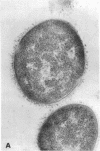
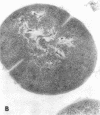
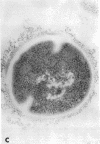
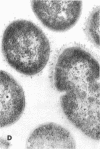
Full text
PDF

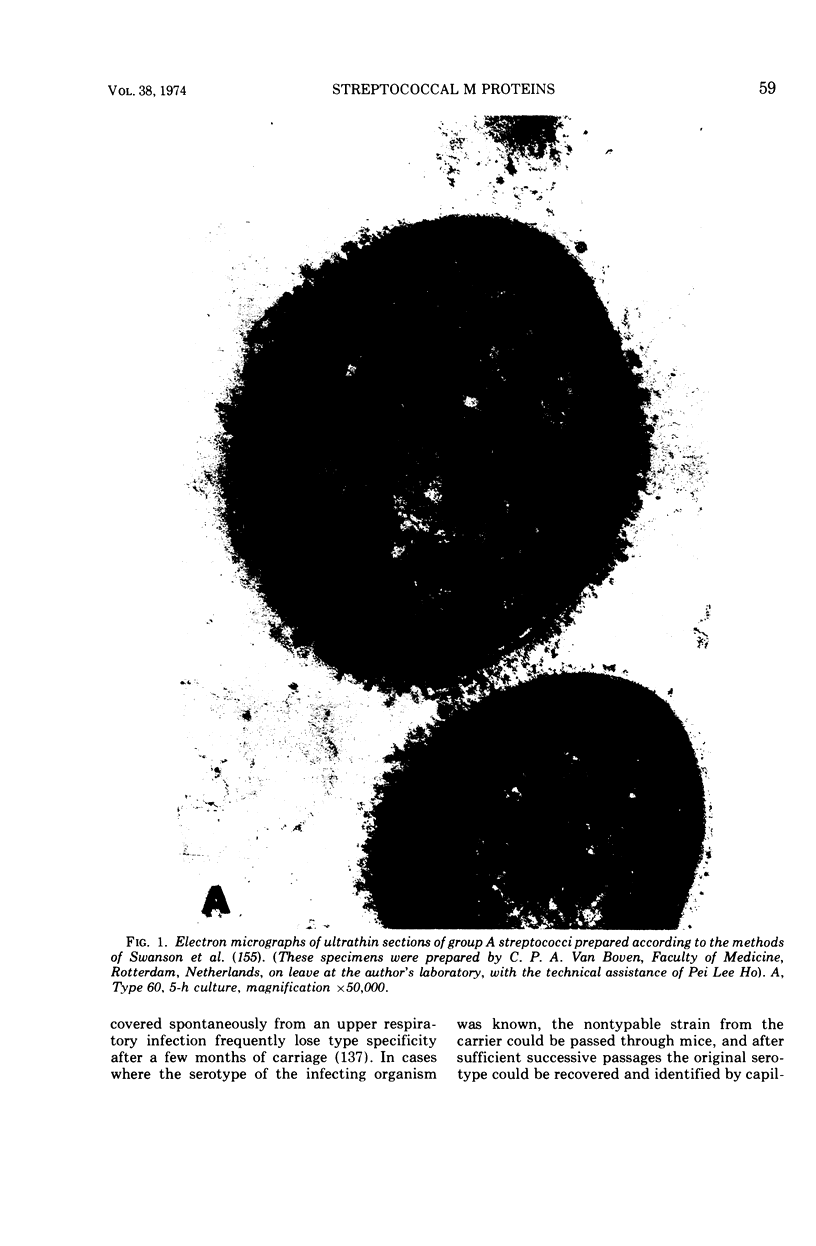

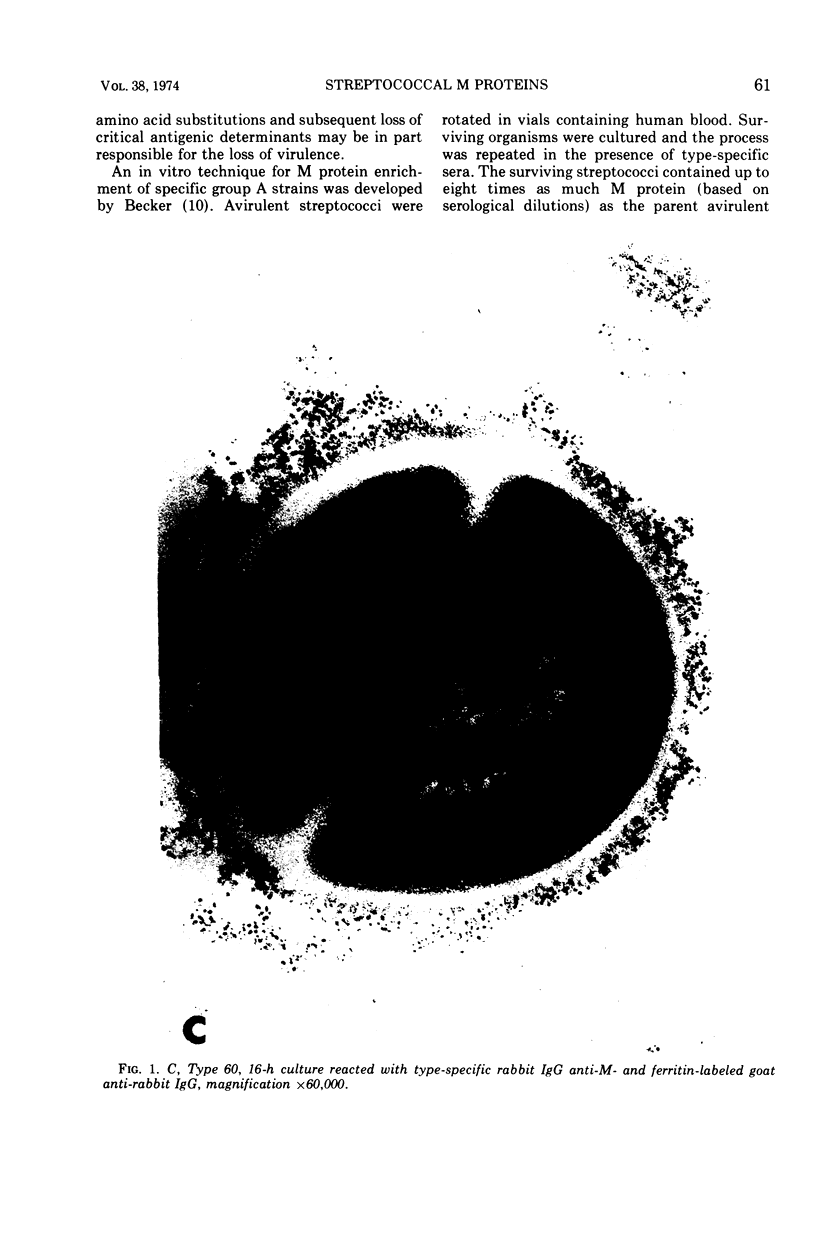
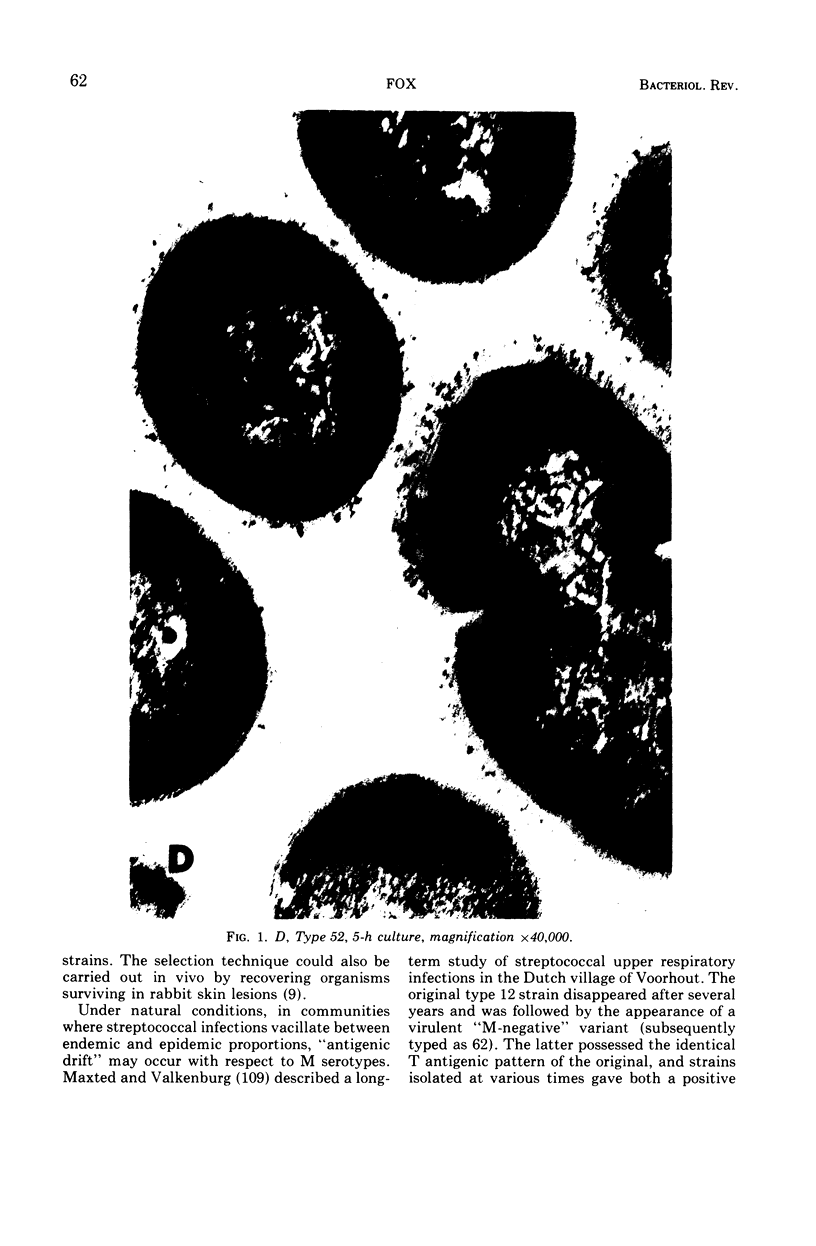






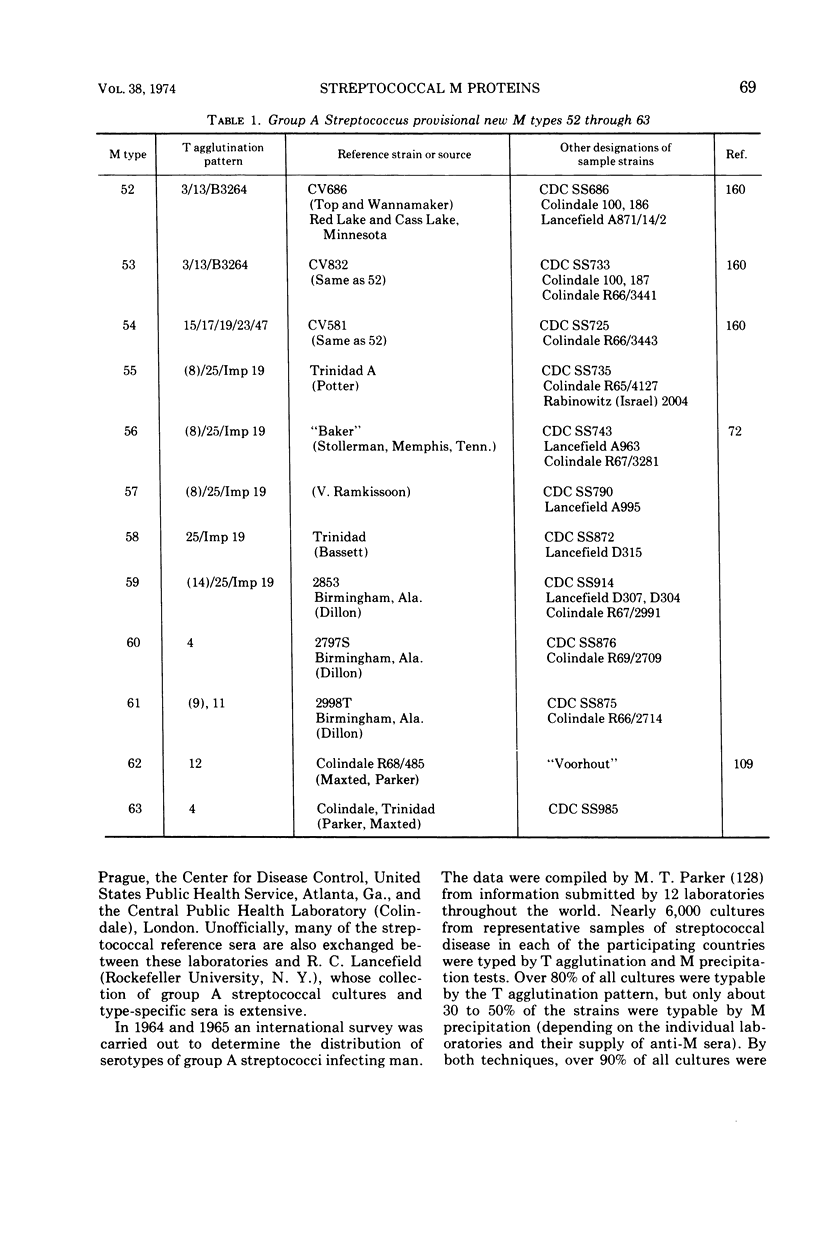
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH H., HARRELL W. K. NEW METHOD OF PREPARING IMMUNIZING ANTIGENS FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ANTI-M SERA AGAINST CERTAIN SEROTYPES OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:141–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.141-145.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F. Quantitative and qualitative studies of antibody to streptococcal M-protein. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGNERRABINOWITZ S. A CELLULOSE ACETATE MEMBRANE IMMUNODIFFUSION TYPING TECHNIQUE FOR GROUP A HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Sep;64:488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS AND INHIBITORS ON M PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.527-531.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Alberti H., Stollerman G. H. Delayed hypersensitivity to purified streptococcal m protein in guinea pigs and in man. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):42–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H. Toxic effects of streptococcal M protein on platelets and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human blood. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):351–365. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck A., Bergner-Rabinowitz S. An absorption method for preparing anti-M-typing streptococcal sera using acid-hydrolyzed cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):834–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G. Enhancing effect of type specific antistreptococcal antibodies on emergence of streptococci rich in M-protein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):331–335. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergner-Rabinowitz S., Beck A., Ofek I., Davies A. M. Identification of type specific streptococcal antibodies by in vitro phagocytosis. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 May-Jun;5(3):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergner-Rabinowitz S., Ofek I., Davies M. A., Rabinowitz K. Type-specific streptococcal antibodies in pyodermal nephritis. J Infect Dis. 1971 Nov;124(5):488–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.5.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergner-Rabinowitz S., Ofek I., Moody M. D. Cross-protection among serotypes of group A streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):339–344. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besdine R. W., Pine L. Preparation and description of high-molecular-weight soluble surface antigens from a group A Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):1953–1960. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.1953-1960.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. O. Effect of culture medium composition and pH on the production of M protein and proteinase by group A Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):737–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.737-744.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. O., Pine L. Quantitative aspects of the M protein capillary precipitin test. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.122-127.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing A. H., Mortimer E. A., Jr A hamster model for streptococcal impetigo. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):224–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNY F. W., Jr, THOMAS L. The demonstration of type specific streptococcal antibody by a hemagglutination technique employing tannic acid. J Clin Invest. 