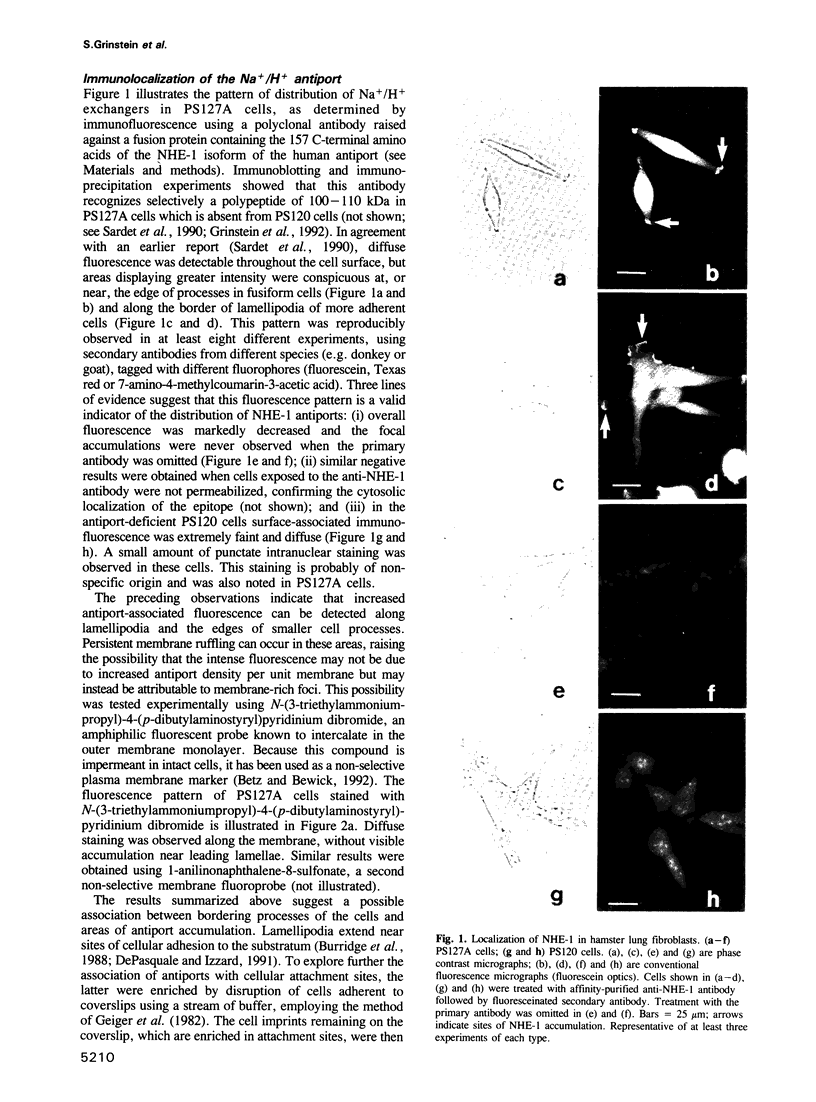
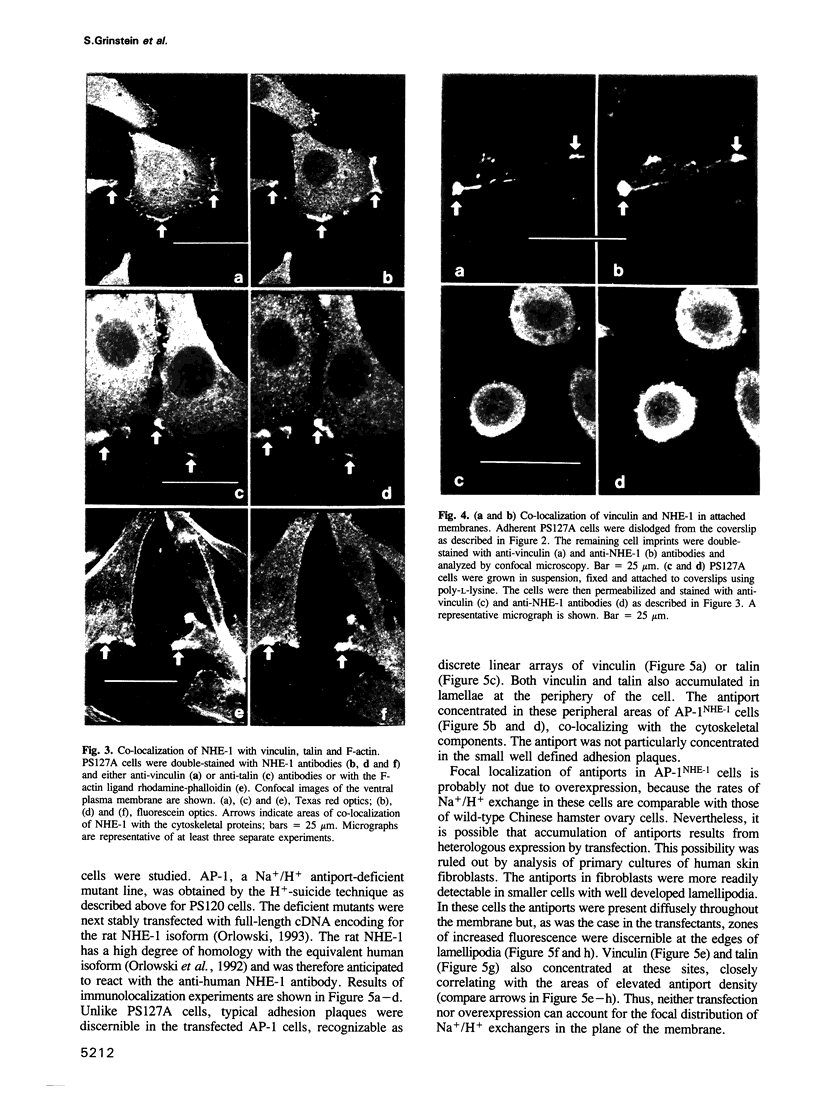
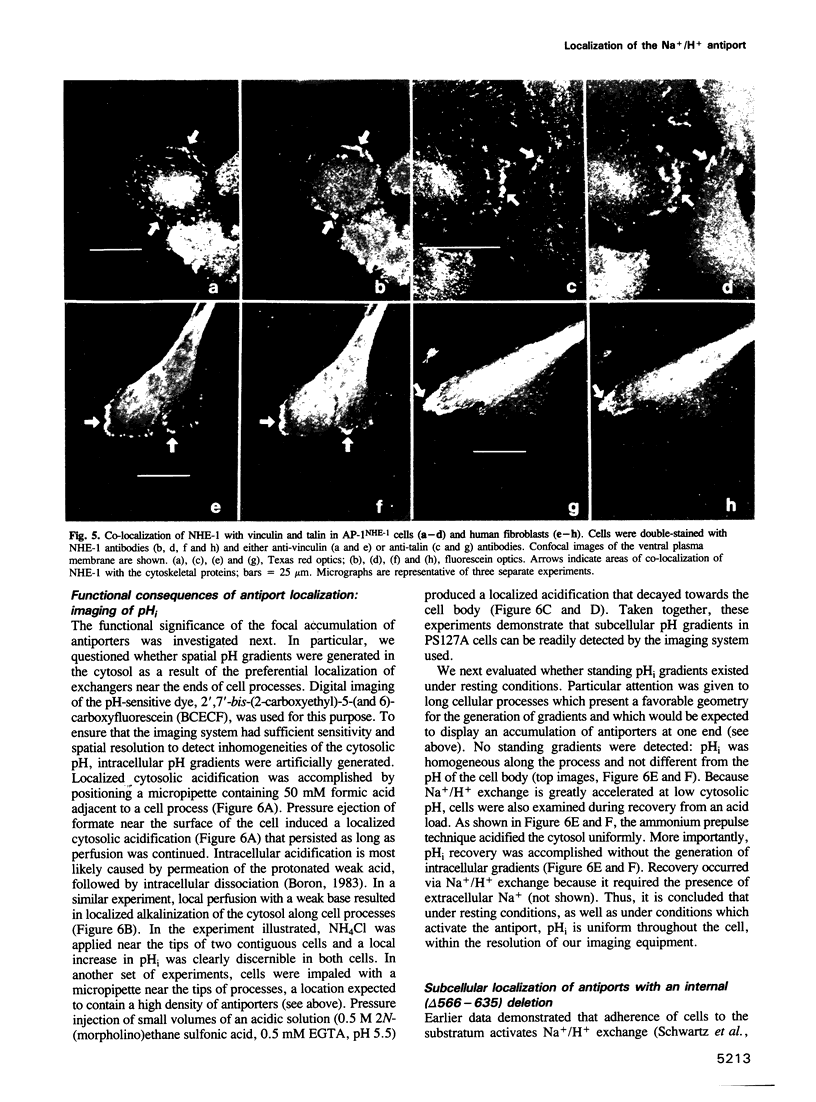
Abstract
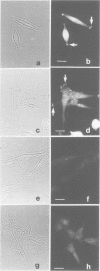
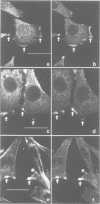
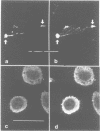
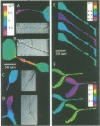
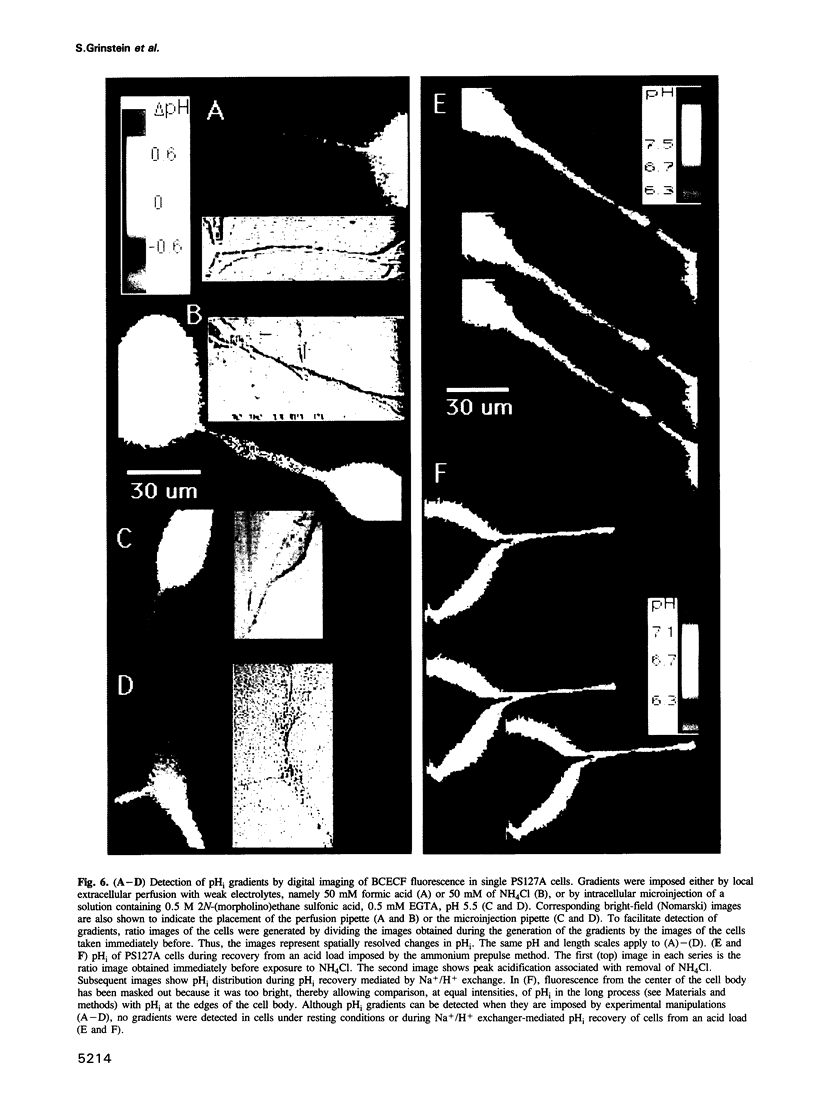
Na+/H+ exchange (antiport) is a major pathway for the regulation of intracellular pH. Antiport activity is stimulated when suspended cells adhere to the substratum. In this report, immunofluorescence was used to study the subcellular localization of the ubiquitous NHE-1 isoform of the antiport. NHE-1 was not distributed homogeneously on the surface of the cells. Instead, antiports were found to accumulate along the border of lamellipodia and near the edge of finer processes. Dual immunofluorescence experiments demonstrated that vinculin, talin and F-actin are concentrated at sites of NHE-1 accumulation. A mutated construct of NHE-1 lacking residues 566-635 of the cytosolic domain also accumulated near marginal lamellae. In contrast, the focal distribution observed in adherent cells was not detectable in cells grown in suspension. Fluorescence ratio imaging was used to define the functional consequences of focal accumulation of NHE-1. In the steady state, the pH was virtually identical throughout the cytosol. Moreover, no pH gradients were found to develop when cells recovered from an acid load by activation of Na+/H+ exchange. This is probably because of the presence of high concentrations of mobile buffers in the cytosol. The focal accumulation of antiporters near the cell margins may be involved in stimulation by adherence and/or generation of local osmotic gradients.