Abstract
The GAL1-10 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are regulated by the interaction of cis- and trans-acting factors which facilitate activated transcription in galactose but not in glucose medium. By selecting mutations that allow expression of a defective gal1-10-his3 hybrid promoter, we have identified a novel gene, NGG1, which is required for glucose repression of the GAL10-related his3-G25 promoter. ngg1 was identified as a recessive null mutation that in the presence of a gal80 background resulted in a 300-fold relief of glucose repression for the his3-G25 promoter. This compared with a 20-fold and negligible relief of repression in gal80 and ngg1 strains, respectively. Deletion analysis of the his3-G25 promoter showed a correlation between the number of GAL4p binding sites and the relative level of NGG1p activity. Relief of glucose repression by NGG1 was dependent on the presence of GAL4, but was independent of the GAL4 promoter. In addition, NGG1p activity was seen for a promoter construct containing independent GAL4p binding sites. These results suggest that NGG1p acts to inhibit GAL4p function in glucose medium. We have cloned NGG1 by complementation and found that it contains an open reading frame of 2106 bp which could encode a protein with a molecular weight of 79,230.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Piña B., Silverman N., Marcus G. A., Agapite J., Regier J. L., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Genetic isolation of ADA2: a potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90100-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P. J., Hopper J. E. Overproduction of the GAL1 or GAL3 protein causes galactose-independent activation of the GAL4 protein: evidence for a new model of induction for the yeast GAL/MEL regulon. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2701–2707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P. J., Oh D., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the GAL3 signal transduction pathway activating GAL4 protein-dependent transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):281–291. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. A GAL family of upstream activating sequences in yeast: roles in both induction and repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):603–608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Martens J. A., Liaw P. C., Furlanetto A. M., Wobbe C. R. TATA-binding protein activates transcription when upstream of a GCN4-binding site in a novel yeast promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20943–20952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Struhl K. A nucleosome-positioning sequence is required for GCN4 to activate transcription in the absence of a TATA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4256–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Kakidani H., Leatherwood J., Mostashari F., Ptashne M. An amino-terminal fragment of GAL4 binds DNA as a dimer. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Neigeborn L., Botstein D. A suppressor of SNF1 mutations causes constitutive high-level invertase synthesis in yeast. Genetics. 1984 May;107(1):19–32. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Kornberg R. D. GAL4 protein: purification, association with GAL80 protein, and conserved domain structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2916–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast upstream activator protein GCN4 can stimulate transcription when its binding site replaces the TATA element. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):261–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D., Barnett J. A. Regulation of sugar utilization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Dec;17(12):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D., Zimmermann F. K. New genes involved in carbon catabolite repression and derepression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1123–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1123-1128.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. R., Johnston M. Direct cloning of yeast genes from an ordered set of lambda clones in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by recombination in vivo. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):151–157. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley R. L., Jr, Chen S., Ma J., Byrne P., West R. W., Jr Opposing regulatory functions of positive and negative elements in UASG control transcription of the yeast GAL genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5663–5670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley R. L., Jr, West R. W., Jr Differential repression of GAL4 and adjacent transcription activators by operators in the yeast GAL upstream activating sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4282–4290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick J. S., Johnston M. Analysis of URSG-mediated glucose repression of the GAL1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Feb;130(2):295–304. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick J. S., Johnston M. Two systems of glucose repression of the GAL1 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4757–4769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter-Graves E. M., Hall B. D. DNA sequence elements required for transcription initiation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ADH gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00264447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo J. M. Carbon catabolite repression in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):297–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. W., Johnston M. Regulated expression of the GAL4 activator gene in yeast provides a sensitive genetic switch for glucose repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8597–8601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Pearlberg J., Last D. H., Ptashne M. GAL11P: a yeast mutation that potentiates the effect of weak GAL4-derived activators. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1299–1309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90425-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Raymond W., Froehlich K. U., Errada P., Kleckner N., Botstein D., Hoyt M. A. A Tn10-lacZ-kanR-URA3 gene fusion transposon for insertion mutagenesis and fusion analysis of yeast and bacterial genes. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):191–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
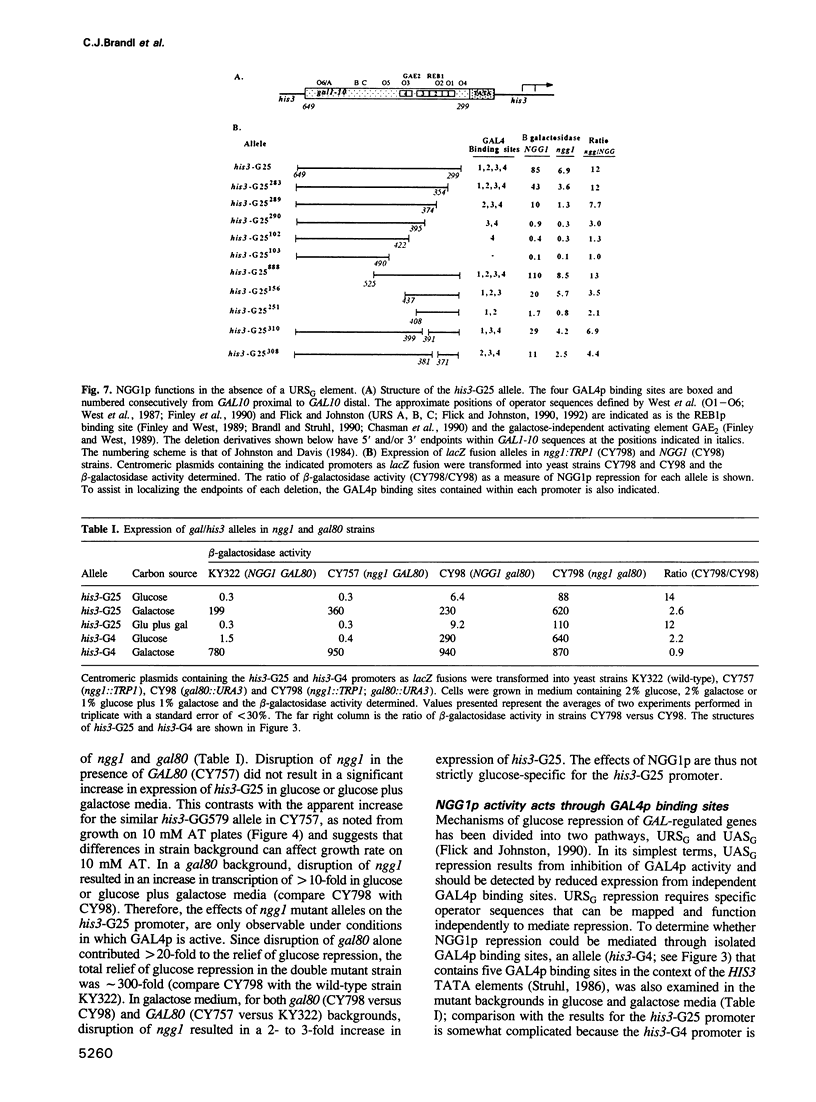
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Salmeron J. M., Jr, Dincher S. S. Interaction of positive and negative regulatory proteins in the galactose regulon of yeast. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90671-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang T., Martins T., Sadowski I. Wild type GAL4 binds cooperatively to the GAL1-10 UASG in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9629–9635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Redd M. J., Schultz J., Carlson M., Johnson A. D. Ssn6-Tup1 is a general repressor of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klopotowski T., Wiater A. Synergism of aminotriazole and phosphate on the inhibition of yeast imidazole glycerol phosphate dehydratase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Dec;112(3):562–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamphier M. S., Ptashne M. Multiple mechanisms mediate glucose repression of the yeast GAL1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5922–5926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuther K. K., Johnston S. A. Nondissociation of GAL4 and GAL80 in vivo after galactose induction. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1333–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.1598579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Chasman D. I., Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. Interaction of GAL4 and GAL80 gene regulatory proteins in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3446–3451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. The carboxy-terminal 30 amino acids of GAL4 are recognized by GAL80. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90670-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
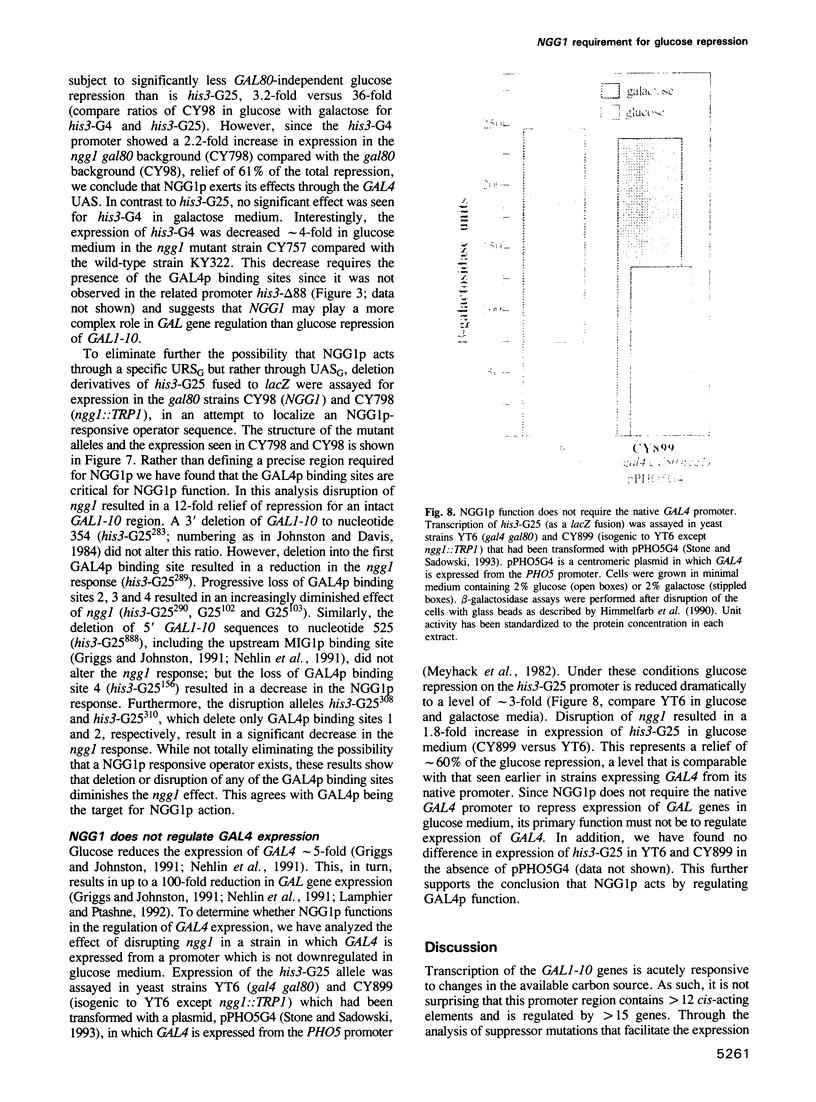
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of dominant mutations resistant to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):83–93. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yoshimatsu T., Oshima Y. Recessive mutations conferring resistance to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1405–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1405-1414.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyhack B., Bajwa W., Rudolph H., Hinnen A. Two yeast acid phosphatase structural genes are the result of a tandem duplication and show different degrees of homology in their promoter and coding sequences. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Carlberg M., Ronne H. Control of yeast GAL genes by MIG1 repressor: a transcriptional cascade in the glucose response. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3373–3377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Ronne H. Yeast MIG1 repressor is related to the mammalian early growth response and Wilms' tumour finger proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2891–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Genes affecting the regulation of SUC2 gene expression by glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):845–858. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Mutations causing constitutive invertase synthesis in yeast: genetic interactions with snf mutations. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):247–253. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Struhl K. Suppressors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 promoter mutations lacking the upstream element. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1901–1909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthun M. R., Jaehning J. A. Purification and characterization of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Characterization and mutational analysis of a cluster of three genes expressed preferentially during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2443–2451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu W. T., Struhl K. The leucine zipper symmetrically positions the adjacent basic regions for specific DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6901–6905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J., Sherman F. Genes affecting the expression of cytochrome c in yeast: genetic mapping and genetic interactions. Genetics. 1980 Apr;94(4):871–889. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Carlson M. Molecular analysis of SSN6, a gene functionally related to the SNF1 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3637–3645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller H. J., Entian K. D. Isolation and expression analysis of two yeast regulatory genes involved in the derepression of glucose-repressible enzymes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):366–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00329667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Majors J. E. In vivo DNA-binding properties of a yeast transcription activator protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3260–3267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
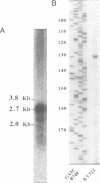
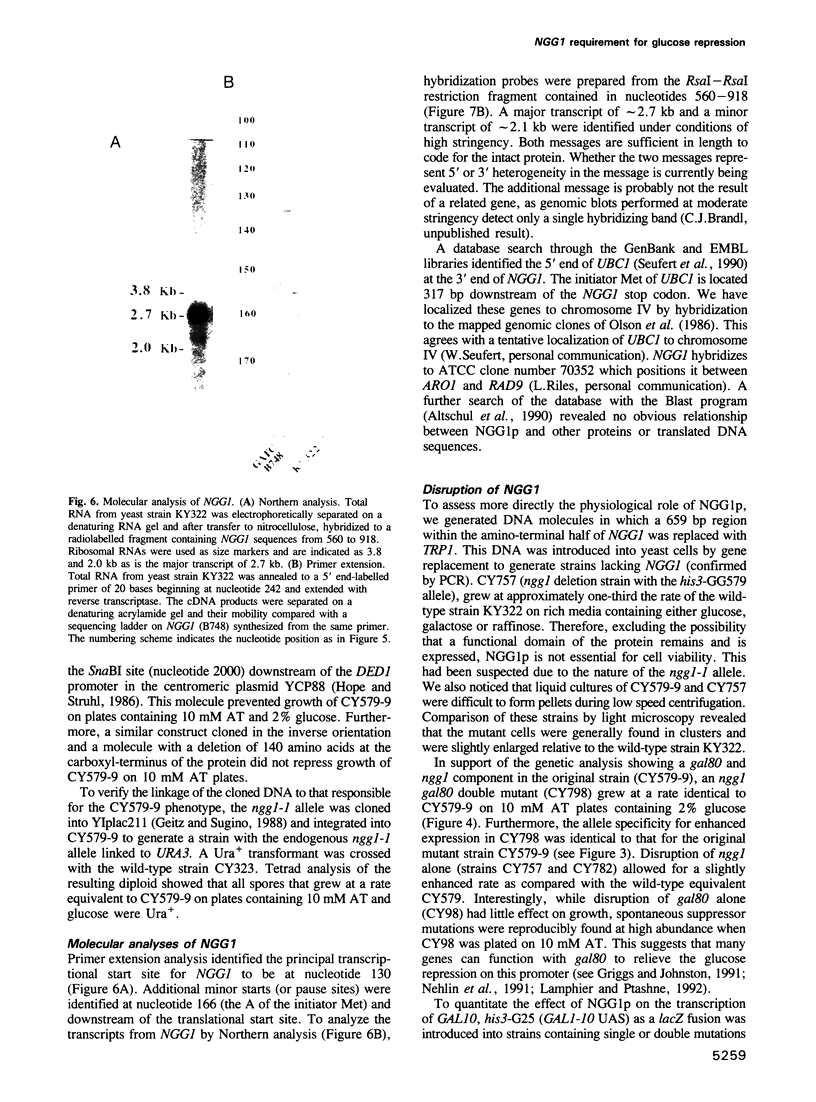
- Seufert W., McGrath J. P., Jentsch S. UBC1 encodes a novel member of an essential subfamily of yeast ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes involved in protein degradation. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4535–4541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone G., Sadowski I. GAL4 is regulated by a glucose-responsive functional domain. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1375–1385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Negative control at a distance mediates catabolite repression in yeast. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):822–824. doi: 10.1038/317822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Nogi Y., Abe A., Fukasawa T. GAL11 protein, an auxiliary transcription activator for genes encoding galactose-metabolizing enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4991–4999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaffield J. C., Bromberg J. F., Johnston S. A. Alterations in a yeast protein resembling HIV Tat-binding protein relieve requirement for an acidic activation domain in GAL4. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):698–700. doi: 10.1038/357698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the GAL3 gene in the expression of the galactose/melibiose regulon of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):229–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumbly R. J. Glucose repression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumbly R. J. Isolation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants constitutive for invertase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1123-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Chen S. M., Putz H., Butler G., Banerjee M. GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region of Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains negative control elements in addition to functionally separate and possibly overlapping upstream activating sequences. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1118–1131. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. E., Trumbly R. J. Characterization of TUP1, a mediator of glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6500–6511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. E., Varanasi U., Trumbly R. J. The CYC8 and TUP1 proteins involved in glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are associated in a protein complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3307–3316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Carlson M. Yeast SNF/SWI transcriptional activators and the SPT/SIN chromatin connection. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90300-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., Hubbard E. J., Carlson M. A protein kinase substrate identified by the two-hybrid system. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):680–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1496382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]