Abstract
Introduction
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) provides significant relief for lumbosacral radiculopathy refractory to both medical and surgical treatment, but historically only offers limited relief for axial low back pain (LBP). We aim to evaluate the response of chronic axial LBP treated with SCS using a surgically implanted epidural paddle lead.
Materials and methods
This is a retrospective review of a consecutive series of patients with exclusive LBP or predominant LBP associated with lower extremity (LE) pain evaluated and treated with SCS using an implanted paddle lead within the dorsal thoracic epidural space. Baseline LBP, and if present LE pain, were recorded using the visual analogue scale (VAS) at an initial evaluation. At a follow-up visit (a minimum of 12 months later), LBP and LE pain after a spinal cord stimulator implantation were again recorded using the VAS. Patients were also asked to estimate total LBP pain relief achieved.
Results
Patients with either exclusive (n=7) or predominant (n=2) axial LBP were treated with SCS by implantation of a paddle lead at an average spine level of T9. The baseline VAS score for LBP was 7.2; after a follow-up of 20 months, the score decreased to 2.3 (P=0.003). The LE pain VAS score decreased from 7.5 to 0.0 (P=0.103). Patients also reported a subjective 66.4% decrease of their LBP at follow-up. There were no surgical complications.
Conclusions
Axial LBP is refractory to many treatments, including SCS. SCS using a surgically implanted paddle electrode provides significant pain relief for chronic axial LPB, and is a safe treatment modality.
Keywords: SCS, LBP, laminotomy, paddle electrodes
Introduction
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) provides significant relief for lumbosacral radiculopathy refractory to both medical and surgical treatment. Clinical series report between 50% to 70% successful pain relief in patients treated with SCS based on reduction in pain severity scores, improvement in function, and decreased pain medication dependence.1–7 Until recently, SCS has been considered relatively ineffective for treatment of chronic axial low back pain (LBP).1,2,4,8–12 Most clinical series report better pain control with SCS in patients with lower extremity (LE) radicular pain than in patients with isolated, axial LBP,1,13 an expected finding based on functional neuroanatomy. The representation of the low back within the sensory homunculus of the cerebral cortex and the dorsal columns of the spinal cord is relatively small compared to the representation of the legs.2 From dorsal to ventral, the representation of the low back within the dorsal columns is evenly distributed, and thus low back fibers may not be available to predominantly superficial stimulation of the dorsal columns.2 Improvements in SCS technology including programmable and percutaneously rechargeable implantable generators, increasing capabilities of implantable programmable generators, and paddle design enhancements reducing device migration14 have resulted in increasingly effective LBP control. Accordingly, some combined low back and LE pain studies have reported satisfactory pain relief with SCS for the chronic LBP component.9
Failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS) is the most common indication for SCS in the United States.15 SCS in non-operated patients (ie, without FBSS) with axial LBP has not been systematically studied. The current study retrospectively analyzes a patient population whose clinical characteristics have generally been considered a poor prognostic indication for SCS. Patients with either exclusive or predominant chronic axial LBP, regardless of previous spinal surgical intervention, are generally expected to respond less favorably to SCS than those patients with predominantly LE radicular pain.1,13 This current study evaluates the direct response of either exclusive or predominant chronic axial LBP to SCS provided with the surgical implantation of paddle leads within the thoracic epidural space.
Materials and methods
Subjects
This is a retrospective review of a consecutive series of patients with either exclusive or predominant chronic axial LBP evaluated and treated at a university health care setting from 2006 to 2011 with surgical implantation of a spinal cord stimulator. A small portion of the patients were also treated for LE radiculopathy that was less severe than the axial LBP, as assessed by a preoperative visual analogue scale (VAS) score for both the axial LBP and LE pain. All patients underwent at least 6 weeks of treatment with physical therapy including heat, ultrasound, and exercises, followed by treatment with lumbar epidural or facet steroid injections as indicated prior to surgical intervention. All patients were found not to be optimal candidates for neural decompressive or fusion procedures after evaluation of their presentation and review of their neuroimaging by a spine surgeon at our institution. The patients were also screened with neuropsychological testing. The study was approved by the university institutional review board.
