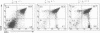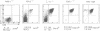Abstract
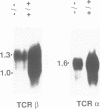
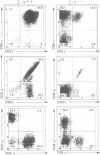
The CD3-zeta and CD3-eta polypeptides are two of the components of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) which contribute to its efficient cell surface expression and account for part of its transducing capability. CD3-zeta and CD3-eta result from the alternative splicing of a single gene designated CD3-zeta/eta. To evaluate the role of these subunits during T cell development, we have produced mice with a disrupted CD3-zeta/eta gene. The analysis of thymocyte populations from the CD3-zeta/eta-/- homozygous mutant mice revealed that they have a profound reduction in the surface levels of TCR complexes and that the products of the CD3-zeta/eta gene appear to be needed for the efficient generation and/or survival of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Despite the almost total absence of mature single positive thymocytes, the lymph nodes from zeta/eta-/- mice were found to contain unusual CD4+CD8- and CD4-CD8+ single positive cells which were CD3-. In contrast to the situation observed in the thymus, the thymus-independent gut intraepithelial lymphocytes present in zeta/eta-/- mice do express TCR complexes on their surface and these are associated with Fc epsilon RI gamma homodimers. These results establish an essential role for the CD3-zeta/eta gene products during intrathymic T cell differentiation and further emphasize the difference between conventional T cells and thymus-independent gut intraepithelial lymphocytes.
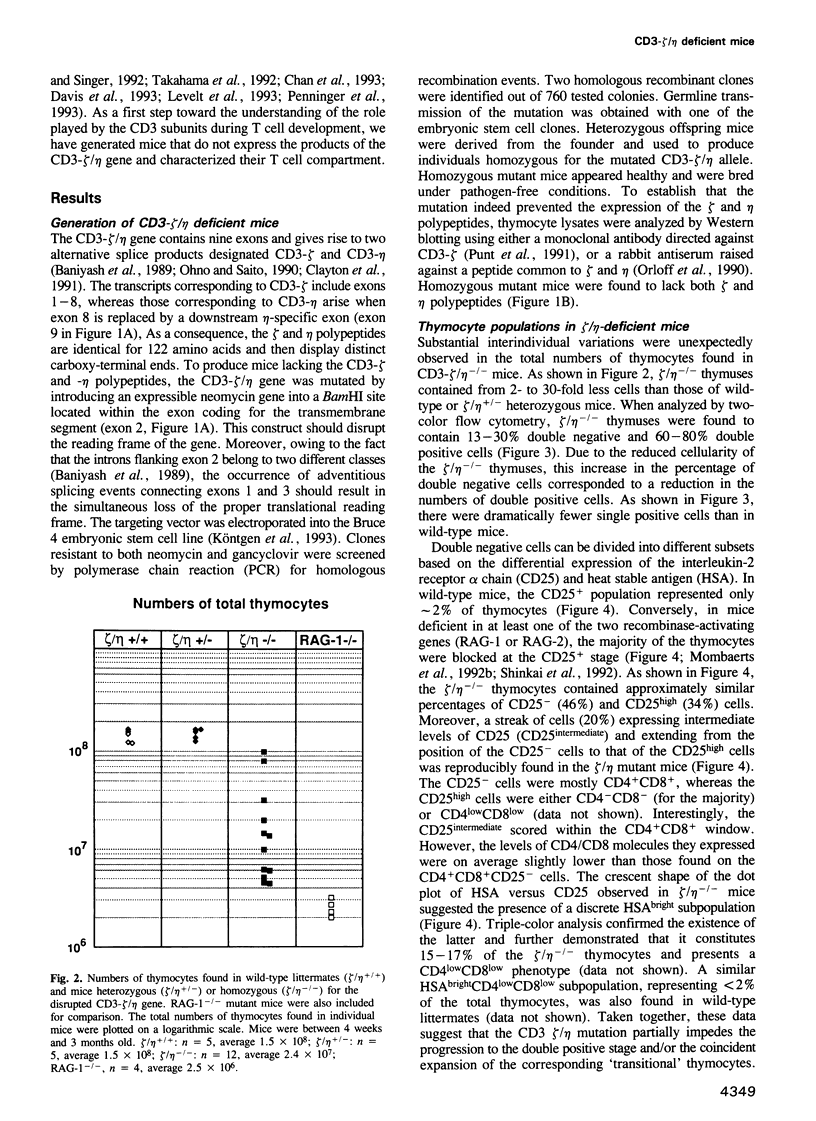
Full text
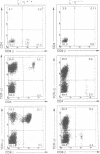
PDF

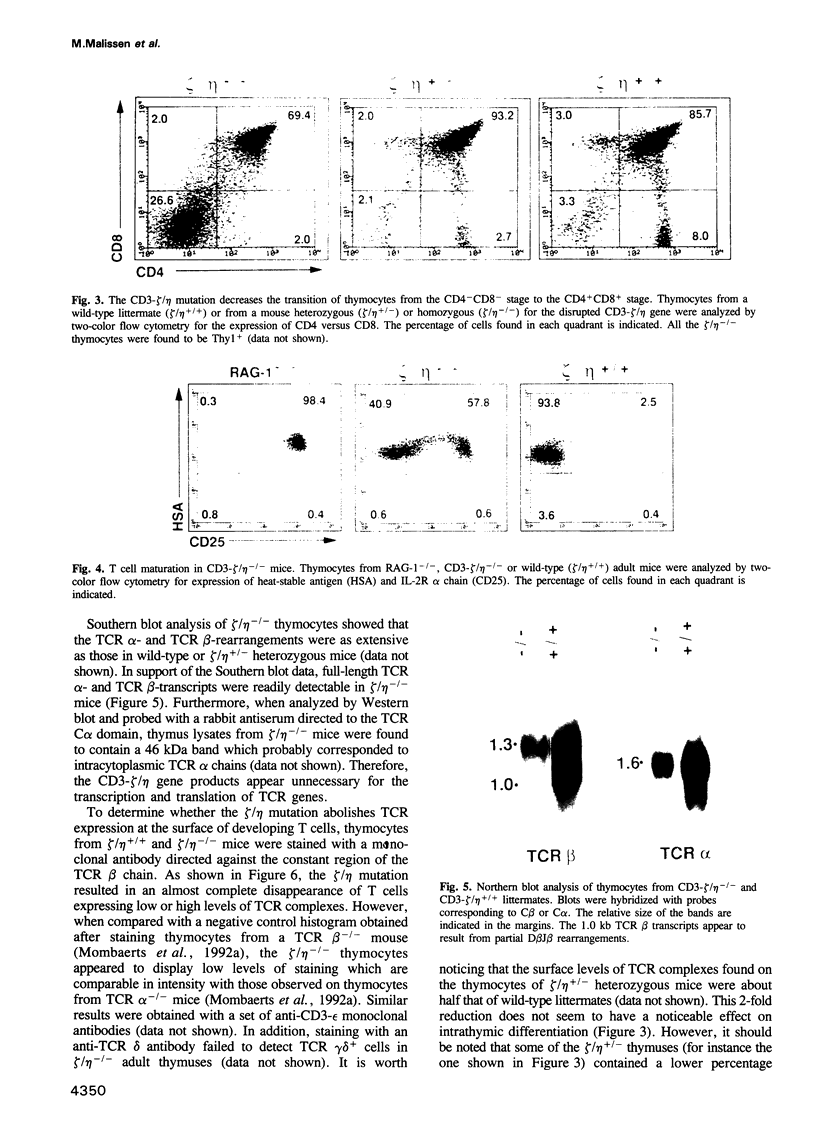
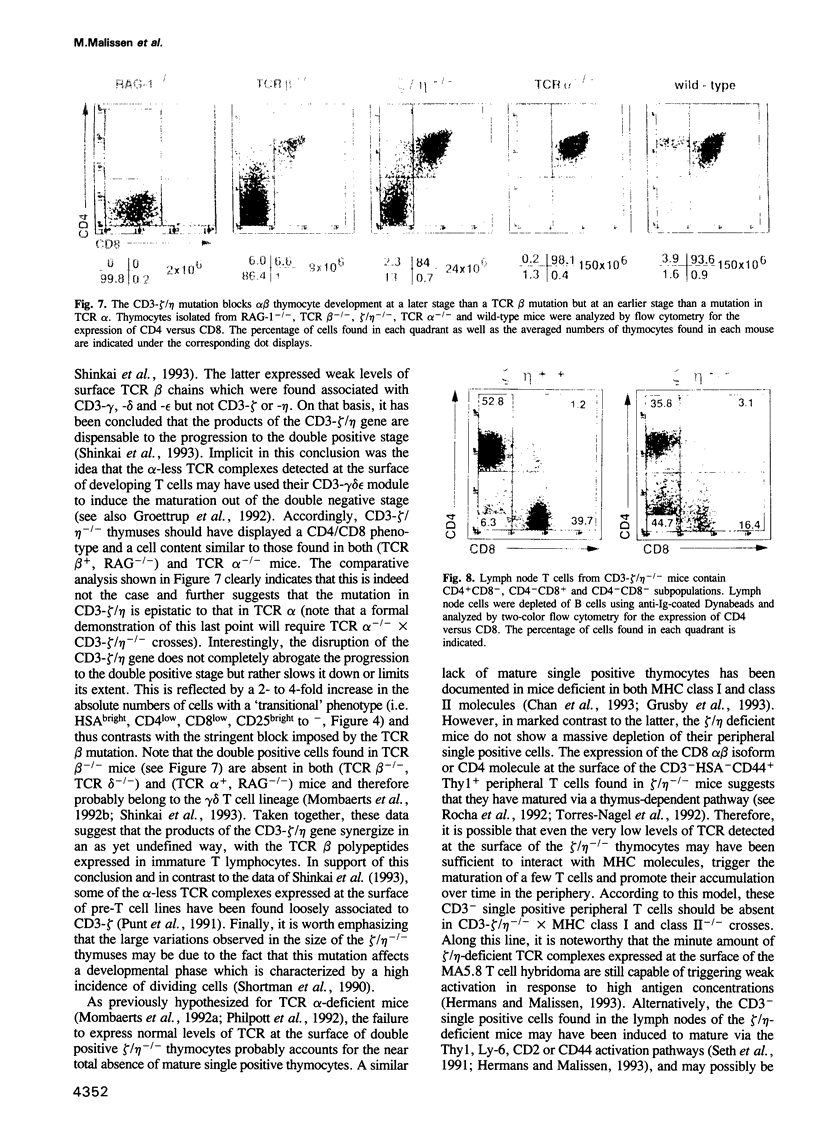
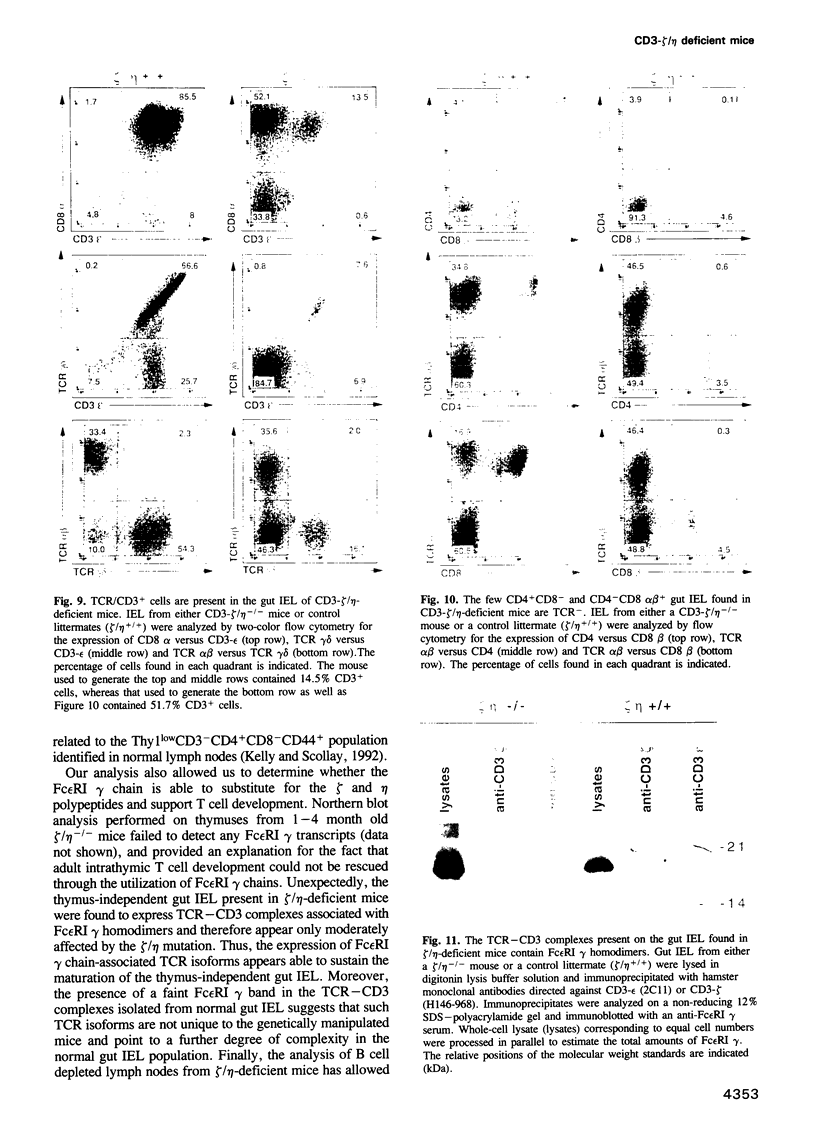


Images in this article
Selected References
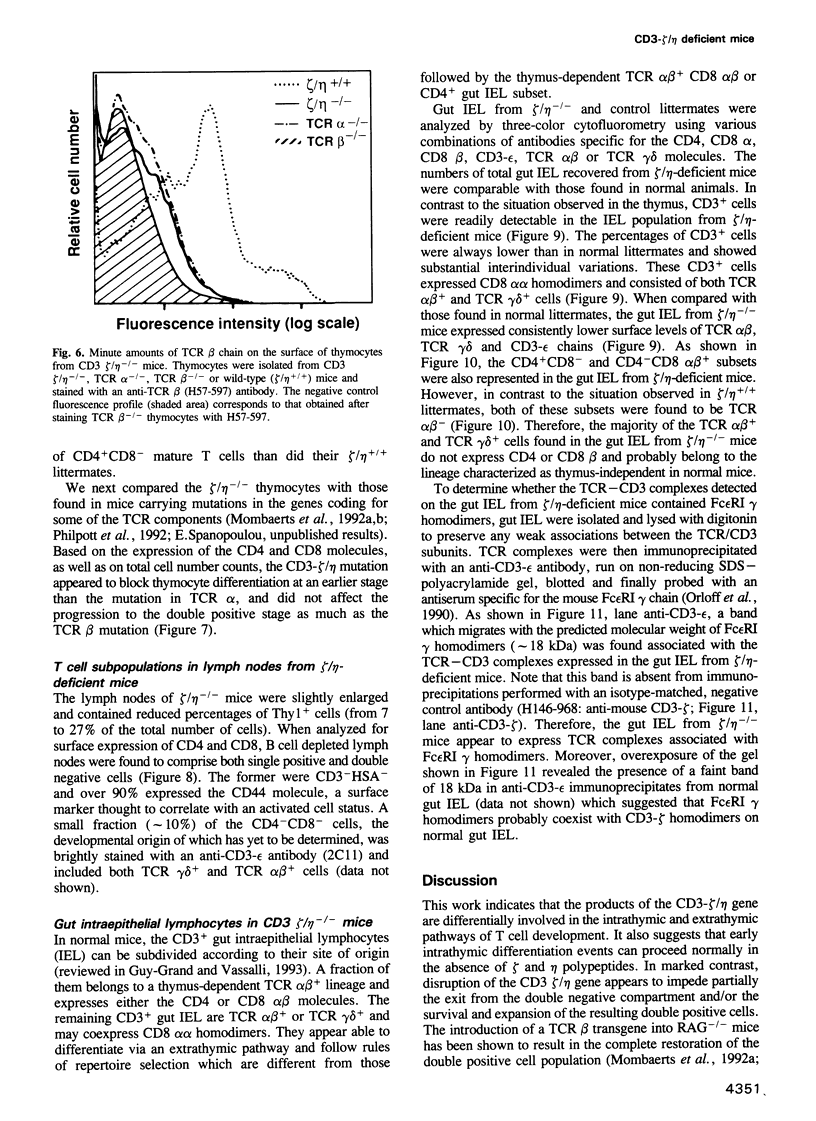
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. J., Abraham K. M., Nakayama T., Singer A., Perlmutter R. M. Inhibition of T-cell receptor beta-chain gene rearrangement by overexpression of the non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase p56lck. