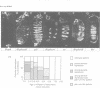
Abstract
During Drosophila embryogenesis, segment polarity genes, such as engrailed (en), wingless (wg) and gooseberry (gsb) show complex interactions that provide positional information along the antero-posterior axis within each segment. Little is known about the specific role of each of these genes in this pattern determining process. Here we demonstrate that the main function of gsb, which encodes a transcription factor containing a paired-domain and a prd-type homeodomain, is the maintenance of wg expression by a wg-gsb autoregulatory loop after 6 h of development. The function of wg, the homologue of the murine Wnt-1 gene, is to specify the denticle pattern by repressing a default state of ubiquitous denticle formation in the ventral epidermis. This repression of denticles by the wg signal is different from the wingless signalling pathways that activate gsb or en. Mutual activations involving gsb, wg and en show temporal asymmetries that lead to their different mutant phenotypes. A general model is proposed for the generation of morphogenetic fields by self-propagating autoregulatory loops.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgartner S., Bopp D., Burri M., Noll M. Structure of two genes at the gooseberry locus related to the paired gene and their spatial expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1247–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejsovec A., Martinez Arias A. Roles of wingless in patterning the larval epidermis of Drosophila. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):471–485. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Burri M., Baumgartner S., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of a large protein domain in the segmentation gene paired and in functionally related genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90818-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Jamet E., Baumgartner S., Burri M., Noll M. Isolation of two tissue-specific Drosophila paired box genes, Pox meso and Pox neuro. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3447–3457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couso J. P., Bate M., Martínez-Arias A. A wingless-dependent polar coordinate system in Drosophila imaginal discs. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):484–489. doi: 10.1126/science.8424170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté S., Preiss A., Haller J., Schuh R., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The gooseberry-zipper region of Drosophila: five genes encode different spatially restricted transcripts in the embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2793–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambly-Chaudière C., Jamet E., Burri M., Bopp D., Basler K., Hafen E., Dumont N., Spielmann P., Ghysen A., Noll M. The paired box gene pox neuro: a determinant of poly-innervated sense organs in Drosophila. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Sher E., Heemskerk-Jongens J., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. Two-tiered regulation of spatially patterned engrailed gene expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):604–609. doi: 10.1038/332604a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan S., DiNardo S. Drosophila wingless generates cell type diversity among engrailed expressing cells. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):347–350. doi: 10.1038/360347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González F., Swales L., Bejsovec A., Skaer H., Martinez Arias A. Secretion and movement of wingless protein in the epidermis of the Drosophila embryo. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90040-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutjahr T., Patel N. H., Li X., Goodman C. S., Noll M. Analysis of the gooseberry locus in Drosophila embryos: gooseberry determines the cuticular pattern and activates gooseberry neuro. Development. 1993 May;118(1):21–31. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama C., Ali Z., Kornberg T. B. Region-specific recombination and expression are directed by portions of the Drosophila engrailed promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1079–1093. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S., Kostriken R., O'Farrell P. H. Multiple modes of engrailed regulation in the progression towards cell fate determination. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):404–410. doi: 10.1038/352404a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo A., Ingham P. Cell patterning in the Drosophila segment: spatial regulation of the segment polarity gene patched. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):291–301. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo A. Interactions between segment polarity genes and the generation of the segmental pattern in Drosophila. Mech Dev. 1991 Sep;35(2):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90059-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. E., Scott M. P. The molecular genetic basis of positional information in insect segments. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1992;18:1–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47191-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Hidalgo A. Regulation of wingless transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):283–291. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Martinez Arias A. Boundaries and fields in early embryos. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90467-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Taylor A. M., Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):184–187. doi: 10.1038/353184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A., Noll E., VanSickle E. P., Odenwald W. F., Perrimon N. Altering the insertional specificity of a Drosophila transposable element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T. Engrailed: a gene controlling compartment and segment formation in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Maden M., Holder N., Wilson S. W. Zebrafish pax[b] is involved in the formation of the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):87–89. doi: 10.1038/360087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A., Johnston P., Macdonald P., Struhl G. Borders of parasegments in Drosophila embryos are delimited by the fushi tarazu and even-skipped genes. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):440–442. doi: 10.1038/328440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., von Kessler D. P., Parks S., Beachy P. A. Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90264-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Gutjahr T., Noll M. Separable regulatory elements mediate the establishment and maintenance of cell states by the Drosophila segment-polarity gene gooseberry. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1427–1436. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbourg-Bouchon B., Busson D., Lamour-Isnard C. Interactions between fused, a segment-polarity gene in Drosophila, and other segmentation genes. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):417–429. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Arias A., Lawrence P. A. Parasegments and compartments in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):639–642. doi: 10.1038/313639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martizez Arias A., Baker N. E., Ingham P. W. Role of segment polarity genes in the definition and maintenance of cell states in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1988 May;103(1):157–170. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea P. D., Turck C. W., Gumbiner B. A homolog of the armadillo protein in Drosophila (plakoglobin) associated with E-cadherin. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1359–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.1962194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J., Vani K. Molecular organization and embryonic expression of the hedgehog gene involved in cell-cell communication in segmental patterning of Drosophila. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):957–971. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Evolution and role of Pax genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordermeer J., Johnston P., Rijsewijk F., Nusse R., Lawrence P. A. The consequences of ubiquitous expression of the wingless gene in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):711–719. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Wnt genes. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90630-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Rauskolb C., Williams M., Riggleman B., Wieschaus E. The segment polarity gene armadillo interacts with the wingless signaling pathway in both embryonic and adult pattern formation. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1029–1043. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Wieschaus E. The segment polarity gene armadillo encodes a functionally modular protein that is the Drosophila homolog of human plakoglobin. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1167–1176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N., Mahowald A. P. Multiple functions of segment polarity genes in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):587–600. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kornberg T. B. Modifying expression of the engrailed gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1988;104 (Suppl):85–93. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.Supplement.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggleman B., Schedl P., Wieschaus E. Spatial expression of the Drosophila segment polarity gene armadillo is posttranscriptionally regulated by wingless. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90451-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggleman B., Wieschaus E., Schedl P. Molecular analysis of the armadillo locus: uniformly distributed transcripts and a protein with novel internal repeats are associated with a Drosophila segment polarity gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):96–113. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampedro J., Johnston P., Lawrence P. A. A role for wingless in the segmental gradient of Drosophila? Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):677–687. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried E., Chou T. B., Perrimon N. wingless signaling acts through zeste-white 3, the Drosophila homolog of glycogen synthase kinase-3, to regulate engrailed and establish cell fate. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1167–1179. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G. Near-reciprocal phenotypes caused by inactivation or indiscriminate expression of the Drosophila segmentation gene ftz. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):677–680. doi: 10.1038/318677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Eaton S., Kornberg T. B. The Drosophila hedgehog gene is expressed specifically in posterior compartment cells and is a target of engrailed regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2635–2645. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Riggleman R. Autonomous requirements for the segment polarity gene armadillo during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert L. Positional information and pattern formation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1971;6(6):183–224. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel M., Nusse R., Johnston P., Lawrence P. A. Distribution of the wingless gene product in Drosophila embryos: a protein involved in cell-cell communication. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]