Spinal cord stimulation implantation technique
Under intravenous sedation and local anesthesia, SCS paddles were implanted in the dorsal thoracic epidural space at an average T9 level through a laminotomy. The patients were positioned prone over chest rolls on the operating table and were fully conscious after the paddle implantation for an intraoperative epidural SCS trial of approximately 15 minutes, performed as previously described.16 After repositioning adjustments of the paddle as needed, the acute intraoperative SCS screening trials ultimately successfully provided at least 50% pain relief in the habitual axial LBP distribution for all patients. Among the two patients with LE radiculopathy, acute intraoperative SCS screening also provided at least 50% pain relief along the LE pain distribution. The epidural SCS paddles used were a three-column Tripole lead (St Jude Medical, Inc., Saint Paul, MN, USA) or a five-column Penta lead (St Jude Medical). The paddle leads were anchored into position after the intraoperative screening trials and the connecting cables were subcutaneously tunneled to a buttock area. The cables were then attached to an implanted programmable generator within a pocket created in the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 1). Implanted programmable generators used were the Eon rechargeable generator (St Jude Medical).
Figure 1.
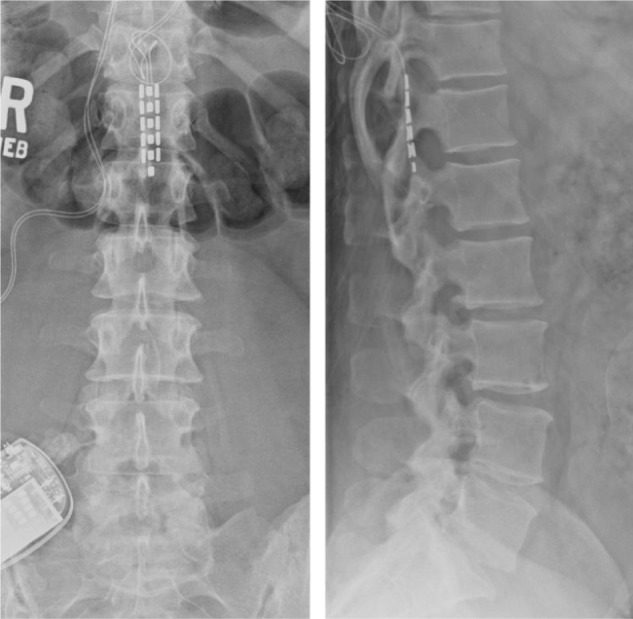
Plain posterior–anterior and lateral radiographs of Case 5.
Notes: A three-column St Jude Medical Tripole lead is depicted within the dorsal epidural space at T12 and attached to an implanted programmable generator within the right buttock subcutaneous tissue. The paddle was initially inserted in a superior direction toward the T9 level, but the patient failed to receive 50% pain relief during the intraoperative trial. The patient did receive 50% pain relief after the paddle was directed in an inferior direction. The patient ultimately reported no benefit from the SCS at a 24-month follow-up visit.
Abbreviation: SCS, spinal cord stimulation.
Pre- and postspinal cord stimulation pain severity
Preoperative pain severity of axial LBP and LE pain were recorded during an initial evaluation using the VAS scale. Following the placement of an implanted spinal cord stimulator, patients were followed for a minimum of 12 months, at which time the VAS scores for axial LBP and LE pain were again recorded. In addition, each patient at their follow-up visit was asked to rate the estimated decrease in axial LBP as a subjective measure of pain relief.
