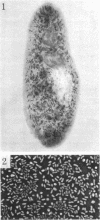
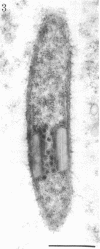
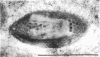
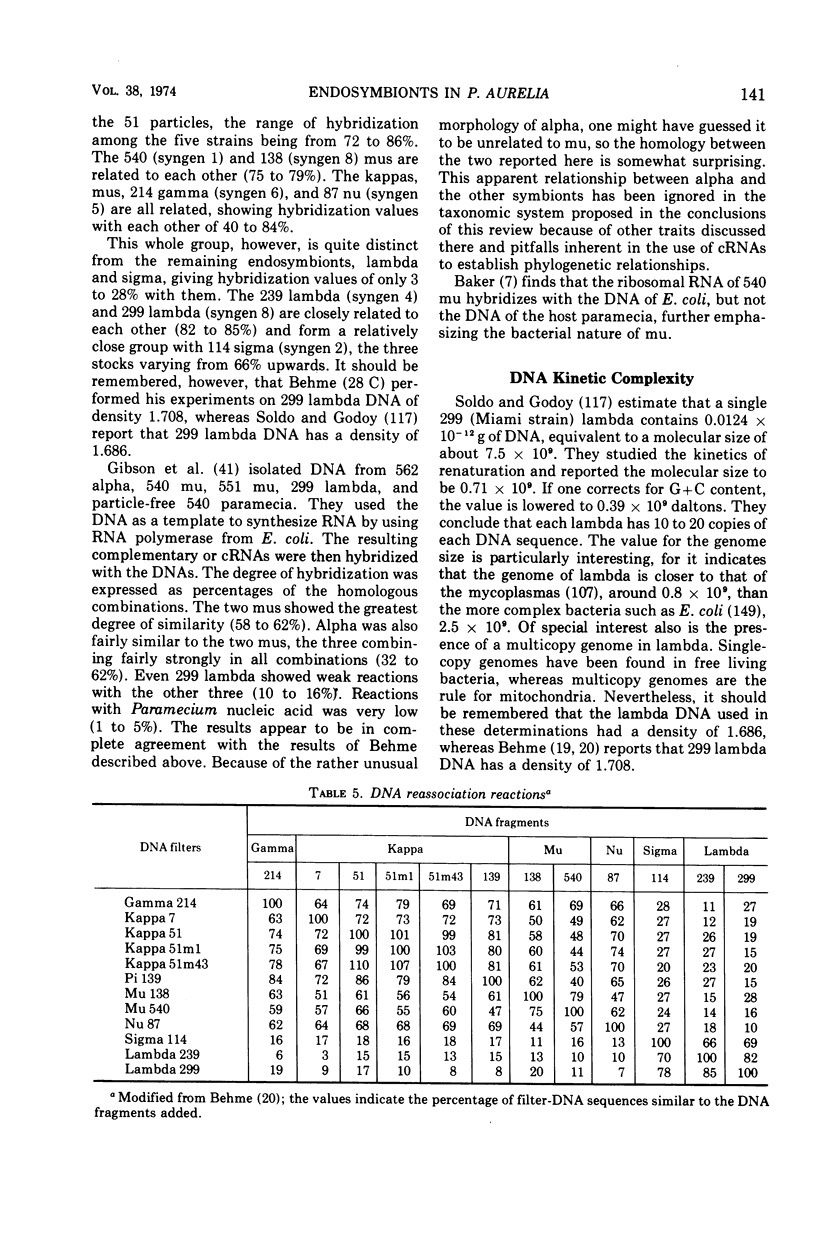
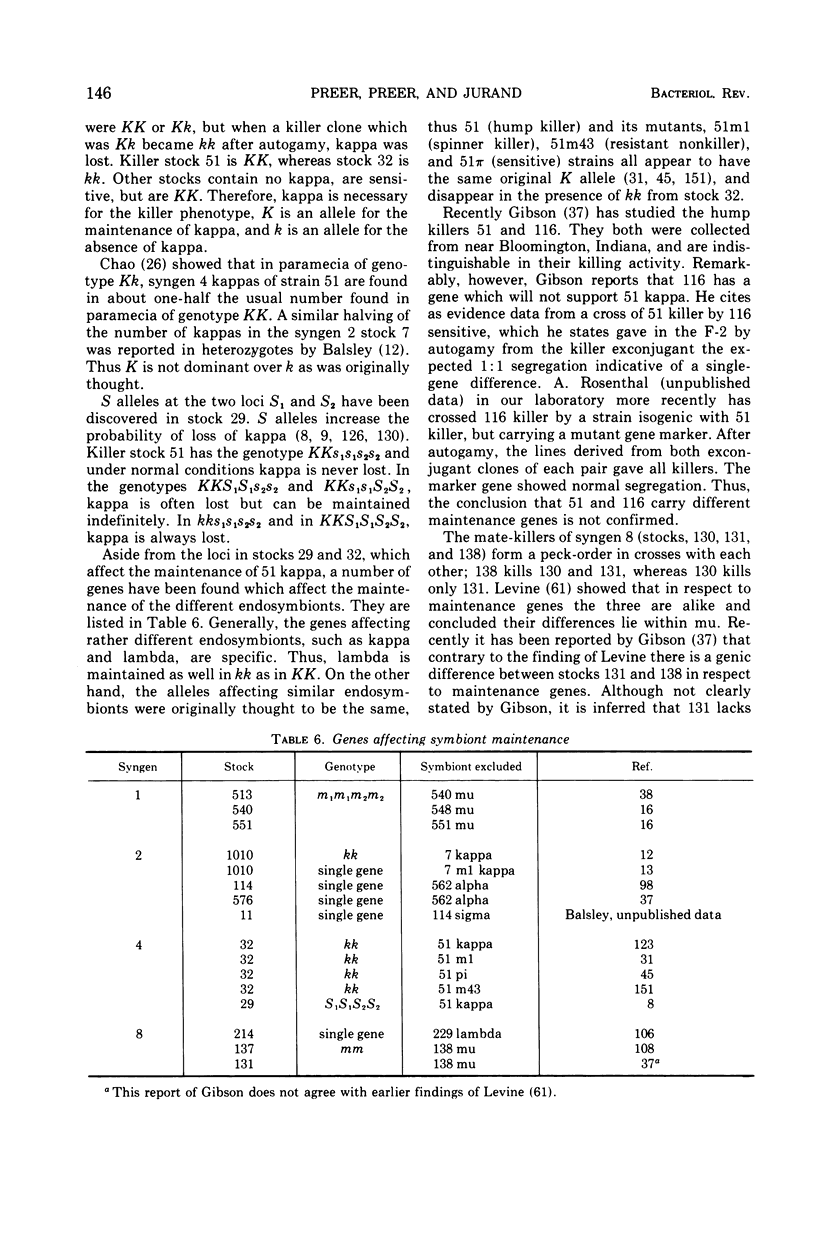
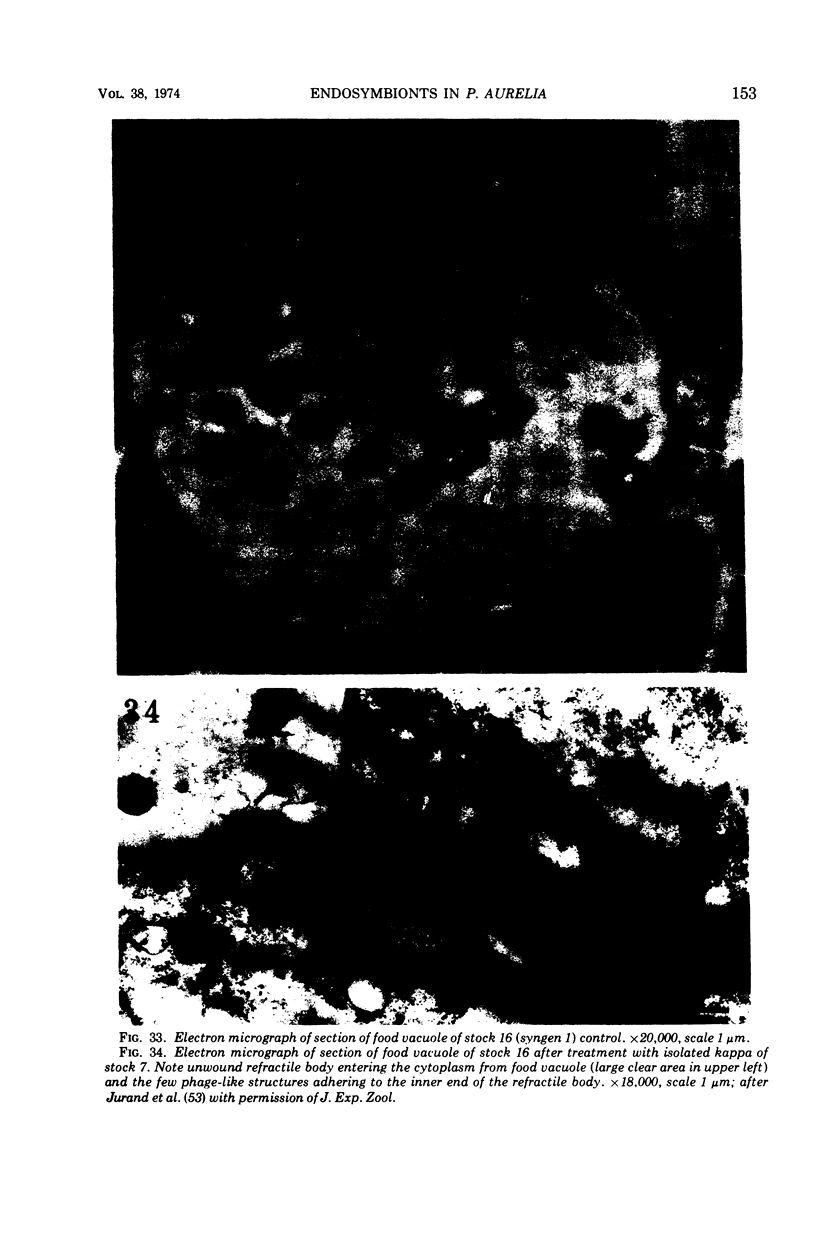
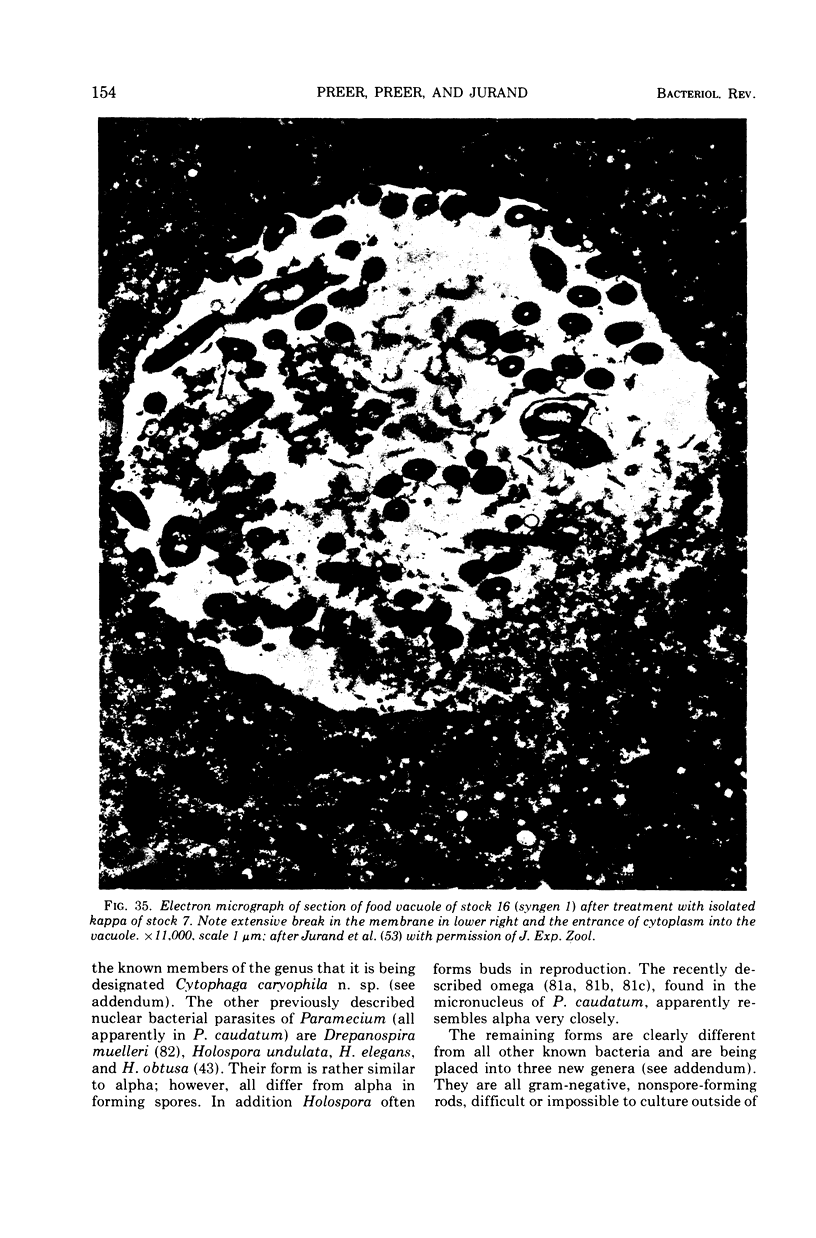
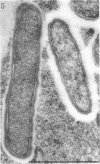Full text
PDF
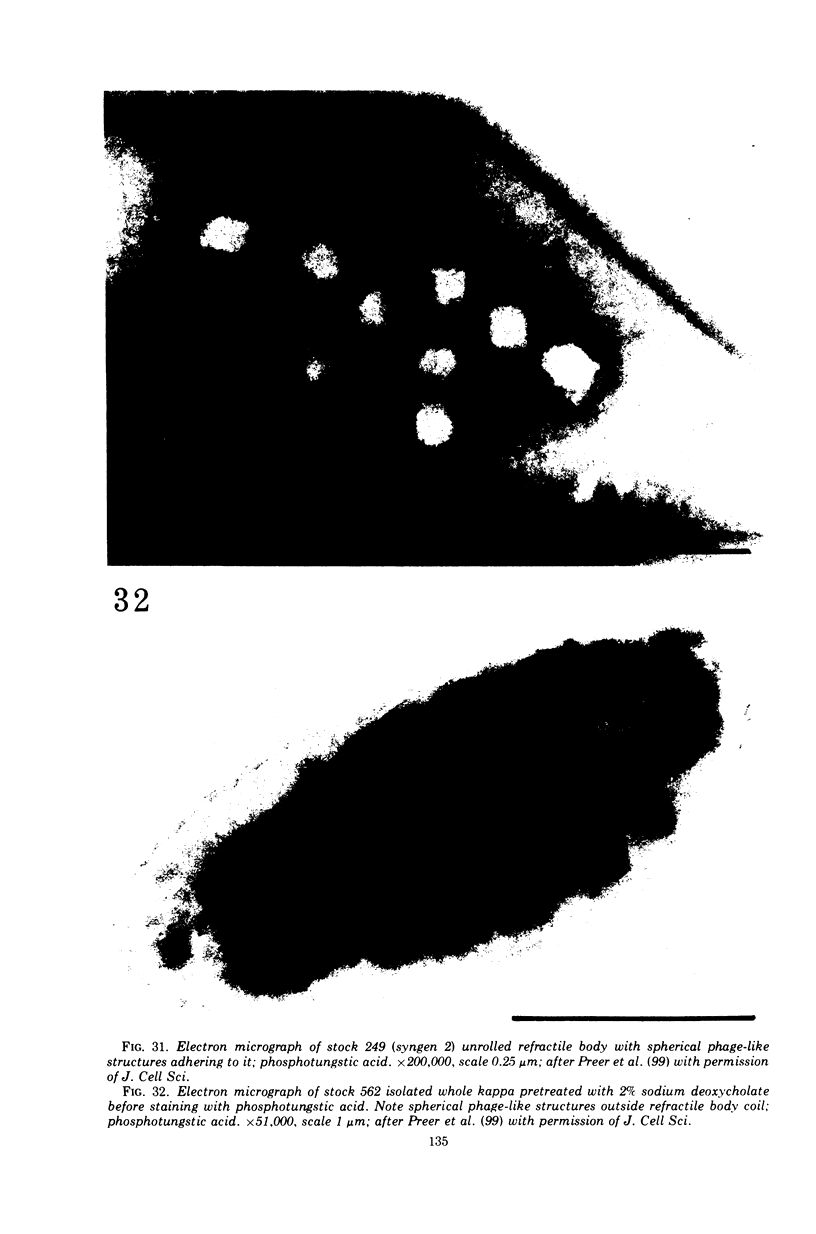


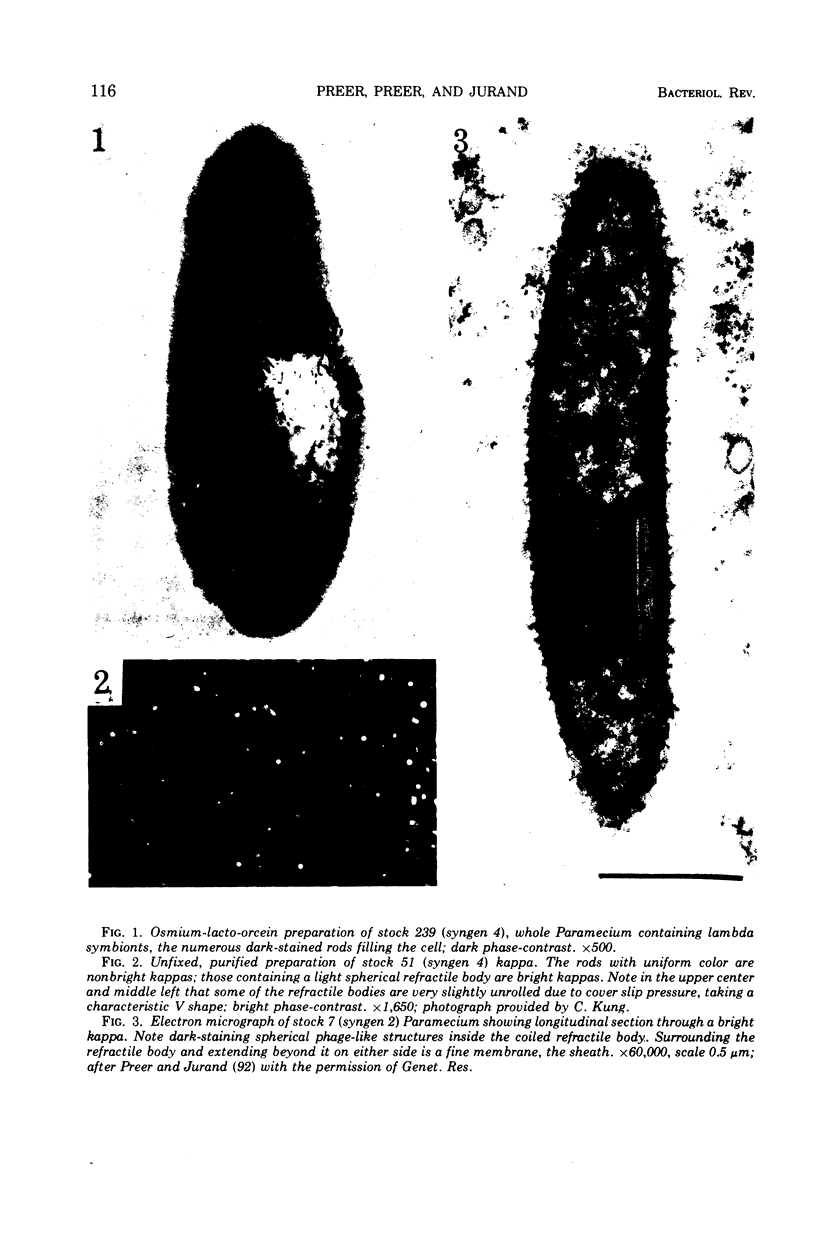
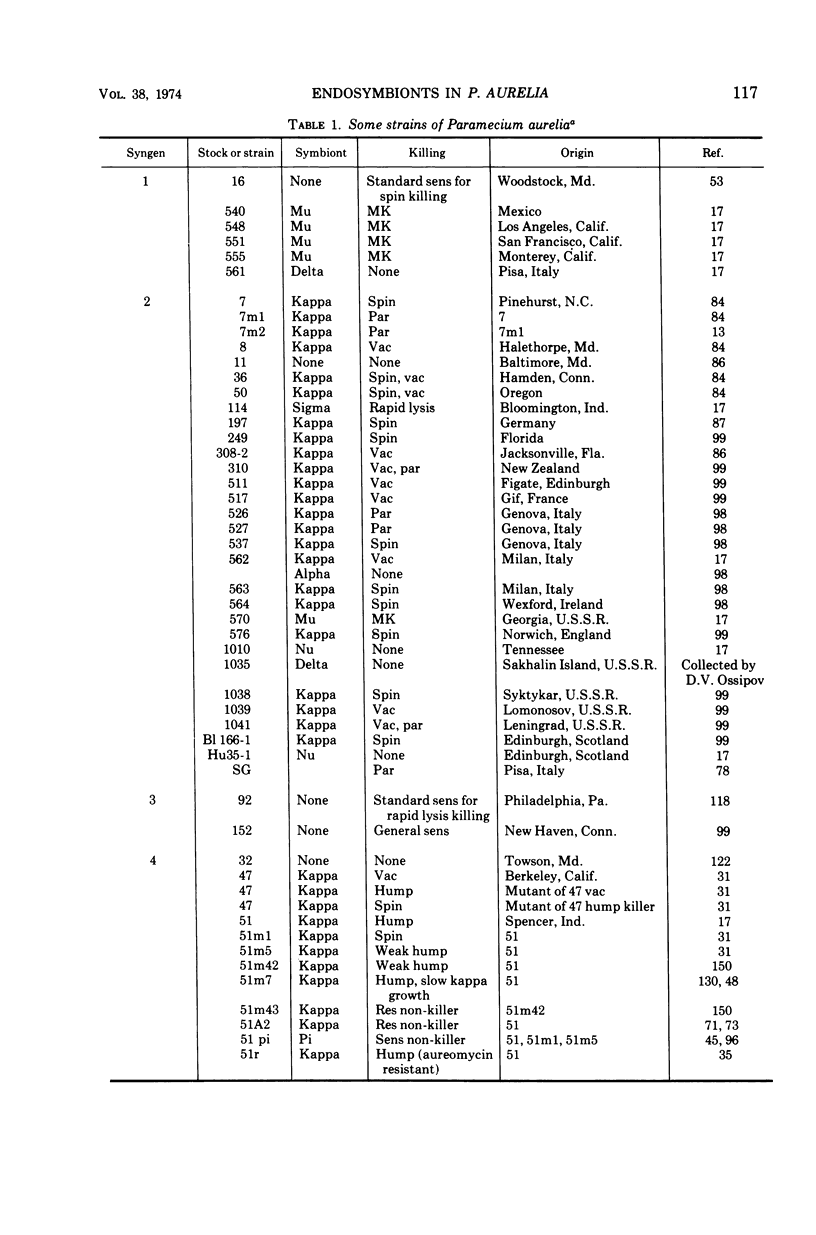
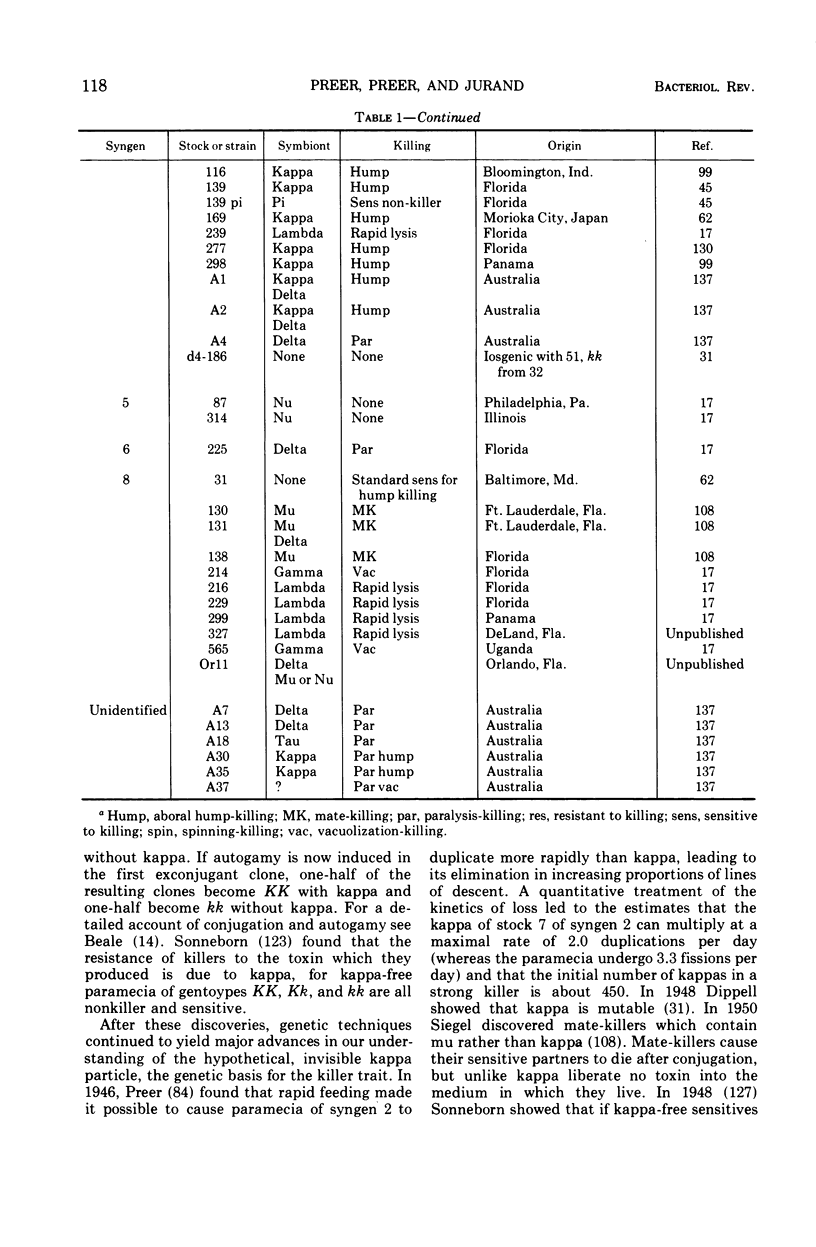

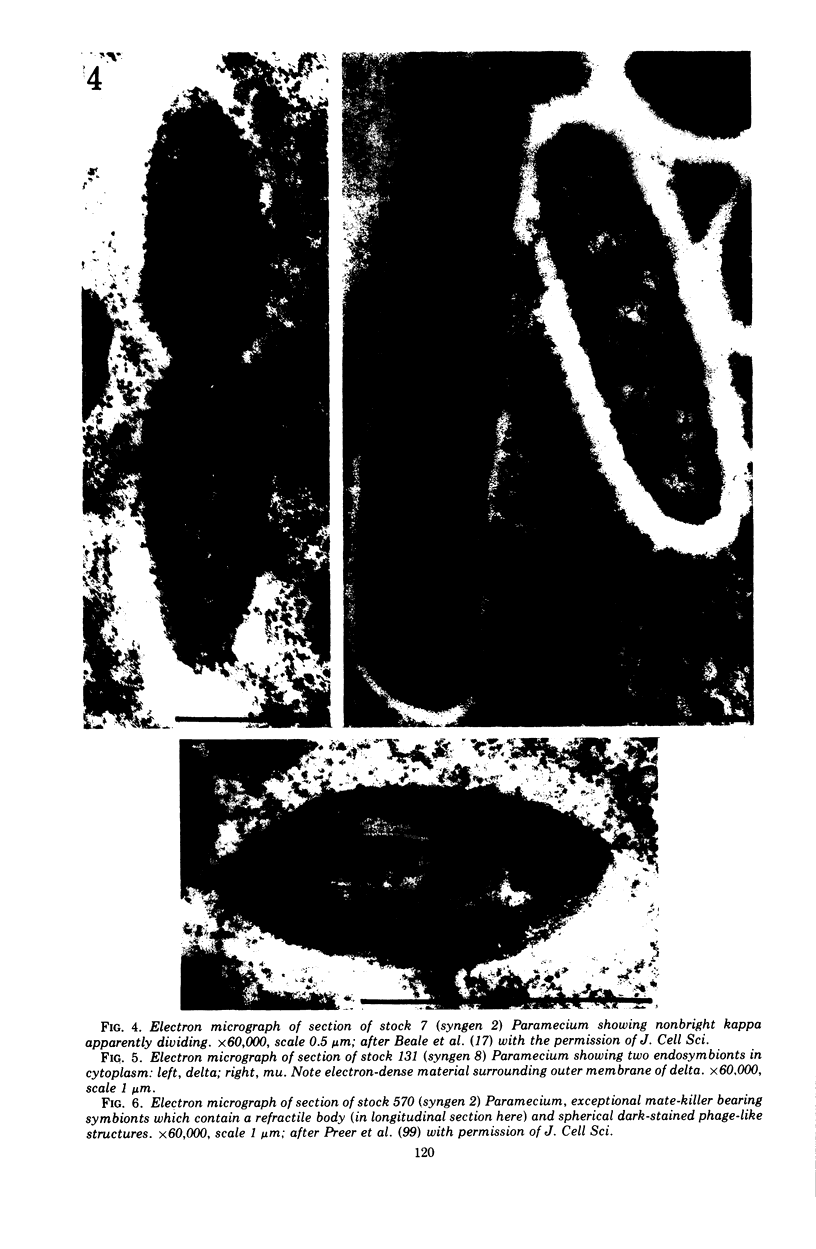
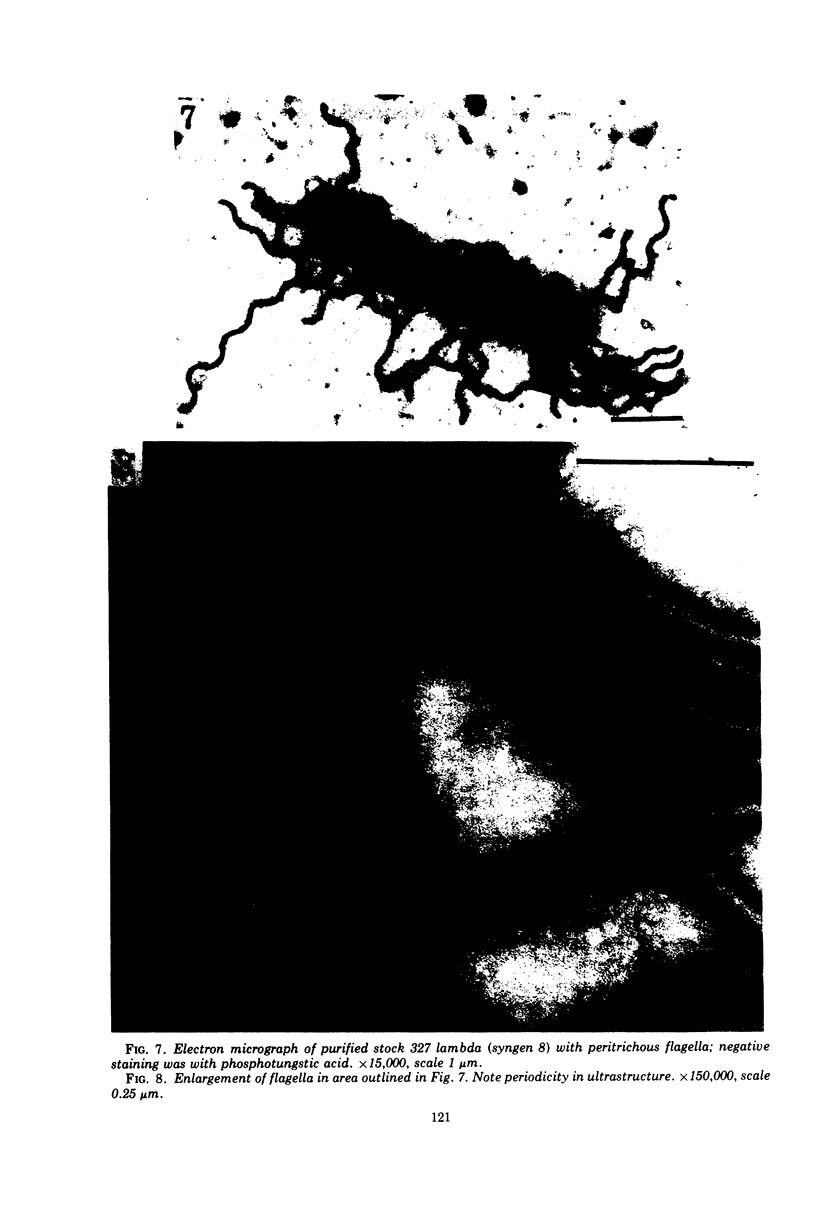

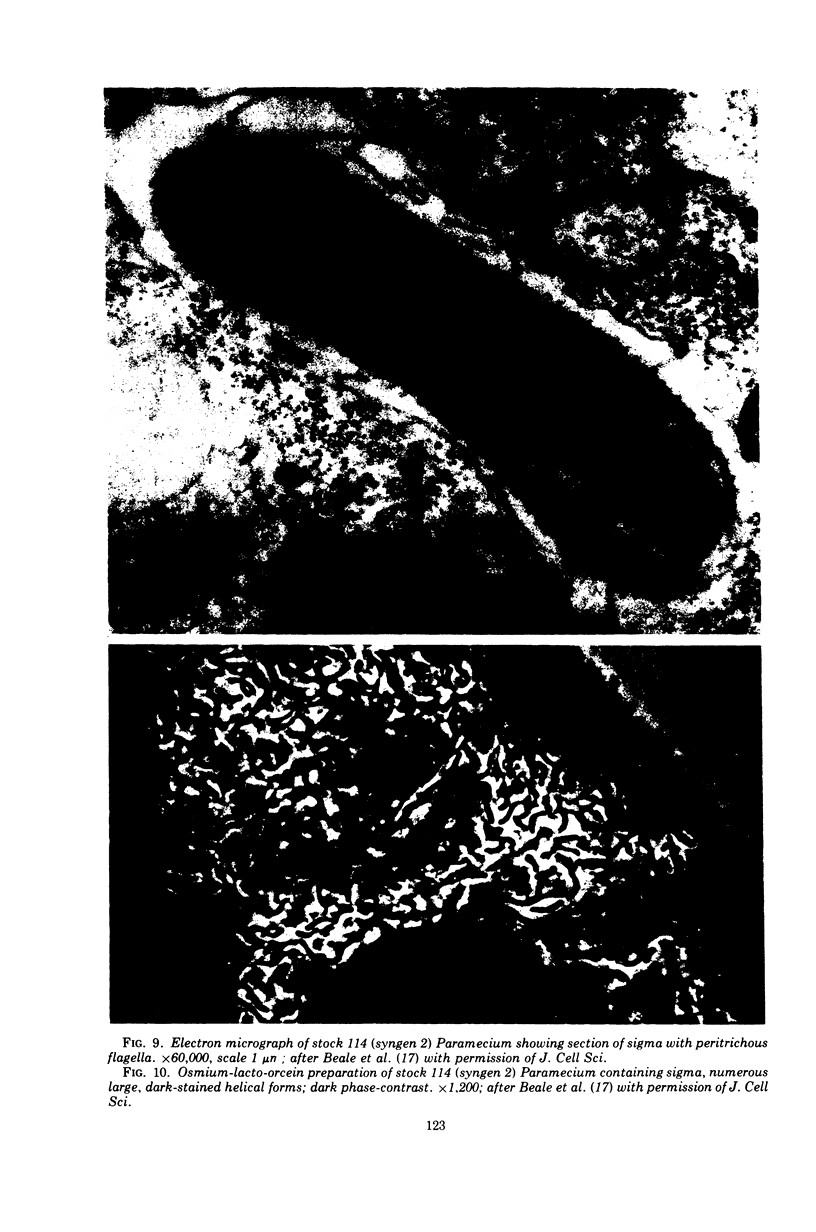
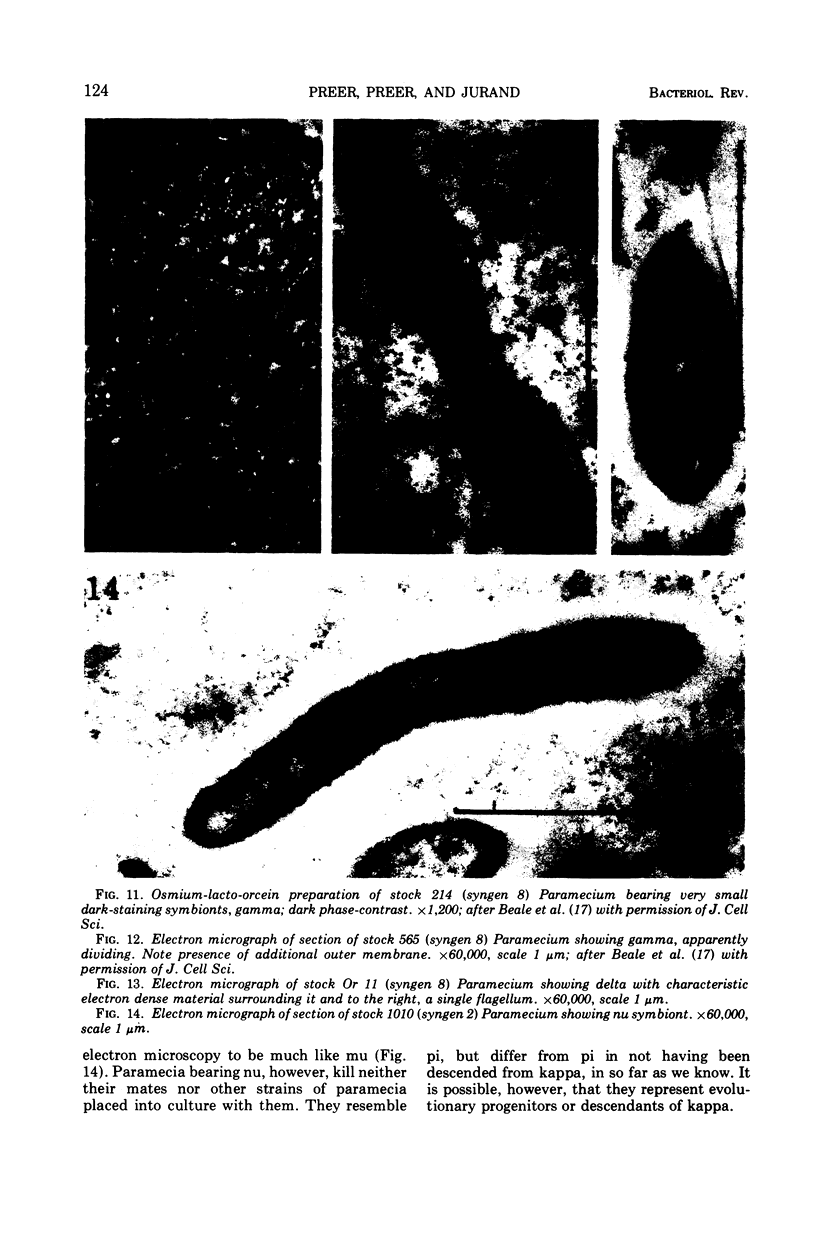

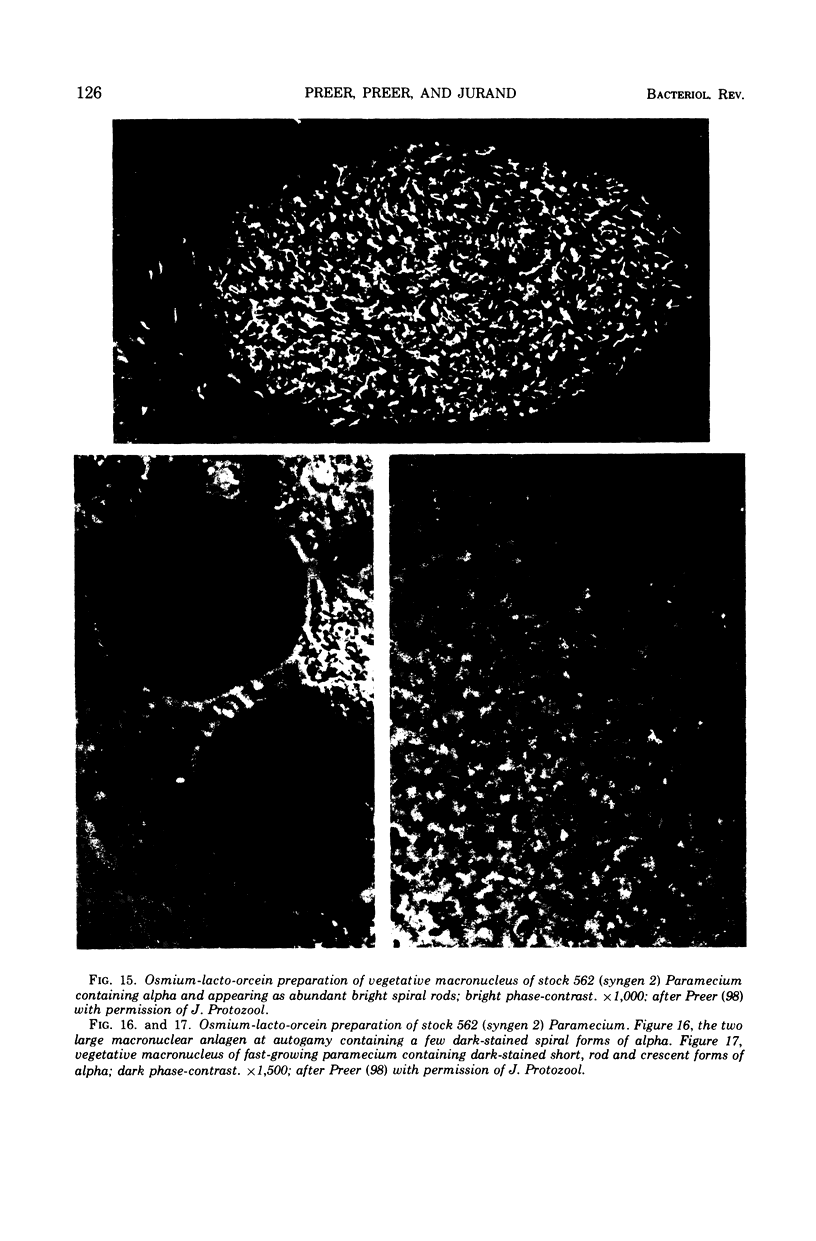





























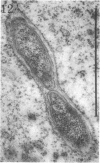
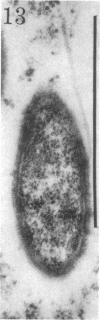
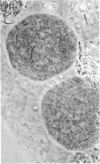
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTIN M. L. Sensitivity to paramecin in paramecium aurelia in relation to stock, serotype, and mating type. Physiol Zool. 1951 Jul;24(3):196–204. doi: 10.1086/physzool.24.3.30152113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Byrne B. C., Cronkite D. L. Intersyngenic variations in the esterases of bacterized Paramecium aurelia. Biochem Genet. 1971 Apr;5(2):135–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00485641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Gibson I. The purification of DNA from the genones of Paramecium aurelia and Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1971 Aug;18(3):518–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALBINDER E., PREER J. R., Jr Gel diffusion studies on serotype and serotype transformation in Paramecium. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:156–167. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEALE G. H., JURAND A. Structure of the mate-killer (mu) particles in Paramecium aurelia, stock 540. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Oct;23:243–252. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTZEL H. M., Jr, PAGLIARA A. The effect of biochemical inhibitors upon the killer-sensitive system in Paramecium aurelia. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Sep;27:382–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. Studies on the RNA of the mate-killer particles of Paramecium. Heredity (Edinb) 1970 Nov;25(4):657–662. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1970.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balbinder E. The Genotypic Control of Kappa in Paramecium Aurelia, Syngen 4, Stock 51. Genetics. 1959 Nov;44(6):1227–1241. doi: 10.1093/genetics/44.6.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsley M. Dependence of the kappa particles of stock 7 of Paramecium aurelia on a single gene. Genetics. 1967 May;56(1):125–131. doi: 10.1093/genetics/56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y. A study of the Moraxella group. II. Oxidative-negative species (genus Acinetobacter). J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1520–1541. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1520-1541.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y. Study of the Moraxella group. I. Genus Moraxella and the Neisseria catarrhalis group. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):58–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.58-73.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. H., Jurand A. Three different types of mate-killer (mu) particle in Paramecium aurelia (syngen 1). J Cell Sci. 1966 Mar;1(1):31–34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. H., McPhail S. Some additional results on the maintenance of kappa particles in Paramecium aurelia (stock 51) after loss of the gene K. Genet Res. 1967 Jun;9(3):369–373. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. N., Jurand A., Preer J. R. The classes of endosymbiont of Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):65–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boell E. J. Respiratory Enzymes in Paramecium: 1. Cytochrome Oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Dec;31(12):396–402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.12.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne B. J. Kappa, mu and the metagon hypothesis in Paramecium aurelia. Genet Res. 1969 Apr;13(2):197–211. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao P. K. Kappa Concentration per Cell in Relation to the Life Cycle, Genotype and Mating Type in Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Feb;39(2):103–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J. Isolation and partial characterization of macro- and micronuclei from Paramecium aurella. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):105–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPPELL R. V. Mutation of the killer cytoplasmic factor in Paramecium aurelia. Heredity (Edinb) 1950 Aug;4(2):165–187. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1950.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPPELL R. V. The fine structure of kappa in killer stock 51 of Paramecium aurelia; preliminary observations. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jan 25;4(1):125–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran D. J. The migration of Eimeria acervulina sporozoites to the duodenal glands of Lieberkühn. J Protozool. 1966 Feb;13(1):27–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1966.tb01864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson I., Chance M., Williams J. Extranuclear DNA and the endosymbionts of Paramecium aurelia. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 17;234(46):75–77. doi: 10.1038/newbio234075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson I. The genetics of protozoan organelles. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1970;24:379–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson I. Transplantation of killer endosymbionts in paramecium. Nature. 1973 Jan 12;241(5385):127–129. doi: 10.1038/241127a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., GETTNER M. E. Fine structure of kappa in Paramecium aurelia. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jan 25;4(1):122–124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON E. D. Test for genetic recombination in kappa particles of Paramecium aurelia, variety 4. Science. 1958 Aug 1;128(3318):254–254. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3318.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson E D. Spontaneous Mutations Affecting the Killer Character in Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 4. Genetics. 1956 Jan;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson E D. Studies on Kappa-like Particles in Sensitives of Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 4. Genetics. 1954 Mar;39(2):229–239. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagel L. A. Properties of DNA associated with raffinose-isolated pellicles of Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Sci. 1969 Nov;5(3):561–573. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurand A., Preer L. B. Ultrastructure of flagellated lambda symbionts in Paramecium aurelia. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):359–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurand A., Rudman B. M., Preer J. R., Jr Prelethal effects of killing action by stock 7 of Paramecium aurelia. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jul;177(3):365–387. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401770311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Cell genetics and hereditary symbiosis. Physiol Rev. 1952 Oct;32(4):403–430. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1952.32.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. An enzymatic comparison of two interbreeding but genetically isolated varieties of Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Physiol. 1955 Jun;45(3):409–419. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030450307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. The Diverse Mate-Killers of Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 8: Their Interrelations and Genetic Basis. Genetics. 1953 Nov;38(6):561–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/38.6.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ROSE H. M., MOORE D. H. An evaluation of host cell changes accompanying viral multiplication as observed in the electron microscope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Oct 21;68(2):302–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb56087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. A. Kappa-affected paramecia develop immunity. J Protozool. 1965 May;12(2):278–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1965.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. A. Resistance of kappa-bearing paramecia to kappa toxin. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Jan;41(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi K., Poulson D. F. A virus associated with SR-spirochetes of Drosophila nebulosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1565–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREER J. R., Jr Microscopically visible bodies in the cytoplasm of the "killer" strains of Paramecium aurelia. Genetics. 