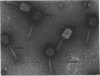
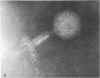
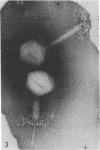
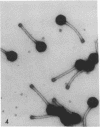
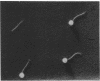
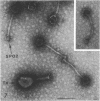
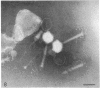
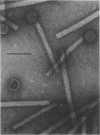
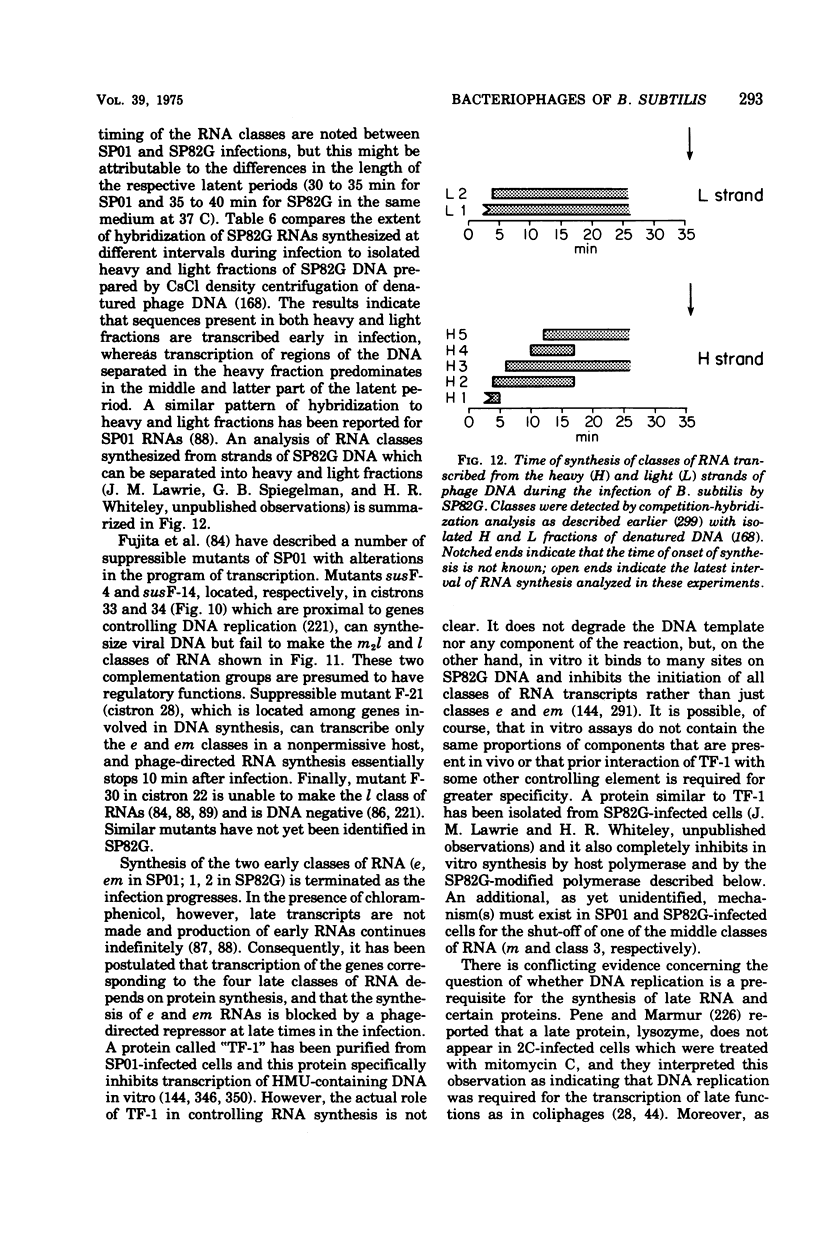
Full text
PDF





















































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alegria A. H., Kahan F. M. Attempts to establish whether glucose is attached to the deoxyribonucleic acid of certain bacteriophages infecting Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1132–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alegria A. H., Kahan F. M., Marmur J. A new assay for phage hydroxymethylases and its use in Bacillus subtilis transfection. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3179–3186. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez G., Salas E., Pérez N., Celis J. E. Phi29 bacteriophage structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1972 Mar;14(3):243–250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-3-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Williamson J. R., Eigner J. Localization of parental deoxyribonucleic acid from superinfecting T4 bacteriophage in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):887–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.887-893.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Mosharrafa E. T. Physical and biological properties of phage phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1185–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1185-1190.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Reilly B. E. Analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 gene function: protein synthesis in suppressor-sensitive mutant infection of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.211-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aposhian H. V., Tremblay G. Y. Deoxythymidylate 5'-nucleotidase. Purification and properties of an enzyme found after infection of Bacillus subtilis with phage SP5C. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5095–5101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentrout R. W., Rutberg L. Heat induction of prophage phi 105 in Bacillus subtilis: replication of the bacterial and bacteriophage genomes. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):455–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.455-468.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentrout R. W., Rutberg L. Mapping of prophage and mature deoxyribonucleic acid from temperate Bacillus bacteriophage phi 105 by marker rescue. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.760-767.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Rutberg L. Induction of prophage SPO2 in Bacillus subtilis by 6-(para)-hydroxyphenylazouracil. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1470-1475.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Rutberg L. Induction of prophage SPO2 in Bacillus subtilis: prophage excision in the absence of bacterial or bacteriophage DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1476–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1476-1481.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Rutberg L. Restriction and modification in Bacillus subtilis. Induction of a modifying activity in Bacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(2):175–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00264838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Venema G. Protease-sensitive transfection of Bacillus subtilis with bacteriophage GA-1 DNA: a probable case of heterologous transfection. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):584–589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.584-589.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Venema G. Transfection of Bacillus subtilis with bacteriophage H1 DNA: fate of transfecting DNA and transfection enhancement in B. subtilis uur+ and uur- strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(1):55–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J., Hermoso J. M., Vinuela E., Salas M. Purification and properties of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis vegetative cells. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 25;21(4):526–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J., Hermoso J. M., Viñuela E., Salas M. Subunit composition of B. subtilis RNA polymerase. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1244–1245. doi: 10.1038/2261244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTT K., STRAUSS B. THE CARRIER STATE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS INFECTED WITH THE TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE SP10. Virology. 1965 Feb;25:212–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baptist J. N., Tevethia M. J., Mandel M., Shaw C. R. Altered proteins with triosephosphate isomerase activity in suppressor-containing strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):976–985. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.976-985.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauld J., Tyler P. A., Marshall K. C. Pleomorphy of a budding bacterium on various carbon sources. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(4):409–416. doi: 10.1007/BF02218511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazill G. W., Gross J. D. Effect of 6-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-azouracil on B. subtilis DNA polymerases. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):82–83. doi: 10.1038/newbio240082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger T., Bruner R. Late gene function in bacteriophage T4 in the absence of phage DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):743–747. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Hathaway G. M., Rutberg L. Characterization of Temperate Bacillus Bacteriophage phi105. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.264-270.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswal N., Kleinschmidt A. K., Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. Physical properties of the DNA of bacteriophage SP50. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;100(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00425774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. W., Gold L. M. Pre-replicative development of the bacteriophage T4: RNA and protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):365–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boice L. B. Evidence that Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP02 is temperate and heteroimmune to bacteriophage phi-105. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):47–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.47-49.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boice L., Eiserling F. A., Romig W. R. Structure of bacillus subtilis phage SPO2 and its DNA: similarity of Bacillus subtilis phages SPO2, phi 1O5 and SPP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolle A., Epstein R. H., Salser W., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: requirements for late messenger synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):339–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott K. F., Wilson G. A. Development of competence in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):562–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.562-570.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott K. F., Wilson G. A. Metabolic and nutritional factors influencing the development of competence for transfection of Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):370–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H., Brooks D., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: analysis of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in biosynthesis of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.281-290.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The isolation and morphology of some new bacteriophages specific for Bacillus and Acetobacter species. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):233–241. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The morphology and physiology of bacteriophages as revealed by the electron microscope. J R Microsc Soc. 1965 Sep;84(3):257–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandon C., Gallop P. M., Marmur J., Hayashi H., Nakanishi K. Structure of a new pyrimidine from Bacillus subtilis phage SP-15 nucleic acid. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 20;239(90):70–71. doi: 10.1038/newbio239070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brevet J. Direct assay for sigma factor activity and demonstration of the loss of this activity during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Feb 6;128(3):223–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00267111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodetsky A. M., Romig W. R. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1655–1663. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1655-1663.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: a selective inhibitor of host DNA replication in phage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1454–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. Inhibition of bacterial DNA replication by 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: differential effect on repair and semi-conservative synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner R., Cape R. E. The expression of two classes of late genes of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):69–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. RNA polymerase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:711–740. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R. The regulation of phage development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:241–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Moreno F., Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. A suppressor of nonsense mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Viñuela E., Salas M. A precursor of the neck appendage protein of B. subtilis phage phi 29. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. Proteins induced in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P., Cafferata R. L., Haselkorn R. T4 DNA replication and viral gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin T., Burger M. M., Glaser L. Synthesis of teichoic acids. VI. The formation of multiple wall polymers in Bacillus subtilis W-23. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Boice L., Davidson N. Map of the partial sequence homology between DNA molecules of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages SPO2 and phi105. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Davidson N. Electron microscope study of the structures of the Bacillus subtilis prophages, SPO2 and phi105. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S., Losick R., Pero J. New RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis infected with phage PBS2. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):21–24. doi: 10.1038/252021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Natale P. J., Buchanan J. M. Transcriptional regulation of T4 bacteriophage-specific enzymes synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):292–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.292-299.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csiszár K., Ivánovics G. Transduction in Bacillus subtilis. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1965;12(1):73–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F. THE STRUCTURE OF BACTERIOPHAGE SP8. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:146–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R. Mutual exclusion between related phages. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):209–217. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.209-217.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., Franklin R. M. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase associated with bacteriophage PM2. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):131–passim. doi: 10.1038/newbio236131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbrück M. Interference Between Bacterial Viruses: III. The Mutual Exclusion Effect and the Depressor Effect. J Bacteriol. 1945 Aug;50(2):151–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Brown L. R., Rodgers G., Hsu Y. Bacillus subtilis mutant altered in spore morphology and in RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):404–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. C., Hadden C. T., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in Bacillus subtilis during development of the competent state. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):668–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.668-679.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R., Scher B., Cirigliano C. Fate of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid after uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis: phenotypic characterization of radiation-sensitive recombination-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):273–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.273-286.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R., Smith I. Transformation and transduction in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for separate modes of recombinant formation. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):155–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. RNA polymerase from phage SP01-infected and uninfected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4530–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription specificity of an RNA polymerase fraction from bacteriophage SP01-infected B. subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Petrusek R. L., Geiduschek E. P. Conversion of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase activity in vitro by a protein induced by phage SP01. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2366–2370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham L. F., Price A. R. Deoxythymidine triphosphate-deoxyuridine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase induced by Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phie. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2667–2672. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham L. T., Price A. R. Mutants of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi e defective in dTTP-dUTP nucleotidohydrolase. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):709–712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.709-712.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISERLING F. A., ROMIG W. R. Studies of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages. Structural characterization by electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:540–546. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earhart C. F. The association of host and phage DNA with the membrane of Escherichia coli. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):420–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiserling F. A. The structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBS 1. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Feb;17(3):342–347. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. T., Mahler I. Mechanisms of enhancement of SP82 transfection. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):710–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.710-715.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. T. Source of the nonlinear dependence of bacteriophage SP82 transfection on deoxyribonucleic acid concentration. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.749-752.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Spatz H. C. Asymmetric transcription of SPP1 in vivo. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jul 31;124(1):57–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00267164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOELDES J., TRAUTNER T. A. INFECTIOUS DNA FROM A NEWLY ISOLATED B. SUBTILIS PHAGE. Z Vererbungsl. 1964 Apr 10;95:57–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00898184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH R. C., LESLEY S. M., GRAHAM A. F., van ROOYEN C. E. Studies on the relationship between virus and host cell. III. The breakdown of P32 labelled T2r+ bacteriophage adsorbed to E. coli previously infected by other coliphages of the T group. Can J Med Sci. 1951 Jun;29(3):144–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock J. I., Rutberg L. Mature DNA from temperate bacillusphage phi105 requires primary recombination to be infectious in transfection. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00264861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Pero J. New phage-SPO1-induced polypeptides associated with Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2761–2765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel R. W., Joys T. M. Adsorption Specificity of Bacteriophage PBS1. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):388–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.388-389.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage SPO1 development: mutations affecting the program of viral transcription. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. M. INFECTIVITY OF DNA ISOLATED FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS BACTERIOPHAGE, SP82. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:438–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Fujita D. J. Effect of nalidixic acid on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteriophage SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.96-103.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriophage SPO1 development: six classes of SPO1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriphage SPO1 development. II. Some modulations and prerequisites of the transcription program. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. Repression of early messenger transcription in the development of a bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J. DNA-mediated prophage induction in Bacillus subtilis lysogenic for phi 105c4. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.18-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J. Isolation and properties of Bacillus subtilis strains lysogenized by a clear plaque mutant of bacteriophage phi 105. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):13–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.13-17.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Law M. F. Relationship between lysogeny, spontaneous induction, and transformation efficiencies in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Leffert H., Marmur J. Genetic mapping of a defective bacteriophage on the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):340–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.340-343.