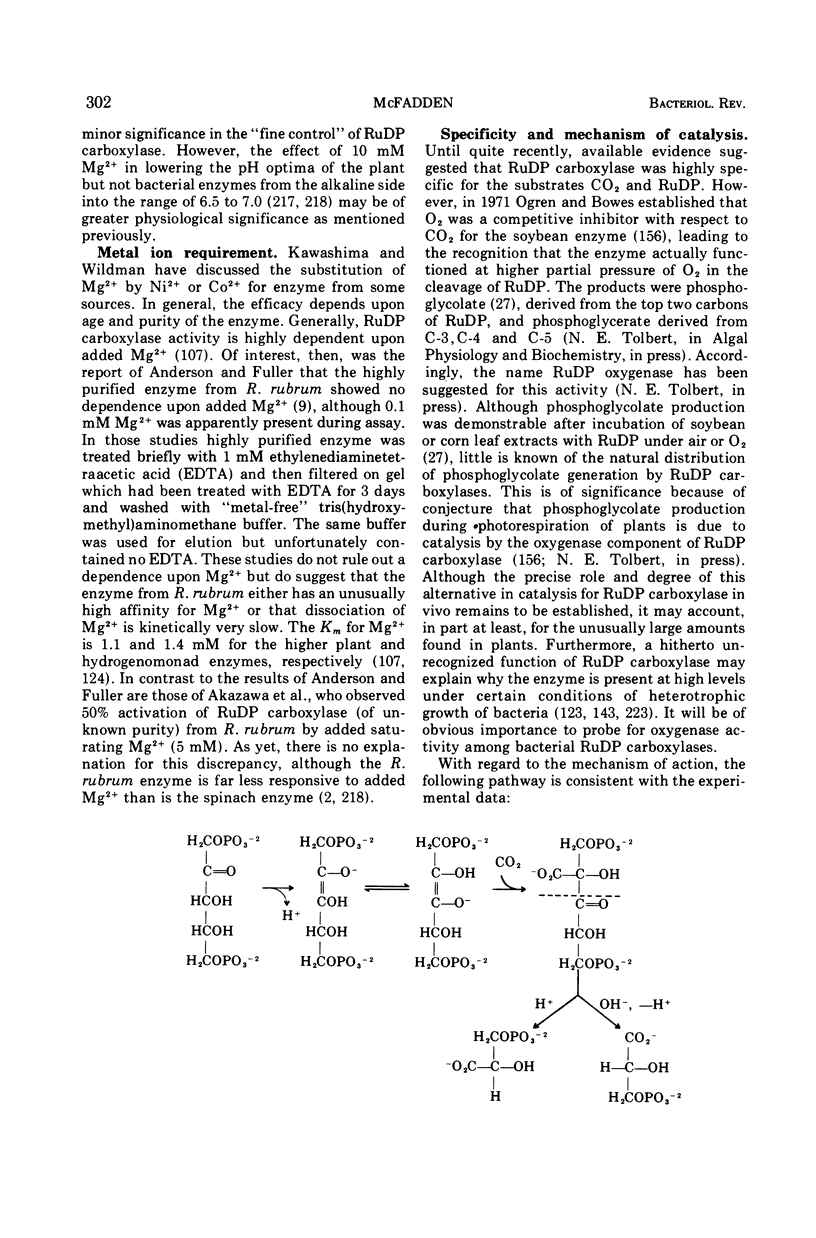
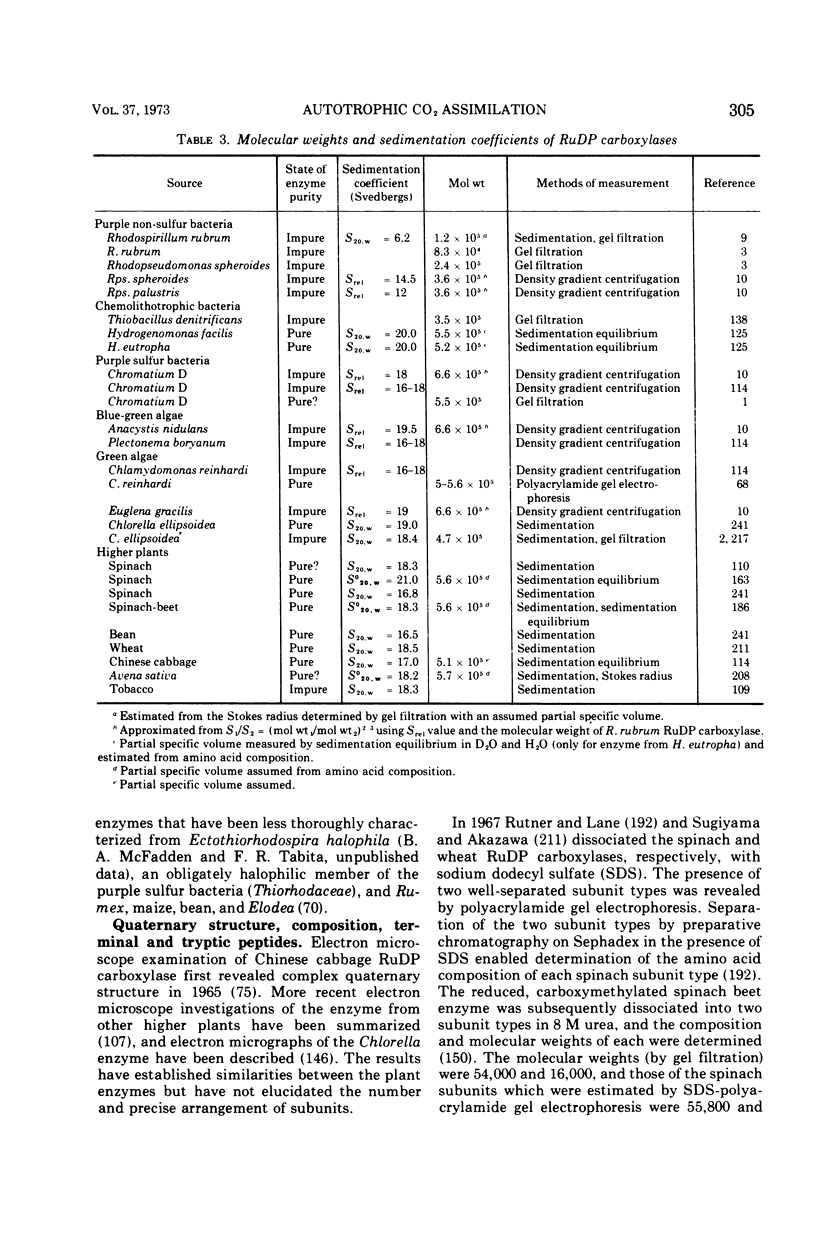
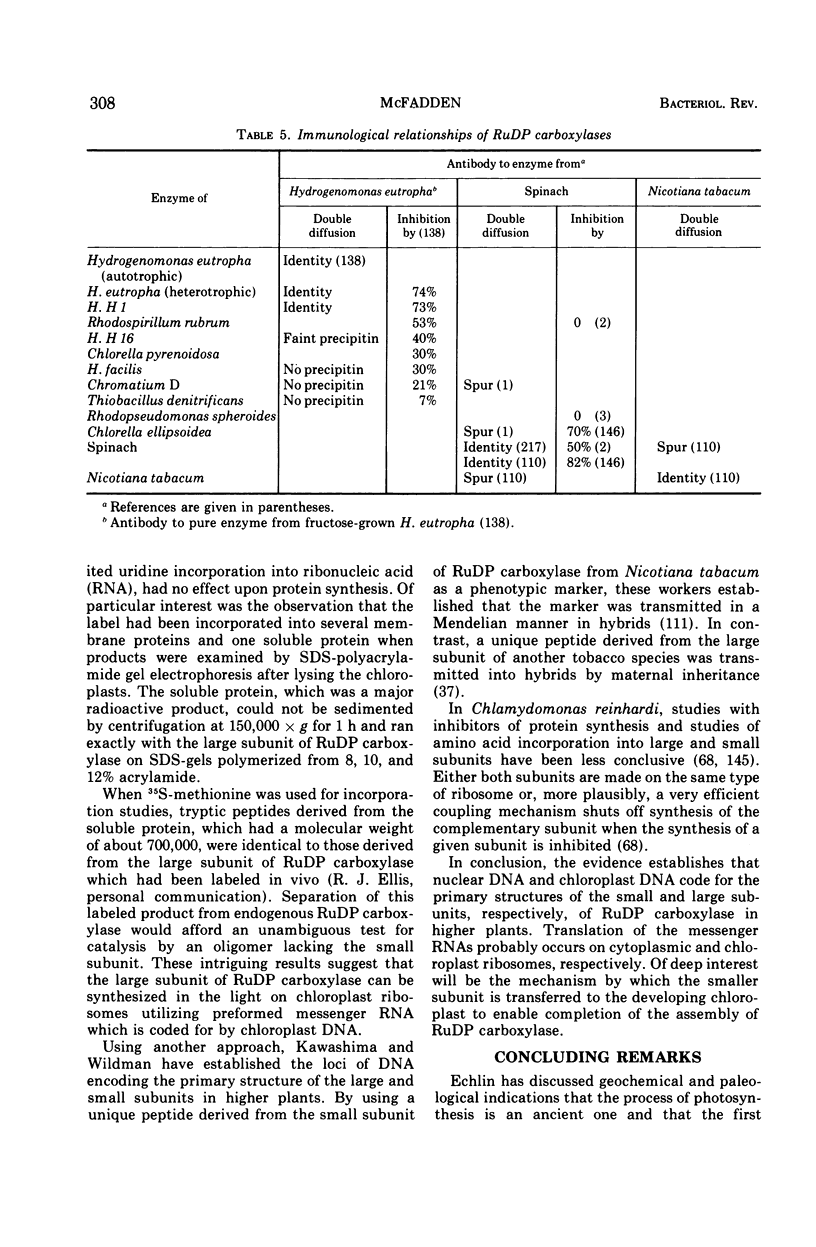
Full text
PDF



























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akazawa T., Kondo H., Shimazue T., Nishimura M., Sugiyama T. Further studies on ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chromatium strain D. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1298–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akazawa T., Sato K., Sugiyama T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. 8. Some properties of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of athiorhodaceae in comparison with those of plant enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleem M. I., Huang E. Carbon dioxide fixation and carboxydismutase in Thiobacillus novellus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleem M. I. Path of carbon and assimilatory power in chemosynthetic bacteria. I. Nitrobacter agilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;107(1):14–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. IV. Isolation and characterization of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3105–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. 3. Metabolic control of reductive pentose phosphate and tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes. Plant Physiol. 1967 Apr;42(4):497–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation. Plant Physiol. 1967 Apr;42(4):487–490. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Photoheterotrophic carbon dioxide fixation. Plant Physiol. 1967 Apr;42(4):491–496. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Lorimer G. H., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. I. Synthesis of phosphoglycolate by fraction-1 protein of leaves. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):11–18. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson D. E. The energy charge of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter. Interaction with feedback modifiers. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4030–4034. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMANN F. H., TOWNE J. C., BURRIS R. H. Assimilation of carbon dioxide by hydrogen bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOATMAN E. S., DOUGLAS H. C. Fine structure of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodomicrobium vannielii. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Nov;11:469–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOATMAN E. S. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FINE STRUCTURE OF SPHEROPLASTS OF RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:297–311. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. W., MacElroy R. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate, a new inhibitor of phosphoribulokinase in pseudomonas facilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 6;44(3):614–618. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barghoorn E. S., Schopf J. W. Microorganisms three billion years old from the precambrian of South Africa. Science. 1966 May 6;152(3723):758–763. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3723.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A. The control of photosynthetic carbon metabolism. Science. 1971 May 7;172(3983):526–534. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3983.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L., Hageman R. H. Phosphoglycolate production catalyzed by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):716–722. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Der Biosyntheseweg der RNS-Ribose in Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H 16 und Pseudomonas facilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00409291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxin-dependent synthesis of labelled pyruvate from labelled acetyl coenzyme A and carbon dioxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 12;20(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Evans M. C., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxin-dependent carbon assimilation in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):32–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00406314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P., Kalberer P. P. Ferredoxin-activated fructose diphosphatase of spinach chloroplasts. Resolution of the system, properties of the alkaline fructose diphosphatase component, and physiological significance of the ferredoxin-linked activation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5952–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P., Shanmugam K. T. Role of the reductive carboxylic acid cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium lacking ribulose I,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972;283(1):136–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALVIN M. The path of carbon in photosynthesis. Science. 1962 Mar 16;135(3507):879–889. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3507.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., PFENNIG N., KUNISAWA R. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF GREEN BACTERIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jul;22:207–225. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. E., Hellebust J. A., Watson S. W. Reductive pentose phosphate cycle in Nitrosocystis oceanus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1178–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1178-1185.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Sakano K., Singh S., Wildman S. G. Crystalline fraction I protein: preparation in large yield. Science. 1972 Jun 9;176(4039):1145–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4039.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA codes for the primary structure of the large subunit of fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Lees H., Postgate J. R. The meaning of "reversed electron flow" and "high energy electron" in biochemistry. Nature. 1972 Aug 11;238(5363):330–331. doi: 10.1038/238330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1972 Aug;50(2):224–227. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Filmer D. The active species of "CO2" utilized by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criddle R. S., Dau B., Kleinkopf G. E., Huffaker R. C. Differential synthesis of ribulosediphosphate carboxylase subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Din G. A., Suzuki I., Lees H. Carbon dioxide fixation and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Nov;13(11):1413–1419. doi: 10.1139/m67-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews G., Lampe H. H., Ladwig R. Die Entwicklung des Photosyntheseapparates in Dunkelkulturen von Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(1):12–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eimhjellen K. E., Steensland H., Traetteberg J. A Thiococcus sp. nov. gen., its pigments and internal membrane system. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):82–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00406319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. E., Nagy B., Nagy L. A., Engel C. G., Kremp G. O., Drew C. M. Alga-like forms in onverwacht series, South Africa: oldest recognized lifelike forms on Earth. Science. 1968 Sep 6;161(3845):1005–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3845.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. A new ferredoxin-dependent carbon reduction cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):928–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER R. C., SMILLIE R. M., SISLER E. C., KORNBERG H. L. Carbon metabolism in Chromatium. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:2140–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Müllhofer G., Trebst A., Rose I. A. Mechanism of ribulose-diphosphate carboxydismutase reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jun;1(4):395–399. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESBRECHT P., DREWS G. [Electron microscope studies on the development of "chromatophores" by Rhodospirillum molischianum Giesberger]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:152–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINGRAS G., GOLDSBY R. A., CALVIN M. Carbon dioxide metabolism in hydrogen-adapted Scenedesmus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Feb;100:178–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOVER J., KAMEN M. D., VAN GENDEREN H. Studies on the metabolism of photosynthetic bacteria. XII. Comparative light and dark metabolism of acetate and carbonate by Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Feb;35(2):384–408. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(52)80020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G., EBERHARDT U., SCHLEGEL H. G. VERWERTUNG VON FRUCTOSE DURCH HYDROGENOMONAS H 16. (I.) Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Apr 2;48:95–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. L., Beck J. V. Competitive inhibition of phosphoribulokinase by AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):792–796. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs S. P., Sistrom W. R., Worden P. B. The photosynthetic apparatus of Rhodospirillum molischianum. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):395–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givan A. L., Criddle R. S. Ribulosediphosphate carboxylase from Chlamydomonas reinhardi: purification, properties and its mode of synthesis in the cell. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. J., Bogorad L. A one-step method for the isolation and determination of leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. H., Fowler C. F., Nugent N. A., Fuller R. C. A reevaluation of the presence of low midpoint potential cytochrome 551.5 in the green photosynthetic bacterium Chloropseudomonas ethylica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 28;47(2):322–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90715-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKMAN D. D., FRENKEL A. W. OBSERVATIONS ON THE STRUCTURE OF RHODOSPIRILLUM MOLISCHIANUM. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:261–278. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKMAN D. D., FRENKEL A. W. OBSERVATIONS ON THE STRUCTURE OF RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBUM. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:279–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH P., GEORGIEV G., SCHLEGEL H. G. CO2-FIXIERUNG DURCH KNALLGASBAKTERIEN. III. AUTOTROPHE UND ORGANOTROPHE CO2-FIXIERUNG. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963 Jul 18;46:79–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARE D. S. The photo-assimilation of acetate by Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:284–301. doi: 10.1042/bj0870284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. C., MARR A. G. LOCATION OF CHLOROPHYLL IN RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1402–1412. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1402-1412.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. E., LASCELLES J. RIBULOSE DIPHOSPHATE CARBOXYLASE IN THIORHODACEAE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:445–458. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. A., Gibson J. Ribulose-5-phosphate kinase from Chromatium sp. strain D. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):308–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90483-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R., Fernández-Morán H., Kieras F. J., Van Bruggen E. F. Electron microscopic and biochemical characterization of fraction I protein. Science. 1965 Dec 17;150(3703):1598–1601. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3703.1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R., Johnson H. S. Further studies on a new pathway of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation in sugar-cane and its occurrence in other plant species. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):417–422. doi: 10.1042/bj1020417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. Photosynthesis by sugar-cane leaves. A new carboxylation reaction and the pathway of sugar formation. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):103–111. doi: 10.1042/bj1010103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber U., Hallier U. W., Hudson M. A. Untersuchungen zur intrazellulären Verteilungen von Enzymen und Substraten in der Blattzelle. II. Lokalisation von Enzymen des reduktiven und dem oxydativen Pentosephosphat-Zyklus in den Chloroplasten und Permeabilität der Chloroplasten-Membran gegenüber Metaboliten. Z Naturforsch B. 1967 Nov;22(11):1200–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D., Rosenberg S. L. The evolution of bacterial enzyme systems. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:429–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall J., Rittenhouse H. G., McFadden B. A., Shumway L. K. Effect of growth conditions on morphology of Hydrogenomonas facilis and on yield of a phospholipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.363-367.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. S., Gibson J. Photoassimilation of acetate and the biosynthesis of amino acids by Chlorobium thiosulphatophilum. Biochem J. 1964 Jun;91(3):546–559. doi: 10.1042/bj0910546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Conti S. F., Fuller R. C. Photosynthetic Apparatus in the Green Bacterium Chloropseudomonas ethylicum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):311–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.311-323.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Trüper H. G., Takács B. J. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis strain 8113 thylakoids: chemical fixation and freeze-etching studies. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;62(2):111–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00410398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz N. H. On the Evolution of Biochemical Syntheses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Jun;31(6):153–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.6.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. J., PECK H. D., Jr COUPLING OF PHOSPHORYLATION AND CARBON DIOXIDE FIXATION IN EXTRACTS OF THIOBACILLUS THIOPARUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1041–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1041-1050.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagendorf A. T., Uribe E. Photophosphorylation and the chemi-osmotic hypothesis. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:215–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. J. Occurrence of the adenosine monophosphate inhibition of carbon dioxide fixation in photosynthetic and chemosynthetic autotrophs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. S., Hatch M. D. The C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Identification of intermediates and products and quantitative evidence for the route of carbon flow. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):127–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1140127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joint I. R., Morris I., Fuller R. C. Purification of a complex of alkaline fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase and phosphoribulokinase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4833–4838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHOUDOKORMOFF V. A. [The assimilation of carbon dioxide by Nitrobacter winogradskyi]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Feb;100:257–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINDEL P., GIBBS M. DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON-14 IN POLYSACCHARIDE AFTER PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN CARBON DIOXIDE LABELLED WITH CARBON-14 BY ANACYSTIS NIDULANS. Nature. 1963 Oct 19;200:260–261. doi: 10.1038/200260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., COLLINS J. F., BIGLEY D. The influence of growth substrates on metabolic pathways in Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 25;39:9–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., LASCELLES J. The formation of isocitratase by the Athiorhodaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:511–517. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Kwok S. Y., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction-I protein. 3. Comparison of the primary structure of the large and small subunits obtained from five species of Nicotiana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 29;236(3):578–586. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N. Non-synchronous incorporation of C14O2 into amino acids of the two subunits of fraction I protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Singh S., Wildman S. G. Reversible cold inactivation and heat reactivation of RuDP carboxylase activity of crystallized tobacco fraction I protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):664–668. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. A model of the subunit structure of fraction I protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1463–1468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90551-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction I protein. II. Comparison of physical, chemical, immunological and enzymatic properties between spinach and tobacco fraction I proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):749–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction I protein. IV. Mode of inheritance of primary structure in relation to whether chloroplast or nuclear DNA contains the code for a chloroplast protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 23;262(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction-I protein. I. Effect of crystallization of fraction-I protein from tobacco leaves on ribulose diphosphate carboxylase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):240–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P. Autotrophy: concepts of lithotrophic bacteria and their organic metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:177–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieras F. J., Haselkorn R. Properties of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase (carboxydismutase) from Chinese cabbage and photosynthetic microorganisms. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1264–1270. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocur M., Martinec T., Mazanec K. Fine structure of Micrococcus denitrificans and M. halodenitrificans in relation to their taxonomy. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1968;34(1):19–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02046410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortschak H. P., Hartt C. E., Burr G. O. Carbon Dioxide Fixation in Sugarcane Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1965 Mar;40(2):209–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Enzymes of the Entner-Doudoroff path in fructose-grown Hydrogenomonas eutropha. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Nov;14(11):1259–1260. doi: 10.1139/m68-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Factors affecting the synthesis and degradation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in Hydrogenomonas facilis and Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.937-946.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha and Hydrogenomonas facilis. I. Purification, metallic ion requirements, inhibition, and kinetic constants. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2394–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha and Hydrogenomonas facilis. II. Molecular weight, subunits, composition, and sulfhydryl groups. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2403–2408. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. Y., Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Specific effect of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate on the solubility of tobacco Fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 11;234(2):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. The formation of ribulose 1:5-diphosphate carboxylase by growing cultures of Athiorhodaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:499–510. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS E. B. Pseudoallelism and gene evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:159–174. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLHOFER G., ROSE I. A. THE POSITION OF CARBON-CARBON BOND CLEAVAGE IN THE RIBULOSE DIPHOSPHATE CARBOXYDISMUTASE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1341–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., WATSON S. W. STRUCTURE OF NITROSOCYSTIS OCEANUS AND COMPARISON WITH NITROSOMONAS AND NITROBACTER. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1594–1609. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1594-1609.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Allosteric regulation of phosphoribulokinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):678–682. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Characterization of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase and phosphoribulokinase from Thiobacillus thioparus and Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):310–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Control of ATP-dependent CO2 fixation in extracts of Hydrogenomonas facilis: NADH regulation of phosphoribulokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Apr;131(1):272–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Mack H. M., Johnson E. J. Properties of phosphoribulokinase from Thiobacillus neapolitanus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):532–538. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.532-538.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney R. P., Edwards M. R. Fine Structure of Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):487–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.487-495.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M. Concerning the sites of synthesis of proteins of chloroplast ribosomes and of fraction I protein (ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 6;44(3):539–545. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto C., Sugiyama T., Akazawa T., Miyachi S. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. IX. Further comparative studies on Chlorella and spinach leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFADDEN B. A. Some products of C1402 fixation by Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):339–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.339-343.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Denend A. R. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from autotrophic microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):633–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.633-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Kuehn G. D., Homann H. R. CO(2) Fixation, Glutamate Labeling, and the Krebs Cycle in Ribose-grown Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):879–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.879-885.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Schuster E. 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):751–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.751-756.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tu C. C. Regulation of autotrophic and heterotrophic carbon dioxide fixation in Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.886-893.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tu C. C. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase and CO2 incorporation in extracts of Hydrogenomonas facilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):728–733. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai T., Akazawa T. Homotropic effect of CO 2 in ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 24;46(6):2121–2126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90768-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neal D., Hew C. S., Latzko E., Gibbs M. Photosynthetic carbon metabolism of isolated corn chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1972 Apr;49(4):607–614. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren W. L., Bowes G. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase regulates soybean photorespiration. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 31;230(13):159–160. doi: 10.1038/newbio230159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. M. The evolution of photosynthesis. Science. 1970 Apr 24;168(3930):438–446. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3930.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond C. B. Beta-carboxylation during photosynthesis in Atriplex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 13;141(1):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PON N. G., RABIN B. R., CALVIN M. MECHANISM OF THE CARBOXYDISMUTASE REACTION. I. THE EFFECT OF PRELIMINARY INCUBATION OF SUBSTRATES, METAL ION AND ENZYME ON ACTIVITY. Biochem Z. 1963;338:7–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Deamer D. W., Crofts A. R. Conformational changes in chloroplasts. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:281–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen J. M., Lane M. D. Spinach ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J., Morris J. G. Acetate utilisation by Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(1):52–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J., Morris J. G. Pyruvate carboxylase in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;59(1):97–101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Bassham J. A. Photosynthetic and dark carbon metabolism in unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(1):25–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00412397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Photosynthetic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:285–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N., cohen-Bazire G. Some properties of the green bacterium Pelodictyon clathratiforme. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):226–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00406336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon N. G. Some physical properties of purified fraction I protein from spinach chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnamperuma C. Primordial organic chemistry and the origin of life. Q Rev Biophys. 1971 Aug;4(2):77–106. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope L. M., Hoare D. S., Smith A. J. Ultrastructure of Nitrobacter agilis grown under autotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):936–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.936-939.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J., Merrett M. J. Influence of Light Intensity on Reductive Pentose Phosphate Cycle Activity during Photoheterotrophic Growth of Rhodospirillum rubrum. Plant Physiol. 1972 Aug;50(2):252–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAYLE J. R., KEECH D. B. Carbon assimilation by Pseudomonas oxalaticus (OX 1). 1. Formate and carbon dioxide utilization during growth on formate. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:623–630. doi: 10.1042/bj0720623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAYLE J. R., KEECH D. B. Carbon assimilation by Pseudomonas oxalaticus (OX 1). 2. Formate and carbon dioxide utilization by cell-free extracts of the organism grown on formate. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0720631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri S. M., Hoare D. S. Formic hydrogenlyase and the photoassimilation of formate by a strain of Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2344–2357. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2344-2357.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E., SCHROEDER E. A. The reductive pentose phosphate cycle. II. Specific C-1 phosphatases for fructose 1,6-diphosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-diphosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Apr;74(2):326–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston E., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. Deoxyribonucleic acid homologies of some so-called "Hydrogenomonas" species. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):465–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.465-466.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. S., Nicholas D. J. Studies on the incorporation of Co2 by cells and cell-free extracts of Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 24;124(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C., Lundgren D. G. Electron microscopy of the cell envelope of Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans prepared by freeze-etching and chemical fixation techniques. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1765–1771. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1765-1771.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindt K. P., Ohmann E. NADH and AMP as allosteric effectors of ribulose-5-phosphate kinase in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutner A. C. Estimation of the molecular weight of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase sub-units. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jun 5;39(5):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutner A. C., Lane M. D. Nonidentical subunits of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGAN C. On the origin and planetary distribution of life. Radiat Res. 1961 Aug;15:174–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., VISHNIAC W. CO2 incorporation by extracts of Thiobacillus thioparus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Sep;18(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMILLIE R. M., RIGOPOULOS N., KELLY H. Enzymes of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle in the purple and in the green photosynthetic sulphur bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:612–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOPPANI A. O., FULLER R. C., CALVIN M. Carbon dioxide fixation by Rhodopseudomonas capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1955 May;69(5):491–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.5.491-501.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI I., WERKMAN C. H. Chemoautotrophic carbon dioxide fixation by extracts of Thiobacillus thiooxidans. II. Formation of phosphoglyceric acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Sep;77(1):112–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler W. R., Stanier R. Y. THE FUNCTION OF ACETATE IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS BY GREEN BACTERIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Oct;46(10):1328–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.10.