1950 May;35(3):344–362. doi: 10.1093/genetics/35.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREER J. R., Jr, STARK P. Cytological observations on the cytoplasmic factor "kappa" in Paramecium aurelia. Exp Cell Res. 1953 Dec;5(2):478–491. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(53)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R. A Study of Some Properties of the Cytoplasmic Factor, "Kappa," in Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 2. Genetics. 1948 Jul;33(4):349–404. doi: 10.1093/genetics/33.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr Extrachromosomal inheritance: hereditary symbionts, mitochondria, chiloroplasts. Annu Rev Genet. 1971;5:361–406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Hufnagel L. A., Preer L. B. Structure and behavior of R bodies from killer paramecia. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Apr;15(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Jurand A. The relation between virus-like particles and R bodies of Paramecium aurelia. Genet Res. 1968 Dec;12(3):331–340. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Rudman B., Jurand A. Isolation and composition of bacteriophage-like particles from kappa of killer Paramecia. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00433105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B. Virus-like bodies in killer paramecia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1774–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Siegel R. W., Stark P. S. The Relationship between Kappa and Paramecin in Paramecium Aurelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Dec;39(12):1228–1233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.12.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer L. B. Alpha, an infectious macronuclear symbiont of Paramecium aurelia. J Protozool. 1969 Aug;16(3):570–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer L. B., Jurand A., Preer J. R., Jr, Rudman B. M. The classes of kappa in Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Sci. 1972 Sep;11(2):581–600. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.2.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINOW C. F. The chromatin bodies of bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Dec;20(4):207–242. doi: 10.1128/br.20.4.207-242.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Rowe J., Macindoe H. M. Structural studies on the ribosomes of Paramecium: evidence for a "primitive" animal ribosome. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 28;32(3):587–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAGUCHI B., OISHI K., KOBAYASHI S. INTERFERENCE BETWEEN "SEX-RATIO" AGENTS OF DROSOPHILA WILLISTONI AND DROSOPHILA NEBULOSA. Science. 1965 Jan 8;147(3654):160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3654.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMONSEN D. H., VAN WAGTENDONK W. J. Respiratory studies on Paramecium aurelia, variety 4, killers and sensitives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Nov;9(5):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH-SONNEBORN J. E., VANWAGTENDONK W. J. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF KAPPA OF STOCK 51, PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:50–59. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH-SONNEBORN J., GREEN L., MARMUR J. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of kappa and Paramecium aurelia, stock 51. Nature. 1963 Jan 26;197:385–385. doi: 10.1038/197385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLDO A. T. Axenic culture of Paramecium-some observations on the growth behavior and nutritional requirements of a particle-bearing strain of Paramecium aurelia 299 lambda. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 29;108:380–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Mandel M. Quantitative aspects of deoxyribonucleic acid renaturation: base composition, state of chromosome replication, and polynucleotide homologies. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):608–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.608-614.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R W. A Genetic Analysis of the Mate-Killer Trait in Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 8. Genetics. 1953 Nov;38(6):550–560. doi: 10.1093/genetics/38.6.