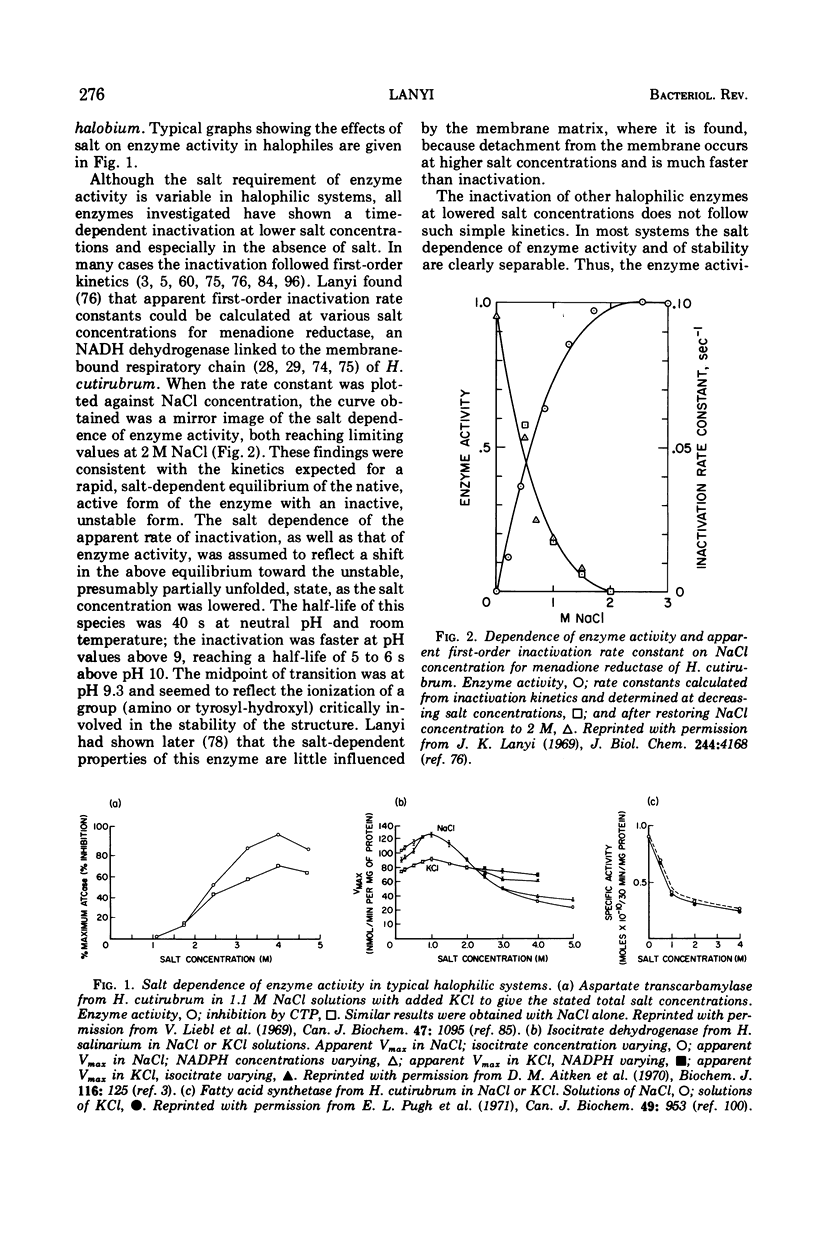
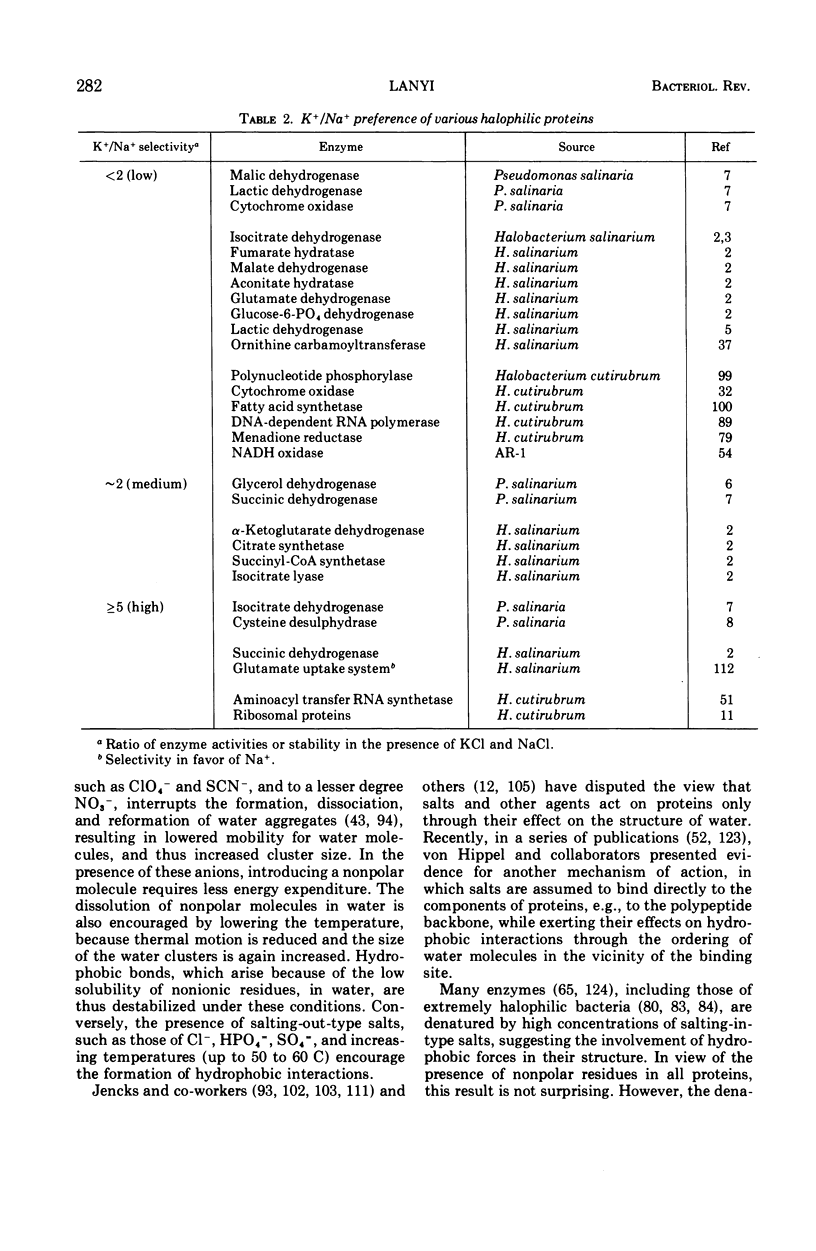
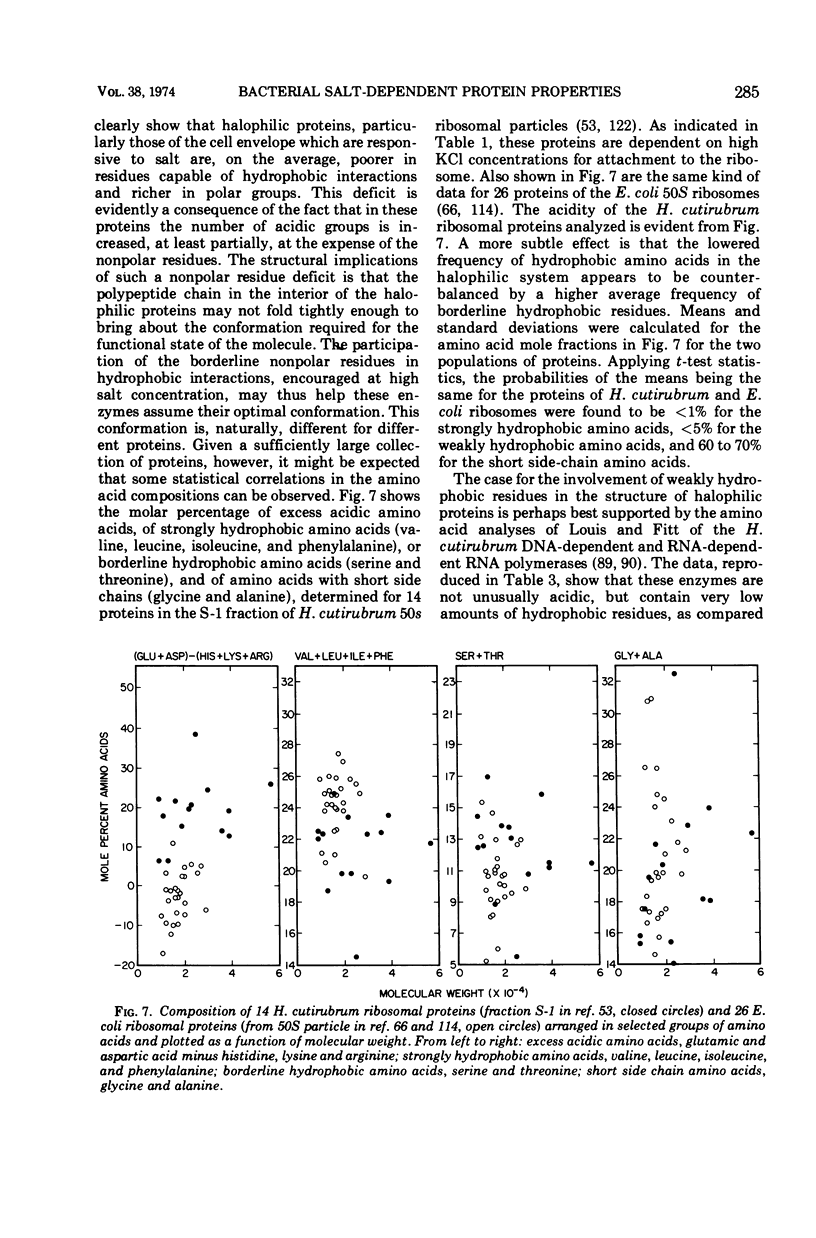
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D., GIBBONS N. E. The effect of chlorides of monovalent cations, urea, detergents, and heat on morphology and the turbidity of suspensions of red halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Oct;7:741–750. doi: 10.1139/m61-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken D. M., Brown A. D. Citrate and glyoxylate cycles in the halophil, Halobacterium salinarium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 1;177(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken D. M., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. Properties of a halophil nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. Preliminary studies of the salt relations and kinetics of the crude enzyme. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(1):125–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1160125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anfinsen C. B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973 Jul 20;181(4096):223–230. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4096.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M. An interpretation of the effects of salts on the lactic dehydrogenase of Halobacterium salinarium. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Feb;5(1):47–57. doi: 10.1139/m59-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. Effects of sodium and potassium chloride on certain enzymes of Micrococcus halodenitrificans and Pseudomonas salinaria. Can J Microbiol. 1956 Oct;2(6):599–606. doi: 10.1139/m56-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. The cysteine desulphydrase of Pseudomonas salinaria. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;3(3):461–465. doi: 10.1139/m57-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. The glycerol dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas salinaria, Vibrio costicolus, and Escherichia coli in relation to bacterial halophilism. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1954 May;32(3):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAYLEY S. T., KUSHNER D. J. THE RIBOSOMES OF THE EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM, HALOBACTERIUM CUTIRUBRUM. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:654–669. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREGMAN J. I. Cation exchange processes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Nov 11;57(3):125–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb36392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. ASPECTS OF BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO THE IONIC ENVIRONMENT. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:296–329. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.296-329.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. HYDROGEN ION TITRATIONS OF INTACT AND DISSOLVED LIPOPROTEIN MEMBRANES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:491–508. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE DEVELOPMENT OF HALOPHILIC PROPERTIES IN BACTERIAL MEMBRANES BY ACYLATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:136–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE PERIPHERAL STRUCTURES OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA.IV. THE CATION-SENSITIVE DISSOLUTION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OF THE HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM, HALOBACTERIUM HALOBIUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:425–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. T. Composition of ribosomes of an extremely halophilic bacterium. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):420–427. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. T., Griffiths E. A cell-free amino acid incorporating system from an extremely halophilic bacterium. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2249–2256. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello J., Haas D., Bello H. R. Interactions of protein-denaturing salts with model amides. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2539–2548. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow C. C. On the average hydrophobicity of proteins and the relation between it and protein structure. J Theor Biol. 1967 Aug;16(2):187–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaurock A. E., Stoeckenius W. Structure of the purple membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):152–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio233152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Hunt L. The thermodynamics of protein denaturation. 3. The denaturation of ribonuclease in water and in aqueous urea and aqueous ethanol mixtures. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Sep 13;89(19):4826–4838. doi: 10.1021/ja00995a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J. On the regulatory properties of a halophilic citrate synthase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 15;30(3):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80683-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Vidal M. C. Effect of monovalent cations on the malic enzyme from the extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.437-439.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazan L. L., Bayley S. T. Some properties of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Biochem. 1973 Sep;51(9):1297–1304. doi: 10.1139/o73-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. Effect of K(+) and Na(+) on the cytochrome oxidase activity of Halobacterium cutirubrum. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. Properties of electron transport particles from Halobacterium cutirubrum. The respiratory chain system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 24;180(2):320–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. Properties of the membrane-bound respiratory chain system of Halobacterium salinarium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. The membrane-bound ascorbate oxidase system of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;205(2):148–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. The membrane-bound carbon monoxide-reactive hemoproteins in the extreme halophiles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 13;197(1):84–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow C. T., Visentin L. P., Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M. Specific ribonucleoprotein fragments from the 30-S ribosomal subunits of Halobacterium cutirubrum, Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):270–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90376-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement G. E., Siegel A., Potter R. Sodium ion binding to pepsin and other proteins. Can J Biochem. 1971 May;49(5):477–483. doi: 10.1139/o71-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dundas I. E., Halvorson H. O. Arginine metabolism in Halobacterium salinarium, an obligately halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.113-119.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dundas I. E. Ornithine carbamoyltransferase from Halobacterium salinarium. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May 23;27(2):376–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER H. F. A LIMITING LAW RELATING THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF PROTEIN MOLECULES TO THEIR COMPOSITION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1285–1291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuoss R. M., Hsia K. L. Association of 1-1 salts in water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1550–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M., Sachs L., Ginzburg B. Z. Ion metabolism in a Halobacterium. I. Influence of age of culture on intracellular concentrations. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):187–207. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gochnauer M. B., Kushner D. J. Growth and nutrition of extremely halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Oct;15(10):1157–1165. doi: 10.1139/m69-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good W. A., Hartman P. A. Properties of the amylase from Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):601–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.601-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Bayley S. T. Properties of transfer ribonucleic acid and aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases from an extremely halophilic bacterium. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):541–551. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES P. K., HALVORSON H. O. PROPERTIES OF A PURIFIED HALOPHILIC MALIC DEHYDROGENASE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.316-326.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES P. K., HALVORSON H. O. PURIFICATION OF A SALT-REQUIRING ENZYME FROM AN OBLIGATELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:312–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.312-315.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabata A., Von Hippel P. H. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. II. Effects of vicinal hydrophobic groups on the specificity of binding of ions to amide groups. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1264–1271. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein L. I., Dalton B. P. Factors affecting the cation requirement of a halophilic NADH dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 19;167(3):638–640. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein L. I., Dalton B. P. Salt specificity of a reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase prepared from a halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.37-42.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein L. I., Dalton B. P. Studies of a halophilic NADH dehydrogenase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):216–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes P. K., Dundas I. E., Halvorson H. O. Halophilic enzymes in cell-free extracts of Halobacterium salinarium. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1159–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1159-1160.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Miller A. B. Nature of the inactivation of the isocitrate dehydrogenase from an obligate halophile. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):677–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.677-681.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Miller A. B. Purification and reversible inactivation of the isocitrate dehydrogenase from an obligate halophile. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):161–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.161-168.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Miller A. B. Reversible inactivation of the isocitrate dehydrogenase from an obligate halophile: changes in the secondary structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jan;148(1):318–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., JORDAN D. O. Deoxypentose nucleic acids. XI. The denaturation of deoxyribonucleic acid in aqueous solution: conductivity and mobility measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Aug 26;42:421–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90819-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., BAYLEY S. T., BORING J., KATES M., GIBBONS N. E. MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CELL ENVELOPES OF THE EXTREME HALOPHILE, HALOBACTERIUM CUTIRUBRUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:483–497. doi: 10.1139/m64-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Dzionara M., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XV. Amino acid compositions of isolated ribosomal proteins from 30S and 50S subunits of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(4):292–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00267698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz M. J., Ballou C. E. Analysis of Halobacterium halobium gas vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1058–1067. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1058-1067.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J. Halophilic bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1968;10:73–99. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J. Lysis and dissolution of cells and envelopes of an extremely halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1147–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1147-1156.