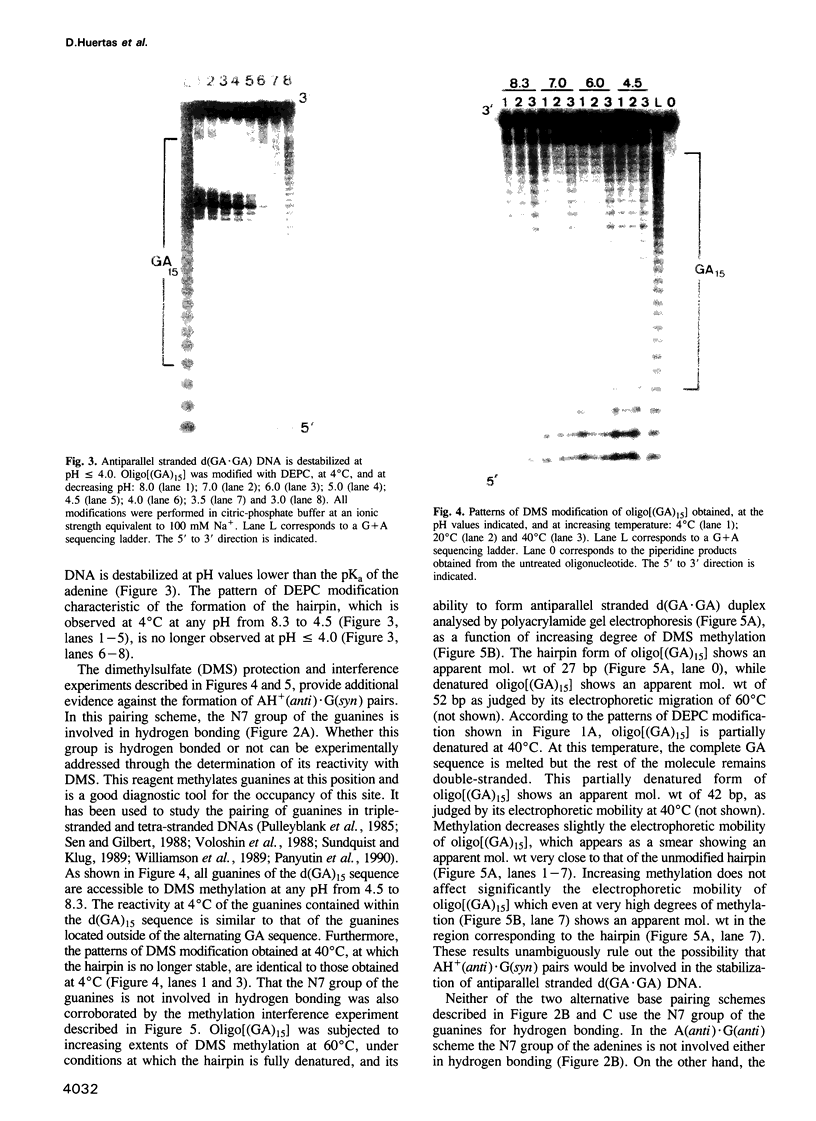
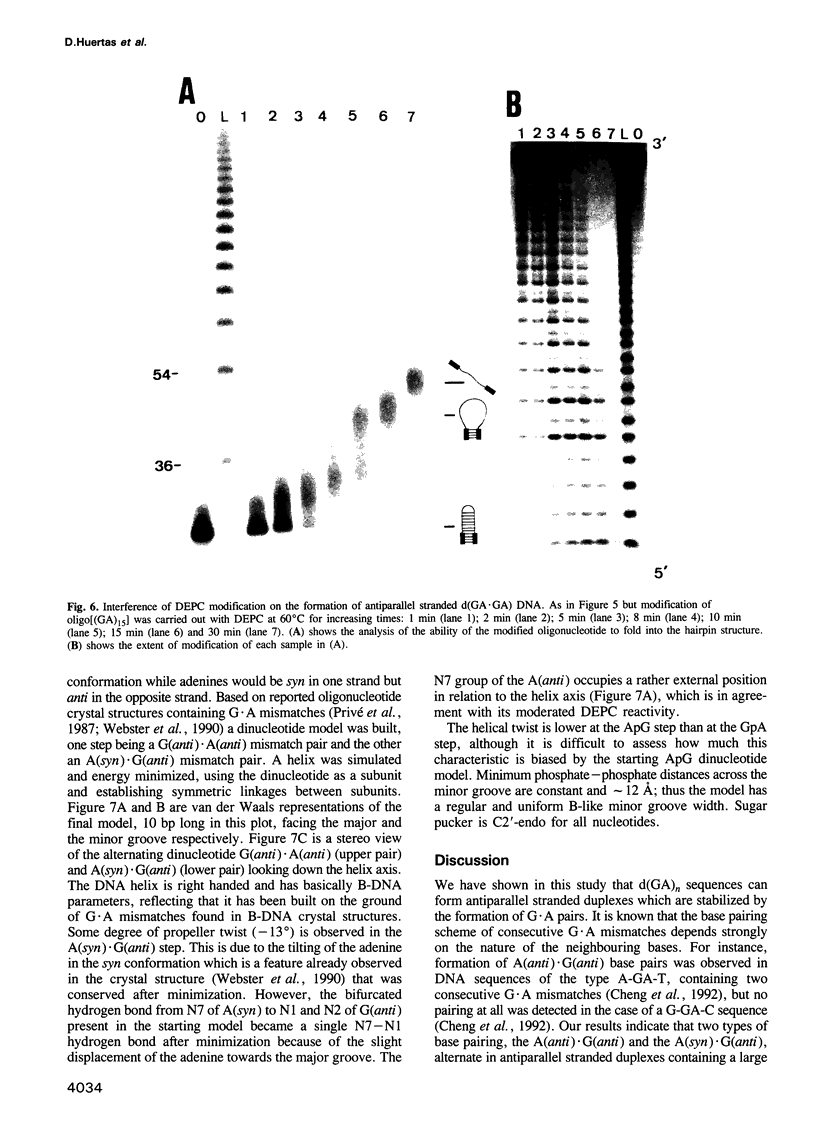
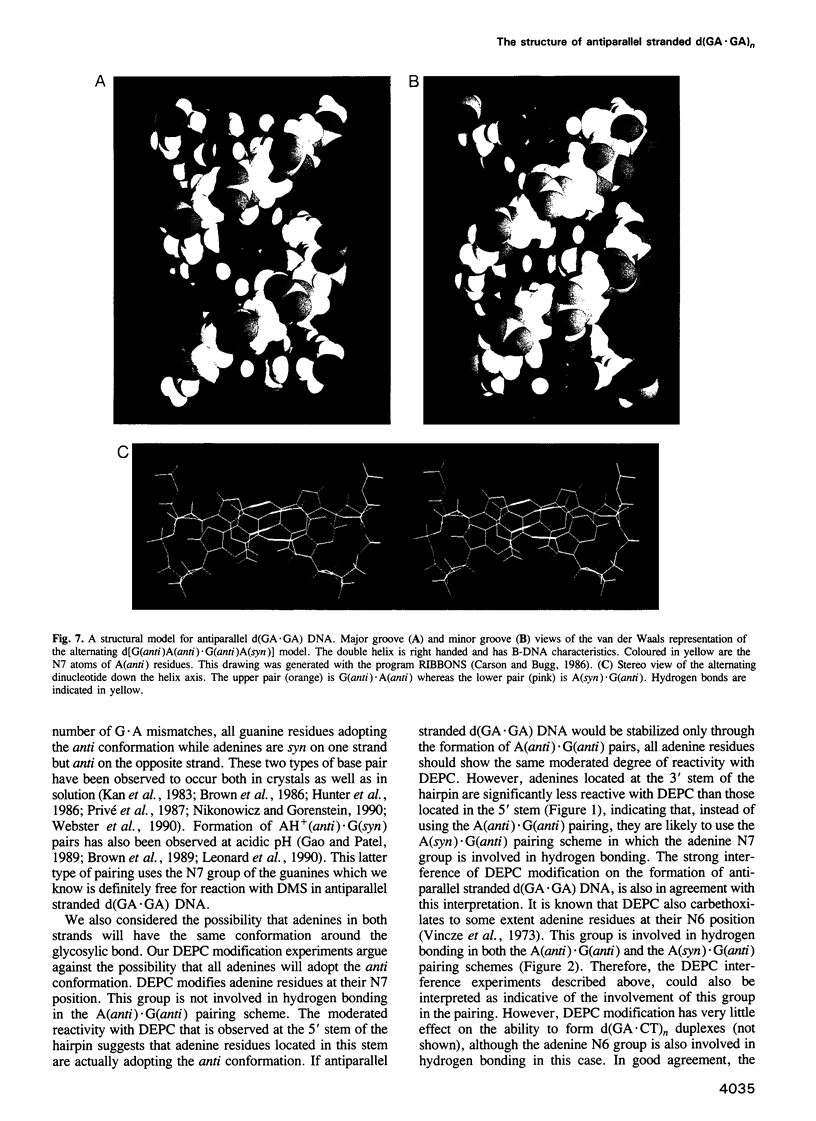
Alternating d(GA)n DNA sequences form antiparallel stranded homoduplexes which are stabilized by the formation of G.A pairs. Three base pairings are known to occur between adenine and guanine: AH+ (anti).G(syn), A(anti).G(anti) and A(syn).G(anti). Protonation of the adenine residues is not involved in the stabilization of this structure, since it is observed at any pH value from 8.3 to 4.5; at pH < or = 4.0 antiparallel stranded d(GA.GA) DNA is destabilized. The results reported in this paper strongly suggest that antiparallel stranded d(GA.GA) homoduplexes are stabilized by the formation of alternating A(anti).G(anti) and G(anti).A(syn) pairs. In this structure, all guanine residues are in the anti conformation with their N7 position freely accessible to DMS methylation. On the other hand, adenines in one strand adopt the anti conformation, with their N7 position also free for reaction, while those of the opposite strand are in the syn conformation, with their N7 position hydrogen bonded to the guanine N1 group of the opposite strand. A regular right-handed helix can be generated using alternating G(anti).A(syn) and A(anti).G(anti) pairs.
Full text
PDF
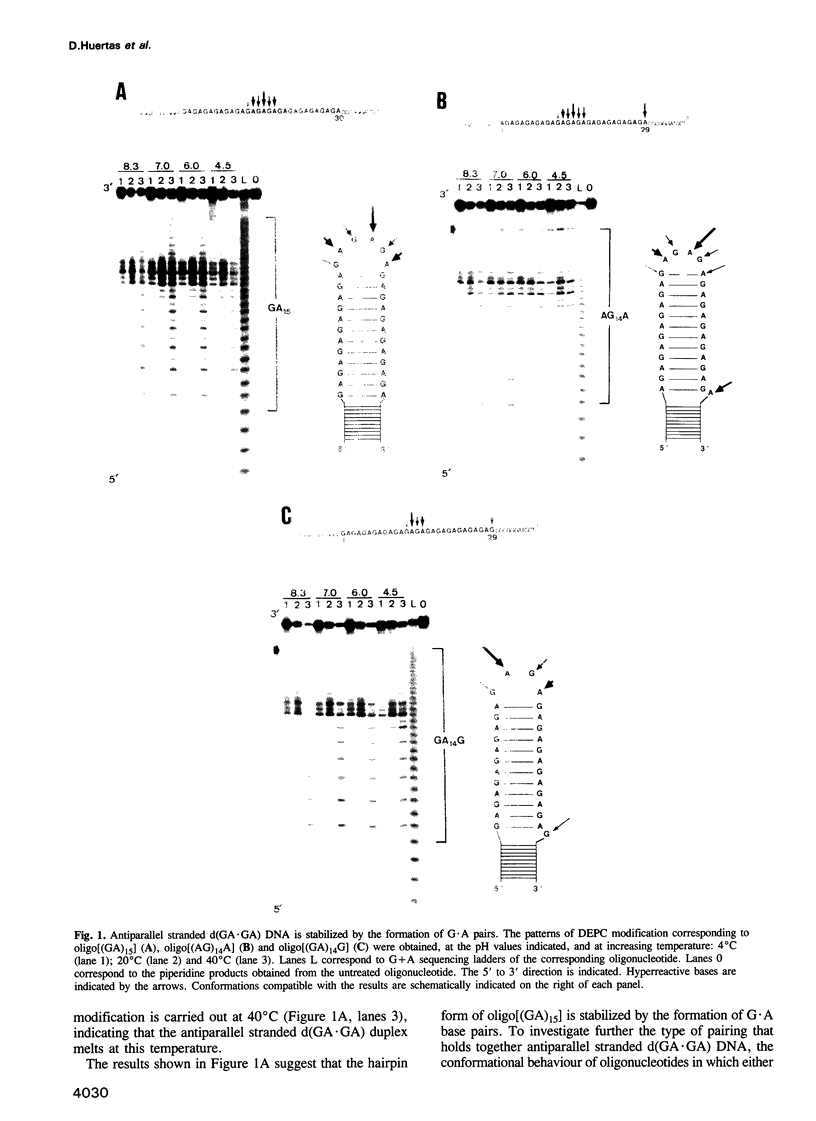




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baran N., Lapidot A., Manor H. Formation of DNA triplexes accounts for arrests of DNA synthesis at d(TC)n and d(GA)n tracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. The influence of single base triplet changes on the stability of a pur.pur.pyr triple helix determined by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2773–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán R., Martínez-Balbás A., Bernués J., Bowater R., Azorín F. Characterization of the zinc-induced structural transition to *H-DNA at a d(GA.CT)22 sequence. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):966–978. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernués J., Beltrán R., Casasnovas J. M., Azorín F. Structural polymorphism of homopurine--homopyrimidine sequences: the secondary DNA structure adopted by a d(GA.CT)22 sequence in the presence of zinc ions. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2087–2094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernúes J., Beltrán R., Azorín F. SV40 recombinants carrying a d(CT.GA)22 sequence show increased genomic instability. Gene. 1991 Dec 15;108(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90444-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Hunter W. N., Kneale G., Kennard O. Molecular structure of the G.A base pair in DNA and its implications for the mechanism of transversion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2402–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Leonard G. A., Booth E. D., Chambers J. Crystal structure and stability of a DNA duplex containing A(anti).G(syn) base-pairs. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):455–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. L., Blattner F. R., Fitzmaurice L., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. Structure of genes for membrane and secreted murine IgD heavy chains. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):410–415. doi: 10.1038/296410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. W., Chou S. H., Reid B. R. Base pairing geometry in GA mismatches depends entirely on the neighboring sequence. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1037–1041. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. A., Griffin J. A., Wells R. D. Non-B right-handed DNA conformations of homopurine.homopyrimidine sequences in the murine immunoglobulin C alpha switch region. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7397–7405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Organization of the rat gamma-fibrinogen gene: alternative mRNA splice patterns produce the gamma A and gamma B (gamma ') chains of fibrinogen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel S., Lane A. N., Brown T. Very stable mismatch duplexes: structural and thermodynamic studies on tandem G.A mismatches in DNA. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12083–12086. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Gargiulo G., Rena-Descalzi L., Worcel A. Escherichia coli single-strand binding protein stabilizes specific denatured sites in superhelical DNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):770–774. doi: 10.1038/303770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Human U1 RNA genes contain an unusually sensitive nuclease S1 cleavage site within the conserved 3' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter W. N., Brown T., Kennard O. Structural features and hydration of d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-A-G-C-G); a double helix containing two G.A mispairs. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):173–191. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan L. S., Chandrasegaran S., Pulford S. M., Miller P. S. Detection of a guanine X adenine base pair in a decadeoxyribonucleotide by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4263–4265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Torrey T. A., Kinniburgh A. J. A CT promoter element binding protein: definition of a double-strand and a novel single-strand DNA binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):111–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Evans D. H., Morgan A. R. Polypurine DNAs and RNAs form secondary structures which may be tetra-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4305–4320. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S. The stability of polypurine tetraplexes in the presence of mono- and divalent cations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6057–6060. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard G. A., Booth E. D., Brown T. Structural and thermodynamic studies on the adenine.guanine mismatch in B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5617–5623. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Zon G., Wilson W. D. NMR and molecular modeling evidence for a G.A mismatch base pair in a purine-rich DNA duplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Zon G., Wilson W. D. Thermodynamics of DNA duplexes with adjacent G.A mismatches. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7566–7572. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor H., Rao B. S., Martin R. G. Abundance and degree of dispersion of genomic d(GA)n.d(TC)n sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(2):96–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Cox D. R., Shine J., Richards R. I. Structure of mouse kallikrein gene family suggests a role in specific processing of biologically active peptides. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):300–307. doi: 10.1038/303300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikonowicz E. P., Gorenstein D. G. Two-dimensional 1H and 31P NMR spectra and restrained molecular dynamics structure of a mismatched GA decamer oligodeoxyribonucleotide duplex. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8845–8858. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palecek E. Local supercoil-stabilized DNA structures. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(2):151–226. doi: 10.3109/10409239109081126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutin I. G., Kovalsky O. I., Budowsky E. I., Dickerson R. E., Rikhirev M. E., Lipanov A. A. G-DNA: a twice-folded DNA structure adopted by single-stranded oligo(dG) and its implications for telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):867–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privé G. G., Heinemann U., Chandrasegaran S., Kan L. S., Kopka M. L., Dickerson R. E. Helix geometry, hydration, and G.A mismatch in a B-DNA decamer. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):498–504. doi: 10.1126/science.3310237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. S., Manor H., Martin R. G. Pausing in simian virus 40 DNA replication by a sequence containing (dG-dA)27.(dT-dC)27. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8077–8094. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam A. C., Shen A., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin mu-delta heavy-chain region. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):483–487. doi: 10.1038/306483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe K., Fritsch V., Westhof E., Jovin T. M. Alternating d(G-A) sequences form a parallel-stranded DNA homoduplex. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3777–3786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5989–5992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S. Mammalian tRNA genes: nucleotide sequence of rat genes for tRNAAsp, tRNAGly and tRNAGlu. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2239–2250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincze A., Henderson R. E., McDonald J. J., Leonard N. J. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Bases and nucleosides derived from guanine, cytosine, and uracil. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 18;95(8):2677–2682. doi: 10.1021/ja00789a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voloshin O. N., Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Belotserkovskii B. P., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Chemical probing of homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeats in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):475–476. doi: 10.1038/333475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster G. D., Sanderson M. R., Skelly J. V., Neidle S., Swann P. F., Li B. F., Tickle I. J. Crystal structure and sequence-dependent conformation of the A.G mispaired oligonucleotide d(CGCAAGCTGGCG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb A., Collier D. A., Birshtein B. K., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA and intramolecular triplex formation at the site of an unequal sister chromatid exchange. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1352–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee H. A., Wong A. K., van de Sande J. H., Rattner J. B. Identification of novel single-stranded d(TC)n binding proteins in several mammalian species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):949–953. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]