1953 Nov;32(11):1085–1093. doi: 10.1172/JCI102831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMINGUE G. J., PIERCE W. A., Jr EFFECT OF PARTIALLY PURIFIED STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN ON THE IN VITRO PHAGOCYTOSIS OF STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:583–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.583-588.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Experimental infection of the skin in the hamster simulating human impetigo. I. Natural history of the infection. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):196–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies H. C., Karush F., Rudd J. H. Synthesis of M protein by group A hemolytic streptococci in completely synthetic media during steady-state growth. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.162-168.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dishon T., Finkel R., Marcus Z., Ginsburg I. Cell-sensitizing products of streptococci. Immunology. 1967 Dec;13(6):555–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap M. B., Harvey H. S. The carrier state and type-specific immunity in streptococcal disease. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Sep;114(3):229–243. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090240043001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT S. D. The crystallization and serological differentiation of a streptococcal proteinase and its precursor. J Exp Med. 1950 Sep;92(3):201–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY M. J., SMITH M. R., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenicity of group A Streptococci. I. Its relation to surface phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:603–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY M. J., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenicity of group A streptococci. II. The antiphagocytic effects of the M protein and the capsular gel. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:617–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. ANTIGENICITY OF THE M PROTEINS OF GROUP A HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:826–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. INTRACELLULAR M PROTEIN OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:536–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.536-540.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., KRAMPITZ L. O. Studies on the biosynthesis of the M-protein of group A hemolytic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):454–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.454-461.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. Measurement of streptococcal antigen synthesis with fluorescent antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Mar;109:577–579. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. Peptide requirements for the synthesis of streptococcal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIMER E. H., KRAUSE R. M., McCARTY M. Studies of L forms and protoplasts of group A streptococci. I. Isolation, growth, and bacteriologic characteristics. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:853–874. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Moody M. D. Production of streptococcal M-typing antisera. I. Antigenic response in different breeds of rabbits. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1822–1825. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1822-1825.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Grossman B. J. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. V. The absence of antigenic determinants common to mammalian heart muscle. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):970–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Pachman L. M., Wittner M. K., Dorfman A. Primary immunization of infants and children with group A streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):598–604. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Peterson R. D. Streptococcal M protein vaccines, rheumatic fever and human histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):1031–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Waldman R. H., Wittner M. K., Mauceri A. A., Dorfman A. Protective study with a group A streptococcal M protein vaccine. Infectivity challenge of human volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1885–1892. doi: 10.1172/JCI107372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. II. Antibody response in rabbits to vaccines prepared with oil emulsions and aluminum hydroxide. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. IV. Cross-reactivity between serotypes. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K., Dorfman A. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. 3. Antibody responses and cutaneous hypersensitivity in humans. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1135–1151. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. New observations on the structure and antigenicity of the M proteins of the group A streptococcus. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL F. A. A review of past attempts and present concepts of producing streptococcal immunity in humans. Q Bull Northwest Univ Med Sch. 1960;34:326–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL F. A., COLE R. M. THE FATE OF A BACTERIAL ANTIGEN (STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN) AFTER PHAGOCYTOSIS BY MACROPHAGES. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:898–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODER H. Association of a serum opacity reaction with serological type in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jul;25:347–352. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M. Studies on the binding between streptococcal M protein and antibody. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:671–683. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):419–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrell W. K., Ashworth H. Absorption of group A streptococcus anti-M typing sera with broken cells. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):422–425. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.422-425.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrell W. K., Ashworth H., Davis R. E., 2nd Cross-protective antigens of group A streptococci types 3 and 31 and types 46 and 51. Infect Immun. 1971 Jul;4(1):79–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.1.79-84.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlícek J., Alouf J. E., Raynaud M. Hétérogénéité antigénique de la protéine M de Streptococcus pyogenes type 24. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Dec;117(6):745–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes: general properties of the streptococcal factor and of the reaction in aged serum. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Mar;66(1):37–47. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata A. A., Terasaki P. I. Cross-reactions between streptococcal M proteins and human transplantation antigens. Science. 1970 May 29;168(3935):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3935.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. E., Braun D., Jönsson J. Antigenic factors common to human kidney and nephritogenic and non-nephritogenic streptococcal strains. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(2):127–130. doi: 10.1159/000229982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz W., Lipinski B., Jeljaszewicz J. Nature of the interaction between M protein of Streptococcus pyogenes and fibrinogen. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):626–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., Moskowitz M. Nature of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2205–2209. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2205-2209.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. C., Stollerman G. H. Nephritogenic streptococci. Annu Rev Med. 1969;20:315–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.20.020169.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Vosti K. L. Purification of two fragments of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 streptococcus. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S., COLE R. M. Preparation and antigenicity of M protein released from group A, type 1 streptococcal cell walls by phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:77–96. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. I. IDENTITY OF THE REACTANTS, AND STOICHIOMETRY OF THE REACTION. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:849–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBROGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. II. RENAL LESIONS INDUCED BY INTRAVENOUS INJECTION OF M PROTEIN INTO MICE AND RATS. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:861–872. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. INDUCTION OF AUTOIMMUNITY TO HEART IN RHEUMATIC FEVER BY STREPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN(S) CROSS-REACTIVE WITH HEART. Fed Proc. 1965 Jan-Feb;24:109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H., MEYESERIAN M. An immunological cross-reaction between group-A streptococcal cells and human heart tissue. Lancet. 1962 Apr 7;1(7232):706–710. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H., SVEC K. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RELATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL AND TISSUE ANTIGENS. III. PRESENCE IN HUMAN SERA OF STREPTOCOCCAL ANTIBODY CROSS-REACTIVE WITH HEART TISSUE. ASSOCIATION WITH STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTION, RHEUMATIC FEVER, AND GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:651–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAKAWA W. W., BORMAN E. K., MCFARLAND C. R. TYPING OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF TYPE I FLUORESCEIN-LABELED ANTIBODY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1377–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1377-1382.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAKAWA W. W., ROTTA J., KRAUSE R. M. DETECTION OF M PROTEIN IN COLONIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL L FORMS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:198–201. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIHARA H., SNELL E. E. Peptides and bacterial growth. VIII. The nature of strepogenin. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. Studies on the bacteriophages of hemolytic streptococci. II. Antigens released from the streptococcal cell wall by a phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1958 Dec 1;108(6):803–821. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUMWIEDE E. Studies on a lipoproteinase of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1954 Dec 1;100(6):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.6.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlich R., Procházka O. Participation of nonspecific factors in the destruction of type M 12 streptococcus in vitro. I. Nonspecific absorption of anti-M 12 bactericidal activity. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1970;14(1):75–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange C. F., Lee R., Merdinger E. Chemistry and end-group analysis on purified M protein of type 12 group A streptococcal cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1277-1283.