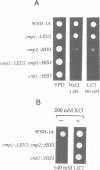
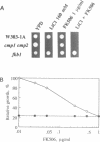
Abstract
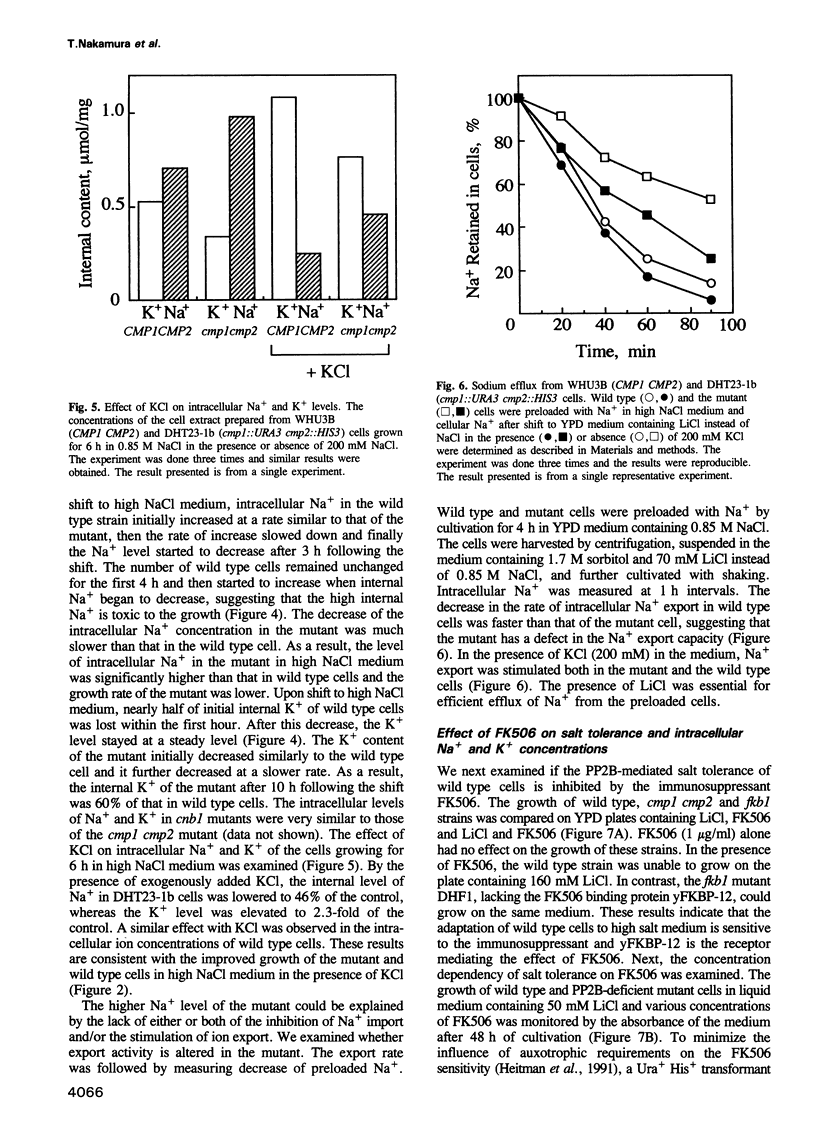
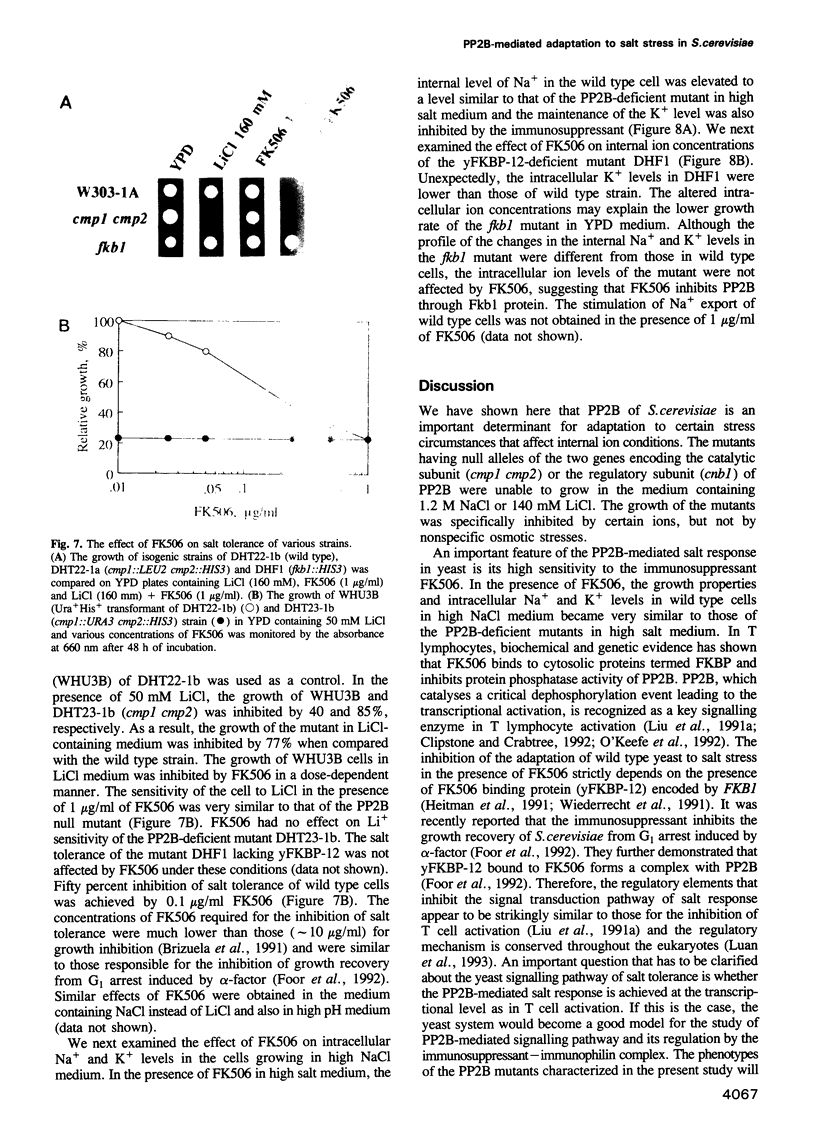
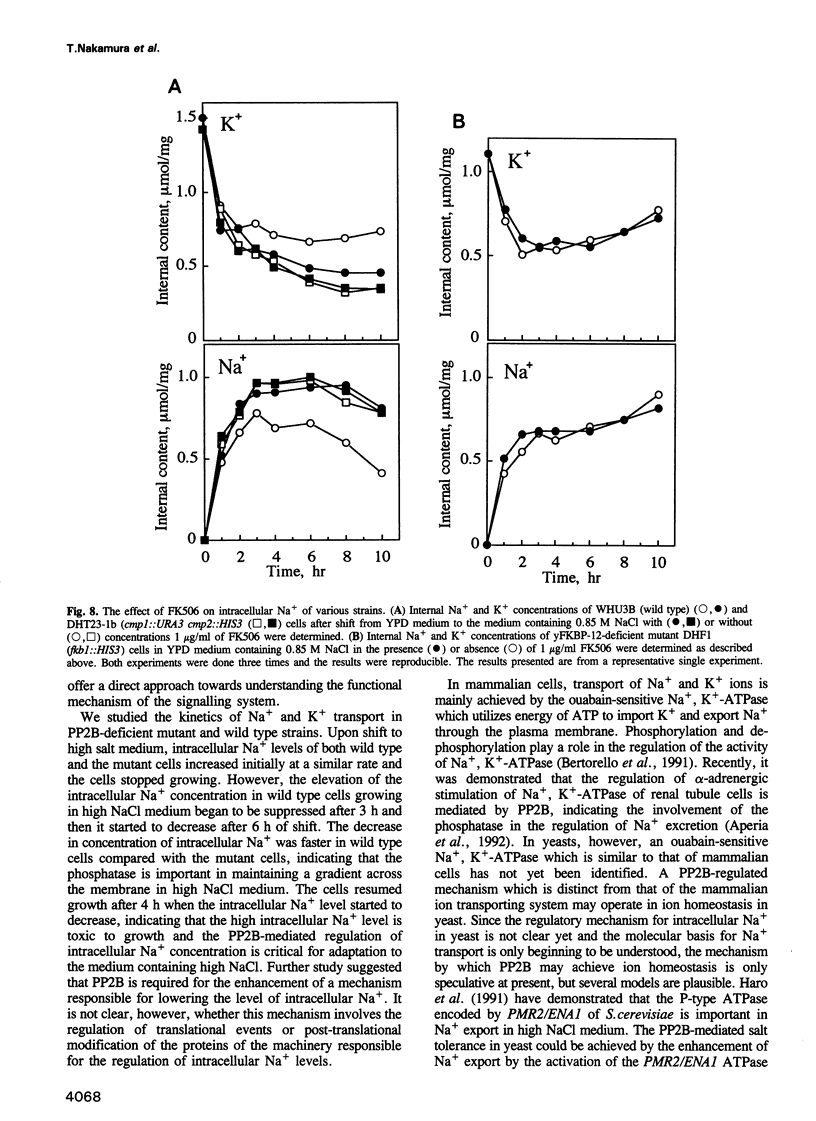
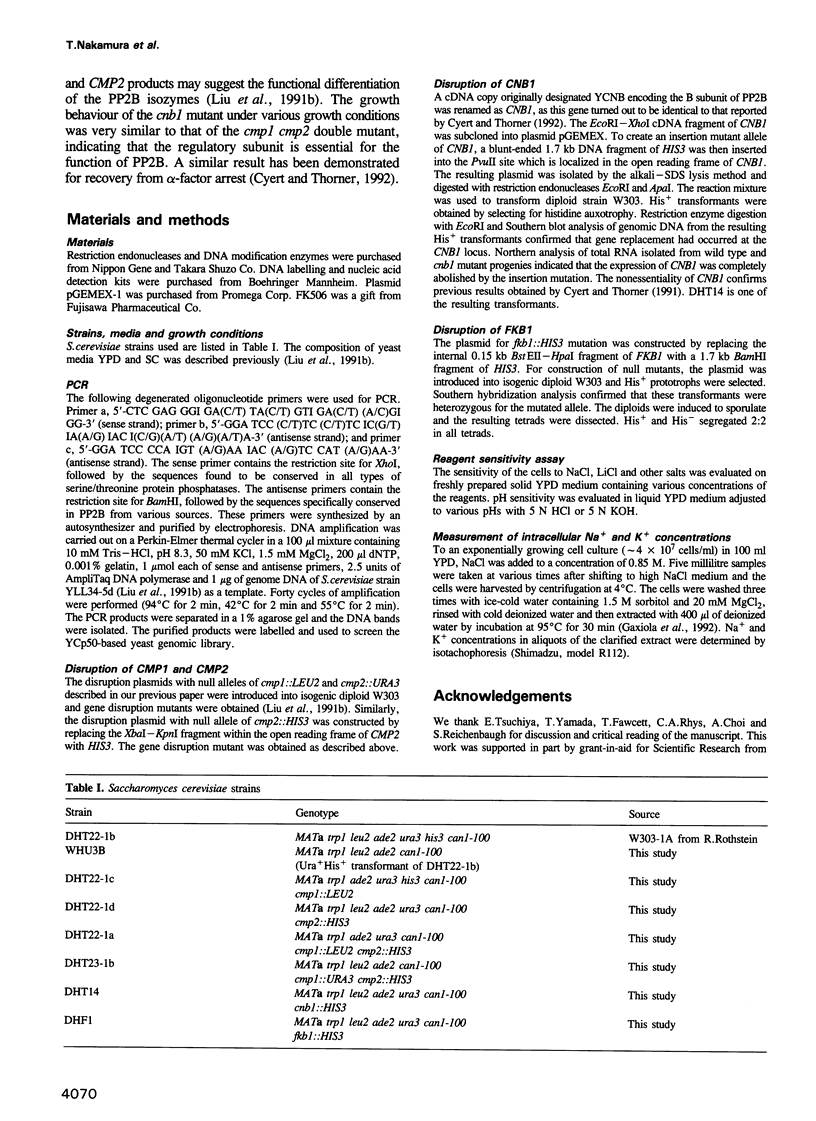
To assess the physiological function of Ca(2+)-dependent protein phosphatase (PP2B) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the phenotypes of PP2B-deficient mutants were investigated. Although PP2B was dispensable for growth under normal conditions, the mutations did, however, cause growth inhibition under certain stress circumstances. The growth of the mutants was inhibited by NaCl and LiCl, but not by KCl, CaCl2, MgCl2 or nonspecific osmotic stresses. Upon shift to high NaCl medium, intracellular Na+ levels of both wild type yeast and the mutants initially increased at a comparable rate. However, internal Na+ in wild type cells started to decline more rapidly than the mutant cells during cultivation in high NaCl medium, indicating that PP2B is important in maintaining a gradient across the membrane. The protection against salt stress was achieved, at