Abstract
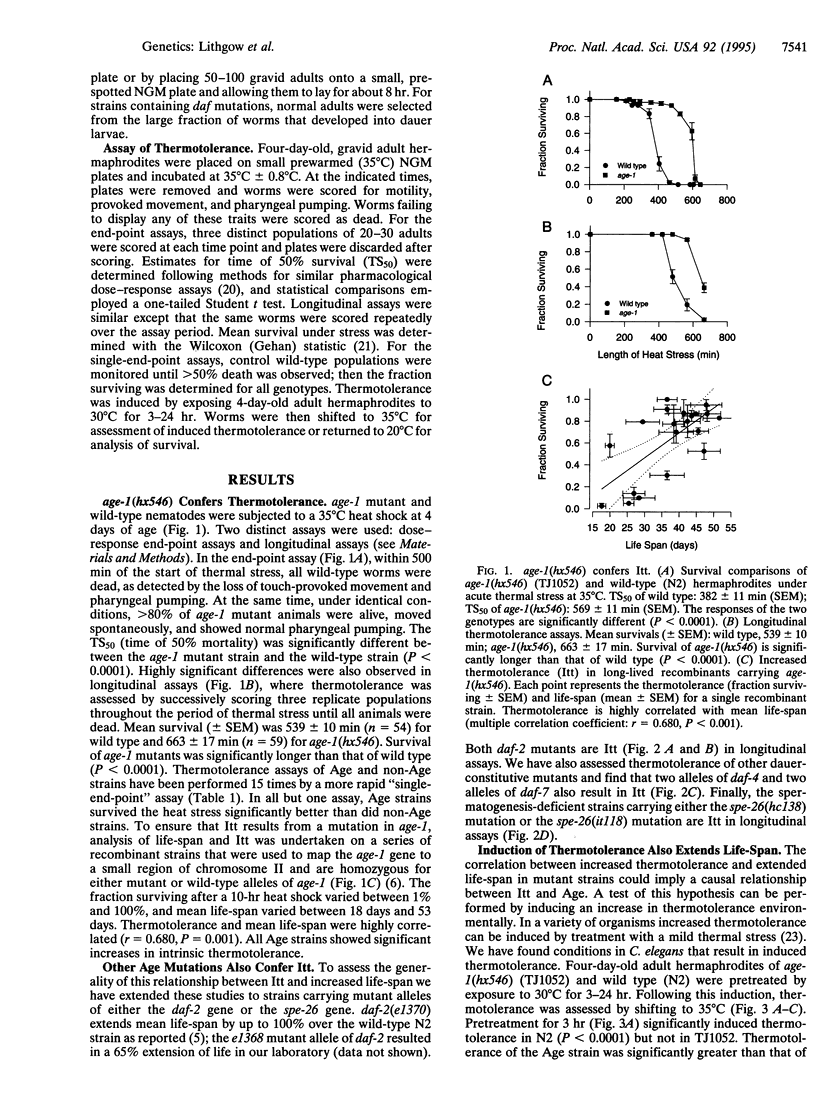
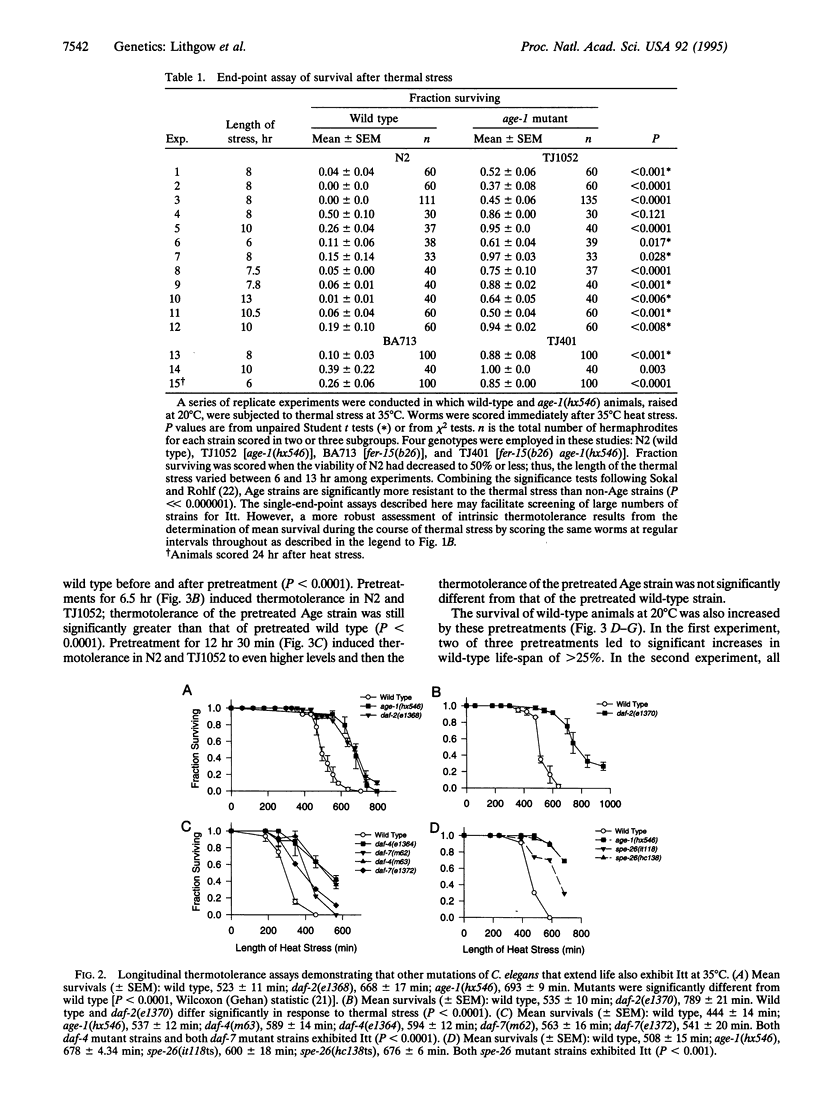
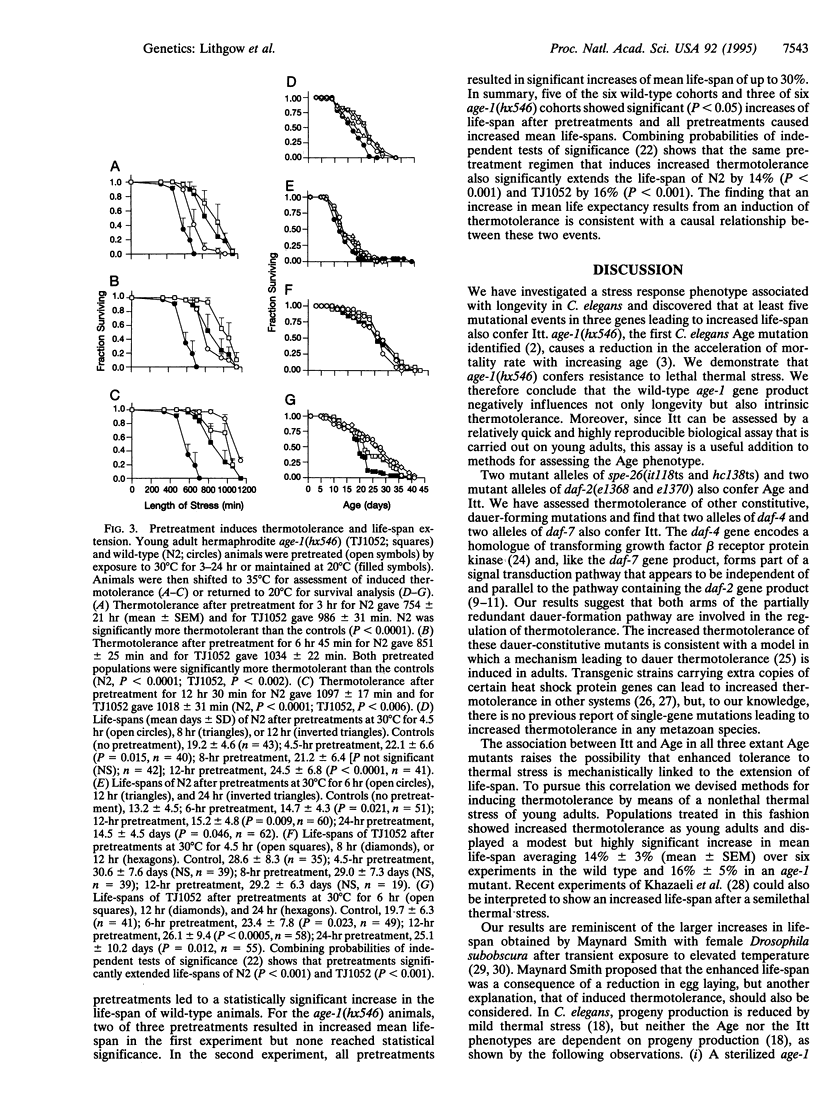
We have discovered that three longevity mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans also exhibit increased intrinsic thermotolerance (Itt) as young adults. Mutation of the age-1 gene causes not only 65% longer life expectancy but also Itt. The Itt phenotype cosegregates with age-1. Long-lived spe-26 and daf-2 mutants also exhibit Itt. We investigated the relationship between increased thermotolerance and increased life-span by developing conditions for environmental induction of thermotolerance. Such pretreatments at sublethal temperatures induce significant increases in thermotolerance and small but statistically highly significant increases in life expectancy, consistent with a causal connection between these two traits. Thus, when an animal's resistance to stress is increased, by either genetic or environmental manipulation, we also observe an increase in life expectancy. These results suggest that ability to respond to stress limits the life expectancy of C. elegans and might do so in other metazoa as well.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. Mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans that form dauer-like larvae. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):270–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. C., Romm E., Selvaag S., Turner S., Marks M. J. A comparison of the effects of chronic nicotine infusion on tolerance to nicotine and cross-tolerance to ethanol in long- and short-sleep mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1390–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati Y. R., Slosman D. O., Polla B. S. Oxidative injury and the heat shock response. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 15;40(12):2571–2577. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90573-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estevez M., Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Albert P. S., Massagué J., Riddle D. L. The daf-4 gene encodes a bone morphogenetic protein receptor controlling C. elegans dauer larva development. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):644–649. doi: 10.1038/365644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargnoli J., Kunisada T., Fornace A. J., Jr, Schneider E. L., Holbrook N. J. Decreased expression of heat shock protein 70 mRNA and protein after heat treatment in cells of aged rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):846–850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. E., Reveillaud I., Niedzwiecki A. Role of oxidative stress in Drosophila aging. Mutat Res. 1992 Sep;275(3-6):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(92)90031-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. B., Johnson T. E. A mutation in the age-1 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans lengthens life and reduces hermaphrodite fertility. Genetics. 