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. A., Moody M. D., Facklam R. R. Antigenic variation in group A streptococci: types 11 and 9. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):40–45. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.40-45.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg L. H., Vosti K. L., Raffel S. Experimental streptococcal glomerulonephritis in rats. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1231–1240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyampert I. M., Vvedenskaya O. I., Danilova T. A. Study on streptococcus group A antigens common with heart tissue elements. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):313–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ A. S., LANGE C. F., Jr STREPTOCOCCAL RELATED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. I. ISOLATION, IMMUNOCHEMISTRY AND COMPARATIVE CHEMISTRY OF SOLUBLE FRACTIONS FROM TYPE 12 NEPHRITOGENIC STREPTOCOCCI AND HUMAN GLOMERULI. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The indirect bactericidal test as a means of identifying antibody to the M antigen of Streptococcus pyogenes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Aug;37(4):415–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. THE ROLE OF D-ALANINE IN THE SEROLOGICAL SPECIFICITY OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCAL GLYCEROL TEICHOIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:259–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. I. Production and fractionation of the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):555–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., MASSELL B. F. USE OF UNABSORBED ANTISERA IN GEL DIFFUSION FOR GROUPING AND TYPING OF HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICKELSON M. N. CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIUM FOR GROWTH STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:158–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.158-164.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., PADULA J., LIZANA D., HALL C. T. EPIDEMIOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY T-AGGLUTINATION AND M-PRECIPITATION TESTS IN THE PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:149–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz A. S. RAPID PRODUCTION OF ANTI-M PROTEIN ANTIBODIES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85(2):495–496. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.495-496.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massell B. F., Honikman L. H., Amezcua J. Rheumatic fever following streptococcal vaccination. Report of three cases. JAMA. 1969 Feb 10;207(6):1115–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massell B. F., Michael J. G., Amezcua J., Siner M. Secondary and apparent primary antibody responses after group A streptococcal vaccination of 21 children. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Mar;16(3):509–518. doi: 10.1128/am.16.3.509-518.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Valkenburg H. A. Variation in the M-antigen of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):199–210. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCARTY M. The occurrence of polyglycerophosphate as an antigenic component of various gram-positive bacterial species. J Exp Med. 1959 Apr 1;109(4):361–378. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael J. G., Massell B. F. Dynamics in development of experimental streptococcal immunity in mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):131–138. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.131-138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson M. N., Slade H. D. Absence of type specific M antigen from group A streptococci grown in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1251–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1251-.