Statistical analysis
Quantitative data were reported as means ± standard error of the mean. All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata 11 statistical software package (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to test for statistically significant differences of the nonparametric means. P values were calculated as two-tailed, and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinical and demographic data
A total of nine patients with either exclusive (n=7) or predominant (n=2) axial LBP were treated with spinal cord stimulation using a surgically implanted paddle lead within the thoracic epidural space (Table 1). In this series, there were three males and six females with a mean age of 54.2 years (range: 33 to 75 years). The etiology of the LBP was FBSS (n=4), lumbar-sacral degenerative joint disease (n=3), lumbar-sacral degenerative disc disease (n=4), and lumbar spine fracture (n=1). Degenerative joint disease was defined as facet arthropathy evident on a magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical data on nine patients with exclusive or predominant low back pain treated with paddle spinal cord stimulation
| Case no | Age, sex | Diagnosis | Implant level, device | VAS preop
|
VAS postop
|
% dec of LBP* | Follow-up (months) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBP | LE | LBP | LE | ||||||
| 1 | 47, F | DDD (L5/S1) DJD (L4/5–L5/S1) |
T8–9, SJM Tripole | 7 | – | 3 | – | 50 | 41 |
| 2 | 46, F | FBSS (L5/S1) | T9–10, SJM Tripole | 4 | – | 1 | – | 75 | 24 |
| 3 | 40, M | DDD (L5/S1) DJD (L3/4–L5/S1) |
T6–7, SJM Tripole | 4 | – | 1 | – | 80 | 12 |
| 4 | 52, M | L2 fracture | T8–9, SJM Tripole | 8 | – | 2 | – | 75 | 24 |
| 5 | 33, F | FBSS (L5/S1) | T12, SJM Tripole | 8 | – | 9 | – | 0 | 24 |
| 6 | 69, F | FBSS (T9–L5) | T6–7, SJM Tripole | 8.5 | – | 1 | – | 80 | 12 |
| 7 | 58, M | DDD (L1–S1) | T8–9, SJM Tripole | 5 | – | 0 | – | 75 | 18 |
| 8 | 68, F | FBSS (L4–L5) | T8–9, SJM Tripole | 10 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 98 | 12 |
| 9 | 75, F | DDD (L3/5–L5/S1) DJD (L3/5–L5/S1) |
T9–10, SJM Penta | 10 | 6 | 3.5 | 0 | 65 | 12 |
Note:
Patient estimated decrease of low back pain at follow-up.
Abbreviations: DDD, degenerative disc disease; dec, decrease; DJD, degenerative joint disease; FBSS, failed back surgery syndrome; LBP, low back pain; LE, lower extremity; SJM, St Jude Medical; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Spinal cord stimulation data
Table 2 summarizes the findings of this current case series. The average thoracic spine level of the epidural spinal cord stimulator paddle lead implant was approximately the T9 level (range, T6–T12). Patients were followed for response to the SCS treatment for a minimum duration of 12 months (range, 12–41 months). The distribution of LBP VAS scores for the initial evaluation and the postspinal cord stimulator implantation is depicted in Figure 2. The mean VAS score for axial LBP prior to implantation of a spinal cord stimulator was 7.2±0.8 and 2.3±0.9 after the spinal cord stimulator implant (P=0.003, Figure 3). Of the two patients with concurrent LE pain, the mean VAS score for the LE pain was 7.5±1.5 prior to SCS and 0.0±0.0 after SCS (P=0.103). The subjective estimated relief of LBP provided by the surgically implanted spinal cord stimulator was 66%±9.3%. There were no surgical complications in this study.
Table 2.
Summary of demographic and clinical data on nine patients with exclusive or predominant low back pain treated with paddle spinal cord stimulation
| Category | Summarized data | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 3 | ||
| Female | 6 | ||
| Mean age in years (range) | 54.2±4.8 (33–75) | ||
| Diagnosis associated with LBP | |||
| FBSS | 4 | ||
| DJD | 3 | ||
| DDD | 4 | ||
| Fracture | 1 | ||
| Mean follow-up in months (range) | 19.9±3.2 (12–41) | ||
| Average SCS paddle lead implant spine level (range) | T9 (T6–T12) | ||
| Before SCS | After SCS | P-value | |
|
| |||
| LBP VAS, n=9 (range) | 7.2±0.8 (4–10) | 2.3±0.9 (0–9) | 0.003 |
| LE pain VAS, n=2 (range) | 7.5±1.5 (6–9) | 0.0±0.0 | 0.103 |
| Patient estimated % | 66.4%±9.3% | ||
| decrease of LBP (range) | (0–100) | ||
Abbreviations: DDD, degenerative disc disease; DJD, degenerative joint disease; FBSS, failed back surgery syndrome; LBP, low back pain; LE, lower extremity; SCS, spinal cord stimulation; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Figure 2.