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4877–4886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniyash M., Hsu V. W., Seldin M. F., Klausner R. D. The isolation and characterization of the murine T cell antigen receptor zeta chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13252–13257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A., McConkey D. J., Howard F. D., Clayton L. K., Novick D., Koyasu S., Reinherz E. L. Differential signal transduction via T-cell receptor CD3 zeta 2, CD3 zeta-eta, and CD3 eta 2 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3842–3846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Schwartz R. H. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells acquire specific lymphokine secretion potentials during thymic maturation. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):68–71. doi: 10.1038/353068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc D., Bron C., Gabert J., Letourneur F., MacDonald H. R., Malissen B. Gene transfer of the Ly-3 chain gene of the mouse CD8 molecular complex: co-transfer with the Ly-2 polypeptide gene results in detectable cell surface expression of the Ly-3 antigenic determinants. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):613–619. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgulya P., Kishi H., Uematsu Y., von Boehmer H. Exclusion and inclusion of alpha and beta T cell receptor alleles. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):529–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90453-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Iwashima M., Turck C. W., Weiss A. ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Cosgrove D., Waltzinger C., Benoist C., Mathis D. Another view of the selective model of thymocyte selection. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90225-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., D'Adamio L., Howard F. D., Sieh M., Hussey R. E., Koyasu S., Reinherz E. L. CD3 eta and CD3 zeta are alternatively spliced products of a common genetic locus and are transcriptionally and/or post-transcriptionally regulated during T-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. B., Killeen N., Crooks M. E., Raulet D., Littman D. R. Evidence for a stochastic mechanism in the differentiation of mature subsets of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90226-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groettrup M., Baron A., Griffiths G., Palacios R., von Boehmer H. T cell receptor (TCR) beta chain homodimers on the surface of immature but not mature alpha, gamma, delta chain deficient T cell lines. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2735–2745. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groettrup M., von Boehmer H. T cell receptor beta chain dimers on immature thymocytes from normal mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jun;23(6):1393–1396. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Auchincloss H., Jr, Lee R., Johnson R. S., Spencer J. P., Zijlstra M., Jaenisch R., Papaioannou V. E., Glimcher L. H. Mice lacking major histocompatibility complex class I and class II molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Cerf-Bensussan N., Malissen B., Malassis-Seris M., Briottet C., Vassalli P. Two gut intraepithelial CD8+ lymphocyte populations with different T cell receptors: a role for the gut epithelium in T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Vassalli P. Gut intraepithelial T lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Apr;5(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90012-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue I., Trucy J., McCoy C., Couez D., Malissen B., Malissen M. A novel type of aberrant T cell receptor alpha-chain gene rearrangement. Implications for allelic exclusion and the V-J recombination process. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4410–4419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes D. J., Tonegawa S. Surface expression of alternative forms of the TCR/CD3 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10619–10623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. A., Scollay R. Seeding of neonatal lymph nodes by T cells and identification of a novel population of CD3-CD4+ cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):329–334. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi H., Borgulya P., Scott B., Karjalainen K., Traunecker A., Kaufman J., von Boehmer H. Surface expression of the beta T cell receptor (TCR) chain in the absence of other TCR or CD3 proteins on immature T cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., D'Adamio L., Arulanandam A. R., Abraham S., Clayton L. K., Reinherz E. L. T cell receptor complexes containing Fc epsilon RI gamma homodimers in lieu of CD3 zeta and CD3 eta components: a novel isoform expressed on large granular lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):203–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köntgen F., Süss G., Stewart C., Steinmetz M., Bluethmann H. Targeted disruption of the MHC class II Aa gene in C57BL/6 mice. Int Immunol. 