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J., Onishi H. Contribution of protein and lipid components to the salt response of envelopes of an extremely halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):653–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.653-660.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Silverman M. P. The state of binding of intracellular K + in Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):993–995. doi: 10.1139/m72-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Stevenson J. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. IV. Role of hydrophobic forces in the structure of menadione reductase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4074–4080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. 3. Mechanism of the effect of salt on menadione reductase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4168–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. I. Spectrophotometric identification of the cytochromes of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):716–724. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. II. Salt dependence of reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2864–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. VII. Solubilization properties of menadione reductase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3001–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Lanyi J. K. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. V. Mode of action of salts on cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Lanyi J. K. Threonine deaminase from extremely halophilic bacteria. Cooperative substrate kinetics and salt dependence. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):211–216. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebl V., Kaplan J. G., Kushner D. J. Regulation of a salt-dependent enzyme: the aspartate transcarbamylase of an extreme halophile. Can J Biochem. 1969 Dec;47(12):1095–1097. doi: 10.1139/o69-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Halobacterium cutirubrum RNA polymerase: Subunit composition and salt-dependent template specificity. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 30;14(3):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Isolation and properties of highly purified Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):69–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1270069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Nucleic acid enzymology of extremely halophilic bacteria. Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):621–627. doi: 10.1042/bj1210621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Nucleic acid enzymology of extremely halophilic bacteria. Halobacterium cutirubrum ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):629–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1210629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Purification and properties of the ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj1280755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. The role of Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase subunits in initiation and polymerization. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj1270081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. L., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. The outer layer of the cell envelope of Halobacterium halobium. Can J Biochem. 1969 Jan;47(1):71–74. doi: 10.1139/o69-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGY B., JENCKS W. P. DEPOLYMERIZATION OF F-ACTIN BY CONCENTRATED SOLUTIONS OF SALTS AND DENATURING AGENTS. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jun 5;87:2480–2488. doi: 10.1021/ja01089a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg P., Kaplan J. G., Kushner D. J. Kinetics and regulation of the salt-dependent aspartate transcarbamylase of Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):680–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.680-686.