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldo A. T., Godoy G. A. Molecular complexity of Paramecium symbiont lambda deoxyribonucleic acid: evidence for the presence of a multicopy genome. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):93–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldo A. T., Musil G., Godoy G. A. Action of penicillin G on endosymbiote lambda particles of Paramecium aurelia. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):966–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.966-980.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldo A. T., Van Wagtendonk W. J., Godoy G. A. Nucleic acid and protein content of purified endosymbiote particles of Paramecium aurelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. Gene and Cytoplasm: II. The Bearing of the Determination and Inheritance of Characters in Paramecium Aurelia on the Problems of Cytoplasmic Inheritance, Pneumococcus Transformations, Mutations and Development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1943 Dec;29(11):338–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.29.11.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M., Gibson I., Schneller M. V. Killer Particles and Metagons of Paramecium Grown in Didinium. Science. 1964 May 1;144(3618):567–568. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3618.567-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson I. Diaminopimelic acid in the Mu particles of Paramecium aurelia. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):434–435. doi: 10.1038/215434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson I. The biochemical status of mu particles in Paramecium aurelia. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jul;57(1):61–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suyama Y., Preer J. R., Jr Mitochondiral DNA from protozoa. Genetics. 1965 Nov;52(5):1051–1058. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.5.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornley M. J. A taxonomic study of Acinetobacter and related genera. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):211–257. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J., Jr, Weiss E., Millar D. B., Bozeman F. M., Ormsbee R. A. DNA base composition of rickettsiae. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN WAGTENDONK W. J., CONNER R. L., MILLER C. A., RAO M. R. Growth requirements of Paramecium aurelia var. 4, stock 51.7 sensitives and killers in axenic medium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):929–937. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN WAGTENDONKW, TANGUAY R. B. THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF LAMBDA IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA, STOCK 299. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:395–400. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANWAGTENDONK W. J., CLARK J. A., GODOY G. A. THE BIOLOGICAL STATUS OF LAMBDA AND RELATED PARTICLES IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:835–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VLOEDMAN D. A., Jr, BERECH J., Jr, JEFFRIES W. B., VAN WAGTENDONK W. J. Carbohydrate metabolism of Paramecium aurelia, variety 4, stock 47.8 (sensitive). J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Jun;16(3):628–641. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-3-628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDMAYER D. J. A NONKILLER RESISTANT KAPPA AND ITS BEARING ON THE INTERPRETATION OF KAPPA IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Genetics. 1965 Apr;51:613–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E., DEWEY D. L. The distribution of alpha, epsilon-diaminopimelic acid among various micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):394–406. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Davidson N. Kinetics of renaturation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):349–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrischer M. Cytoplasmatische Einschlüsse in virusinfizierten Bohnenblättern. Z Naturforsch B. 1968 Jan;23(1):80–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung K. K. Maintenance of kappa particles in cells recently deprived of gene K (stock 51, syngen 4) of Paramecium aurelia. Genet Res. 1965 Nov;6(3):411–418. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILL L. P., VAN WAGTENDONK W. J. The influence of ultrasonic vibrations upon the activity of paramecin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1951 Mar;6(4):524–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]