1988 Jan;118(1):75–86. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. B., Johnson T. E. Three mutants that extend both mean and maximum life span of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, define the age-1 gene. J Gerontol. 1988 Jul;43(4):B102–B109. doi: 10.1093/geronj/43.4.b102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S., Ruvkun G. daf-2, daf-16 and daf-23: genetically interacting genes controlling Dauer formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1994 May;137(1):107–120. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heydari A. R., Wu B., Takahashi R., Strong R., Richardson A. Expression of heat shock protein 70 is altered by age and diet at the level of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2909–2918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. E., Hartman P. S. Radiation effects on life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Gerontol. 1988 Sep;43(5):B137–B141. doi: 10.1093/geronj/43.5.b137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. E. Increased life-span of age-1 mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans and lower Gompertz rate of aging. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):908–912. doi: 10.1126/science.2392681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. E., Tedesco P. M., Lithgow G. J. Comparing mutants, selective breeding, and transgenics in the dissection of aging processes of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetica. 1993;91(1-3):65–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01435988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C., Chang J., Gensch E., Rudner A., Tabtiang R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):461–464. doi: 10.1038/366461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaeli A. A., Xiu L., Curtsinger J. W. Stress experiments as a means of investigating age-specific mortality in Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Gerontol. 1995 Mar-Apr;30(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(94)00058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Chrétien P., Lambert H., Hickey E., Weber L. A. Heat shock resistance conferred by expression of the human HSP27 gene in rodent cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):7–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. L. Aging and resistance to oxidative damage in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. Genes that regulate both development and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1995 Apr;139(4):1567–1583. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.4.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithgow G. J., White T. M., Hinerfeld D. A., Johnson T. E. Thermotolerance of a long-lived mutant of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Gerontol. 1994 Nov;49(6):B270–B276. doi: 10.1093/geronj/49.6.b270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone E. A., Thomas J. H. A screen for nonconditional dauer-constitutive mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):879–886. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Sohal R. S. Extension of life-span by overexpression of superoxide dismutase and catalase in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1128–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.8108730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle D. L., Swanson M. M., Albert P. S. Interacting genes in nematode dauer larva formation. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):668–671. doi: 10.1038/290668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. H., Birnby D. A., Vowels J. J. Evidence for parallel processing of sensory information controlling dauer formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1993 Aug;134(4):1105–1117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udelsman R., Blake M. J., Stagg C. A., Li D. G., Putney D. J., Holbrook N. J. Vascular heat shock protein expression in response to stress. Endocrine and autonomic regulation of this age-dependent response. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):465–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI116224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhies W. A. Production of sperm reduces nematode lifespan. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):456–458. doi: 10.1038/360456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanfleteren J. R. Oxidative stress and ageing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):605–608. doi: 10.1042/bj2920605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte M. A., Tetrault J. M., Dellavalle R. P., Lindquist S. L. A new method for manipulating transgenes: engineering heat tolerance in a complex, multicellular organism. Curr Biol. 1993 Dec 1;3(12):842–853. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90218-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