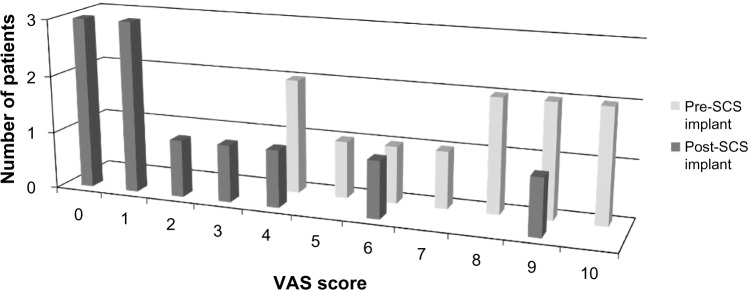
Distributions of LBP VAS scores recorded from patients pre- and post-SCS paddle lead implantation.
Note: Pre-SCS implantation scores (n=9) were recorded at the initial evaluation of the patients and post-SCS implantation scores (n=9) were recorded at least 12 months after the surgical SCS implantation.
Abbreviations: LBP, low back pain; SCS, spinal cord stimulation; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Figure 3.
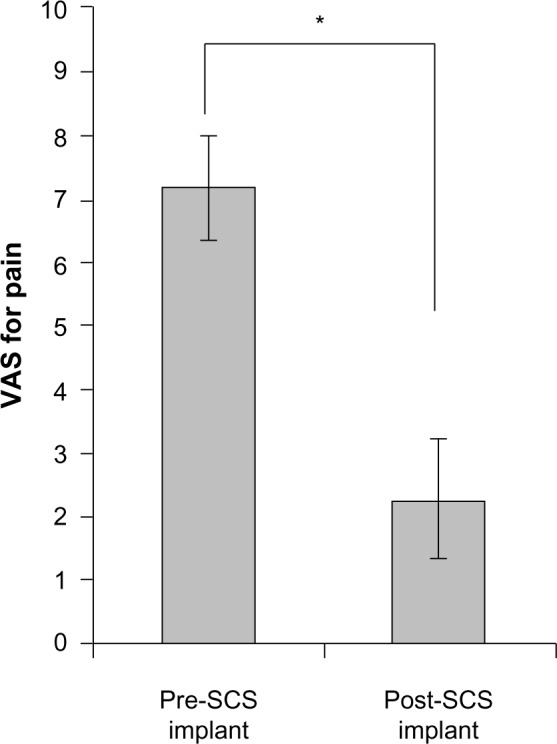
Mean LBP VAS scores recorded for pre- and post-SCS with paddle lead implantation.
Notes: Post-SCS VAS scores were documented at a minimum of 12 months after implantation (n=9). The error bars represent the standard error of the mean. *P=0.003.
Abbreviations: LBP, low back pain; SCS, spinal cord stimulation; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Discussion
SCS has been traditionally recognized as an effective treatment for chronic pain of neuropathic origin, including LE radiculopathy.1–7 Axial LBP pain, on the other hand, has been difficult to treat with SCS alone,1,2,4,8–12 possibly due to the nociceptive origin of the axial spine pain. Vascularized granulation tissue, for example, has been found to be associated with chronic lumbar disc disease and histologically contains nociceptors that may be the cause of the nociceptive nature of isolated LBP in this population.17 FBSS and chronic, unhealed fractures likely contain granulation tissue which may contribute to chronic LBP. This study demonstrates that SCS with surgical implantation of an epidural paddle lead can provide effective long-term pain control in patients with exclusive or predominant axial LBP. The etiology of axial LBP in this series was diverse including FBSS, degenerative joint the diverse utility of SCS as a treatment of axial LBP.
