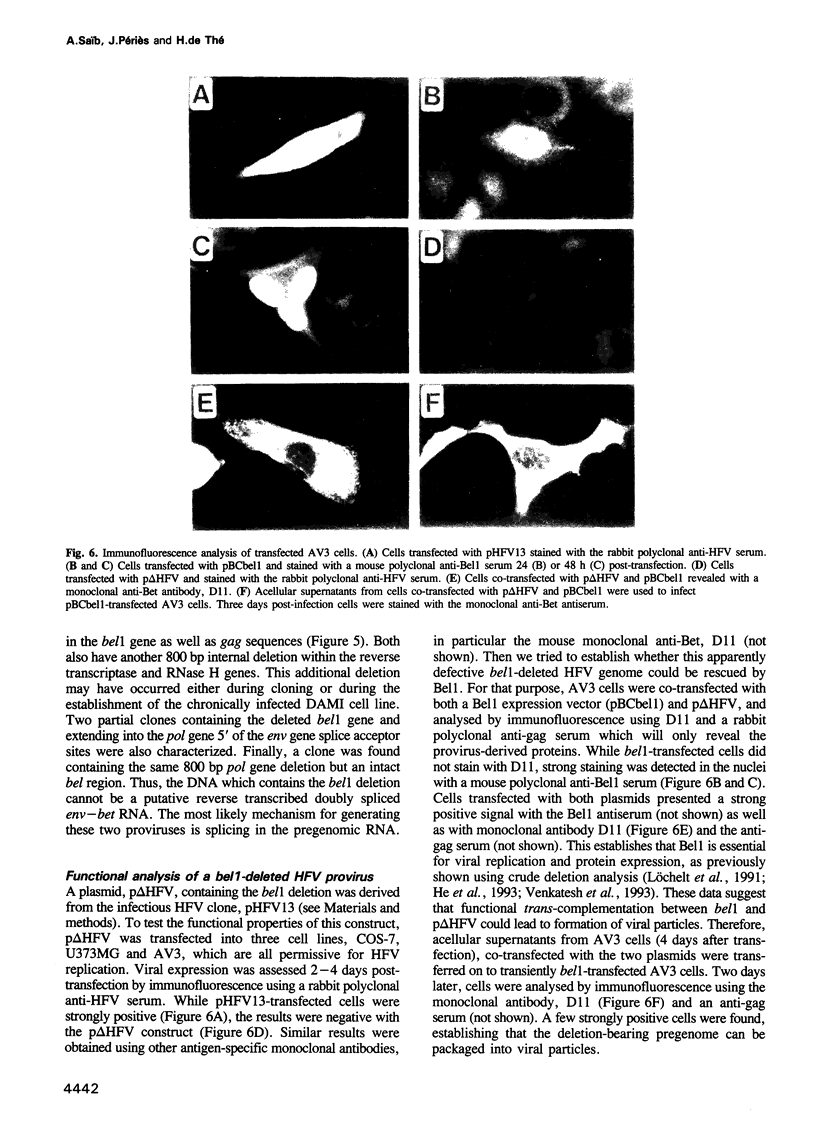
Abstract
Foamy viruses are a group of retroviruses of complex structure which were thought to be non-pathogenic. The recent demonstration of neurological diseases in mice transgenic for human foamy virus (HFV) and the high prevalence of HFV sequences in Graves' disease question this idea. By PCR, we have detected HFV sequences with a non-random deletion in the bel1 transactivator gene in other autoimmune conditions. Sequence analysis revealed that this deleted area corresponds to the excision of a known intron in bet, one of HFV's regulatory genes. The same phenomenon was observed in both acute and chronic infections, in vitro or in vivo, although the deleted forms were distinctly more abundant in chronic states. The viral DNA containing the bel1 deletion is apparently part of an otherwise complete genome, strongly suggesting that this provirus derives from the reverse transcription of a spliced pregenomic RNA. Bel1-spliced provirus was shown to be defective when transfected into permissive cells. However, co-expression with the Bel1 transactivator led to functional trans-complementation and formation of viral particles. Splicing of the genome may be an important factor in HFV biology: genomes with the deletion may either interfere with wild-type virus expression or alter host cell functions through background expression of viral regulatory proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguzzi A., Bothe K., Anhauser I., Horak I., Rethwilm A., Wagner E. F. Expression of human foamy virus is differentially regulated during development in transgenic mice. New Biol. 1992 Mar;4(3):225–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berneman Z. N., Gartenhaus R. B., Reitz M. S., Jr, Blattner W. A., Manns A., Hanchard B., Ikehara O., Gallo R. C., Klotman M. E. Expression of alternatively spliced human T-lymphotropic virus type I pX mRNA in infected cell lines and in primary uncultured cells from patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and healthy carriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodor J., Svoboda J. The LTR, v-src, LTR provirus generated in the mammalian genome by src mRNA reverse transcription and integration. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):1015–1018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.1015-1018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothe K., Aguzzi A., Lassmann H., Rethwilm A., Horak I. Progressive encephalopathy and myopathy in transgenic mice expressing human foamy virus genes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.1650034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciminale V., Pavlakis G. N., Derse D., Cunningham C. P., Felber B. K. Complex splicing in the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) family of retroviruses: novel mRNAs and proteins produced by HTLV type I. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1737–1745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1737-1745.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M. Spumaviruses: a group of complex retroviruses. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(8):739–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He F., Sun J. D., Garrett E. D., Cullen B. R. Functional organization of the Bel-1 trans activator of human foamy virus. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1896–1904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1896-1904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Takatsuji H., Ubasawa A., Ikeda J. E. Site-specific deletion in cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: possible involvement of RNA splicing and reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1673–1680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Garrett E. D., Cullen B. R. The Bel-1 protein of human foamy virus activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression via a novel DNA target site. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3946–3949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3946-3949.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec J. J., Tobaly-Tapiero J., Canivet M., Santillana-Hayat M., Flügel R. M., Périès J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Evidence for a gapped linear duplex DNA intermediate in the replicative cycle of human and simian spumaviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9557–9565. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagaye S., Vexiau P., Morozov V., Guénebaut-Claudet V., Tobaly-Tapiero J., Canivet M., Cathelineau G., Périès J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Human spumaretrovirus-related sequences in the DNA of leukocytes from patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10070–10074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. H., Lee K. J., Kim S., Sung Y. C. Transactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat-directed gene expression by the human foamy virus bel1 protein requires a specific DNA sequence. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3236–3240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3236-3240.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Lindholm P. F., Reid R. L., Brady J. N. Soluble HTLV-I Tax1 protein stimulates proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. New Biol. 1991 Jul;3(7):678–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Viral alteration of cell function. Sci Am. 1989 Aug;261(2):42–48. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0889-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw R. W., Gonda M. A., Casey J. W. Structure and transcriptional status of bovine syncytial virus in cytopathic infections. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Mori K., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. Transacting transcriptional activation of human spumaretrovirus LTR in infected cells. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):568–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90442-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholthof H. B., Wu F. C., Richins R. D., Shepherd R. J. A naturally occurring deletion mutant of figwort mosaic virus (caulimovirus) is generated by RNA splicing. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):290–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W. Expression of a subgenomic retroviral messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):811–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terré S., Petit M. A., Bréchot C. Defective hepatitis B virus particles are generated by packaging and reverse transcription of spliced viral RNAs in vivo. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5539–5543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5539-5543.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobaly-Tapiero J., Kupiec J. J., Santillana-Hayat M., Canivet M., Peries J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Further characterization of the gapped DNA intermediates of human spumavirus: evidence for a dual initiation of plus-strand DNA synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):605–608. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Yang C., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Functional dissection of the human spumaretrovirus transactivator identifies distinct classes of dominant-negative mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.161-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