least in part, by the stimulation of Na+ export. The maintenance of a high level of internal K+ in high NaCl medium was also PP2B-dependent. In the presence of the immunosuppressant FK506, the growth behaviour and intracellular Na+ and K+ of wild type cells in high NaCl medium became very similar to those of the PP2B-deficient mutant in a manner dependent on the presence of the FK506 binding protein.
Full text
PDF
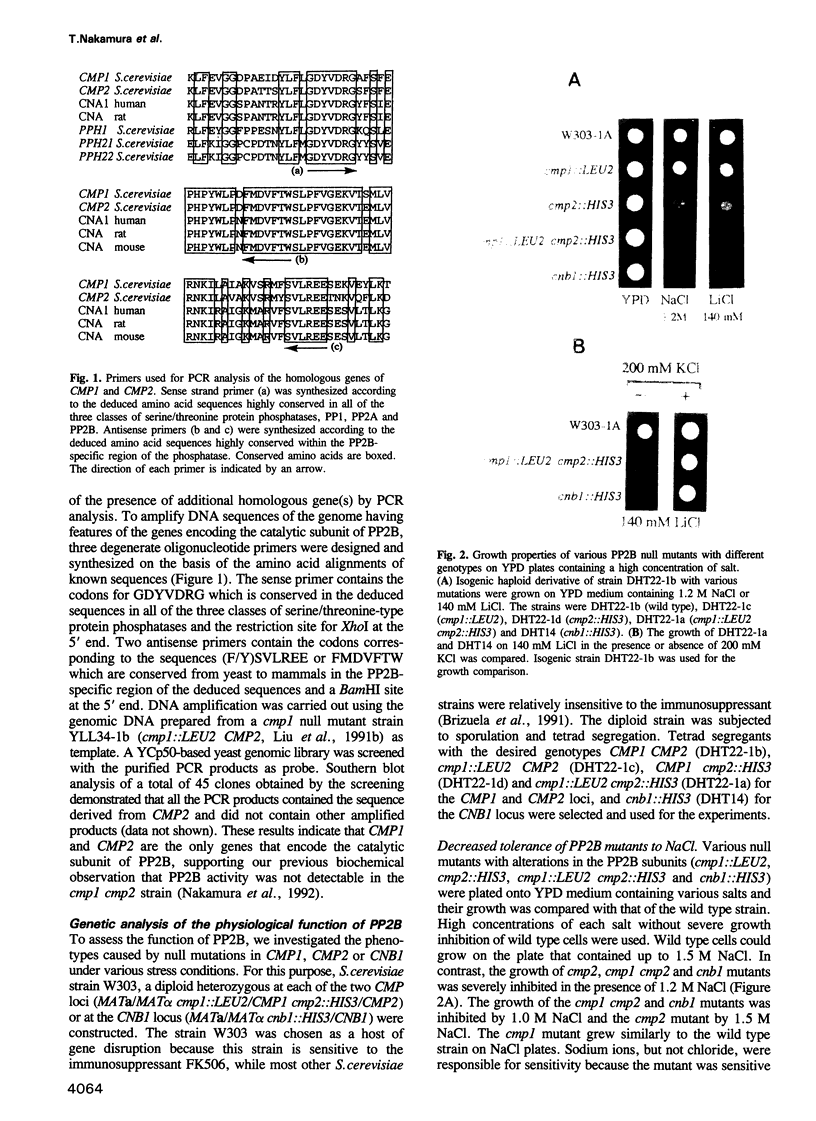
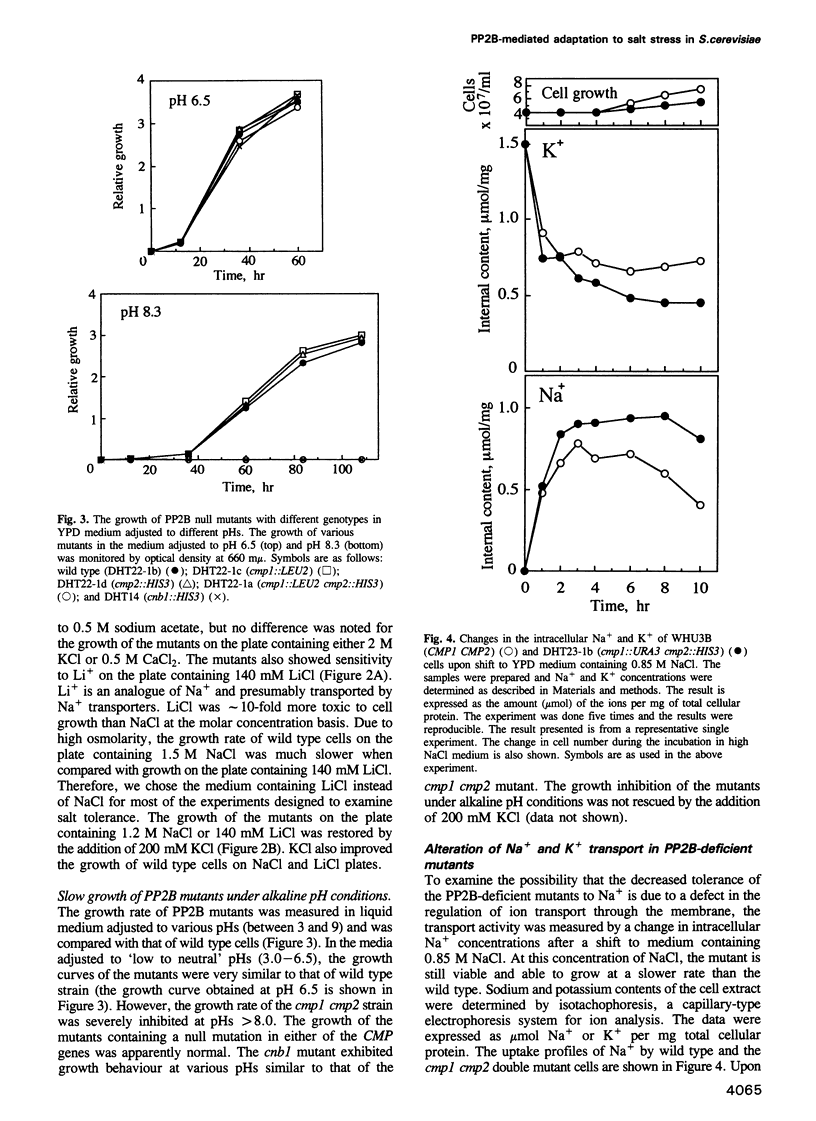


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aperia A., Ibarra F., Svensson L. B., Klee C., Greengard P. Calcineurin mediates alpha-adrenergic stimulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7394–7397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Aperia A., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11359–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Chrebet G., Bostian K. A., Parent S. A. Antifungal properties of the immunosuppressant FK-506: identification of an FK-506-responsive yeast gene distinct from FKB1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4616–4626. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone N. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):695–697. doi: 10.1038/357695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kunisawa R., Kaim D., Thorner J. Yeast has homologs (CNA1 and CNA2 gene products) of mammalian calcineurin, a calmodulin-regulated phosphoprotein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7376–7380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Thorner J. Regulatory subunit (CNB1 gene product) of yeast Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphoprotein phosphatases is required for adaptation to pheromone. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3460–3469. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foor F., Parent S. A., Morin N., Dahl A. M., Ramadan N., Chrebet G., Bostian K. A., Nielsen J. B. Calcineurin mediates inhibition by FK506 and cyclosporin of recovery from alpha-factor arrest in yeast. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):682–684. doi: 10.1038/360682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaxiola R., de Larrinoa I. F., Villalba J. M., Serrano R. A novel and conserved salt-induced protein is an important determinant of salt tolerance in yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3157–3164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haro R., Garciadeblas B., Rodríguez-Navarro A. A novel P-type ATPase from yeast involved in sodium transport. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81280-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Movva N. R., Hall M. N. Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):905–909. doi: 10.1126/science.1715094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia Z. P., McCullough N., Martel R., Hemmingsen S., Young P. G. Gene amplification at a locus encoding a putative Na+/H+ antiporter confers sodium and lithium tolerance in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1631–1640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Draetta G. F., Hubbard M. J. Calcineurin. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:149–200. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Tanaka H., Mukai H., Chang C. D., Hiraga K., Miyakawa T., Tanaka C. cDNA cloning of a calcineurin B homolog in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1159–1163. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Ishii S., Tokai M., Tsutsumi H., Ohki O., Akada R., Tanaka K., Tsuchiya E., Fukui S., Miyakawa T. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes (CMP1 and CMP2) encoding calmodulin-binding proteins homologous to the catalytic subunit of mammalian protein phosphatase 2B. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;227(1):52–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00260706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luan S., Li W., Rusnak F., Assmann S. M., Schreiber S. L. Immunosuppressants implicate protein phosphatase regulation of K+ channels in guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2202–2206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tsutsumi H., Mukai H., Kuno T., Miyakawa T. Ca2+/calmodulin-activated protein phosphatase (PP2B) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PP2B activity is not essential for growth. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80749-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Tamura J., Kincaid R. L., Tocci M. J., O'Neill E. A. FK-506- and CsA-sensitive activation of the interleukin-2 promoter by calcineurin. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):692–694. doi: 10.1038/357692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Navarro A., Ortega M. D. The mechanism of sodium efflux in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H. K., Antebi A., Fink G. R., Buckley C. M., Dorman T. E., LeVitre J., Davidow L. S., Mao J. I., Moir D. T. The yeast secretory pathway is perturbed by mutations in PMR1, a member of a Ca2+ ATPase family. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesser A., Ulaszewski S., Ghislain M., Goffeau A. A second transport ATPase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19480–19487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Brizuela L., Elliston K., Sigal N. H., Siekierka J. J. FKB1 encodes a nonessential FK 506-binding protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and contains regions suggesting homology to the cyclophilins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]