1993 Aug;5(8):957–964. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Malissen B. Derivation of a T cell hybridoma variant deprived of functional T cell receptor alpha and beta chain transcripts reveals a nonfunctional alpha-mRNA of BW5147 origin. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2269–2274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levelt C. N., Ehrfeld A., Eichmann K. Regulation of thymocyte development through CD3. I. Timepoint of ligation of CD3 epsilon determines clonal deletion or induction of developmental program. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):707–716. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Transmembrane signalling through the T-cell-receptor-CD3 complex. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Trucy J., Letourneur F., Rebaï N., Dunn D. E., Fitch F. W., Hood L., Malissen B. A T cell clone expresses two T cell receptor alpha genes but uses one alpha beta heterodimer for allorecognition and self MHC-restricted antigen recognition. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick C. A., Dudley E. C., Viney J. L., Owen M. J., Hayday A. C. Rearrangement and diversity of T cell receptor beta chain genes in thymocytes: a critical role for the beta chain in development. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90138-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Sutherland L. C., Adra C. N., Leclair B., Rudnicki M. A., Jardine K. The mouse Pgk-1 gene promoter contains an upstream activator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5755–5761. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi H., O'Shea J. J., Longo D. L., Loeffler C. M., McVicar D. W., Ochoa A. C. Alterations in signal transduction molecules in T lymphocytes from tumor-bearing mice. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1795–1798. doi: 10.1126/science.1465616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Clarke A. R., Rudnicki M. A., Iacomini J., Itohara S., Lafaille J. J., Wang L., Ichikawa Y., Jaenisch R., Hooper M. L. Mutations in T-cell antigen receptor genes alpha and beta block thymocyte development at different stages. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):225–231. doi: 10.1038/360225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Iacomini J., Johnson R. S., Herrup K., Tonegawa S., Papaioannou V. E. RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Loh D. Y. No requirement for p56lck in the antigen-stimulated clonal deletion of thymocytes. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):94–96. doi: 10.1126/science.1621101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Ueda Y., Yamada H., Shores E. W., Singer A., June C. H. In vivo calcium elevations in thymocytes with T cell receptors that are specific for self ligands. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.1621102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Saito T. CD3 zeta and eta chains are produced by alternative splicing from a common gene. Int Immunol. 1990;2(11):1117–1119. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.11.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff D. G., Ra C. S., Frank S. J., Klausner R. D., Kinet J. P. Family of disulphide-linked dimers containing the zeta and eta chains of the T-cell receptor and the gamma chain of Fc receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):189–191. doi: 10.1038/347189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossendorp F., Jacobs H., van der Horst G., de Vries E., Berns A., Borst J. T cell receptor-alpha beta lacking the beta-chain V domain can be expressed at the cell surface but prohibits T cell maturation. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3714–3722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penninger J., Kishihara K., Molina T., Wallace V. A., Timms E., Hedrick S. M., Mak T. W. Requirement for tyrosine kinase p56lck for thymic development of transgenic gamma delta T cells. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.8469988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpott K. L., Viney J. L., Kay G., Rastan S., Gardiner E. M., Chae S., Hayday A. C., Owen M. J. Lymphoid development in mice congenitally lacking T cell receptor alpha beta-expressing cells. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1448–1452. doi: 10.1126/science.1604321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punt J. A., Kubo R. T., Saito T., Finkel T. H., Kathiresan S., Blank K. J., Hashimoto Y. Surface expression of a T cell receptor beta (TCR-beta) chain in the absence of TCR-alpha, -delta, and -gamma proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):775–783. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., Vassalli P., Guy-Grand D. The extrathymic T-cell development pathway. Immunol Today. 1992 Nov;13(11):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90074-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald H. R., Arulanandam A. R., Koyasu S., Reinherz E. L. The high affinity Fc epsilon receptor gamma subunit (Fc epsilon RI gamma) facilitates T cell receptor expression and antigen/major histocompatibility complex-driven signaling in the absence of CD3 zeta and CD3 eta. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15974–15978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D. Tyrosine kinases and tyrosine-based activation motifs. Current research on activation via the T cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24913–24916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Weissman A. M., Robey F. A., Berkower I., Klausner R. D. Characterization of an anti-peptide antibody that recognizes the murine analogue of the human T cell antigen receptor-T3 delta-chain. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3254–3258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gote L., Nagarkatti M., Nagarkatti P. S. T-cell-receptor-independent activation of cytolytic activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes mediated through CD44 and gp90MEL-14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7877–7881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Koyasu S., Nakayama K., Murphy K. M., Loh D. Y., Reinherz E. L., Alt F. W. Restoration of T cell development in RAG-2-deficient mice by functional TCR transgenes. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):822–825. doi: 10.1126/science.8430336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Rathbun G., Lam K. P., Oltz E. M., Stewart V., Mendelsohn M., Charron J., Datta M., Young F., Stall A. M. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):855–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shores E. W., Nakayama T., Wiest D. L., Takahama Y., Sharrow S., Singer A. Structurally distinct T cell receptor complexes on developmentally distinct T cell populations in severe combined immunodeficiency mice expressing a TCR beta transgene. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1263–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K. Cellular aspects of early T-cell development. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Apr;4(2):140–146. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90003-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Egerton M., Spangrude G. J., Scollay R. The generation and fate of thymocytes. Semin Immunol. 1990 Jan;2(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Schuetze S., Vanek M., Wagner E. F. Expression of retroviral vectors in transgenic mice obtained by embryo infection. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):383–388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swat W., Dessing M., Baron A., Kisielow P., von Boehmer H. Phenotypic changes accompanying positive selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2367–2372. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama Y., Shores E. W., Singer A. Negative selection of precursor thymocytes before their differentiation into CD4+CD8+ cells. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.1357752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama Y., Singer A. Post-transcriptional regulation of early T cell development by T cell receptor signals. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.1439838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Nagel N., Kraus E., Brown M. H., Tiefenthaler G., Mitnacht R., Williams A. F., Hünig T. Differential thymus dependence of rat CD8 isoform expression. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2841–2848. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turka L. A., Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Chun J. J., Gorka C., Lee K., McCormack W. T., Thompson C. B. Thymocyte expression of RAG-1 and RAG-2: termination by T cell receptor cross-linking. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):778–781. doi: 10.1126/science.1831564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Kisielow P. Lymphocyte lineage commitment: instruction versus selection. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):207–208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90220-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]