Of the nine patients enrolled in this series, eight patients (89%) reported ≥50% relief of chronic axial LBP at a mean follow-up evaluation at 19.9 months after a spinal cord stimulator implant. The 33-year-old patient that did not report benefit from the implanted spinal cord stimulator, Case 5, was the youngest patient of the series (Table 1). She reported that her LBP increased from 8 to 9 at a 24-month follow-up visit. The paddle lead was initially inserted into the epidural space at approximately the T9 level through a laminotomy at T10, but she did not receive pain relief in the distribution of her chronic LBP. Ultimately, the paddle lead was passed inferiorly through the T10 laminotomy and provided at least 50% pain relief during the intraoperative SCS trial (Figure 1). The failure of the SCS benefit at follow-up emphasizes the point that the T9 level may be the optimal level to place SCS leads for adequate coverage of the low back.2
SCS epidural leads can be generally classified into percutaneously placed linear leads or paddle leads surgically implanted through a laminotomy. SCS for relief of axial LBP has been demonstrated to be superior to conservative medical management alone in a recent multicenter, randomized trial,18 but SCS for axial LBP had been primarily evaluated with percutaneously placed epidural electrodes. Placement of three individual percutaneously placed linear leads creating a tripolar configuration, for instance, was shown to benefit a single case of FBSS utilizing a guarded cathode arrangement.19 Several larger case series studies demonstrate improved axial LBP with SCS using various configurations of percutaneously placed leads.12,20–22
Laminotomy for paddle lead placement is a more invasive procedure relative to placement of percutaneous leads, but laminotomy placed paddle leads have been shown to provide more durable pain coverage with less tendency to migrate.23–25 Newer hybrid lead designs that mimic the benefits of paddle leads can be placed percutaneously into the epidural space. A few recent studies have reported encouraging results using hybrid leads for treatment of axial LBP.14,26,27 Another study showed that SCS using a paddle lead with external radio-frequency stimulation benefited patients with predominantly axial LBP.28 Our current study shows that SCS with paddle leads connected to an implanted pulse generator provides sustained relief of axial LBP.
There are clear limitations to this current study. This was a small case series at a single institution, limiting the generalization of the findings. As with other studies evaluating SCS, this series was not blinded and did not include a control group to evaluate treatment relative to the natural progression of axial LBP, though in one study SCS has been shown superior to medical treatment alone.18 This current study also does not include standardized functional outcome scores for the patients at follow-up. The study does, however, add to the growing amount of evidence found in the literature that axial LBP can be successfully treated by SCS using paddle leads in a carefully selected population of patients.
Conclusion
SCS using a surgically implanted paddle electrode within the thoracic epidural space provides significant pain relief for chronic axial LBP and is a safe treatment modality. These findings support the development of a multicenter, prospective trial of SCS for axial LBP.
Acknowledgments
Dr Weinand has received research grant support from St Jude Medical. Dr Weinand developed the hypothesis for this study. Dr Stidd performed clinical study coordination and IRB administration. All authors participated in drafting the manuscript and data analysis. All authors have approved the submitted version of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Stojanovic MP, Abdi S. Spinal cord stimulation. Pain Physician. 2002;5(2):156–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oakley JC. Spinal cord stimulation in axial low back pain: solving the dilemma. Pain Medicine. 2006;7(S1):S58–S63. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kumar K, Nath R, Wyant GM. Treatment of chronic pain by epidural spinal cord stimulation: a 10-year experience. J Neurosurg. 1991;75(3):402–407. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.3.0402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burchiel KJ, Anderson VC, Brown FD, et al. Prospective, multicenter study of spinal cord stimulation for relief of chronic back and extremity pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21(23):2786–2794. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199612010-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cahana A, Mavrocordatos P, Geurts JW, Groen GJ. Do minimally invasive procedures have a place in the treatment of chronic low back pain? Expert Rev Neurother. 2004;4(3):479–490. doi: 10.1586/14737175.4.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rainov NG, Demmel W, Heidecke V. Dual electrode spinal cord stimulation in chronic leg and back pain. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;97(Pt 1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-33079-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taylor RJ, Taylor RS. Spinal cord stimulation for failed back surgery syndrome: a decision-analytic model and cost-effectiveness analysis. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2005;21(3):351–358. doi: 10.1017/s0266462305050464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Slavin KV, Burchiel KJ, Anderson VC, Cooke B. Efficacy of transverse tripolar stimulation for relief of chronic low back pain: results of a single center. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1999;73(1–4):126–130. doi: 10.1159/000029770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.North RB, Ewend MG, Lawton MT, Kidd DH, Piantadosi S. Failed back surgery syndrome: 5-year follow-up after spinal cord stimulator implantation. Neurosurgery. 1991;28(5):692–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.North RB, Ewend MG, Lawton MT, Piantadosi S. Spinal cord stimulation for chronic, intractable pain: superiority of “multi-channel” devices. Pain. 1991;44(2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90125-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dario A, Fortini G, Bertollo D, Bacuzzi A, Grizzetti C, Cuffari S. Treatment of failed back surgery syndrome. Neuromodulation. 2001;4(3):105–110. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1403.2001.00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.North RB, Kidd DH, Olin J, et al. Spinal cord stimulation for axial low back pain: a prospective, controlled trial comparing dual with single percutaneous electrodes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30(12):1412–1418. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000166502.05449.a8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Krames E. Spinal Cord Stimulation: Indications, Mechanism of Action, and Efficacy. Curr Rev Pain. 1999;3(6):419–426. doi: 10.1007/s11916-999-0068-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kinfe TM, Schu S, Quack FJ, Wille C, Vesper J. Percutaneous implanted paddle lead for spinal cord stimulation: technical considerations and long-term follow-up. Neuromodulation. 2012;15(4):402–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2012.00473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.North RB, Nigrin DJ, Fowler KR, Szymanski RE, Piantadosi S. Automated ‘pain drawing’ analysis by computer-controlled, patient-interactive neurological stimulation system. Pain. 1992;50(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90111-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Weinand ME, Madhusudan H, Davis B, Melgar M. Acute vs prolonged screening for spinal cord stimulation in chronic pain. Neuromodulation. 2003;6(1):15–19. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1403.2003.03002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Peng B, Wu W, Hou S, Li P, Zhang C, Yang Y. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L, et al. Spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management for neuropathic pain: a multicentre randomised controlled trial in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Pain. 2007;132(1–2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.07.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Buvanendran A, Lubenow TJ. Efficacy of transverse tripolar spinal cord stimulator for the relief of chronic low back pain from failed back surgery. Pain Physician. 2008;11(3):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ohnmeiss DD, Rashbaum RF. Patient satisfaction with spinal cord stimulation for predominant complaints of chronic, intractable low back pain. Spine J. 2001;1(5):358–363. doi: 10.1016/s1529-9430(01)00083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mironer YE, Satterthwaite JR, Lewis EM, et al. Efficacy of a Single, Percutaneous, Across Midline, Octrode® Lead Using a “Midline Anchoring” Technique in the Treatment of Chronic Low Back and/or Lower Extremity Pain: A Retrospective Study. Neuromodulation. 2008;11(4):286–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2008.00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Van Buyten JP, Van Zundert J, Milbouw G. Treatment of failed back surgery syndrome patients with low back and leg pain: a pilot study of a new dual lead spinal cord stimulation system. Neuromodulation. 1999;2(4):258–265. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1403.1999.00258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Villavicencio AT, Leveque JC, Rubin L, Bulsara K, Gorecki JP. Laminectomy versus percutaneous electrode placement for spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery. 2000;46(2):399–405. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200002000-00025. discussion 405–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.North RB, Kidd DH, Olin JC, Sieracki JM. Spinal cord stimulation electrode design: prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing percutaneous and laminectomy electrodes-part I: technical outcomes. Neurosurgery. 2002;51(2):381–389. discussion 389–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.North RB, Kidd DH, Petrucci L, Dorsi MJ. Spinal cord stimulation electrode design: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing percutaneous with laminectomy electrodes: part II-clinical outcomes. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(5):990–996. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000180030.00167.b9. discussion 990–996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vonhögen LH, Vancamp T, Vanneste S, et al. Percutaneously implanted plates in failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS) Neuromodulation. 2011;14(4):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2011.00368.x. discussion 324–325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.de Vos CC, Dijkstra C, Lenders MW, Holsheimer J. Spinal cord stimulation with hybrid lead relieves pain in low back and legs. Neuromodulation. 2012;15(2):118–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2011.00404.x. discussion 123–. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barolat G, Oakley JC, Law JD, North RB, Ketcik B, Sharan A. Epidural spinal cord stimulation with a multiple electrode paddle lead is effective in treating intractable low back pain. Neuromodulation. 2001;4(2):59–66. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1403.2001.00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


