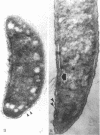
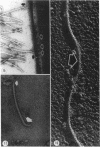
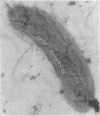
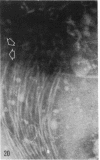
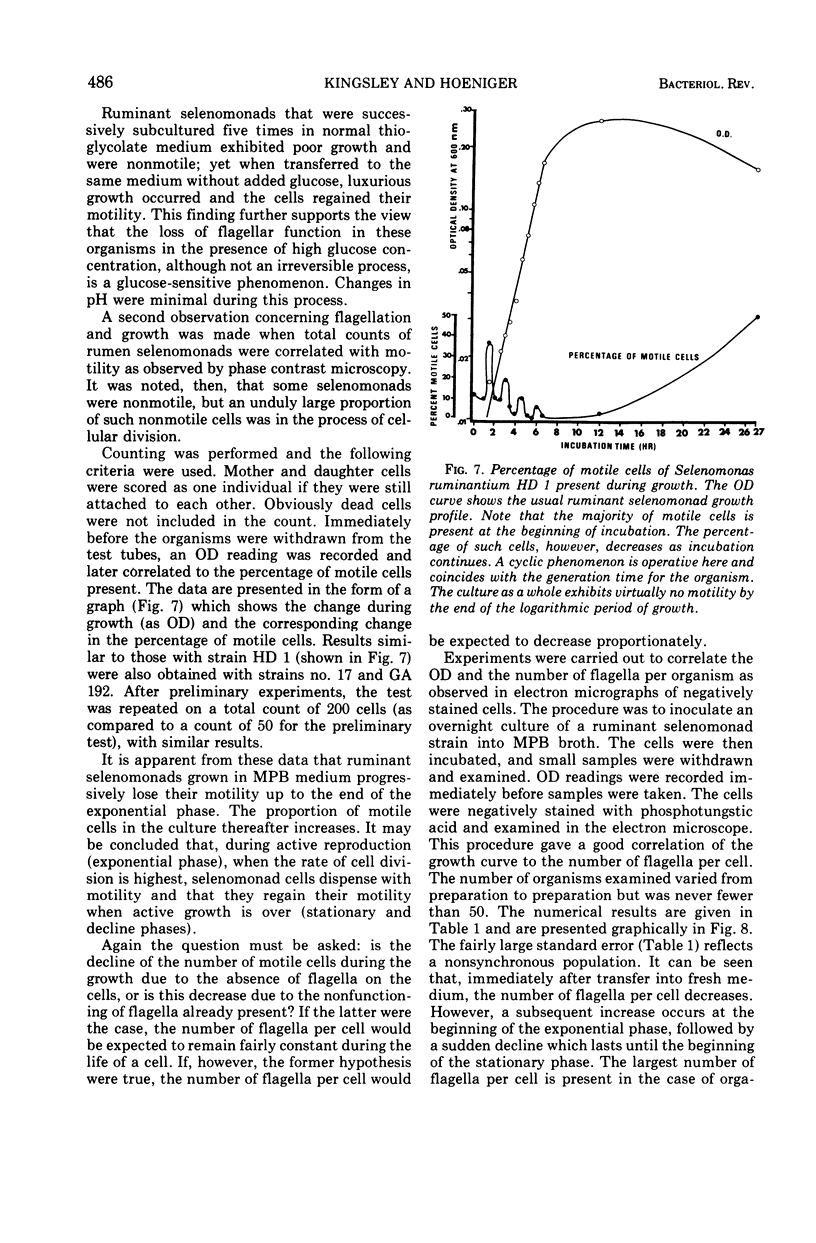
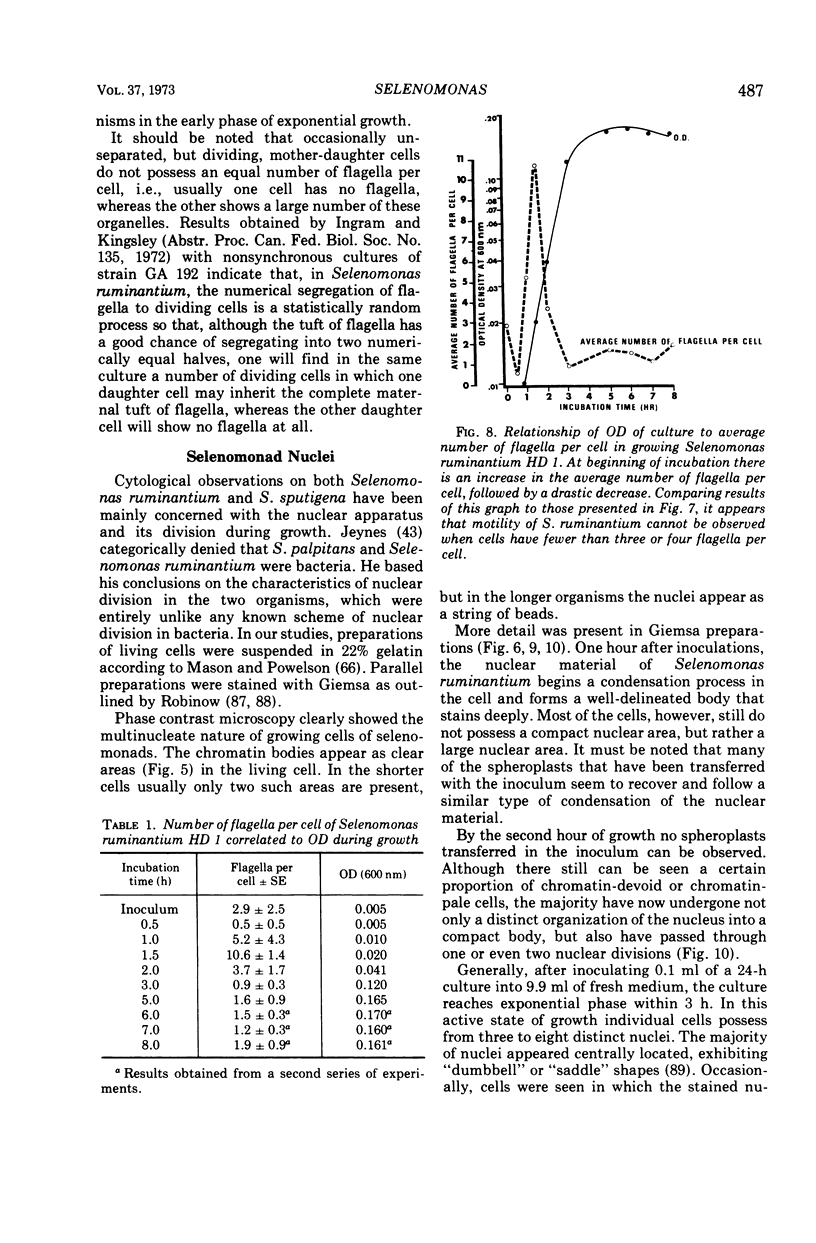
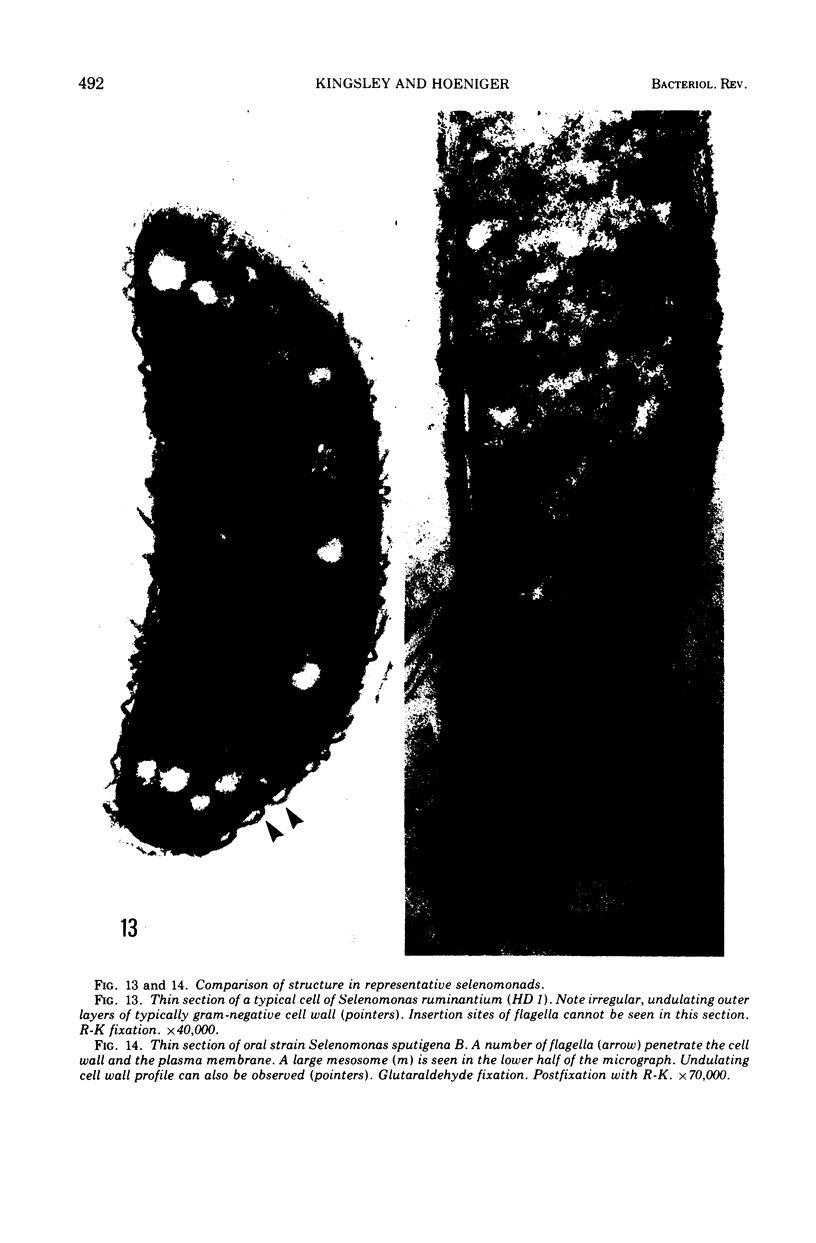
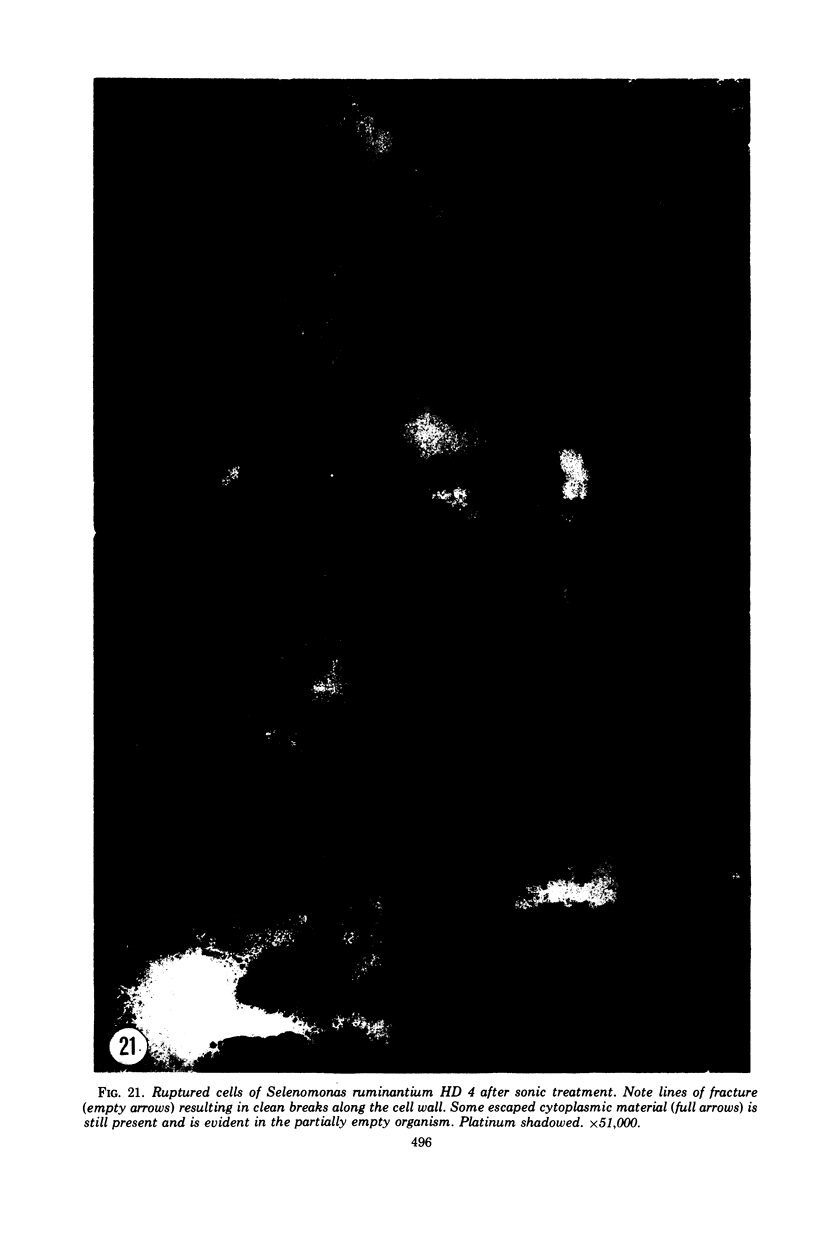
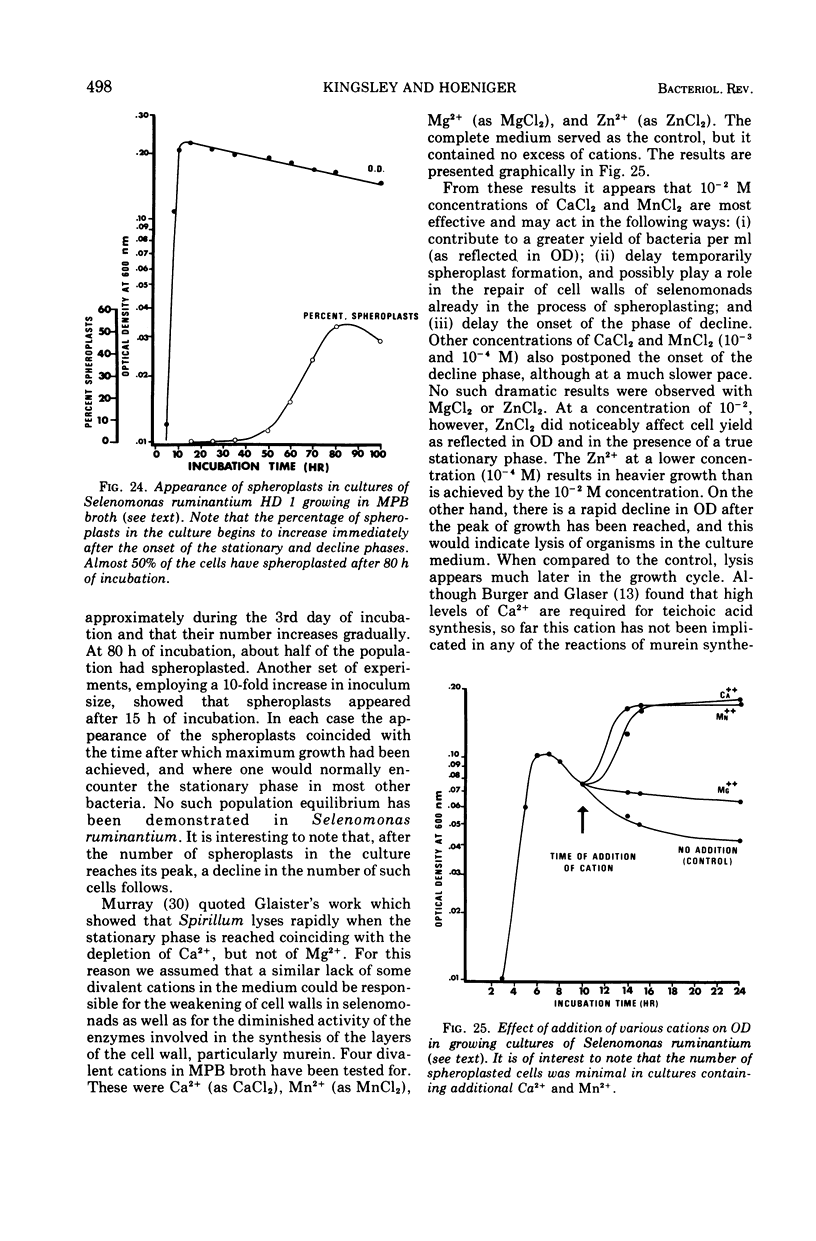
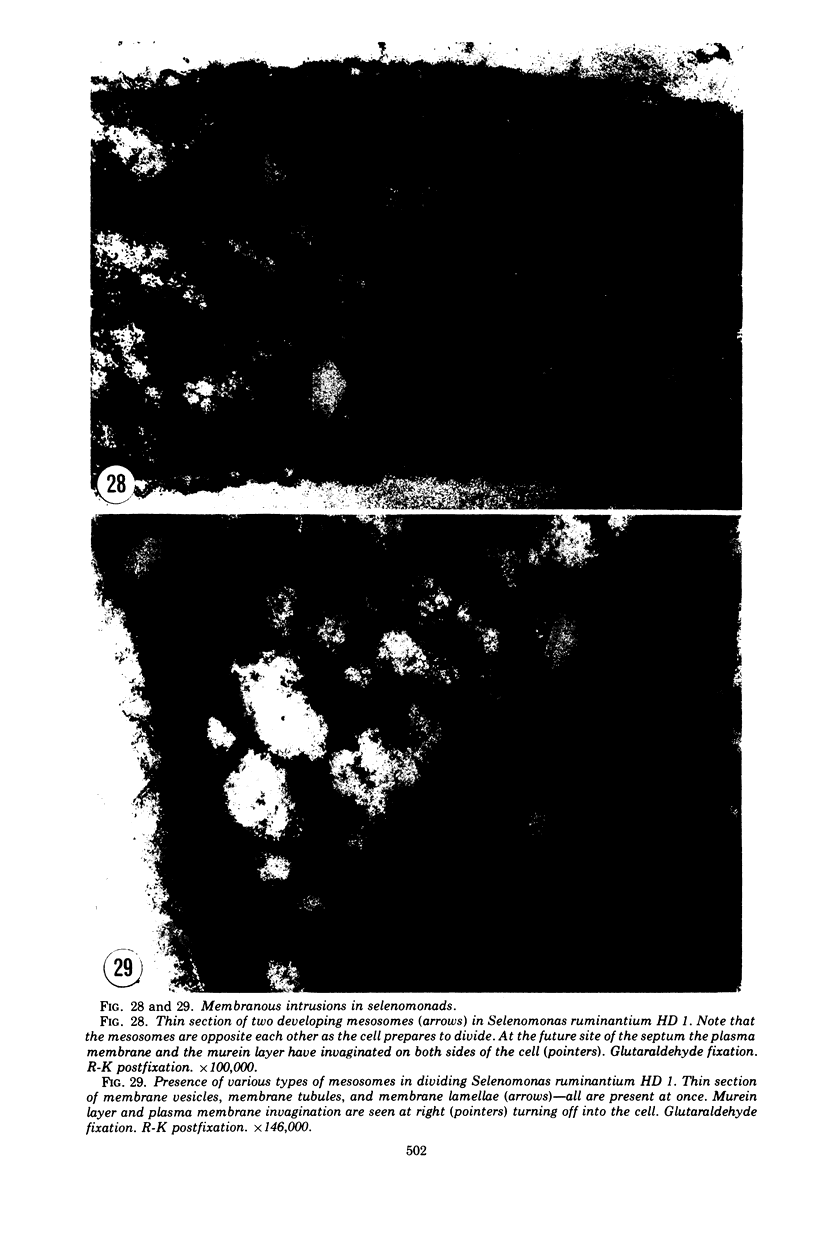
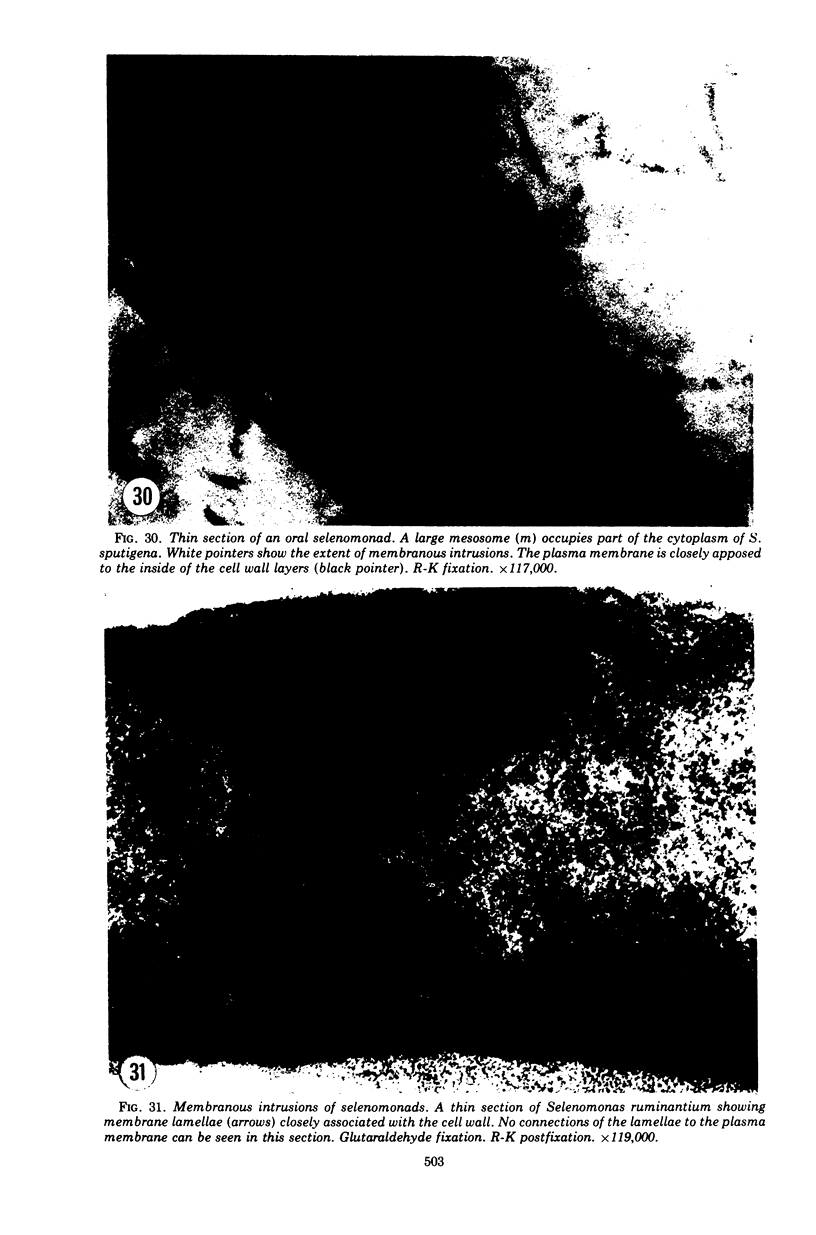
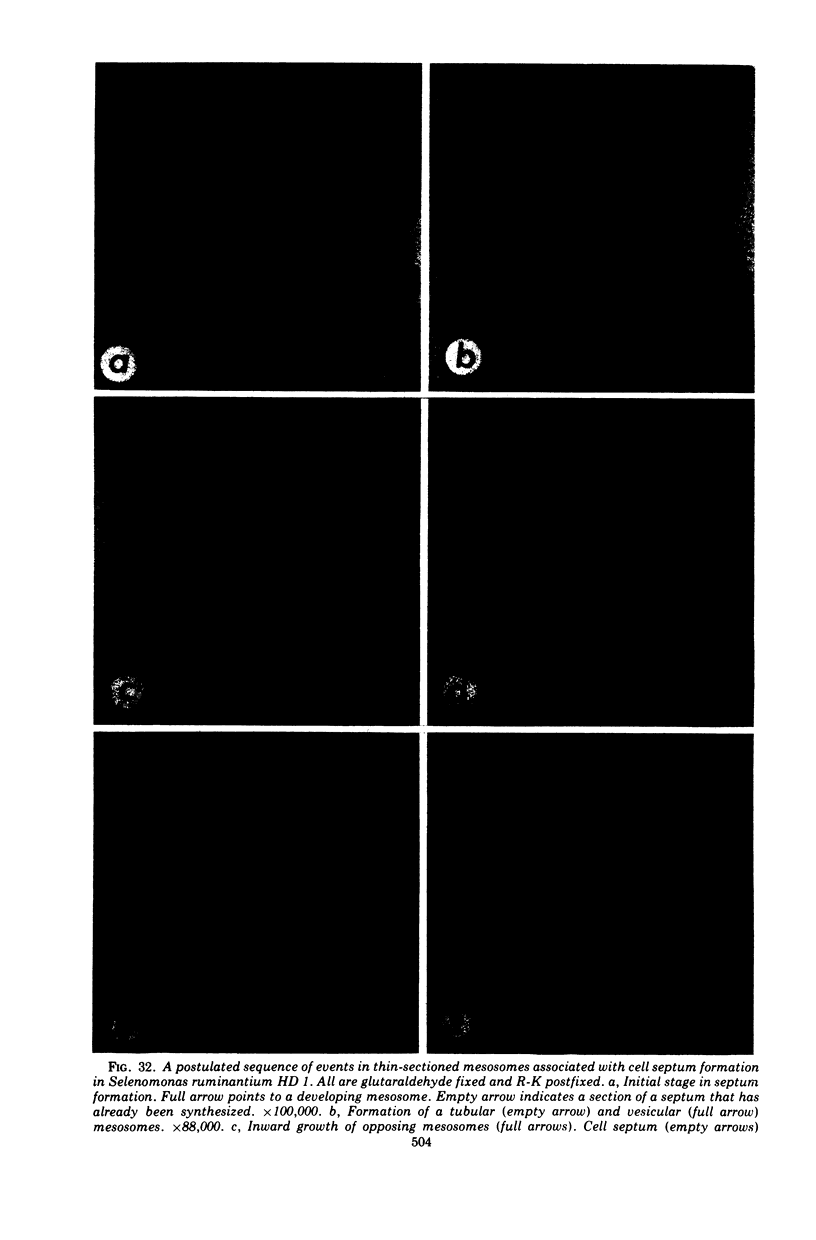
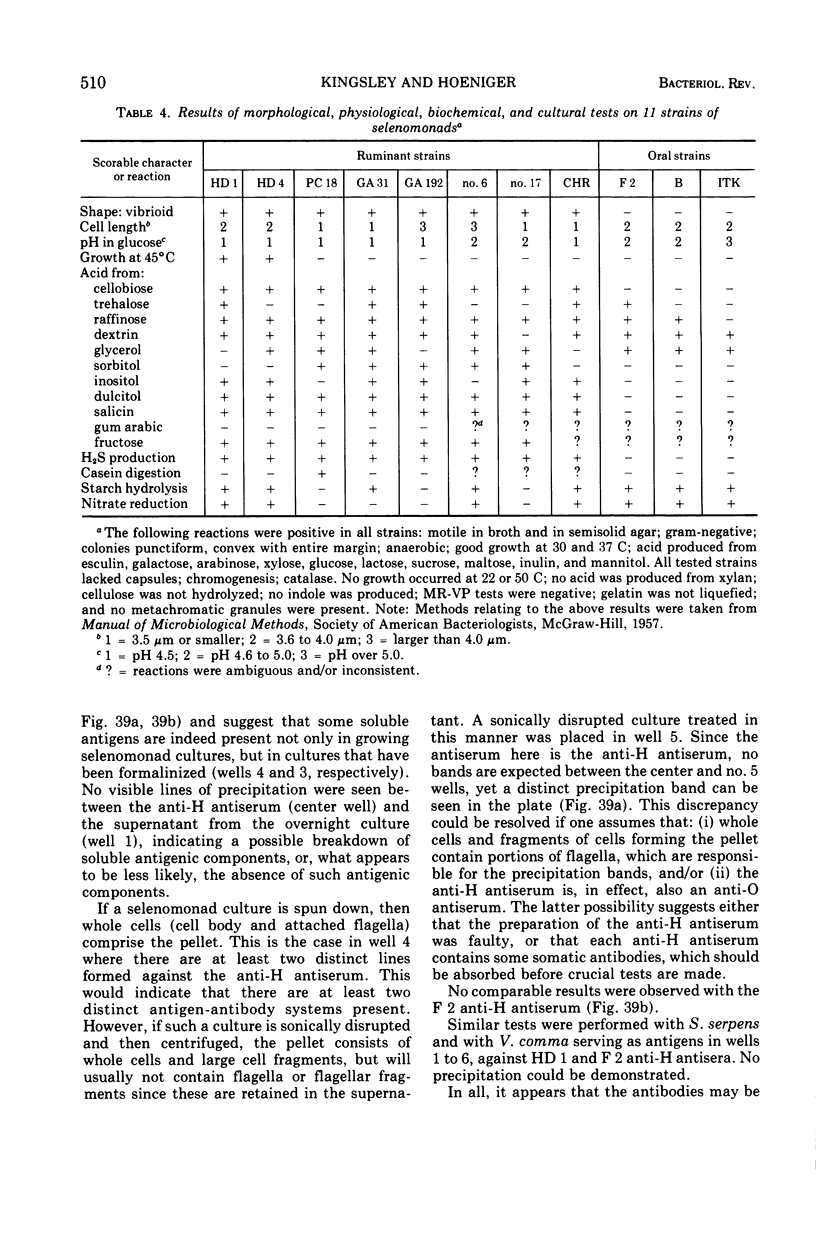
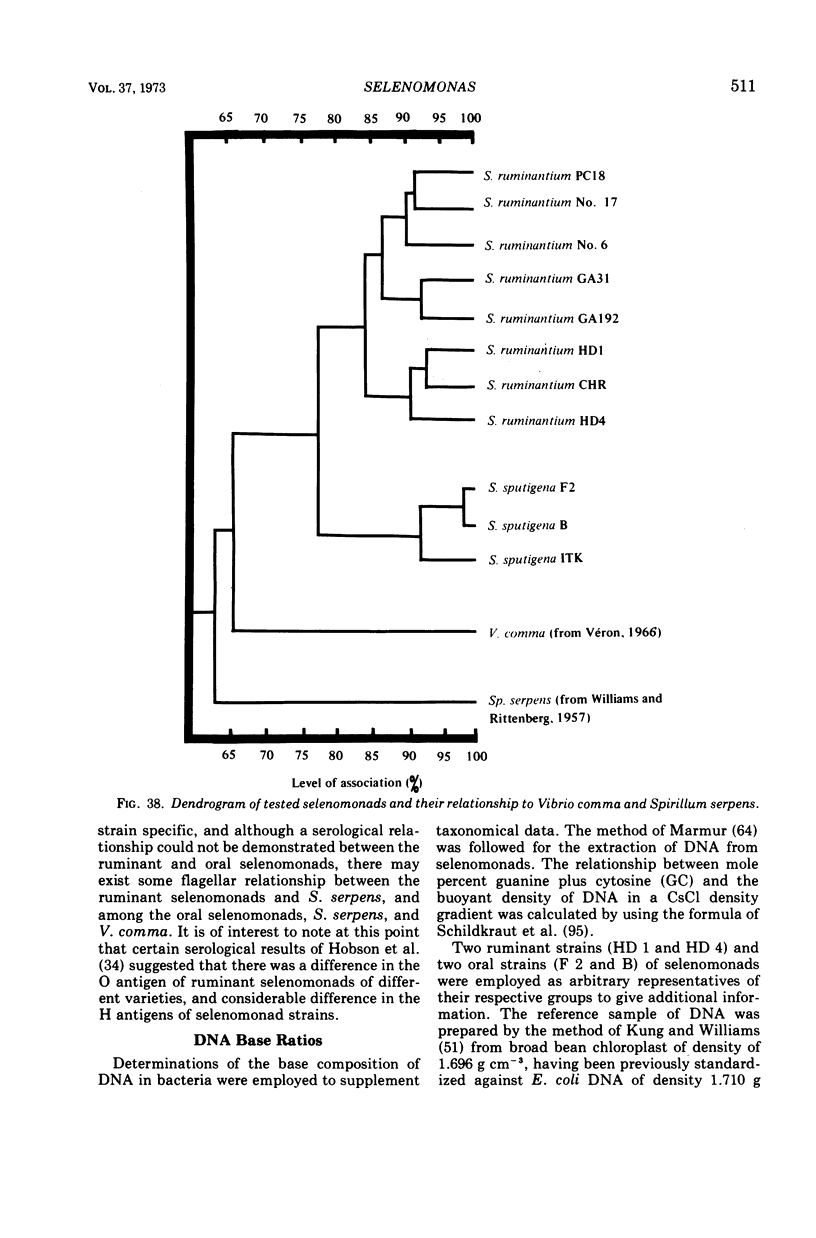
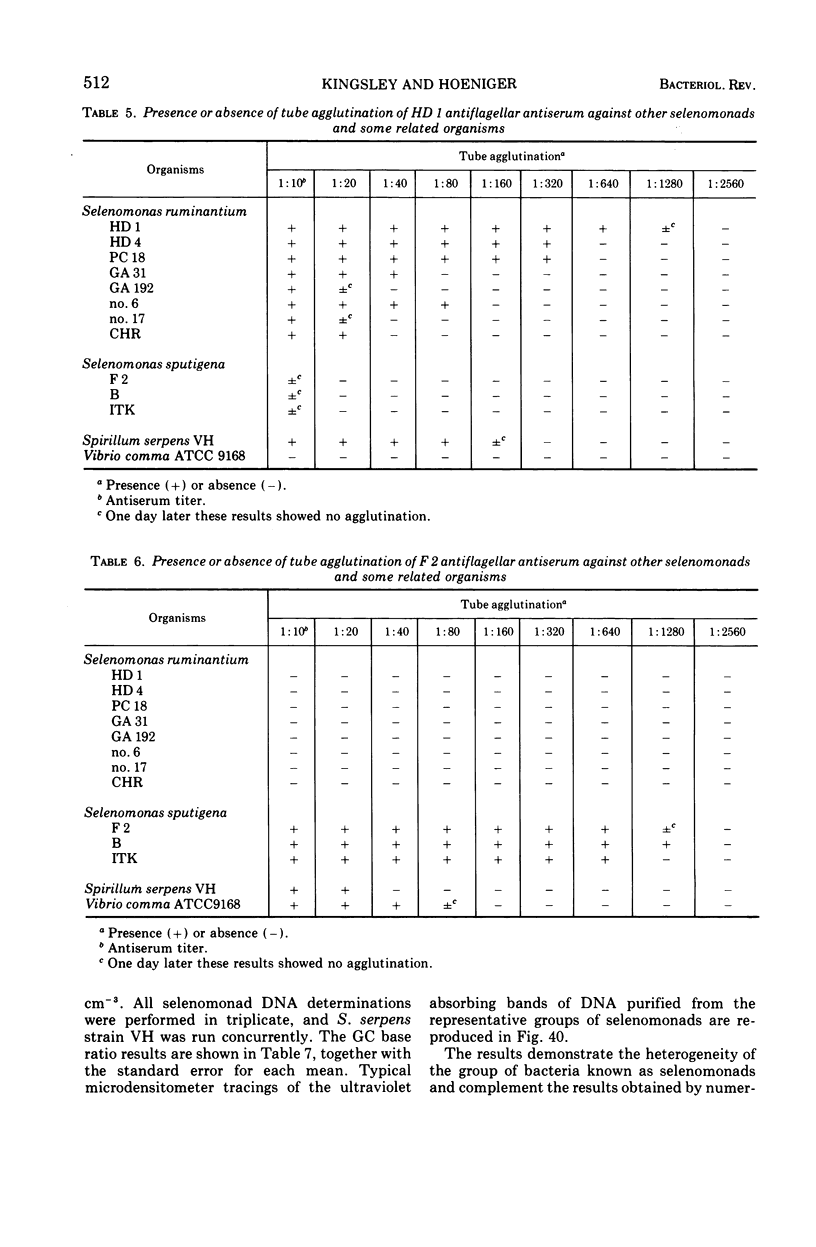
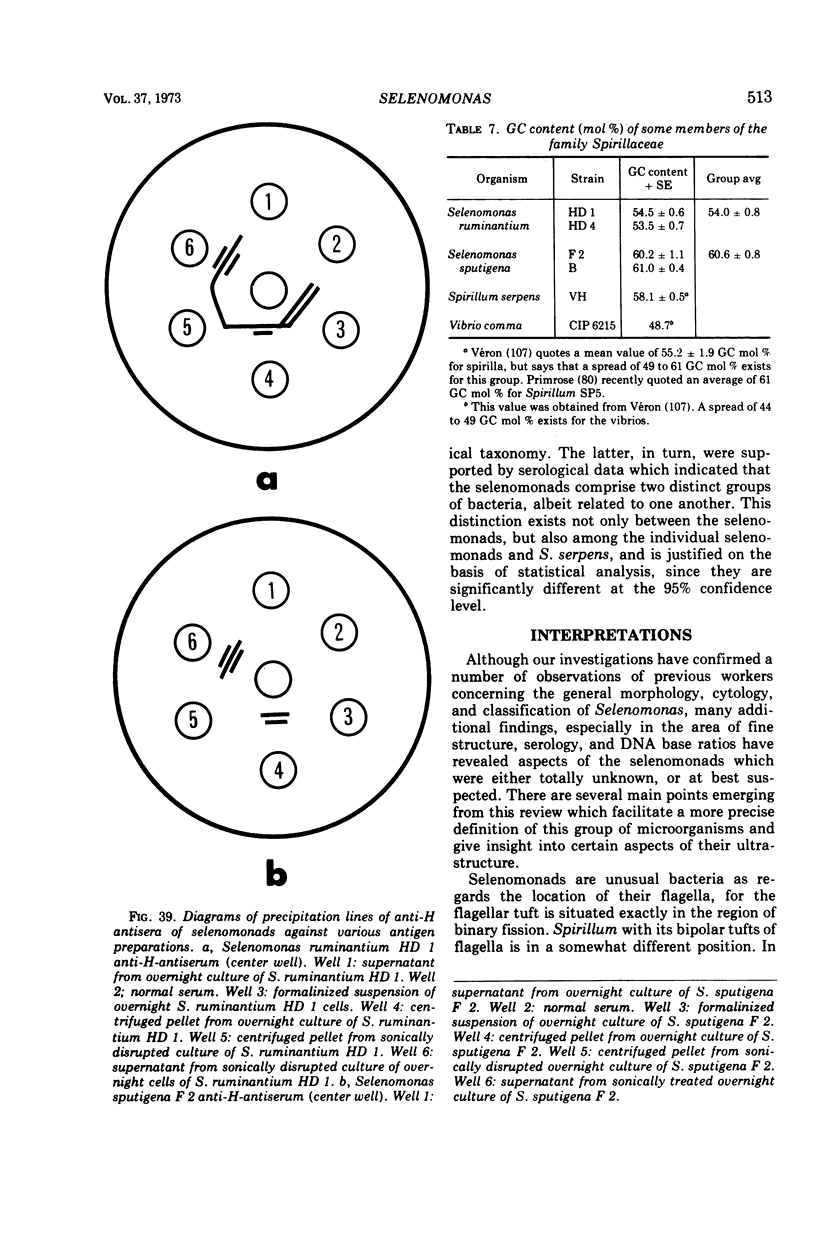
Full text
PDF



























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOU AKKADA A. R., BLACKBURN T. H. Some observations on the nitrogen metabolism of rumen proteolytic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jun;31:461–469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-3-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAMSON M. B., KATZMAN R., WILSON C. E., GREGOR H. P. IONIC PROPERTIES OF AQUEOUS DISPERSIONS OF PHOSPHATIDIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4066–4072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOSCOTT R. J., KAR A. B. Paper chromatographic and biological properties of reserpine and related compounds. Nature. 1955 Dec 3;176(4492):1077–1078. doi: 10.1038/1761077b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. The characteristics of strains of Selenomonas isolated from bovine rumen contents. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):162–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.162-167.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. I. POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3168–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Burton G. C. The effect of hibernation on the caecal flora of the thirteen-lined ground squirrel (Citellus tridecemlineatus). J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;33(3):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb02227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Rogers H. J. Modification of the appearance of mesosomes in sections of Bacillus licheniformis according to the fixation procedures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Feb;30(3):354–367. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Rogers H. J. The structure and development of mesosomes studied in Bacillus licheniformis strain 6346. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jan;38(1):113–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., KUNISAWA R. The fine structure of Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:401–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE R. M. CELL WALL REPLICATION IN SALMONELLA TYPHOSA. Science. 1964 Feb 21;143(3608):820–822. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3608.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Jones G. A., Simpson F. J., Bryant M. P. Isolation and identification of rumen bacteria capable of anaerobic rutin degradation. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1365–1371. doi: 10.1139/m69-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. Y., Doy C. H., Mercer E. H. Ultrastructure of the obligate halophilic bacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.196-201.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., London J. Basal organelles of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.458-465.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N. Functional aspects of bacterial flagellar motility. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1971 May;1(1):73–103. doi: 10.3109/10408417109104478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. C. Participation of the cytoplasmic membrane in the growth and spore fromation of bacilli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:507–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULGHUM R. S., MOORE W. E. ISOLATION, ENUMERATION, AND CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTEOLYTIC RUMINAL BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:808–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.808-815.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Murray R. G. Fractionation and characterization of the plasma and mesosome membrane of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):426–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.426-440.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunetileke K. G., Anwar R. A. Biosynthesis of uridine diphospho-N-acetyl muramic acid. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5740–5743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF SOME ANEROBIC AND FACULTATIVELY ANAEROBIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Feb;38:167–180. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N., MANN S. O., SMITH W. Serological tests of a relationship between rumen selenomonads in vitro and in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:265–270. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N., MANN S. O. The isolation of glycerol-fermenting and lipolytic bacteria from the rumen of the sheep. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:227–240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., GALL L. S. Rumen organisms. I. Curved rods and a related rod type. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.548-553.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERRIDGE D. The effect of inhibitors on the formation of flagella by Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:519–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNAREV V. M., PEREVERZEV N. A. SISTEMA MEMBRAN V KLETKAKH E. COLI. Mikrobiologiia. 1964 Jul-Aug;33:610–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Takahashi H. Function of growth factors for rumen microorganisms. I. Nutritional characteristics of Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.456-463.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Williams J. P. Chloroplast DNA from broad bean. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 16;195(2):434–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90650-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESSEL E. F., Jr, BREED R. S. Selenomonas Boskamp, 1922; a genus that includes species showing an unusual type of flagellation. Bacteriol Rev. 1954 Sep;18(3):165–168. doi: 10.1128/br.18.3.165-169.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifson E. Development of Flagella on Germinating Spores. J Bacteriol. 1931 May;21(5):357–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.21.5.357-359.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Gibbons R. J. A practical scheme for identification of the most numerous oral gram negative anaerobic rods. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 Jul-Aug;10(4):723–725. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Oxygen sensitivity of various anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):723–727. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.723-727.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., MADLENER E. M., SOCRANSKY S. S. Observations on Spirillum sputigenum and its relationship to Selenomonas species with special reference to flagellation. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):559–565. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.559-565.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., MADLENER E. M. Studies on the isolation of Spirillum sputigenum. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Aug;3(5):679–686. doi: 10.1139/m57-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON D. J., POWELSON D. M. Nuclear division as observed in live bacteria by a new technique. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):474–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.474-479.