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg P., von Hofsten B. Proteolytic enzymes from extremely halophilic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Feb;55(2):251–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H., Kushner D. J. Mechanism of dissolution of envelopes of the extreme halophile Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):646–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.646-652.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkin P. I., Fitt P. S. Nucleic acid enzymology of extremely halophilic bacteria. Halobacterium cutirubrum polynucleotide phosphorylase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):613–620. doi: 10.1042/bj1210613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre T. S., Jencks W. P. Interactions of salts and denaturing agents with a polyacrylamide gel. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Aug;133(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90491-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. L., Wassef M. K., Kates M. Inhibition of fatty acid synthetase in Halobacterium cutirubrum and Escherichia coli by high salt concentrations. Can J Biochem. 1971 Aug;49(8):953–958. doi: 10.1139/o71-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D. R., JENCKS W. P. THE EFFECT OF COMPOUNDS OF THE UREA-GUANIDINIUM CLASS ON THE ACTIVITY COEFFICIENT OF ACETYLTETRAGLYCINE ETHYL ESTER AND RELATED COMPOUNDS. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jun 5;87:2462–2470. doi: 10.1021/ja01089a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D. R., JENCKS W. P. THE EFFECT OF CONCENTRATED SALT SOLUTIONS ON THE ACTIVITY COEFFICIENT OF ACETYLTETRAGLYCINE ETHYL ESTER. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jun 5;87:2470–2479. doi: 10.1021/ja01089a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAHR P. F. Amino acid composition of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:395–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier E. E., Schrier E. B. The salting-out behavior of amides and its relation to the denaturation of proteins by salts. J Phys Chem. 1967 May;71(6):1851–1860. doi: 10.1021/j100865a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soo-Hoo T. S., Brown A. D. A basis of the specific sodium requirement for morphological integrity of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 1;135(1):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensland H., Larsen H. A study of the cell envelope of the halobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):325–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. The specific requirement for sodium chloride for the active uptake of L-glutamate by Halobacterium salinarium. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):257–260. doi: 10.1042/bj0990257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Daya L., Rak K. H., Garrett R. A. Ribosomal proteins. XXX. Specific protein binding sites on 23S RNA of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):125–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00332783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suelter C. H. Enzymes activated by monovalent cations. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):789–795. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:121–282. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timasheff S. N., Townend R., Mescanti L. The optical rotatory dispersion of the beta-lactoglobulins. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1863–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toeckenius W., Kunau W. H. Further characterization of particulate fractions from lysed cell envelopes of Halobacterium halobium and isolation of gas vacuole membranes. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):337–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visentin L. P., Chow C., Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M., Rollin F. Halobacterium cutirubrum ribosomes. Properties of the ribosomal proteins and ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj1300103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., Peticolas V., Schack L., Karlson L. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. I. Ion binding to polyacrylamide and polystyrene columns. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1256–1264. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