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhla L. S., Glynn L. E. Studies on the antigen in beta-haemolytic streptococci that cross-reacts with an antigen in human myocardium. Immunology. 1967 Aug;13(2):209–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb R. W. Immunoglobulin composition of human antibodies to type 12 streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):242–249. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. C., Moody M. D. Acid-precipitated M protein compared with a column-eluted M protein preparation from type 12, group A Streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):5–10. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.5-10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER E. V., STOLLERMAN G. H., SIEGEL A. C. Recall of type specific antibodies in man by injections of streptococcal cell walls. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:301–310. doi: 10.1172/JCI104483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachman L. M., Fox E. N. Cellular and antibody reactions to streptococcal M protein types 1, 3, 6 and 12. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):898–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T. International survey of the distribution of serotypes of Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci). Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(4):513–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Safford J. W., Jr, Hirata A. A., Terasaki P. I., Reisfeld R. A. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by streptococcal type M1 protein: relationship to HL-A antigens. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Pine L. Evaluation of methods used to purify acid-extracted group A streptococcal M protein. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):963–973. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.963-973.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Reeves M. W. Correlation of M protein production with those factors found to influence growth and substrate utilization of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):668–680. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.668-680.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pranitis P. A., Murray R. H., Kornfeld J. M. Effect of phenol extraction of group A streptococcus on titer and specificity of fluorescent M-typing antisera. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):250–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUINN R. W., LOWRY N. P. STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN ANTIBODIES. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jul-Aug;113:33–38. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn R. W., Lowry P. N. Streptococcal M protein antibodies acquired at birth. Pediatrics. 1967 May;39(5):778–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTTA J., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. ISOLATION OF L FORMS FROM GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI EXPOSED TO BACITRACIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1581–1585. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1581-1585.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWEN R., MARTIN J. ENHANCEMENT OF CHOLESTEROL ESTERIFICATION IN SERUM BY AN EXTRACT OF GROUP-A STREPTOCOCCUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:396–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Krause R. M., Lancefield R. C., Everly W., Lackland H. New approaches for the laboratory recognition of M types of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1298–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT W. C. THE LYSIS OF CELL WALLS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY STREPTOMYCES ALBUS ENZYME TREATED WITH DIISOPROPYL FLUOROPHOSPHATE. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE LYTIC REACTION AND THE SOLUBLE CELL WALL FRAGMENTS. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:771–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT W. C. Type-specific antibody formation in man following injection of streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1960 May-Jun;106:250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/106.3.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB J. H., CROMARTIE W. J., ROBERSON B. S. Identification of a toxic cellular component of group A streptococci as a complex of group-specific C polysaccharide and a protein. J Exp Med. 1959 Jan 1;109(1):43–54. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., VETTER J. K. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. I. Observations on the microscopical and biological aspects of the disintegration and solubilization of a type 6 strain by sonic oscillation. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.236-243.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLERMAN G. H., EKSTEDT R. Long chain formation by strains of group A streptococci in the presence of homologous antiserum: a type-specific reaction. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):345–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLERMAN G. H., KANTOR F. S., GORDON B. D. Accessory plasma factors involved in the bactericidal test for type-specific antibody to group A streptococci. I. A typical behavior of some human and rabbit bloods. J Exp Med. 1958 Oct 1;108(4):475–491. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y. Biological activity of papain digeted streptococcal anti-M antibody. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Mar;13(1):19–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H. Biological properties of streptococcal cell-wall particles. I. Determinants of the chronic nodular lesion of connective tissue. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1405–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1405-1411.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H., Alberti H., Plemmons J. A. Opsonization of group A streptococci by complement deficient blood from a patient with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H. Nephritogenic and rheumatogenic group A streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):258–263. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H. Prospects for a vaccine against group A streptococci: the problem of the immunology of M proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Jun;10(3):245–255. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C., Lange C. F. Immunochemistry and end-group analyses of group A streptococcal M proteins. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):927–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.927-932.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W., Maxted W. R., Anthony B. F. M antigens among group A streptococci isolated from skin lesions. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):667–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes. The demonstration of multiple, strain-specific lipoproteinase antigens. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):1013–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes: frequency of production of streptococcal lipoproteinase by strains of different serological types and the relationship of M protein production. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Mar;66(1):49–58. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treser G., Semar M., Sagel I., Ty A., Sterzel R. B., Schaerf R., Lange K. Independence of the nephritogenicity of group A streptococci from their M types. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jul;9(1):57–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent W. F., Lisiewski K. J., Ullmann W. W. Immunofluorescent identification of Type 12 group A streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):590–592. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.590-592.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Johnson R. H., Dillon M. F. Further characterization of purified fractions of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 Streptococcus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Lindberg L. H., Kosek J. C., Raffel S. Experimental streptococcal glomerulonephritis: longitudinal study of a laboratory model resembling human acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1970 Oct;122(4):249–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY G. G., WILSON A. T. The occurrence of two M antigens in certain group A streptococci related to type 14. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:451–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE C. K., Jr, HAYASHI J. A., WALSH G., BARKULIS S. S. Type-specific antibody response in man to injections of cell walls and M protein from group A, type 14 streptococci. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Mar;61:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl R., Goichot J., Drach G. Recherches immunologiques sur les antigènes protéiques basiques spécifiques et non spécifiques de type de Streptococcus pyogenes (groupe A). 3. Electrophorèse et immunoélectrophorése. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Oct;109(4):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W. Differences between streptococcal infections of the throat and of the skin. I. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 1;282(1):23–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001012820106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L., Pinney A. M. The relationship between M-antigen and opacity factor in group A streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jan;65(1):69–80. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L. The production of opacity in serum by group A streptococci and its relationship withthe presence of M antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):343–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Pinney A. M. An M-associated protein antigen (MAP) of group A streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Dec;69(4):553–564. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley G. G., Bruno P. N. Cross-reactions among Group A streptococci. I. Precipitin and bactericidal cross-reactions among types 33, 41, 43, 52, and Ross. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):959–968. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley G. G., Bruno P. N. Cross-reactions among group A streptococci. II. Further analysis of antigens related to type-specificity and protection. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittner M. K., Fox E. N. Micro complement fixation assay for type-specific group A streptococcal antibody. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):441–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.441-445.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Freimer E. H. An immunological relationship between the group. A streptococcus and mammalian muscle. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):661–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B. Mimetic relationships between group A streptococci and mammalian tissues. Adv Immunol. 1967;7:147–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Hill H. R. Placental transfer of group A type-specific streptococcal antibody. Pediatrics. 1969 May;43(5):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Mathews J., Wilson E. Microtiter indirect hemagglutination procedure for identification of streptococcal M-protein antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1640–1645. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1640-1645.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]