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Sklar J. Continual requirement for a host RNA polymerase component in a bacteriophage development. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):833–836. doi: 10.1038/221833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. Suppressor system in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1397–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1397-1402.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L., Ionesco H., Schaeffer P. Teichoic acids as components of a specific phage receptor in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 24;124(2):415–417. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G. Chemical structure of a modification of the Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase alpha polypeptides induced by bacteriophage T4 infection. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6181–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. D., Bryan T. Productive infection of Bacillus subtilis 168, with bacteriophage SP-10, dependent upon inducing treatments. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):805–812. doi: 10.21236/ad0686354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. M. Gene dislinkage in transfection of SP82G phage DNA. Genetics. 1968 Dec;60(4):673–680. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. M., Laman D. Organization of gene function in Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP82G. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):1033–1046. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.1033-1046.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. M., Urban M. I. Recombination and transfection mapping of cistron 5 of bacteriophage sp82g. Genetics. 1972 Feb;70(2):187–203. doi: 10.1093/genetics/70.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Linn T. G., Losick R. Isolation of a new RNA polymerase-binding protein from sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):490–494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Peterson V. Isolation and properties of rex - mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.760-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwinn D. D., Lawton W. D. Alteration of host specificity in Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):297–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwinn D. D., Thorne C. B. Helper phage-dependent transfection in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):260–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective Bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis: III. Properties of Adenine-16 Marker in Purified Bacteriophage Deoxyribonucleic Acid. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):844–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.844-850.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis. I. Induction, purification, and physical properties of the bacteriophage and its deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):233–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.233-247.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis. II. Intracellular development of the induced prophage. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):248–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.248-260.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden C., Nester E. W. Purification of competent cells in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):876–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.876-885.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen E. W., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. A genetic study of temperature-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford N. Genetic analysis of rec mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Evidence for at least six linkage groups. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Mar 27;129(3):269–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00267919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havender W. R., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B. subtilis phage SP50. 3. Biological effects of DNA cleavage and the physical basis of the map. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(1):51–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00334260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havender W. R., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B. subtilis phage SP50. II. Temperature sensitive mutants and the establishment of a linkage map. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00343185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley L. A., Reilly B. E., Hagen E. W., Anderson D. L. Viral protein synthesis in bacteriophage phi 29-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1149-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. Inhibition of bacterial DNA and protein synthesis in Bacillus subtilis by phage SP82. Effect of changes of temperature on the inhibition. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):538–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R., Brown L. R., Doi R. H. The effect of rifampin on the production of beta22 phage by Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 6;37(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Nucleic acid synthesis in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage beta-22. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):381–392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.381-392.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. E., McCorquodale D. J. Genetic and physiological studies of bacteriophage T5. 2. The relationship between phage DNA synthesis and protein synthesis in T5-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 21;43(4):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa H., Kadlubar F. Length of deoxyribonucleic acid of PBSX-like particles of Bacillus subtilis induced by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):205–209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.205-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa H. Transfecting deoxyribonucleic acid of Bacillus bacteriophage phi 29 that is protease sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1555–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Anagnostopoulos C. Chromosomal location and properties of radiation sensitivity mutations in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.295-301.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Whiteley H. R. A new polypeptide associated with RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis during late stages of vegetative growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M., Whiteley H. R. RNA polymerase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens infected with phi29 bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2234–2237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz H. R. Polypeptide bound to the host RNA polymerase is specified by T4 control gene 33. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio244137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter B. I., Yamagishi H., Takahashi I. Molecular weight of bacteriophage PBS 1 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):841–842. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.841-842.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IONESCO H., RYTER A., SCHAEFFER P. SUR UN BACT'ERIOPHAGE H'EBERG'E PAR LA SOUCHE MARBURG DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Dec;107:764–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. W., Eremenko-Volpe T., Greenwald L., Meadow W. L., Marmur J. Physical and genetic mapping of the SPO2 prophage on the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):627–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.627-628.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Meinke W., Hathaway G., Spizizen J. Studies on Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 15. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):110–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J. Pleiotropic nature of bacteriophage tolerant mutants obtained in early-blocked asporogenous mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Aug 10;124(2):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00265143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Spizizen J. Abortive infection of sporulating Bacillus subtilis 168 by phi 2 bacteriophage. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):515–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.515-523.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivarie R. D., Pène J. J. DNA replication in bacteriophage ø29: the requirement of a viral-specfic product for association of ø29 DNA with the cell membrane of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman R. Transcription of bacteriophage T4 DNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro: identification of some immediate-early and delayed-early genes. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90537-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Venema G. Different nuclease activities in competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):25–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.25-33.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. G., Geiduschek E. P. Purification of the bacteriophage SP01 transcription factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3571–3578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson J., Rutberg L., Young F. E. Lysogenic Conversion in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H Affecting Viral Adsorption. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.309-310.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. Correlation between susceptibility to bacteriophage PBS1 and motility in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1575–1577. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1575-1577.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan E. A genetic study of temperature-sensitive mutants of the subtilis phage SP82. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):650–660. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan E. Early and late gene function in bacteriophage SP82. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):634–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Landman O. E. Nature of the carrier state of bacteriophage SP-10 in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1804-1812.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Ito J. Bacteriophage gene expression in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis 168. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):414–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T4. I. Continued synthesis of host ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1262–1271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1262-1271.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T4. II. Induction of host messenger ribonucleic acid and its exclusion from polysomes. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):208–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.208-217.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjan P., Szulmajster J. Intracellular ribonuclease activity in stationary phase cells of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1079–1087. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz G. Direction of SPP1 DNA replication in transfected B. subtilis cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 18;120(1):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00332987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz G. Establishment of a correlation between physical molecule and genetic map in one segment of the SPP1 chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;134(3):273–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00267721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz G., Spatz H. C. A biological assay for intracellular SPP1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(4):367–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00438279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Mixed infections of Bacillus subtilis involving bacteriophage SPO2c 1 . J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):25–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.25-34.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Nucleic acid synthesis in bacteriophage SPO2c 1 -infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):776–784. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.776-784.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGRIDGE R., MARMUR J. X-RAY DIFFRACTION STUDY OF A DNA WHICH CONTAINS URACIL. Science. 1964 Mar 27;143(3613):1450–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3613.1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMontagne J. R., McDonald W. C. A bacteriophage of Bacillus subtilis which forms plaques only at temperatures above 50 C. I. Physical and chemical characteristics of TSP-1. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):646–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.646-651.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMontagne J. R., McDonald W. C. A bacteriophage of Bacillus subtilis which forms plaques only at temperatures above 50 C. II. Reduction of TSP-1-specific receptor sites on cells grown at 37 C or 45 C, and the temperature-dependent inactivation of replicating phage. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):652–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.652-658.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMontagne J. R., McDonald W. C. A bacteriophage of bacillus subtilis which forms plaques only at temperatures above 50 C. 3. Inhibition of TSP-1-specific deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis at 37 C and 45 C. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):659–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.659-663.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi U., Marcus M. Arrest of host DNA synthesis in Bacillus subtilis infected with phage phi e. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi U., Nattenberg A., Ronen A., Marcus M. Bacillus subtilis DNA polymerase III is required for the replication of the virulent bacteriophage phi e. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1337–1342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1337-1342.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrie J. M. DNA strand specificity of transcripts produced in vivo and in vitro by RNA polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1286–1288. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1286-1288.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M. H., Cozzarelli N. R. Replication of viral DNA in SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. I. Replicative intermediates. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):402–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M. H. Eclipse of viral DNA infectivity in SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M. H. Replication of viral DNA in SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. II. DNA maturation during abortive infection. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):417–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Studies of heat-inducible lambda bacteriophage. I. Order of genetic sites and properties of mutant prophages. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Anderson D. L. Morphology and physiology of the intracellular development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi25. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):114–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.114-124.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Anderson D. L. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi25 and phi25 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.107-113.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. G., Greenleaf A. L., Shorenstein R. G., Losick R. Loss of the sigma activity of RNA polymerase of Bacillus subtilis during sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R. In vitro transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:409–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Sonenshein A. L. Change in the template specificity of RNA polymerase during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):35–37. doi: 10.1038/224035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Pène J. J., Andrews D. P. Gene expression during the development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. I. Analysis of viral-specific transcription by deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid competition hybridization. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):78–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.78-86.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Pène J. J. Gene expression during the development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi29. II. Resolution of viral-specific ribonucleic acid molecules. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):87–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.87-97.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. PBPI: a flagella specific bacteriophage mediating transduction in Bacillus pumilus. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90564-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S., Young F. E. Genetic analysis in Bacillus pumilus by PBSI-mediated transduction. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):603–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.603-608.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S., Young F. E. Identification of Bacillus subtilis NRRL B-3275 as a strain of Bacillus pumilus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):658–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.658-661.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S., Young F. E. Linkage groups in Bacillus pumilus determined by bacteriophage PBS1-mediated transduction. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):697–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.697-699.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. L., Rashbaum S. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of inhibition of Bacillus subtilis DNA polymerase 3 by the arylhydrazinopyrimidine antimicrobial agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2973–2977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., GREENSPAN C. M. TRANSCRIPTION IN VIVO OF DNA FROM BACTERIOPHAGE SP8. Science. 1963 Oct 18;142(3590):387–389. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3590.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U. Induction of a new RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90773-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Newlon M. C. Control of DNA synthesis in Bacillus subtilis by phage phi e. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmur J., Brandon C., Neubort S., Ehrlich M., Mandel M., Konvicka J. Unique properties of nucleic acid from Bacillus subtilis phage SP-15. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 20;239(90):68–70. doi: 10.1038/newbio239068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T. Bacteriophage infection: which end of the SP82G genome goes in first? J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):194–198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.194-198.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Green D. M. Bacteriophage SP82G inhibition of an intracellular deoxyribonucleic acid inactivation process in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.51-59.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Pène J. J., Barrow-Carraway J. Gene expression during the development of bacteriophage phi 29. 3. Analysis of viral-specific protein synthesis with suppressible mutants. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):690–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.690-698.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanesi G., Cassani G. Transcription after bacteriophage SPP1 infection in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):187–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.187-192.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanesi G., Melgara F. In vivo and in vitro transcription of SPP1 DNA by host RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1613–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1613-1614.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno F. Suppressor-sensitive mutants and genetic map of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosharrafa E. T., Schachtele C. F., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Complementary Strands of Bacteriophage phi29 Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Preparative Separation and Transcription Studies. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):855–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.855-864.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Harris A. W., Fuerst C. R., Siminovitch L. Mutations in bacteriophage lambda affecting particle morphogenesis. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):134–149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. D., Pun P., Strauss N. Template specificity changes of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in B. subtilis during sporulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez E., Ramírez G., Salas M., Viñuela E. Structural proteins of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTER E. W., STOCKER B. A. BIOSYNTHETIC LATENCY IN EARLY STAGES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDTRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:785–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.785-796.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIHARA M., ROMIG W. R. TEMPERATURE-SENSTIVIE MUTANTS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BACTERIOPHAGE SP3. I. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1220–1229. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1220-1229.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubort S., Marmur J. Synthesis of the unusual DNA of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP-15. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1078–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1078-1084.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. M., Brown N. C. Inhibition of a discrete bacterial DNA polymerase by 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil and 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo-)-isocytosine. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):80–82. doi: 10.1038/newbio240080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara M., Chrambach A., Aposhian H. V. The deoxycytidylate deaminase found in Bacillus subtilis infected with phage SP8. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1877–1886. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara M., Friedman N., Vasken Aposhian H. Biological activity of 5-hydroxymethyluracil and its deoxynucleoside in noninfected and phage-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):164–170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.164-170.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C., Mantei N., Echols H. Inhibition of host nucleic acid synthesis by bacteriophage T4: effect of chloramphenicol at various multiplicities of infection. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K., Kennell D. Polypeptide synthesis by extracts from Escherichia coli treated with T2 ghosts. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1199-1204.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Gold L. M. Transcription and translation of prereplicative bacteriophage T4 genes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5512–5519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUBO S., STODOLSKY M., BOTT K., STRAUSS B. SEPARATION OF THE TRANSFORMING AND VIRAL DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS OF A TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:679–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUBO S., STRAUSS B., STODOLSKY M. THE POSSIBLE ROLE OF RECOMBINATION IN THE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:552–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Mudd J. A., Mangan J., Huang W. M., Subbaiah T. V., Marmur J. Properties of the defective phage of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Mudd J. A., Marmur J. Conversion of Bacillus subtilis DNA to phage DNA following mitomycin C induction. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Comparison of ultraviolet sensitivity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO2 and its infectious DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):130–142. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Impaired transformability of Bacillus subtilis mutant sensitive to mitomycin C and ultraviolet radiation. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T., Fujita D. J., Olsson-Wilhelm B. M. The genetics of bacteriophage SPO1. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):81–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T. Isolation of a suppressor mutant in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1187–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1187-1188.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego C., Kerjan P., Manca de Nadra M. C., Szulmajster J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in a thermosensitive sporulation mutant (ts-4) of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):636–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.636-647.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortin J., Viñuela E., Salas M., Vasquez C. DNA-protein complex in circular DNA from phage phi-29. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):275–277. doi: 10.1038/newbio234275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palefski S., Hemphill H. E., Kolenbrander P. E., Whiteley H. R. Dominance relationships in mixedly infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):594–601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.594-601.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J., Nelson J., Fox T. D. Highly asymmetric transcription by RNA polymerase containing phage-SP01-induced polypeptides and a new host protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1589–1593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pispa J. P., Sirbasku D. A., Buchanan J. M. Patterns of ribonucleic acid synthesis in T5-infected Escherichia coli. IV. Examination of the role of deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsinelli M., Milanesi G., Ganesan A. T. Short fragments from both complementary strands in the newly replicated DNA of bacteriophage SPP-1. Science. 1969 Oct 10;166(3902):243–245. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3902.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. R., Cook S. J. New deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase induced by Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBS2. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):602–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.602-610.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. R., Dunham L. F., Walker R. L. Thymidine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase and deoxyuridylate hydroxymethylase induced by mutants of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP82G. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1240–1241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1240-1241.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. R., Fogt S. M. Deoxythymidylate phosphohydrolase induced by bacteriophage PBS2 during infection of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1372–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. R., Fogt S. M. Resistance of bacteriophage PBS2 infection to 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil, an inhibitor of Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):338–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.338-340.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. R., Frabotta M. Resistance of bacteriophage PBS2 infection to rifampicin, an inhibitor of Bacillus subtilis RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1578–1585. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90894-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J. J. Host macromolecular synthesis in bacteriophage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):379–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J. J., Marmur J. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication and expression of early and late bacteriophage functions in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.86-91.