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Proteins involved in membrane--cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes: spectrin, ankyrin, and band 3. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Bewick G. S. Optical analysis of synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):200–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1553547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Transport of H+ and of ionic weak acids and bases. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01870311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePasquale J. A., Izzard C. S. Accumulation of talin in nodes at the edge of the lamellipodium and separate incorporation into adhesion plaques at focal contacts in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1351–1359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foskett J. K. Simultaneous Nomarski and fluorescence imaging during video microscopy of cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):C566–C571. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.4.C566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Avnur Z., Schlessinger J. Restricted mobility of membrane constituents in cell-substrate focal contacts of chicken fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):495–500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Foskett J. K. Ionic mechanisms of cell volume regulation in leukocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:399–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Rotin D. Activation of the Na+/H+ antiporter during cell volume regulation. Evidence for a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23823–23828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Prusty D., Frangioni J. V., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C., Schwartz M. A. Control of intracellular pH and growth by fibronectin in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1803–1811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Maylie J., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Intracellular diffusion in the presence of mobile buffers. Application to proton movement in muscle. Biophys J. 1990 Apr;57(4):717–721. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82592-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Veshnock P. J. Ankyrin binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase and implications for the organization of membrane domains in polarized cells. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):533–536. doi: 10.1038/328533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J. Heterologous expression and functional properties of amiloride high affinity (NHE-1) and low affinity (NHE-3) isoforms of the rat Na/H exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16369–16377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Kandasamy R. A., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9331–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Sardet C., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. A specific mutation abolishing Na+/H+ antiport activity in hamster fibroblasts precludes growth at neutral and acidic pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiporter, glycoprotein of 110 kD. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.2154036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C. Adhesion is required for protein kinase C-dependent activation of the Na+/H+ antiporter by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6138–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C., Ingber D. E. Insoluble fibronectin activates the Na/H antiporter by clustering and immobilizing integrin alpha 5 beta 1, independent of cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7849–7853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A. Transmembrane signalling by integrins. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90120-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Cragoe E. J., Jr Regulation of human neutrophil chemotaxis by intracellular pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6492–6500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Bradford A. L., Joe E. H., Angelides K. J., Benos D. J., Saccomani G. Gastric parietal cell H(+)-K(+)-ATPase microsomes are associated with isoforms of ankyrin and spectrin. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C63–C70. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Saccomani G., Joe E. H., Angelides K. J., Benos D. J. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel is linked to the cytoskeleton in renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Sardet C., Fafournoux P., Counillon L., Meloche S., Pagés G., Pouysségur J. Structure function of the growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE1). Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:157–186. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L. Reorganization of actin filament bundles in living fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1478–1485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]