Abstract
The c-Myc protein (Myc) is involved in cellular transformation and mitogenesis, but is also a potent inducer of programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Whether these apparently opposite functions are mediated through common or distinct molecular mechanisms remains unclear. Myc and its partner protein, Max, dimerize and bind DNA in vitro and in vivo through basic/helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper motifs (bHLH-LZ). By using complementary leucine zipper mutants (termed MycEG and MaxEG), which dimerize efficiently with each other but not with their wild-type partners, we demonstrate that both cell cycle progression and apoptosis in nontransformed rodent fibroblasts are induced by Myc-Max dimers. MycEG or MaxEG alone are inactive, but co-expression restores ability to prevent withdrawal from the cell cycle and to induce cell death upon removal of growth factors. Thus, Myc can control two alternative cell fates through dimerization with a single partner, Max.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin C., Wagner A. J., Hay N. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation by Myc and repression by Max. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Ner M., Messing L. T., Cultraro C. M., Birrer M. J., Segal S. Regions within the c-Myc protein that are necessary for transformation are also required for inhibition of differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Mar;3(3):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J., Birrer M. J., Kato G. J., Dosaka-Akita H., Dang C. V. Activation domains of L-Myc and c-Myc determine their transforming potencies in rat embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3130–3137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Leder A., Kuo A., Leder P. An embryonically expressed gene is a target for c-Myc regulation via the c-Myc-binding sequence. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2513–2523. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S. J., Cole M. D. Casein kinase II inhibits the DNA-binding activity of Max homodimers but not Myc/Max heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):166–176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max function as a nucleoprotein complex. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch D. H., Fisher F., Clark W., Jayaraman P. S., Goding C. R., Gillespie D. A. Gene-regulatory properties of Myc helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper mutants: Max-dependent DNA binding and transcriptional activation in yeast correlates with transforming capacity. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1849–1855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. J., Halazonetis T. D. Both the helix-loop-helix and the leucine zipper motifs of c-Myc contribute to its dimerization specificity with Max. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Littlewood T. D. The role of c-myc in cell growth. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):44–49. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
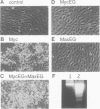
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Cechova K., Tassi V., Dalla-Favera R. Opposite regulation of gene transcription and cell proliferation by c-Myc and Max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2935–2939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood T. D., Amati B., Land H., Evan G. I. Max and c-Myc/Max DNA-binding activities in cell extracts. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1783–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Hancock D. C., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I. A sensitive and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbence assay for the c-myc and N-myc oncoproteins. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee B., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A. Myc family oncoproteins function through a common pathway to transform normal cells in culture: cross-interference by Max and trans-acting dominant mutants. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1480–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Koskinen P. J., Västrik I., Alitalo K. Alternative forms of Max as enhancers or suppressors of Myc-ras cotransformation. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):373–377. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori Y., Tanabe J., Takada S., Lee W. M., Obinata M. Functional domains of c-Myc involved in the commitment and differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Land H. Negative autoregulation of c-myc transcription. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1113–1121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Littlewood T. D., Morgenstern J. P., Evan G. I., Lee W. M., Land H. Domains of human c-myc protein required for autosuppression and cooperation with ras oncogenes are overlapping. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4961–4966. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Laufer E. M., Land H. C-MYC: evidence for multiple regulatory functions. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):69–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Hopewell R., Gorham B. J., Ziff E. B. Biphasic effect of Max on Myc cotransformation activity and dependence on amino- and carboxy-terminal Max functions. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2429–2439. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. D., Dasgupta P., Saikumar P., Dudek H., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Reddy E. P. Mutational analysis of Max: role of basic, helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper domains in DNA binding, dimerization and regulation of Myc-mediated transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Elkind N. B., Roy B., Beamon J., Rotter V. c-Myc trans-activates the p53 promoter through a required downstream CACGTG motif. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Feb;4(2):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resar L. M., Dolde C., Barrett J. F., Dang C. V. B-myc inhibits neoplastic transformation and transcriptional activation by c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1130–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Glynn J. M., Guilbert L. J., Cotter T. G., Bissonnette R. P., Green D. R. Role for c-myc in activation-induced apoptotic cell death in T cell hybridomas. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1378649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres R., Schreiber-Agus N., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A. Myc and Max: a putative transcriptional complex in search of a cellular target. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Small M. B., Hay N. Myc-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2432–2440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]