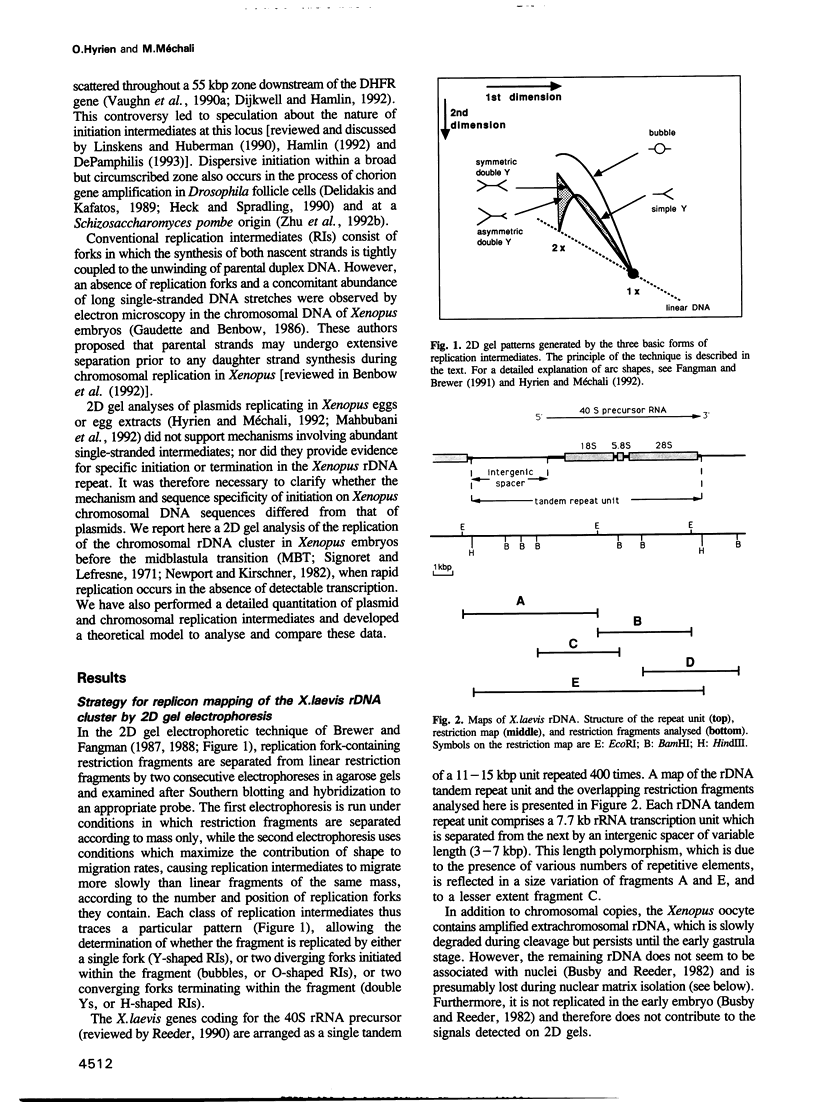
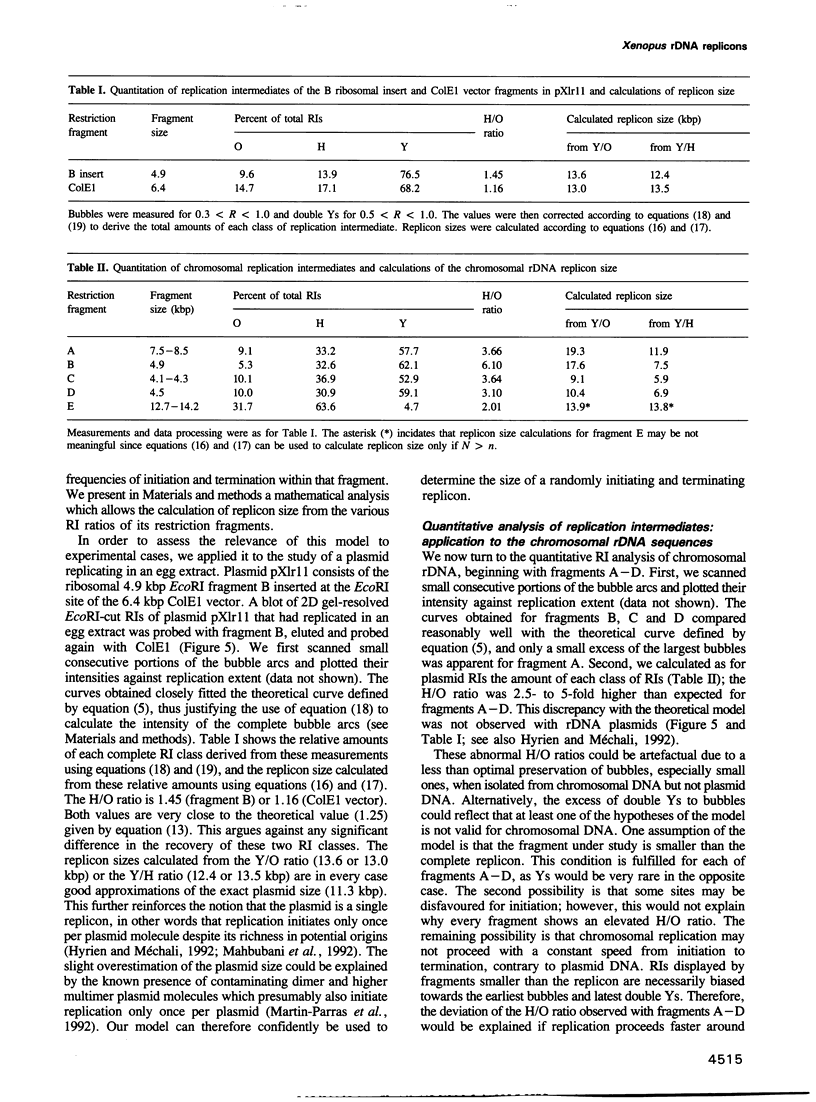
Abstract
We have analysed the replication of the chromosomal ribosomal DNA (rDNA) cluster in Xenopus embryos before the midblastula transition. Two-dimensional gel analysis showed that replication forks are associated with the nuclear matrix, as in differentiated cells, and gave no evidence for single-stranded replication intermediates (RIs). Bubbles, simple forks and double Ys were found in each restriction fragment analysed, showing that replication initiates and terminates without detectable sequence specificity. Quantification of the results and mathematical analysis showed that the average rDNA replicon replicates in 7.5 min and is 9-12 kbp in length. This time is close to the total S phase duration, and this replicon size is close to the maximum length of DNA which can be replicated from a single origin within this short S phase. We therefore infer that (i) most rDNA origins must be synchronously activated soon in S phase and (ii) origins must be evenly spaced, in order that no stretch of chromosomal DNA is left unreplicated at the end of S phase. Since origins are not specific sequences, it is suggested that this spatially and temporally concerted pattern of initiation matches some periodic chromatin folding, which itself need not rely on DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Laemmli U. K. Identification of nuclear pre-replication centers poised for DNA synthesis in Xenopus egg extracts: immunolocalization study of replication protein A. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):1–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A., Morgan G., Sollner-Webb B., Roan J., Busby S., Reeder R. H. Mapping of transcription initiation and termination signals on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C. T., Amaldi F., Buongiorno-Nardelli M. Electron microscopic analysis of replicating DNA of sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1095–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zhao J., Larson D. D. On the nature of origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):661–670. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear protein matrix: association with newly synthesized DNA. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1145202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal A. B., Kriegstein H. J., Hogness D. S. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P. M., Dayton A. I. A specific replication origin in the chromosomal rDNA of Lytechinus variegatus. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):453–456. doi: 10.1038/299453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B. Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Baldari C. T., Amaldi F., Buongiorno-Nardelli M. Replication of ribosomal DNA in Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Lockshon D., Fangman W. L. The arrest of replication forks in the rDNA of yeast occurs independently of transcription. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Micheli G., Carri M. T., Marilley M. A relationship between replicon size and supercoiled loop domains in the eukaryotic genome. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):100–102. doi: 10.1038/298100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Fate of amplified nucleoli in Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):458–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénard M., Pierron G. Mapping of a Physarum chromosomal origin of replication tightly linked to a developmentally-regulated profilin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3309–3315. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Calos M. P. Analysis of the autonomous replication behavior in human cells of the dihydrofolate reductase putative chromosomal origin of replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5971–5978. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. Replication of DNA in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Apr 18;181(1062):19–41. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton and the topology of replication. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90109-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox L. S., Laskey R. A. DNA replication occurs at discrete sites in pseudonuclei assembled from purified DNA in vitro. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90617-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidakis C., Kafatos F. C. Amplification enhancers and replication origins in the autosomal chorion gene cluster of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):891–901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Initiation of DNA replication in the dihydrofolate reductase locus is confined to the early S period in CHO cells synchronized with the plant amino acid mimosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3715–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Vaughn J. P., Hamlin J. L. Mapping of replication initiation sites in mammalian genomes by two-dimensional gel analysis: stabilization and enrichment of replication intermediates by isolation on the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Brewer B. J. A question of time: replication origins of eukaryotic chromosomes. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90505-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Brewer B. J. Activation of replication origins within yeast chromosomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette M. F., Benbow R. M. Replication forks are underrepresented in chromosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5953–5957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L. Mammalian origins of replication. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):651–659. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Spradling A. C. Multiple replication origins are used during Drosophila chorion gene amplification. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Dailey L., Held P., Heintz N. Eukaryotic replication origins as promoters of bidirectional DNA synthesis. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90298-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H. Transcription factors and the control of DNA replication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Tran C. T., Calos M. P. Autonomous DNA replication in human cells is affected by the size and the source of the DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2263–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández P., Martín-Parras L., Martínez-Robles M. L., Schvartzman J. B. Conserved features in the mode of replication of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1475–1485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C., Kill I. Changes in the nuclear distribution of DNA polymerase alpha and PCNA/cyclin during the progress of the cell cycle, in a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1989 Aug;93(Pt 4):605–613. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Méchali M. Plasmid replication in Xenopus eggs and egg extracts: a 2D gel electrophoretic analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1463–1469. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A. Structure-function relationships in eukaryotic nuclei. Bioessays. 1991 Jan;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kill I. R., Bridger J. M., Campbell K. H., Maldonado-Codina G., Hutchison C. J. The timing of the formation and usage of replicase clusters in S-phase nuclei of human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1991 Dec;100(Pt 4):869–876. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.4.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Hidaka M., Nishizawa M., Horiuchi T. Identification of a site required for DNA replication fork blocking activity in the rRNA gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):355–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00265431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Calos M. P. Replication initiates at multiple locations on an autonomously replicating plasmid in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1464–1472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. Chromosome replication in early development of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):285–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovici M., Monod G., Géraudie J., Bravo R., Méchali M. Nuclear distribution of PCNA during embryonic development in Xenopus laevis: a reinvestigation of early cell cycles. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):63–69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. The two faces of higher eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):845–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90258-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahbubani H. M., Paull T., Elder J. K., Blow J. J. DNA replication initiates at multiple sites on plasmid DNA in Xenopus egg extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1457–1462. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Parras L., Hernández P., Martínez-Robles M. L., Schvartzman J. B. Initiation of DNA replication in ColE1 plasmids containing multiple potential origins of replication. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22496–22505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Bustin M., Miller O. L., Jr Electron microscopic analysis of chromosome metabolism in the Drosophila melanogaster embryo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):741–754. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micheli G., Baldari C. T., Carri M. T., Di Cello G., Buongiorno-Nardelli M. An electron microscope study of chromosomal DNA replication in different eukaryotic systems. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):127–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A. D., Blow J. J., White J. G., Amos W. B., Wilcock D., Laskey R. A. Replication occurs at discrete foci spaced throughout nuclei replicating in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):471–477. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montag M., Spring H., Trendelenburg M. F. Structural analysis of the mitotic cycle in pre-gastrula Xenopus embryos. Chromosoma. 1988;96(3):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00302357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Burdett I., West S. C. Unusual stability of recombination intermediates made by Escherichia coli RecA protein. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2685–2693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Morita T., Sato C. Structural organizations of replicon domains during DNA synthetic phase in the mammalian nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Aug;165(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90583-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu H., Berezney R. Mapping replicational sites in the eucaryotic cell nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Ina S. Analysis of chromosomal replicons in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3935–3941. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran C. T., Caddle M. S., Calos M. P. The replication behavior of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA in human cells. Chromosoma. 1993 Jan;102(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00356030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van't Hof J., Lamm S. S. Single-stranded replication intermediates of ribosomal DNA replicons of pea. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1949–1953. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L. Mapping an origin of DNA replication at a single-copy locus in exponentially proliferating mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4685–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Mullenders L. H., Hamlin J. L. Replication forks are associated with the nuclear matrix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1965–1969. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Johnson K. H. The pathogenesis of maturity-onset diabetes mellitus: is there a link to islet amyloid polypeptide? Bioessays. 1988 Jul;9(1):30–33. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Brun C., Kurooka H., Yanagida M., Huberman J. A. Identification and characterization of a complex chromosomal replication origin in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Chromosoma. 1992;102(1 Suppl):S7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02451780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Newlon C. S., Huberman J. A. Localization of a DNA replication origin and termination zone on chromosome III of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4733–4741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Velden H. M., Wanka F. The nuclear matrix--its role in the spatial organization and replication of eukaryotic DNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1987;12(2):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00368873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]