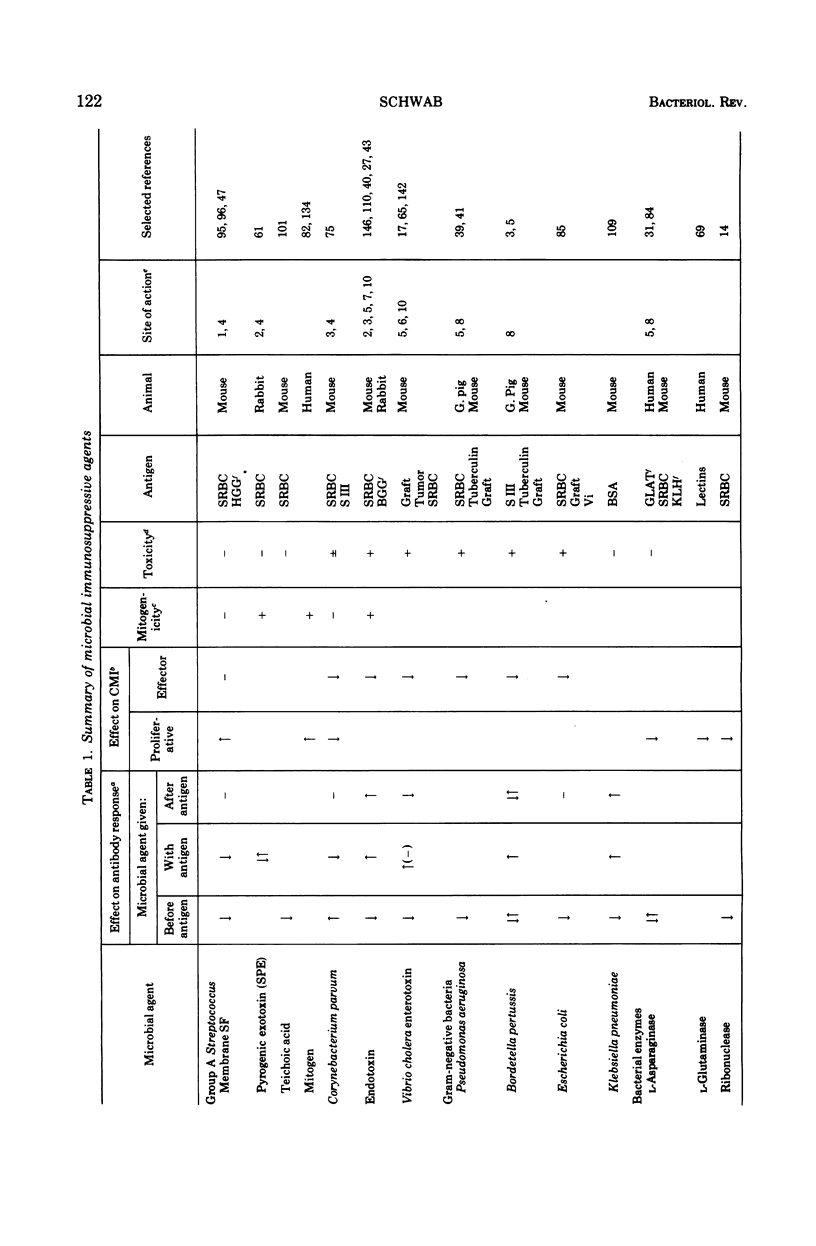
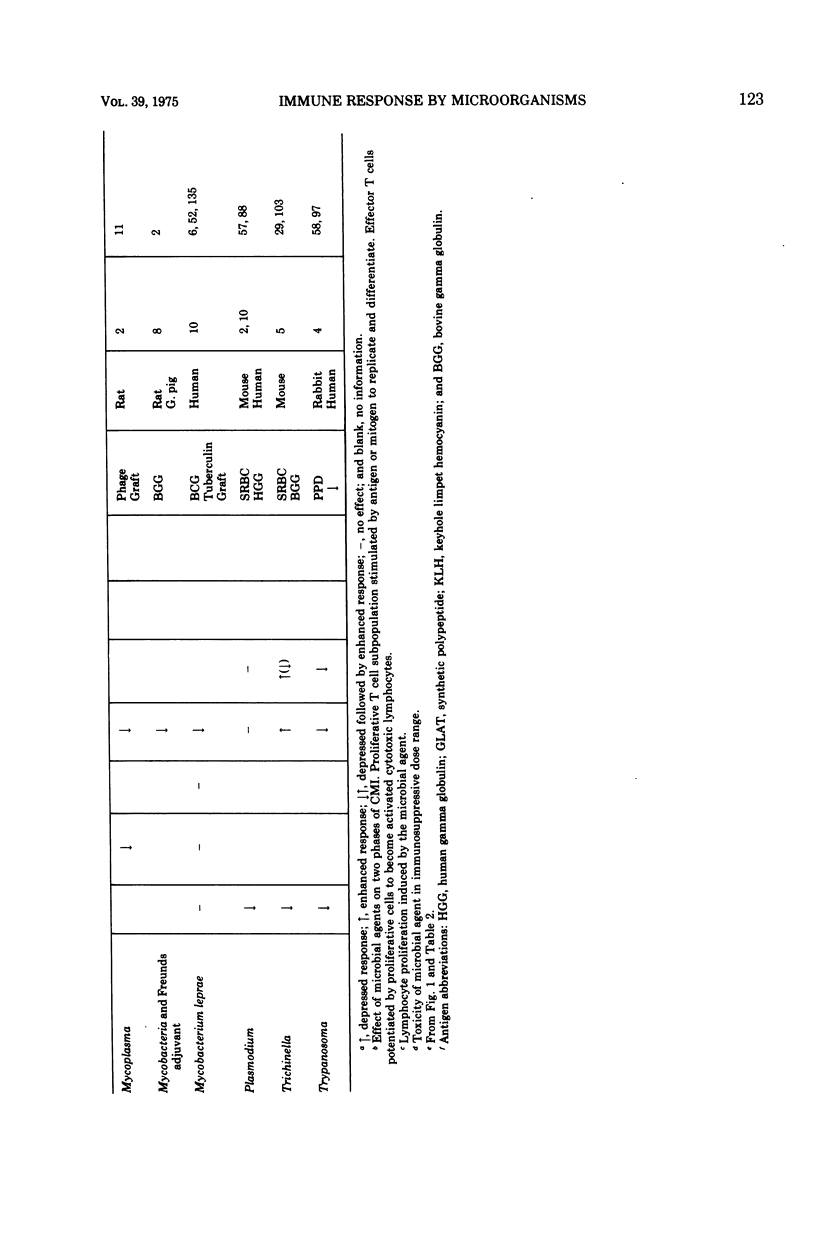
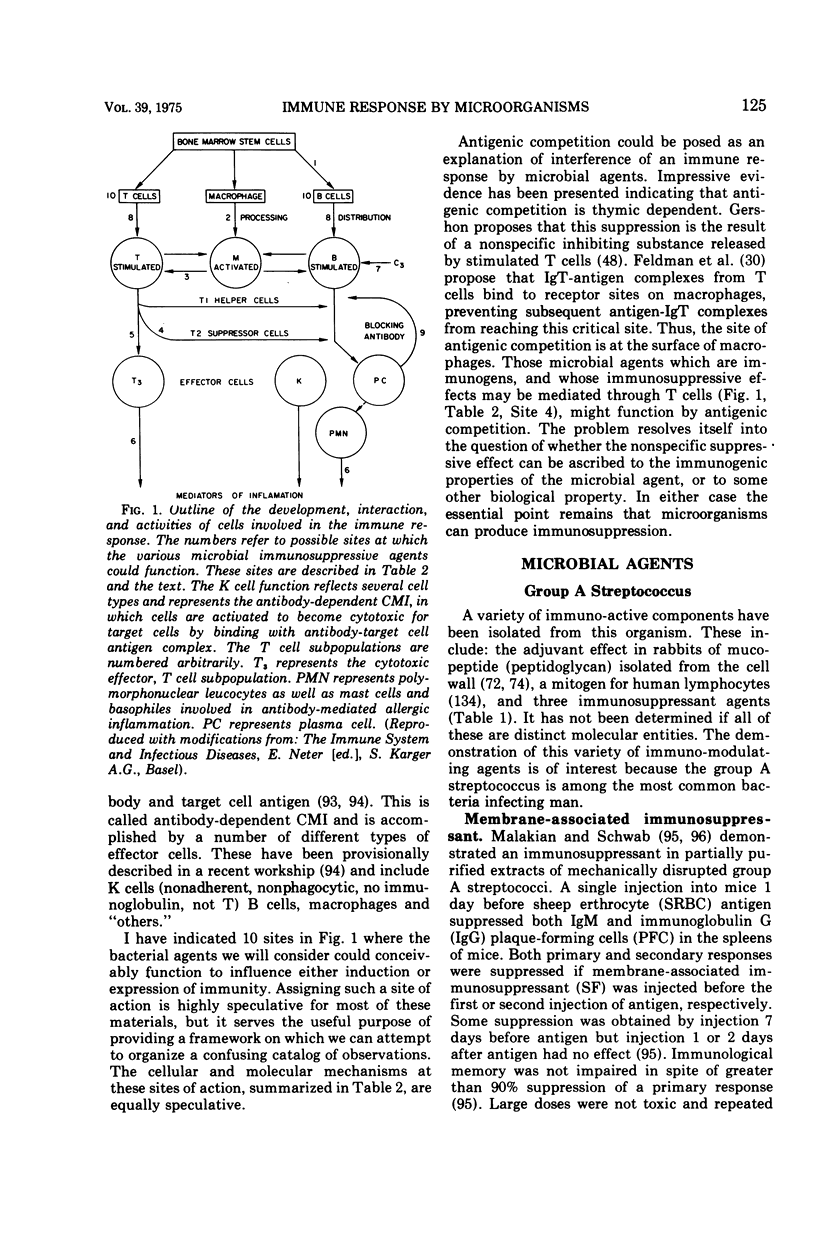
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Broughton E. S., Scott M. T. Enhanced resistance of mice to infection with bacteria following pre-treatment with Corynebacterium parvum. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):219–220. doi: 10.1038/newbio235219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allwood G. G., Asherson G. L. Depression of delayed hypersensitivity by pretreatment with Freund-type adjuvants. 3. Depressed arrival of lymphoid cells at recently immunized lymph nodes in mice pretreated with adjuvants. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):579–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa S. Effects of the lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis on antibody production in mice. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1969 Feb;22(1):23–42. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.22.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Allwood G. G. Depression of delayed hypersensitivity by pretreatment with Freund-type adjuvants. I. Description of the phenomenon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):249–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athanassiades T. J., Morse S. I. Lymphocytosis induced in mice by supernatant fluids of Bordetella pertussis cultures: a histopathological study. Blood. 1973 Oct;42(4):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H., Harboe M., Closs O., Godal T. BCG antibody profiles in tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):952–958. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.952-958.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY S. G., WATSON D. W. SUPPRESSION BY ENDOTOXIN OF THE IMMUNE RESPONSE TO ACTINOPHAGE IN THE MOUSE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:570–572. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Leventhal B. G. Possible mechanism for Mycoplasma inhibition of lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1968 Aug 17;219(5155):750–752. doi: 10.1038/219751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Prescott B., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Baker P. J. Regulation of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. 3. Role of regulatory T cells in the development of an IgG and IgA antibody response. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1042–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer H., Paronetto F., Burns W. A., Einheber A. The enhancing effect of the microbial flora on macrophage function and the immune response. A study in germfree mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Jun 1;123(6):1013–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.6.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C., Cope W. A., Jeffery W. Differential asparaginase sensitivity of T-cell and B-cell responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist L. M., Lau B. H., Winter C. E. Mycoplasma-associated immunosuppression: effect on hemagglutinin response to common antigens in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.410-415.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent L., Pinto M. Induction of specific unresponsiveness with the aid of Bordetella pertussis. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):697–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. B., Milton J. D., Mowbray J. F., Butterworth A. E. Immunosuppressive properties of a ribonuclease-containing fraction from bacterial cultures. Immunology. 1972 Aug;23(2):171–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernyakhovskaya I. Y., Shaghijan H. S., Slavina E. G., Svet-Moldavsky G. J. Helminths and allotransplantation. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1972 Apr;17(4):395–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Northrup R. S., Chen L. C. The modulating effect of cholera enterotoxin on the immune response. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):729–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Northrup R. S. Pathophysiologic effects of lethal and immunoregulatory doses of cholera enterotoxin in the mouse. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):740–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C., Munoz J., Bergman R. K. Lymphocytosis and histamine sensitization of mice by fractions from Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1484–1487. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1484-1487.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Stauber L. A., Palczuk N. C. Leishmania donovani: antibody response to chicken ovalbumin by infected golden hamsters. Exp Parasitol. 1969 Aug;25(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(69)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Scott M. T. Effect of Corynebacterium parvum treatment on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):863–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.863-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J., Fincham W. J. The effect of streptococcal L-form cultures on lymphocytes. Life Sci. 1969 Apr 15;8(8):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copperman R., Morton H. E. Reversible inhibition of mitosis in lymphocyte cultures by non-viable Mycoplasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):790–795. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cypess R. H., Lubiniecki A. S., Hammon W. M. Immunosuppression and increased susceptibility to Japaneses B encephalitis virus in Trichinella spiralis-infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jun;143(2):469–473. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cypess R. H., Lubiniecki A. S., Swidwa D. M. Decreased susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes in mice after infection with Trichinella spiralis. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):477–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.477-479.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cypess R. H., Molinari J. A., Ebersole J. L., Lubiniecki A. S. Immunological sequelae of Trichinella spiralis infection in mice. II. Potentiation of cell-mediated response to BCG after infection with Trichinella spiralis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):107–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.107-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Schumann G., Gisler R. H., Dierich M., König W., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Complement-dependent B-cell activation by cobra venom factor and other mitogens? J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):337–354. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elekes E., Finger H. Recovery of the antibody-forming potential in cyclophosphamide-treated mice, with special reference to the influence of Bordetella pertussis. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1974;40(1):1–14. doi: 10.1159/000162495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOERSHEIM G. L. EFFECT OF PERTUSSIS VACCINE ON THE TUBERCULIN REACTION. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;26:340–344. doi: 10.1159/000229587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faubert G., Tanner C. E. Trichinella spiralis: inhibition of sheep hemagglutinins in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Aug;30(1):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Montgomery P. C. Effects of L-asparaginase on lymphocyte surface and blastogenesis. Cancer Res. 1972 Nov;32(11):2400–2406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Bartoschek M., Emmerling P. Time relationships between injection of antigen and adjuvant. II. Immunosuppression induced by Bordetella pertussis vaccine when given before secondary antigenic stimulation. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1972;38(2):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Emmerling P., Brüss E. Variable Adjuvant Activity of Bordetella pertussis with Respect to the Primary and Secondary Immunization of Mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):251–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.251-258.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Emmerling P., Hof H., Plager L. Time relationships between injection of antigen and adjuvant. V. Primary and secondary immune responses to sheep erythrocytes in mice pretreated with incomplete freund's adjuvant. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1973 May;145(3):227–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Emmerling P., Plager L. Time relationships between injection of antigen and adjuvant. 