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péne J. J., Murr P. C., Barrow-Carraway J. Synthesis of bacteriophage phi 29 proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):61–67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.61-67.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REILLY B. E., SPIZIZEN J. BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:782–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.782-790.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMIG W. R., BRODETSKY A. M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of bacteriophages for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:135–141. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.135-141.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMIG W. R. Infection of Bacillus subtilis with phenol-extracted bacteriophages. Virology. 1962 Apr;16:452–459. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racine F. M., Steinberg W. Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP01, SP82, and phi e require host lysyl- and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetases for phage development. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):402–406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.402-406.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondo L. M., Lundh N. P., Martinez R. J. Primary adsorption site of phage PBS1: the flagellum of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1968 Mar;2(3):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.3.256-264.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez G., Méndez E., Salas M., Viñuela E. Head-neck connecting protein in phage phi29. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):263–265. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner D. The interaction bacterial and phage proteins with immobilized Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. Genetic study of suppressor-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):756–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.756-760.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Hemphill H. E. Abortive infection of lysogenic Bacillus subtilis 168(SPO2) by bacteriophage phi 1. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.870-880.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Hemphill H. E. Prophage-mediated interference affecting the development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi e. J Virol. 1973 Mar;11(3):372–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.3.372-377.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Hemphill H. E. Viral mutation affecting bacteriophage phi 1 development in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):820–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.820-827.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Thomas C. A., Jr The anatomy of the SP50 bacteriophage DNA molecule. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., Takahashi I. The synthesis of nucleic acids in Bacillus subtilis infected with phage PBS 1. Can J Biochem. 1973 Sep;51(9):1219–1224. doi: 10.1139/o73-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., van Kleeff B. H. Similarity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages PBS 1, 3 NT and I10. Some remarks on the morphology of phage heads. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(3):265–274. doi: 10.1007/BF02218495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S. C. Asymmetric transcription of B. subtilis phage SPP1 DNA in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):824–830. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Coupling of late transcription to viral replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Polsinelli M., Falaschi A. A new phage of Bacillus subtilis with infectious DNA having separable strands. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Polsinelli M. Relationship between competence for transfection and for transformation. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):587–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.587-593.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romig W. R. Infectivity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acids extracted from mature particles and from lysogenic hosts. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):349–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe D. H. Synthesis of DNA in phage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe D. H. Thymidine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase: a phage-induced enzyme in Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe D. H., Tucker R. G. The biosynthesis of 5-hydroxymethyldeoxyuridylic acid in bacteriophage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1966 May;29(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe D. H., Tucker R. G. The biosynthesis of a pyrimidine replacing thymine in bacteriophage DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Jun 1;16(2):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottländer E., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B, subtilis phage SP 50. I. Phage mutants with restricted growth on B. subtilis strain 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00343184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio V., Salas M., Viñuela E., Usobiaga P., Saiz J. L., Llopis J. F. Biophysical properties of bacteriophage phi29. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Rutberg L. Growth of bacteriophage phi 105 and its deoxyribonucleic acid in radiation-sensitive mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):919–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.919-921.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity in a deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I-deficient mutant of Bacillus subtilis infected with temperature bacteriophage SPO2. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):658–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.658-660.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W., Jonasson J. Unrelatedness of temperate Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages SP02 and phi105. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.732-737.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W. Low-frequency rescue of a genetic marker in deoxyribonucleic acid from Bacillus bacteriophage phi 105 by superinfecting bacteriophage. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.768-771.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Heat induction of prophage phi 105 in Bacillus subtilis: bacteriophage-induced bidirectional replication of the bacterial chromosome. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):9–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.9-12.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Hoch J. A., Spizizen J. Mechanism of transfection with deoxyribonucleic acid from the temperate Bacillus bacteriophage phi-105. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):50–57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.50-57.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.38-44.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN E., TARMY E., MARMUR J. INDUCIBLE PHAGES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:607–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Vásquez C., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Head fibers of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):180–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90358-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samojlenko I., Harford N., Mergeay M. Phenotypic properties of Bacillus subtilis mutants defective in recombination and repair functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 May 21;130(2):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00269085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi29: definition of "early" and "late" phi29 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.9-16.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Hawley L. A., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi 29: production of host- and phi 29-specific ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1170–1178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1170-1178.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Hagen E. W., Anderson D. L. Temperature-shift analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 gene expression in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):352–354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.352-354.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Oman R. W., Anderson D. L. Effect of elevated temperature on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteriophage phi-29-infected Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.430-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Reilly B. E., De Sain C. V., Whittington M. O., Anderson D. L. Selective replication of bacteriophage phi29 deoxyribonucleic acid in 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil-treated Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):153–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.153-155.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade S. Z., Adler J., Ris H. How bacteriophage chi attacks motile bacteria. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):599–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.599-609.