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopf J. W., Barghoorn E. S. Alga-like fossils from the early precambrian of South Africa. Science. 1967 Apr 28;156(3774):508–512. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Decker G. L., Greenawalt J. W. Comparative ultrastructure of the thiobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):618–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.618-627.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. I., Lane M. D. Interaction of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase with 2-carboxyribitol diphosphate, an analogue of the proposed carboxylated intermediate in the CO 2 fixation reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):508–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90377-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirevåg R., Ormerod J. G. Carbon dioxide fixation in green sulphur bacteria. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):399–408. doi: 10.1042/bj1200399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjödin B., Vestermark A. The enzymatic formation of a compound with the expected properties of carboxylated ribulose 1,5-diphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 24;297(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C. R., Hatch M. D. Comparative studies on the activity of carboxylases and other enzymes in relation to the new pathway of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation in tropical grasses. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):660–665. doi: 10.1042/bj1030660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. H., Morris I. Photosynthetic carbon dioxide assimilation by Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(3):213–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00421847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spomer G. G. Molecular diversity of the ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from photosynthetic microorganisms. Science. 1968 Aug 2;161(3840):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springgate C. F., Stachow C. S. Fructose 1,6-diphosphatase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. I. Purification and properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springgate C. F., Stachow C. S. Fructose 1,6-diphosphatase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. II. Regulatory properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springgate C. F., Stachow C. S. Ligand induced molecular weight transitions in Rhodopseudomonas palustris fructose 1,6-diphosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):522–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. E., Hoare D. S. Reductive pentose cycle and formate assimilation in Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):890–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.890-894.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Akazawa T., Nakayana N. Sulfydryl groups of spinach leaf fraction-I protein in relation to ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):522–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. I. Subunit structure of wheat-fraction-I protein. J Biochem. 1967 Oct;62(4):474–482. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Akazawa T. Subunit structure of spinach leaf ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 10;9(23):4499–4504. doi: 10.1021/bi00825a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Ito T., Akazawa T. Subunit structure of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chlorella ellipsoidea. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3406–3411. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Matsumoto C., Akazawa T., Miyachi S. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. VII. Ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of Chlorella ellipsoidea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Matsumoto C., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. XI. Dissociation of spinach leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by urea. J Biochem. 1970 Dec;68(6):821–831. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Nakayama N., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. V. Homotropic effect of bicarbonate in RuDP carboxylase reaction and the mechanism of activation by magnesium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 10;126(3):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Nakayama N., Ogawa M., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. II. Effect of p-chloromercuribenzoate treatment on the ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase activity of spinach leaf fraction I protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):98–106. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUDINGER P. A. Fixation of carbon dioxide by extracts of the strict autotroph Thiobacillus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1956 Oct;64(2):274–286. doi: 10.1042/bj0640274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUEPER H. G. CO2-FIXIERUNG UND INTERMEDIAERSTOFFWECHSEL BEI CHROMATIUM OKENII PERTY. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Jul 15;49:23–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita R., Lundgren D. G. Utilization of glucose and the effect of organic compounds on the chemolithotroph Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):328–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.328-333.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Stewart G. J., Jones G. E. Marine Thiobacilli. II. Culture and ultrastructure. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Nov;13(11):1529–1534. doi: 10.1139/m67-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Newman D. J., LeGall J., Peck H. D., Jr The amino acid sequence of ferredoxin from the sulfate reducing bacterium, Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):452–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90840-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentini W. C., Starr M. P. Growth and ultrastructure of Rhodomicrobium vannielii as a function of light intensity. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1699–1704. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1699-1704.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüper H. G. Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh, a photosynthetic sulfur bacterium depositing sulfur outside the cells. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1910–1920. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1910-1920.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VATTER A. E., DOUGLAS H. C., WOLFE R. S. Structure of Rhodomicrobium vannielii. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jun;77(6):812–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.6.812-813.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VATTER A. E., WOLFE R. S. The structure of photosynthetic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):480–488. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.480-488.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Caeseele L., Lees H. The ultrastructures of autotrophically and heterotrophically grown Thiobacillus novellus. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):651–654. doi: 10.1139/m69-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. S., Lundgren D. G. Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in the chemolithotrophic bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):947–950. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.947-950.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Drews G., Tauschel H. D. Zur Feinstruktur und Taxonomie von Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(4):346–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., McCalla D. R. A simple method for the isolation of fraction I protein of chloroplasts. Can J Biochem. 1968 May;46(5):441–444. doi: 10.1139/o68-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnick M., Lane M. D. Inhibition of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase by cyanide. Inactive ternary complex of enzyme, ribulose diphosphate, and cyanide. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnick M., Lane M. D., Scrutton M. C., Mildvan A. S. The presence of tightly bound copper in ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from spinach. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5761–5763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnick M., Lane M. D., Scrutton M. C. The interaction of metal ions with ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from spinach. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4939–4947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Lin E. C., Tanaka S. Mutants of Aerobacter aerogenes capable of utilizing xylitol as a novel carbon. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):447–456. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.447-456.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Lindstrom E. S. Photosynthetic conversion of formate and CO2 to glutamate by rhodopseudomonas palustris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 10;28(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Fine structure of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: effect of growth temperature on morphology and ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):461–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.461-467.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer W. E. On ultrastructures in Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa and Rhodospirillum tenue. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(2):241–242. doi: 10.1007/BF02219141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool A. P., Lambert R., Laudelout H. The fine structure of frozen etched nitrobacter cells. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;69(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00408570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Niel C. B. THE CULTURE, GENERAL PHYSIOLOGY, MORPHOLOGY, AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE NON-SULFUR PURPLE AND BROWN BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1944 Mar;8(1):1–118. doi: 10.1128/br.8.1.1-118.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