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOIR R. J., MASSON M. J. An illustrated scheme for the microscopic identification of the rumen microorganisms of sheep. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Apr;64(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Gordee E. Z. Formation of bacterial flagella. I. Demonstration of a functional flagellin pool in spirillum serpens and bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):870–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.870-875.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rosenkranz H. S., Chan B., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of magnesium-depleted bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):891–895. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.891-895.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch-Petersen E. A new culture medium for rumen bacteria. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1964 Jul;193(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogimoto K. Uber Selenomonas aus dem Caecum von Ratten. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Sep;221(4):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON N. W., MAITLAND H. B. The influence of temperature on the motility of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Aug;7(1-2):117–128. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-1-2-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontefract R. D., Thatcher F. S. An electron microscopy study of mesosomes in irradiation-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Jan;30(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primrose S. B. Studies on the deoxyribonucleic acid from Spirillum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 30;247(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90804-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prins R. A. Isolation, culture, and fermentation characteristics of Selenomonas ruminantium var. bryantivar. n. from the rumen of sheep. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):820–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.820-825.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purser D. B., Buechler S. M. Amino acid composition of rumen organisms. J Dairy Sci. 1966 Jan;49(1):81–84. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(66)87791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINOW C. F. Morphology of the bacterial nucleus. Br Med Bull. 1962 Jan;18:31–35. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. E., Keeler R. F., Bryner J. H. Anatomical features of Vibrio fetus: Electron microscopic survey. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):427–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Structure and functions of mesosomes of gram positive bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;49:151–177. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46166-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER B. A., CAMPBELL J. C. The effect of non-lethal deflagellation on bacterial motility and observations on flagellar regeneration. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):670–685. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T. Electron microscopic study on the effect of the oxidation of ultrathin sections of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 May;18(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Koffler H. Bacterial flagella. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:219–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAITUZIS Z., DOETSCH R. N. FLAGELLA OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1586–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1586-1593.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ITERSON W. Some features of a remarkable organelle in Bacillus subtilis. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Jan;9:183–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Flagella of Escherichia coli spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2103–2104. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2103-2104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Relationship between cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, and bacterial motility. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.512-521.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Véron M. Taxonomie numériques de vibrions et de certaines bactéries comparables. II. Corrélation entre les similitudes phénétiques et la composition en bases de l'ADN. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Dec;111(6):671–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]