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeger E. J., Spatz H. C. Specific recognition in gene conversion. The extent of repair synthesis in SPP1 transfection of B. subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 May 21;130(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00269087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. A., Mazaitis A. J., Kasai T., Bautz E. K. Involvement of a phage T4 sigma factor and an anti-terminator protein in the transcription of early T4 genes in vivo. Nature. 1970 Mar 14;225(5237):1012–1016. doi: 10.1038/2251012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Gold L. M. Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis phage deoxyribonucleic acid-directed deoxycytidylate deaminase synthesis in Escherichia coli extracts. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5022–5025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Tjian R., Pero J., Losick R. Chloramphenicol restores sigma factor activity to sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4860–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert W., Qasba P., Walter G., Palm P., Schachner M., Zillig W. Kinetics of the alteration and modification of DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase in T4-infected E. coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(3):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A., Dean D. H., Halvorson H. O. Low-frequency specialized transduction with Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 105. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90401-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Carlton B. C. Suppression of tryptophan mutants in Bacillus subtilis by apparent nonsense suppressors. Genetics. 1971 Oct;69(2):133–143. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Ando T. Host controlled modification and restriction in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00264858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Miura K., Aoki H. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage. II. Isolation and morphology of phage Nf and properties of its DNA. J Biochem. 1970 Sep;68(3):277–286. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A. Bacteriophage SPO1 DNA- and RNA-directed protein synthesis in vitro: comparison with in vivo control. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;137(2):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00341683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Johnson G. G. Bacteriophage SPO1 DNA- and RNA-directed protein synthesis in vitro: the effect of TF1, a template-selective transcription inhibitor. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;137(2):161–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00341682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A. Nature of the suppressor of Bacillus subtilis HA101B. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):788–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.788-790.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Smith H. Location of the SPO2 attachment site and the bryamycin resistance marker on the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1138–1142. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1138-1142.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., Geiduschek E. P. In vitro synthesis of T4 late messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):459–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Losick R. RNA polymerase mutants blocked in sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):906–909. doi: 10.1038/227906a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Roscoe D. H. The course of phage phi-e infection in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis strain 3610. Virology. 1969 Oct;39(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. One way to do experiments on gene conversion? Transfection with heteroduplex SPP1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(1):84–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00334048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. The role of recombination in transfection of B. subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(2):174–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00333191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. In vivo and in vitro transcription by ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. Purification of ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1476–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J., Reilly B. E., Evans A. H. Microbial transformation and transfection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:371–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. New small polypeptides associated with DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli after infection with bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):603–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Click B., Tole M. F. DNA replication and late protein synthesis during SP82 infection of Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):653–663. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Pagel M. F. Relationship between transformation in Bacillus subtilis and infection by bacteriophage SP02. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1082–1083. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1082-1083.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Tole M. F. A host mutation affecting the synthesis of late proteins during infection of Bacillus subtilis by bacteriophage SP82. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Okamoto T., Takanami M. RNA polymerase sigma-factor and the selection of initiation site. Nature. 1970 Feb 14;225(5233):598–600. doi: 10.1038/225598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szulmajster J., Arnaud M., Young F. E. Some properties of a sporulating Bacillus subtilis mutant containing heavy DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jul;57(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. Genetic transduction in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 28;5:171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. INCORPORATION OF BACTERIOPHAGE GENOME BY SPORES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1499–1502. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1499-1502.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I., MARMUR J. Glucosylated DNA from a transducing phage for Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Feb 18;10:289–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I., MARMUR J. Replacement of thymidylic acid by deoxyuridylic acid in the deoxyribonucleic acid of a transducing phage for Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1963 Feb 23;197:794–795. doi: 10.1038/197794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. Transducing phages for Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:211–217. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR M. J., THORNE C. B. TRANSDUCTION OF BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS AND BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY EACH OF TWO PHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:452–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.452-461.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE C. B. Transduction in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:106–111. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.106-111.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Jimenez F., Salas M., Viñuela E. Mapping of temperature sensitive mutants of bacteriophage phi 29. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(1):31–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00272215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Jimenez F., Salas M., Viñuela E. Temperature-sensitive mutants of bacteriophage phi-29. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):586–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Salas M., Viñuela E. Temperature-sensitive mutants affected in DNA synthesis in phage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. J., Thorne C. B. Concurrent changes in transducing efficiency and content of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP-10. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.81-88.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Baptist J. N., Mandel M. Pleiotropic effects of suppressor mutations in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):961–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.961-975.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Mandel M. Nature of the ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid requirement for transformation of Bacillus subtilis with single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):844–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.844-850.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurm P., Garro A. J. Bacteriophage-specific protein synthesis during induction of the defective Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBSX. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):179–183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.179-183.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurm P., Garro A. J. Isolation and characterization of prophage mutants of the defective Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBSX. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.184-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Losick R. An immunological assay for the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase in extracts of vegetative and sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2872–2876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita F. Changes in DNase activities in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage PBS 1. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1073–1080. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1073-1080.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita F., Takahashi I. A novel enzyme, dCTP deaminase, found in Bacillus subtilis infected with phage PBS I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;179(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita F., Takahashi I. DNase Specific for Uracil-Containing Bacteriophage DNA. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1081–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1081-1087.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Anderson D. L. Antigenic properties of bacteriophage phi 29 structural proteins. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1548–1559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1548-1559.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner T. A., Pawlek B., Bron S., Anagnostopoulos C. Restriction and modification in B. subtilis. Biological aspects. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(3):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00267958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner T. A., Spatz H. C. Transfection in B. subtilis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;62:61–88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65772-6_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Bacteriophage sigma factor for RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1107–1110. doi: 10.1038/2231107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Burgessrr Cyclic re-use of the RNA polymerase sigma factor. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):537–540. doi: 10.1038/222537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Positive control of transcription by a bacteriophage sigma factor. Nature. 1970 Mar 14;225(5237):1009–1012. doi: 10.1038/2251009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trilling D. M., Aposhian H. V. A deoxyribonuclease found after infection of Bacillus subtilis with phage SP3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):622–628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffaut N., Revet B., Soulie M. O. Etude comparative des DNA de phages 2C, SP8*, SP82, phi e, SP01 et SP50. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. G. Acquisition of thymidylate synthetase activity by a thymine-requiring mutant of Bacillus subtilis following infection by the temperate phage phi 3. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):489–504. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J., Jr, Taylor M. J., Lawton W. D., Goldberg I. D. Cotransduction and cotransformation of genetic markers in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1027–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1027-1036.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISCONTI N. Resistance to lysis from without in bacteria infected with T2 bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):247–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.247-253.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heijenoort J., Menjon D., Flouret B., Szulmajster J., Laporte J., Batelier G. Cell walls of a teichoic acid deficient mutant of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Seifert W., Zillig W. Modified DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from E. coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):240–247. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Kolenbrander P. E., Hemphill H. E. Mixed infections of Bacillus subtilis involving bacteriophages SP82 and beta 22. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1463–1469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1463-1469.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Johnson G., Haselkorn R., Geiduschek E. P. Specific inhibition of bacteriophage SPO1 DNA-directed protein synthesis by the SPO1 transcription factor, TF 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1970–1977. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. L., Green D. M. Early extracellular events in infection of competent Bacillus subtilis by DNA of bacteriophage SP82G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Ennis H. L. Potassium requirement for synthesis of macromolecules in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage 2C. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.1-7.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. L., Gage L. P. Certain aspects of SPO1 development. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. L., Geiduschek E. P. A template-selective inhibitor of in vitro transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):514–520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Bott K. F. Nutritional factors influencing the development of competence in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1439–1449. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1439-1449.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Williams M. T., Baney H. W., Young F. E. Characterization of temperate bacteriophages of Bacillus subtilis by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI: evidence for three different temperate bacteriophages. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):1013–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.1013-1016.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG F. E., SPIZIZEN J., CRAWFORD I. P. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF COMPETENCE IN THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS TRANSFORMATION SYSTEM. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL WALLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3119–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi H. Single strand interruptions in PBS 1 bacteriophage DNA molecule. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):623–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi H., Takahashi I. Transducing particles of PBS 1. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Ganesan A. T., Young F. E. Bacteriophage interference in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):916–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.916-921.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Effect of lysogeny on transfection and transfection enhancement in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):305–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.305-312.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):540–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.540-548.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis: evidence for selective induction of prophage in competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):296–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.296-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Young F. E. The influence of temperate bacteriophage phi105 on transformation and transfection in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 28;47(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90722-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Young F. E. Transduction in Bacillus subtilis by bacteriophage SPP1. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1343–1348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1343-1348.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasunaka K., Tsukamoto H., Okubo S., Horiuchi T. Isolation and properties of suppressor-sensitive mutants of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP02. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):819–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.819-821.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O., Brenner D. J. Lack of nucleotide sequence relationship among the temperate bacteriophage SPO2, Bacillus subtilis, and virulent bacteriophages beta 3 and beta 22. J Virol. 1970 Jan;5(1):39–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.1.39-44.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O., Doi R. H. Differential expression of bacteriophage genomes in vegetative and sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):935–947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.935-947.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O., Ganesan A. T. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteriophage SP01-infected Bacillus subtilis. II. Purification and catalytic properties of a deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase induced after infection. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7456–7463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O., Ganesan A. T. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteriophage SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. I. Bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and fate of host deoxyribonucleic acid in normal and polymerase-deficient strains. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):263–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.263-272.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Requirement of glucosylated teichoic acid for adsorption of phage in Bacillus subtilis 168. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2377–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E., Smith C., Reilly B. E. Chromosomal location of genes regulating resistance to bacteriophage in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1087–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1087-1097.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]