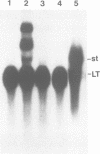Abstract
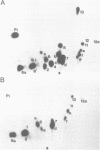
We found that simian virus 40 (SV40), in addition to the SV40 early proteins large T antigen (large T) and small antigen (small t), codes for a third early protein with a molecular weight of 17 kDa. This protein (17kT) is expressed from an alternatively spliced third SV40 early mRNA, using a splice donor site at position 4425 and a splice acceptor site at position 3679 of the SV40 genome. The 17kT protein consists of 135 amino acids. Of these, 131 correspond to the amino-terminus of large T, while the four carboxy-terminal amino acids are unique and encoded by a different reading frame. 17kT mRNA, and the corresponding protein, were found in all SV40 transformed cells analyzed, as well as in SV40 infected cells. Transfection of a cDNA expression vector encoding the 17kT protein into rat F111 fibroblasts induced phenotypic transformation of these cells. The expression of the transforming amino-terminal domain of large T as an independent 17kT protein might provide a means for individually regulating the various functions associated with this domain.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer M., Guhl E., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Cellular mutation mediates T-antigen-positive revertant cells resistant to simian virus 40 transformation but not to retransformation by polyomavirus and adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1821–1827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1821-1827.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., McCormack M., Zinn K. G., Farrell M. P., Bikel I., Livingston D. M. A recombinant murine retrovirus for simian virus 40 large T cDNA transforms mouse fibroblasts to anchorage-independent growth. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):290–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.290-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Wong C., Evans B. K. Fluctuation of simian virus 40 (SV40) super T-antigen expression in tumors induced by SV40-transformed mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):817–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.817-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry F., Harvey R., Smith A. E. Structure and biochemical functions of four simian virus 40 truncated large-T antigens. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):54–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.54-66.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Lovett M., Rigby P. W. A fragment of the SV40 large T-antigen gene transforms. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):59–61. doi: 10.1038/299059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Rigby P. W. Cloning and characterization of the integrated viral DNA from three lines of SV40-transformed mouse cells. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Shenk T. Fragments of the simian virus 40 transforming gene facilitate transformation of rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Kurth M., Graessmann M., Graessmann A., Knippschild U. Altered phosphorylation at specific sites confers a mutant phenotype to SV40 wild-type large T antigen in a flat revertant of SV40-transformed cells. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1931–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Igel H. J., Price P. J. I. In vitrol transformation of rat embryo cells: correlations with the known tumorigenic activities of chemicals in rodents. In Vitro. 1975 Mar-Apr;11(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02624083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gallie B. L., Phillips R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle regulation. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):180–185. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90221-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzpeter M., Deppert W. Analysis of biological and biochemical parameters for chromatin and nuclear matrix association of SV40 large T antigen in transformed cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzpeter M., Fanning E., Deppert W. A new sensitive target-bound DNA binding assay for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höss A., Moarefi I., Scheidtmann K. H., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L., Dornreiter I., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. Altered phosphorylation pattern of simian virus 40 T antigen expressed in insect cells by using a baculovirus vector. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4799–4807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4799-4807.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierstead T. D., Tevethia M. J. Association of p53 binding and immortalization of primary C57BL/6 mouse embryo fibroblasts by using simian virus 40 T-antigen mutants bearing internal overlapping deletion mutations. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1817–1829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1817-1829.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Kurimura T., Dubbs D. R. Transplantable mouse tumor line induced by injection of SV40-transformed mouse kidney cells. Int J Cancer. 1969 Jul 15;4(4):384–392. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippschild U., Kiefer J., Patschinsky T., Deppert W. Phenotype-specific phosphorylation of simian virus 40 tsA mutant large T antigens in tsA N-type and A-type transformants. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4414–4423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4414-4423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The p53 protein and its interactions with the oncogene products of the small DNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90505-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt A., Chen S., Blanck G., George D., Pollack R. E. Two integrated partial repeats of simian virus 40 together code for a super-T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):742–750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Rigby P. W., Smith A. E., Chaudry F. Structure and synthesis of a simian virus 40 super T-antigen. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):963–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.963-973.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Jeltsch J. M., Gannon F. Characterization of a gene encoding a 115 K super T antigen expressed by a SV40-transformed rat cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4111–4128. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Chaudry F., Harvey R., Smith R., Rigby P. W., Paucha E., Smith A. E. T antigens of SV40-transformed cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Bouck N., di Mayorca G. Separation of lytic and transforming functions of the simian virus 40 A region: two mutants which are temperature sensitive for lytic functions have opposite effects on transformation. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):518–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.518-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M. Common and unique features of T antigens encoded by the polyomavirus group. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):3979–3985. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.3979-3985.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risser R., Pollack R. A nonselective analysis of SV40 transformation of mouse 3T3 cells. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Huebner K. Effect of cell chromosome number on simian virus 40 replication. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Sep;81(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Buck M., Schneider J., Kalderon D., Fanning E., Smith A. E. Biochemical characterization of phosphorylation site mutants of simian virus 40 large T antigen: evidence for interaction between amino- and carboxy-terminal domains. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1479–1490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1479-1490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmbeck R., Deppert W. Specific interaction of simian virus 40 large T antigen with cellular chromatin and nuclear matrix during the course of infection. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3561–3569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3561-3569.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. A new SV40 mutant that encodes a small fragment of T antigen transforms established rat and mouse cells. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. An amino-terminal fragment of SV40 T antigen transforms REF52 cells. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):439–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. Simian virus 40 deletion mutants that transform with reduced efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):484–489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. The SV40 T-antigen gene can have two introns. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):432–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. The amino-terminal 147 amino acids of SV40 large T antigen transform secondary rat embryo fibroblasts. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):412–415. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90516-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler G. J., Griffin J. D., Rubin H., Livingston D. M. Identification and initial characterization of a new low-molecular-weight virus-encoded T antigen in a line of simian virus 40-transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):488–498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.488-498.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Peden K. W., Pipas J. M. The large tumor antigen of simian virus 40 encodes at least two distinct transforming functions. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5459–5463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5459-5463.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Different structural systems of the nucleus are targets for SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf E., Deboben A., Bautz F. A., Faulstich H., Wieland T. Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Carter M. C., Pipas J. M., Moran E. Simian virus 40 large-T antigen expresses a biological activity complementary to the p300-associated transforming function of the adenovirus E1A gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2116–2124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerrahn J., Deppert W. Analysis of simian virus 40 small t antigen-induced progression of rat F111 cells minimally transformed by large T antigen. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1555–1563. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1555-1563.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]