3. Adjuvancy of Bordetella pertussis given at various times after the primary antigenic stimulus. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):783–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.783-791.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Fresenius H., Angerer M. Bacterial endotoxins as immunosuppressive agents. Experientia. 1971 Apr 15;27(4):456–458. doi: 10.1007/BF02137310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Heymer B., Hof H., Meister H., Bültmann B., Haferkamp O. Studies on an immunosuppressant present in cytoplasmic preparations of beta-hemolytic streptococci. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1974 Nov;147(5):449–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L., Borel J. F., Wiesinger D., Brundell J., Kis Z. Antiarthritic and immunosuppressive effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Agents Actions. 1972;2(5):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02087047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L., Hopff W. H., Gasser M., Bucher K. Impairment of cell-mediated immune responses by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):241–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L., Szeszak J. J. Poly I-poly C and endotoxins share immunosuppressive properties and increase the toxicity of alpha-amanitin and hexobarbital. Agents Actions. 1971 Nov;2(3):150–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01966754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. In vitro responses of rat lymphocytes following adult thymectomy. II. Increased inhibition by splenic adherent cells of responses to phytohemagglutinin. Cell Immunol. 1973 Oct;9(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzl R. E., McMaster P. D. The primary immune response in mice. I. The enhancement and suppression of hemolysin production by a bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jun 1;127(6):1087–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlaender M. H., Baer H., McMaster P. R. Contact sensitivity and immunologic tolerance in germfree guinea pigs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):522–526. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. L-asparaginase induced immunosuppression: inhibition of bone marrow derived antibody precursor cells. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):139–141. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaumer H. R., Schwab J. H. Differential susceptibility of mouse lymphocytes to an immunosuppressant from group A streptococci. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):394–406. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Cohen P., Hencin R., Liebhaber S. A. Suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Kondo K. Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970 May;18(5):723–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K. T cell control of antibody production. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:1–40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Shin H. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide: consumption of each of the six terminal complement components. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Myklestad B., Samuel D. R., Myrvang B. Characterization of the cellular immune defect in lepromatous leprosy: a specific lack of circulating Mycobacterium leprae-reactive lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Dec;9(6):821–831. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Roe F. J. Influence of germ-free status on hepatoma induction by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene in C3H mice. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1282–1283. doi: 10.1038/2221282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Bradley-Moore A. M., Bryceson A. D., Palit A. Immunosuppression in children with malaria. Lancet. 1972 Jan 22;1(7743):169–172. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Herrick E. M., Voller A. Suppression of autoimmune disease in NZB and (NZB x NZW) F1 hybrid mice by infection with malaria. Nature. 1970 Apr 18;226(5242):266–267. doi: 10.1038/226266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Playfair J. H., Torrigiani G. Immunosuppression in murine malaria. I. General characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):467–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Voller A., Herrick E. M. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis by infection with a strain of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):321–323. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Whittle H. C., Molyneux D. H. Immunosuppression in Gambian trypanosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1973;67(6):846–850. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(73)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVAS H. F., DONNELLY A. J. Mixed bacterial toxins in the treatment of tumors. IV. Response of methylcholanthrene-induced, spontaneous, and transplanted tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 1961 Jan;21:17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T., Onuma T. L-asparaginase and in vitro lymphocyte blastogenesis. Cell membrane alteration as possible mechanism of inhibitory effect. Immunology. 1974 Jan;26(1):169–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Enhanced immune response after immunosuppression by Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):1009–1011. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.1009-1011.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Host-parasite relationships among group A streptococci. IV. Suppression of antibody response by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):14–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.14-21.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Mori A. Antitumor activity of anaerobic Corynebacterium isolated from the human bone marrow. Gan. 1973 Feb;64(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Mori A. Antitumor activity of anaerobic Corynebacterium isolated from the human bone marrow. Gan. 1973 Feb;64(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Mäkelä O. Suppression or augmentation of the antihapten response in mice by antibodies of different specificities. J Exp Med. 1973 Jul 1;138(1):103–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Lichtenstein L. M., Gillespie E., Rolley R. T. In vivo suppression of the immune response to alloantigen by cholera enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1172/JCI107481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Beverley J. K., Shortland J. R., Coup A. J. Experimental toxoplasmic lymphadenopathy in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Jun;54(3):312–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M. Immunosuppressive enzymes. Transplant Proc. 1973 Sep;5(3):1211–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M. L-glutaminase: suppression of lymphocyte blastogenic responses in vitro. Science. 1971 May 14;172(3984):736–738. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3984.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Bültmann B., Schachenmayr W., Spanel R., Haferkamp O., Schmidt W. C. Migration inhibition of rat peritoneal cells induced by streptococcal mucopeptides. Characteristics of the reaction and properties of the mucopeptide preparations. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1743–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Sinkovics J. G., Shullenberger C. C., Howe C. D. Murine lymphoma: augmented growth in mice with pertussis vaccine-induced lymphocytosis. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1061–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton J. B., Schwab J. H. Adjuvant properties of bacterial cell wall mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Christie G. H., Scott M. T. Biological effects of Corynebacterium parvum. IV. Adjuvant and inhibitory activities on B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1973 May;7(2):290–301. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M., Berman L., Cohen L. Relationship between proliferative and effector phases of the mixed lymphocyte reaction and graft-vs-host reaction. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1243–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. M., Fidler I. J. L-asparaginase and alteration of lymphocyte surface. Inhibition of the rat mixed leukocyte interaction. J Med. 1973;4(4):248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaklamanis E., Pavlatos M. The immunosuppressive effect of mycoplasma infection. I. Effect on the humoral and cellular response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):695–702. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Pierce C. W., Schlossman S., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of immune responses in vitro. V. Stimulation of suppressor T cells in nonresponder mice by the terpolymer L-glutamic acid 60-L-alanine 30-L-tyrosine 10 (GAT). J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):648–659. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H., Kushner I., Kaplan M. H. "Nonspecific" stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by cellular fractions and acid extracts of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1593–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Levine S. Further studies on the inhibition of allergic encephalomyelitis by L-asparaginase. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):367–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpatovski I. D., Stanislavski E. S. Immunosuppressive effect of cell-free extracts from Escherichia coli. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettli A. U., Nussenzweig R. Depletion of T and B lymphocytes during malarial infections. Cell Immunol. 1974 Sep;13(3):440–446. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. B., Tan E. M., Vaughan J. H. Extraction and partial purification of the histamine-sensitizing factor of Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Battisto J. R. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in germ-free guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1970 Jul;19(1):47–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S., Bourne H. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of cholera toxin on in vitro models of immediate and delayed hypersensitivity. Further evidence for the role of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):691–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI107230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. STUDIES ON THE LYMPHOCYTOSIS INDUCED IN MICE BY BORDETELLA PERTUSSIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:49–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNOZ J. EFFECT OF BACTERIA AND BACTERIAL PRODUCTS ON ANTIBODY RESPONSE. Adv Immunol. 1964;27:396–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Harding B. The role of immunoglobulins in lymphocyte-mediated cell damage, in vitro. II. The mechanism of target cell damage by lymphoid cells from immunized rats. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):405–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakian A., Schwab J. H. Immunosuppressant from group A streptococci. Science. 1968 Feb 23;159(3817):880–881. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3817.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. M., Wallace J. H. Suppression of cell-mediated immunity in experimental African trypanosomiasis. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):335–339. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.335-339.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire K. R., Princler G. L. Prolonged adjuvant stimulation in germ-free BALB-c mice: development of plasma cell neoplasia. Immunology. 1969 Sep;17(3):481–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster P. D., Franzl R. E. The primary immune response in mice. II. Cellular responses of lymphoid tissue accompanying the enhancement or complete suppression of antibody formation by a bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jun 1;127(6):1109–1125. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.6.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Jackson R. W. The effect of a streptococcus pyogenes teichoic acid on the immune response of mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. J., 3rd, Johnsen D. O., Ada G. L. Differences in localization of Salmonella flagella in lymph node follicles of germ-free and conventional rats. Nature. 1968 Mar 16;217(5133):1059–1061. doi: 10.1038/2171059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Barron B. A. Studies on the leukocytosis and lymphocytosis induced by Bordetella pertussis. 3. The distribution of transfused lymphocytes in pertussis-treated and normal mice. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):663–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Andersson J., Sjöberg O. Lipopolysaccharides can convert heterologous red cells into thymus-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVEU T., BRANELLEC A., BIOZZI G. PROPRI'ET'ES ADJUVANTES DE CORYNEBACTERIUM PARVUM SUR LA PRODUCTION D'ANTICORPS ET SUR L'INDUCTION DE L'HYPERSENSIBILIT'E RETARD'EE ENVERS LES PROT'EINES CONJUGU'EES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 May;106:771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima I., Kobayashi T., Kato N. Alterations in the antibody response to bovine serum albumin by capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1112–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S. Production by stimulated macrophages of factors depressing lymphocyte transformation. Nature. 1973 Nov 30;246(5431):306–307. doi: 10.1038/246306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig R. S. Increased nonspecific resstance to malaria produced by administration of killed Corynebacterium parvum. Exp Parasitol. 1967 Oct;21(2):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(67)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai T., Okumura K., Tada T., Iwasa S. Effect of lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis on the immune response. I. Suppression of cellular hypersensitivity reactions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(2):196–206. doi: 10.1159/000230837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M., Simpson E., Keller R. Tumour growth in nematode-infected animals. Lancet. 1971 Apr 3;1(7701):678–680. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92683-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno R., Hersh E. M. Immunosuppressive effects of L-asparaginase. Cancer Res. 1970 Jun;30(6):1605–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Shands J. W., Jr, Adler W. H., Smith R. T. Mitogenicity of bacterial endotoxins: characterization of the mitogenic principle. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):352–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryjma J., Humphrey J. H., Klaus G. G. C3 activation and T-independent B cell stimulation. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):505–506. doi: 10.1038/252505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliata F., Taranta A. Suppression of adjuvant disease by bacterial extracellular products. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Nov;31(6):500–507. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.6.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLANDS D. T., Jr, CLAMAN H. N., KIND P. D. THE EFFECT OF ENDOTOXIN ON THE THYMUS OF YOUNG MICE. Am J Pathol. 1965 Feb;46:165–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. Receptor for monomeric IgM on guinea-pig splenic macrophages. Nature. 1973 Jun 29;243(5409):527–528. doi: 10.1038/243527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Steerenberg P. A. Possible immunosuppressive effect of Corynebacterium parvum on infection with Trichinella spiralis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):149–150. doi: 10.1038/newbio242149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C. M., ALVORD E. C., Jr, FAHLBERG W. J., KIES M. W. Adjuvant-antigen relationships in the production of experimental "allergic" encephalomyelitis in the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:169–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaman M. H., Wedderburn N., Bruce-Chwatt L. J. The immunodepressive effect of a murine plasmodium and its interaction with murine oncogenic viruses. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(3):383–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H., Suzuki K. Leukocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. 3. Its identity with protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):801–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.801-810.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H., Suzuki K. Leukocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. II. Biological properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):992–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.992-999.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S. Immunosuppression by L-asparaginase. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):275–276. doi: 10.1038/224275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Biological effects of the adjuvant Corynebacterium parvum. I. Inhibition of PHA, mixed lymphocyte and GVH reactivity. Cell Immunol. 1972 Nov;5(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Biological effects of the adjuvant Corynebacterium parvum. II. Evidence for macrophage-T-cell interaction. Cell Immunol. 1972 Nov;5(3):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Depression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by Corynebacterium parvum: mandatory role of the spleen. Cell Immunol. 1974 Aug;13(2):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seravalli E., Taranta A. Release of macrophage migration inhibitory factor(s) from lymphocytes stimulated by streptococcal preparations. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jul;8(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Thorbecke G. J., Thomas L. Studies of PPLO infection. V. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitosis and antibody formation by mycoplasmal extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1163–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soru E., Teodorescu M., Zaharia O., Szabados J., Rudescu K. L-Asparaginase from the BCG strain of Mycobacterium bovis. I. Purification and in vitro immunosuppressive properties. Can J Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(11):1149–1157. doi: 10.1139/o72-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Voller A., Pettit L. E., Fleck D. G. Immunodepression associated with concomitant toxoplasma and malarial infections in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):54–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranta A., Cuppari G., Quagliata F. Dissociation of hemolytic and lymphocyte-transforming activities of streptolysin S preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):605–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Bryceson A. D. Immunological phenomena in leprosy and related diseases. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:209–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Möller G. Regulatory effect of antibody on the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:81–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A., Allison A. C. A role of macrophages in the stimulation of immune responses by adjuvants. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. The regulatory role of macrophages in antigenic stimulation. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:95–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. W., Sljivić V. S. Enhancement and depression of the antibody response in mice caused by Corynebacterium parvum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):519–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Mahmoud A. A., Boros D. L., Rall T. W., Mandel M. A., Carpenter C. C., Jr In vivo suppression by cholera toxin of cell-mediated and foreign body inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):996–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang H. Y., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Neter E. Inhibition by lipoid A of formation of antibodies against common antigen of enterobacteriaceae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):371–374. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchurch R., Ishizuka M., Webb D., Braun W. Adenyl cyclase activity of spleen cells exposed to immunoenhancing synthetic oligo- and polynucleotides. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1399–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Inchley M. P., Dunbar N. Further observations on the effect of C. parvum and anti-tumour globulin on syngeneically transplanted mouse tumours. Br J Cancer. 1972 Apr;26(2):67–76. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wostmann B. S., Olson G. B. Persistence of primary antibody formation caused by the absence of antigen of microbial origin in the germ-free chicken. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):199–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B. Mimetic relationships between group A streptococci and mammalian tissues. Adv Immunol. 1967;7:147–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., Gershon R. K. Thymus dependence of lymphocyte trapping. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



